The peach plant (Prunus persica) belongs to the subgenus of almonds in the pink family. To date, there is no exact data on where this plant came from. It is known that under natural conditions the peach of David is found in the territory of Northern China, it is a wild form of the common peach. This crop is grown in regions with a warm climate, while China is considered the leader in the industrial cultivation of peaches.
Content
Peach features
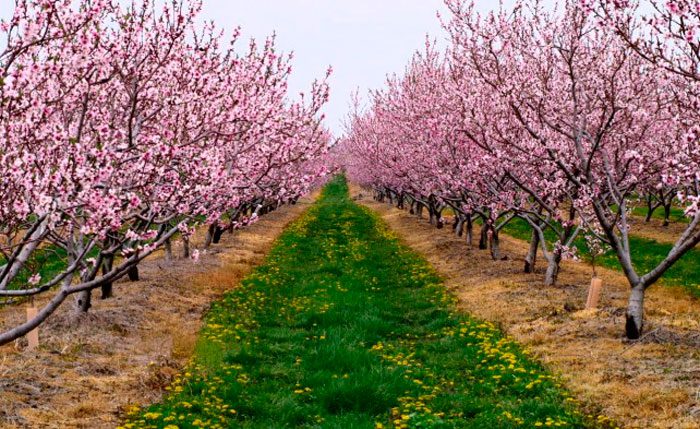
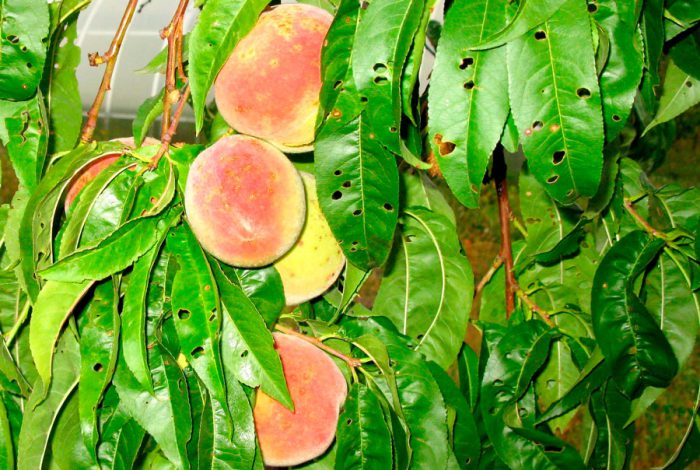
The peach's root system is close to the surface of the site at a depth of 0.2–0.5 meters. Such plants have an average height of 4 meters, while the diameter of their crown can be 6 meters. Lanceolate leaf plates have a finely toothed edge. Almost sessile flowers are red or pink in color. Their disclosure is observed in the second half of April before the appearance of foliage. In this regard, from a distance, a peach tree covered with flowers is very similar to sakura. As a rule, the fruit is velvety, its shape can be round, flat or elongated-elliptical, with a groove on one side. The furrowed, wrinkled bone has a pointed apex.
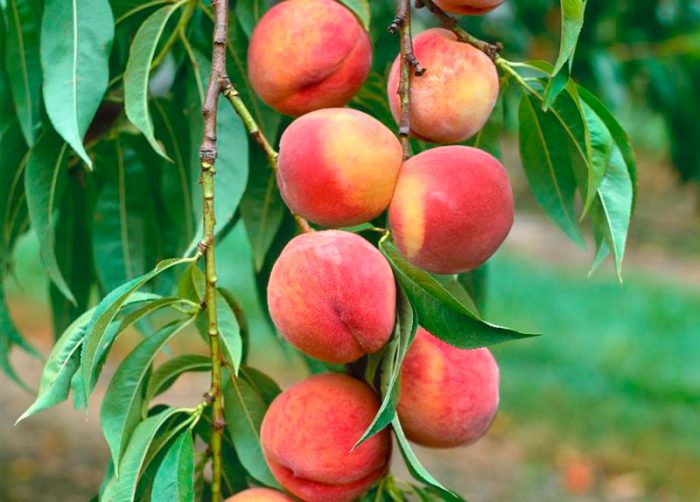
After the tree is planted, it will begin to bear fruit in 2–4 years. The duration of the fruiting period is 10 to 15 years. Peach, along with orange and mango, is one of the most delicious fruits, it has a refreshing taste and a very delicate smell. The following fruit trees are related to the peach: almonds (differ only in fruits), apricot, irga, quince, chokeberry, plum, mountain ash, hawthorn, wild rose, cotoneaster, apple tree, pear and medlar.
Planting a peach in open ground
What time to plant
The climatic conditions in your region have a strong influence on choosing the right time for planting peaches in open ground.In more southern areas, it is recommended to plant it in the fall. In more northern regions, it is recommended to plant this culture in the spring, because in the spring and summer the plant will have time to take root well and start growing. In the middle lane, this procedure can be carried out in spring and autumn, but experienced gardeners prefer autumn planting.
The planting site should be well lit, located in the southern part of the garden on a hill and protected from strong gusts of wind. Make sure that the seedling is not shaded by other large trees, buildings or bushes. The minimum distance between a peach and any other plant should be 300 cm. The area where alfalfa, strawberries, strawberries, clover, melons and nightshades were previously grown is not suitable for planting such a tree, because it is highly likely to be infected with verticillosis. Such areas will be suitable for planting peaches only after 3 or 4 years.
Planting a peach in spring
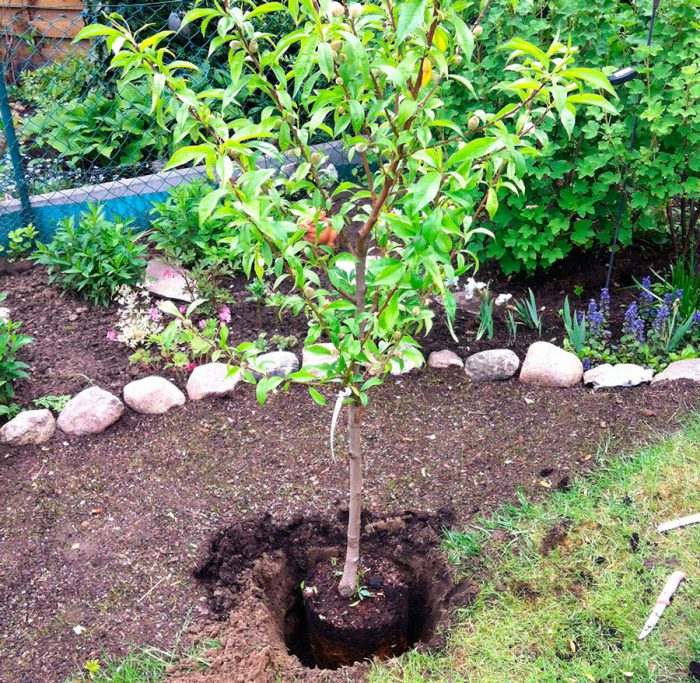
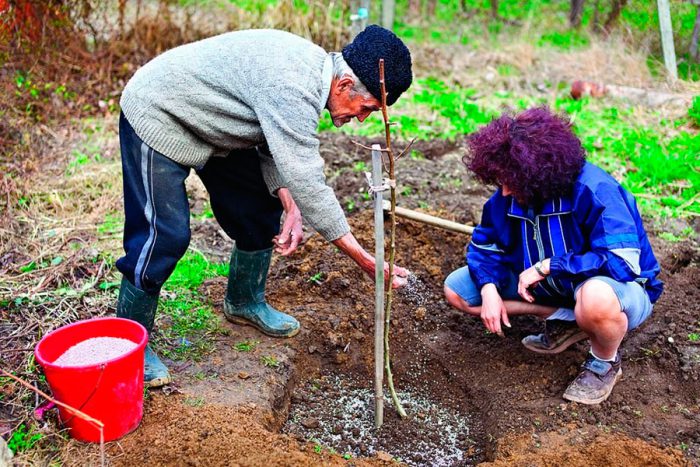
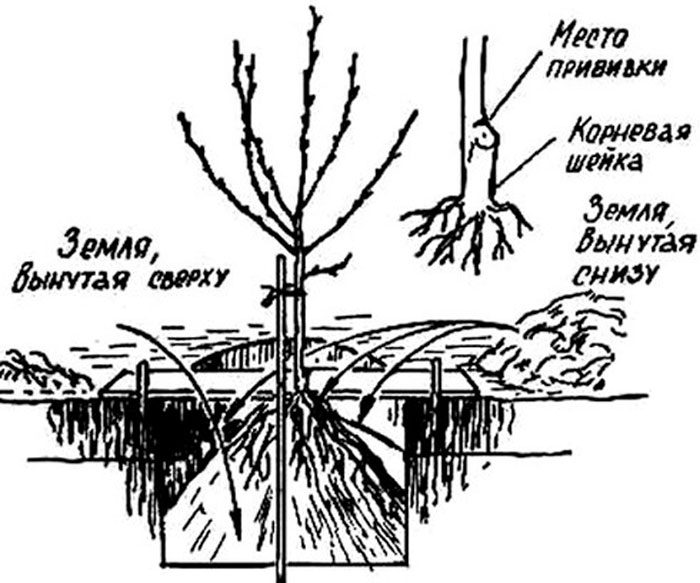
The preparation of the planting pit should be done as early as possible. Since the earlier you prepare the pit, the better the soil will be. Preparing the pit for spring planting should be done in autumn about 6 months before the day of planting. The size of the pit directly depends on the size of the root system of the seedling, on average, its depth and diameter are 0.5–0.7 m. A powerful and sufficiently long peg should be installed in the center of the bottom of the pit; it should rise above the soil surface by at least 50 cm.
If the soil on the site is infertile, then when digging a hole, the top layer of the soil should be thrown back separately. It is combined with humus, rotted manure or compost, while taking from 5 to 8 kilograms, 50 grams of potassium chloride and superphosphate are also added, and another 200 to 300 grams of wood ash. If the soil on the site is nutritious, then only wood ash and mineral fertilizers should be added to it. This soil mixture must be poured into the center of the pit to make a mound.
When choosing a peach seedling, try asking the seller if it is adapted to your region or not. Inspect the vaccination site, it should be smooth and free from sagging. Also make a thorough inspection of the seedling's root system and its bark, they must be completely healthy. Break off a small piece of bark and check the color of its seamy surface, if it is green, then the seedling is alive, and brown color may mean that the plant is dead. The root system should not be dry or decayed. It is recommended to choose annual seedlings for planting, because they take root very well in open soil.
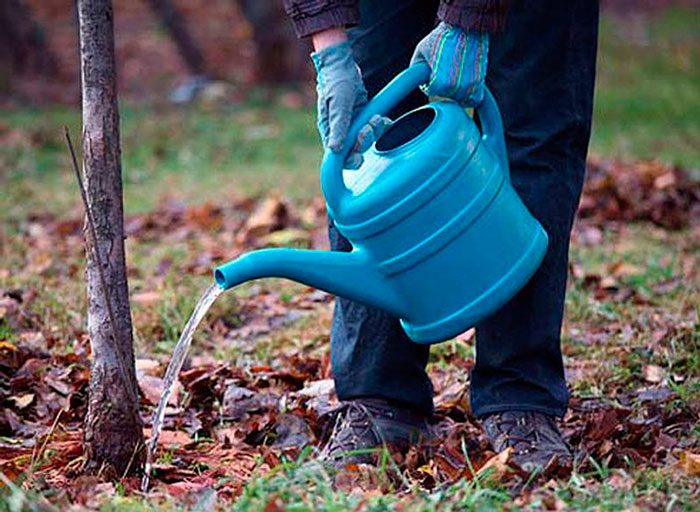
The seedling must be installed on a mound, poured into the center of the bottom of the pit. After the roots are neatly spread out, the hole must be filled with soil. Make sure that after planting the graft site rises above the ground by a few centimeters. The trunk circle should be trampled in the direction from the edges to the seedling. After that, 20-30 liters of water should be poured into the formed hole. After the liquid is completely absorbed into the ground and the soil settles, it will be necessary to tie the plant to the peg, as well as mulch the trunk circle, for this it is covered with a thick layer of manure (from 8 to 10 centimeters). It should be borne in mind that the trunk of the plant should not come into contact with manure.


Watch this video on YouTube
Planting a peach in autumn
For planting a peach in the fall, the pit is prepared in 15–20 days, while the soil should be combined only with wood ash and mineral fertilizers. The resulting nutrient mixture should be poured with a mound around a peg installed in the center of the bottom of the pit. The further order of planting the plant is exactly the same as in the spring. The planted peach should be hilled high (to a height of 0.2 to 0.3 m).Before severe frosts, the tree trunk should be wrapped in burlap, while on the south side several holes should be made in it for ventilation.


Watch this video on YouTube
Peach care
Spring peach care
They begin to take care of the peach tree in mid-April. First, the plant must be sprayed along the swelling buds from aphids, moths and other harmful insects. After that, it is treated with a Bordeaux mixture (3%) in order to destroy the fungi. Pruning for replacement should be carried out on a pink bud, at the same time the plant is sprayed from fungi with a product that can replace the Bordeaux mixture. The fact is that during the growing season, it is prohibited to use copper-containing products for treating trees.
When the plant has bloomed, it will need a combined spraying against diseases and pests.
In the event that in winter there was practically no snow, and in spring there was no rain, then the tree will need to be watered abundantly in May.
Summer peach care
When the shedding of the excess ovary is over, it will be necessary to start distributing the load of the fruits on the plant. It should be remembered that on each fruiting shoot there should be 1 ovary per 8-10 centimeters in length. Extra ovaries should be plucked out. The surface of the trunk circle must be systematically loosened and weeded. In summer, the peach needs to be watered regularly, especially if there is prolonged hot weather. But you can start watering this culture only after the stone has hardened, otherwise there is a high probability of cracking the fruit. Inspect the tree systematically and spray for pests and diseases if necessary.
Experienced gardeners advise to make 2 or 3 foliar dressings before harvesting, using potash fertilizer for this. This will increase the amount of sugar in the fruit. This top dressing can be combined with spraying the plant against powdery mildew and pests. No later than 4 weeks before harvesting, the tree must be watered. In this case, the fruits will grow by about 1/3.
Peach care in autumn
In August – September, the setting and formation of flower buds is observed. It should be remembered that their frost resistance depends on how much moisture there is in the soil at this time. In this regard, during this period, it is very important to carry out water charging irrigation.
In the event that fungal diseases are not uncommon for your plant, in the autumn, around October, when the foliage begins to change color, it will need to be sprayed with Bordeaux mixture (3%). And when all the leaves fall off, the tree will need to be treated with a solution of urea (7%) or copper sulfate (1%).
Also in the autumn, mineral fertilizers and organic matter should be embedded in the soil of the trunk circle. They will feed the peach until spring.
Watering the peach
The number of waterings throughout the growing season is significantly influenced by weather conditions. On average, late-ripening varieties are watered 5 or 6 times, and early-maturing ones - 2 or 3 times throughout the season. Pour 20-50 liters of water under one plant for 1 watering. Water the peach very early in the morning or in the evening. The first watering occurs at the beginning of June. However, if in winter there was little snow, and in spring it rains, then it will be necessary to water the peach in the last days of May. The second time you will need to water the tree from early to mid-July. Then it is watered from early to mid-August. When watering, try to get the soil soaked to the depth of the root system (about 0.6–0.7 m).
For the fruits to be larger, it is imperative to water the peach 20-30 days before harvest. In this case, they will have time to build up mass. When watering 1 square meter, you should take 3–6 buckets of water, depending on the age of the plant.Remember that you can then water the peach only after picking the fruits, otherwise they will be watery and not so sweet.
Also, special attention should be paid to the moisture-charging podzimny watering of the plant, which improves its frost resistance. In this case, 9-10 buckets of water are taken per 1 square meter of the trunk circle.
Peach feeding
You need to feed the peach every year. The amount and composition of fertilizers directly depends on the quality of the soil on the site. For example, if the soil is poor, then it is necessary to apply both organic and mineral fertilizers every year. If the soil is nutritious, then organic matter should be added to it 1 time in 2 or 3 years. If the tree is watered relatively often, then the amount of fertilizers applied to the soil should be increased, because during watering, they are washed out.
In the spring, before the buds swell, the peach can be sprayed with a urea solution (7%). This drug will not only become a source of nitrogen for the plant, but will also exterminate all pests and pathogenic microorganisms that have settled down for the winter in the bark, as well as in the upper layer of the trunk circle. Remember that such treatment should not be carried out if the kidneys begin to open, as they can be burned. In the event that you are late with spraying the bush with urea, then you need to dig the trunk circle, while adding 50 grams of urea and 70 grams of ammonium nitrate to the soil under the young tree per 1 square meter of the trunk circle. As the plant matures, the amount of fertilizer per unit area should be gradually increased. So, once every 2 or 3 years it is necessary to increase the dosage of each fertilizer by 15–20 grams.
In summer, it is recommended to feed the peach by foliar method. During the growth and ripening of fruits, experienced gardeners recommend using the following nutrient mixture for feeding: for 1 bucket of water, take from 30 to 50 grams of urea or 50 to 60 grams of ammonium nitrate, 100–150 grams of superphosphate water extract, 50–70 grams of potassium sulfate, or 30-60 grams of potassium chloride, 50-80 grams of ammonium sulfate, 10 grams of borax and 15 grams of manganese. In the event that the ripening of the fruits is already coming to an end, then it is not necessary to add borax and nitrogen-containing fertilizer to this nutrient mixture.
During the ripening of the fruits, the tree is fed foliarly with a solution of potassium sulfate or potassium salt (for 1 bucket of water, 30 grams of substance). This will increase the sugar content of the fruit, as well as make their color more intense.
In autumn, the trunk circle is dug up, while 50 grams of calcium chloride and 40 grams of superphosphate are added to the soil per 1 square meter. 1 time in 2 or 3 years in the fall, organic matter (compost or humus) should be added to the soil. You can replace such a top dressing by growing siderates in the aisles (for example: rape, rapeseed, oil radish or lupine).
Peach wintering
This culture is thermophilic, so it should be covered for the winter. In the immediate vicinity of the trunk, you need to drive in 2 stakes, reaching the height of the plant stem. Then both the stakes and the stem should be wrapped in a bag of sugar. This design can be replaced with a cardboard box, which is installed around the barrel, wrapped with film. In the event that in your region the winters are quite mild, then you can do with hilling the plant stem to a height of 0.5-0.6 m. For the winter, the surface of the trunk circle should be covered with a layer of mulch (humus or peat), the thickness of which should be from 10 to 15 centimeters.


Watch this video on YouTube
Peach pruning
What time is pruning
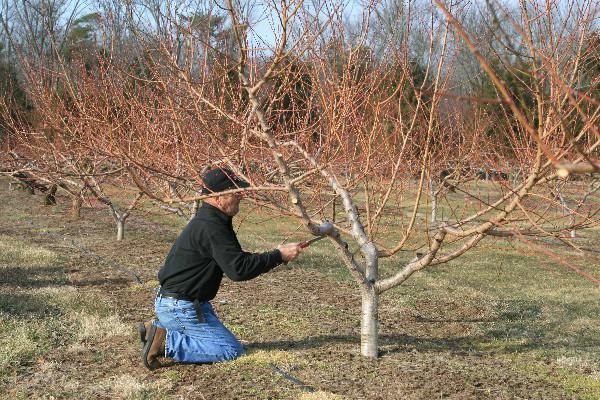
It is recommended to prune the peach tree in a time interval of 15–20 days between the beginning of sap flow and the beginning of flowering.If you want the tree to tolerate pruning easily enough, then it must be carried out from the beginning of the formation of pink buds to the beginning of their blooming, the duration of this time interval is about 7 days. At this time, the risk of infection of a peach with cytosporosis is the lowest. When all the fruits are collected from the tree, it is necessary to carry out sanitary pruning.
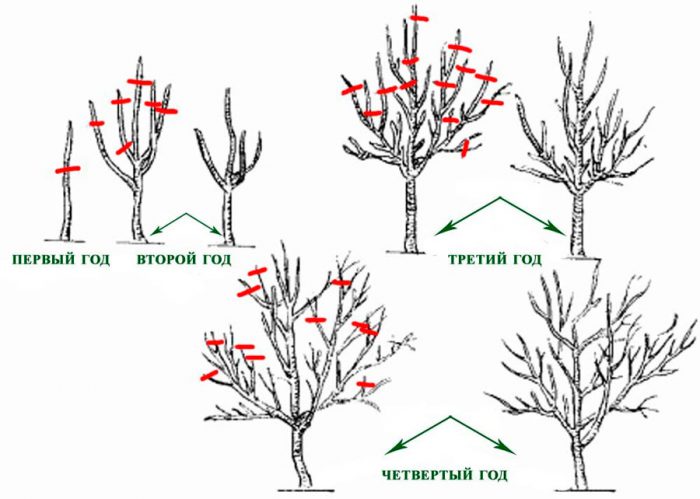
You will need to start shaping the tree from the first year of growth. The crown will be fully formed only after 4 years. Is shaping crown pruning really necessary? First of all, this procedure helps to regulate the balance between the root system and the crown. Also, thanks to this pruning, plant health is maintained. Such pruning also contributes to the fact that the peach begins to bear fruit earlier than usual, while collecting fruits from this plant is easier and more convenient.
How to trim a peach
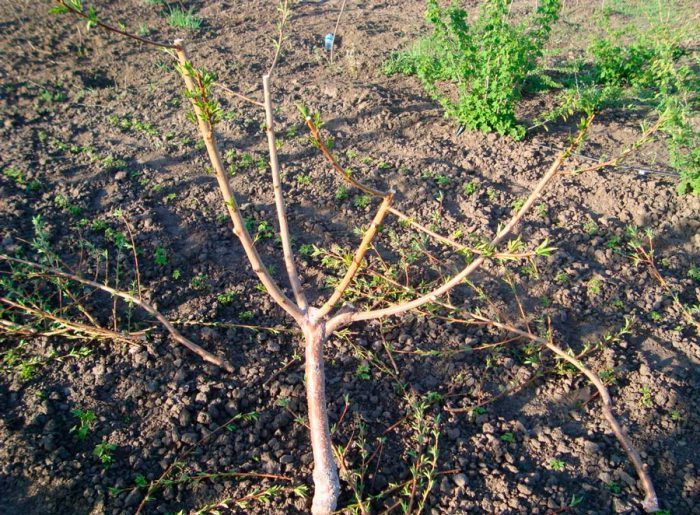
The rules for pruning peach trees of different ages differ. As a rule, the crown is given a bowl shape. To do this, after the seedling is planted in the open ground, its guide should be cut at a height of 0.6–0.7 m. The branch, which is located above all others, should have a wide angle of discharge. Find 2 more growths, which should be located slightly lower and at the same angle. All 3 branches should be shortened to 10 centimeters for the outer buds. The remaining shoots that are placed on the conductor and the trunk must be cut off immediately after bud break.
It is very important that the optimal slope is maintained on the skeletal branches of plants in the second year of life. Shorten the extension increments to 0.6–0.7 m. Powerful lower and upper extensions should be cut out, and the lateral ones should be thinned out. And the remaining growths must be shortened by 2 buds.
In a plant of the third year of life, on the upper skeletal branch, it is necessary to find the 2 strongest branches of the second order, they are shortened to 0.6 m from the bifurcation of the main branch. The part of the conductor that is located above the upper branch should be removed. All strong growths should be cut off from the lower and upper sides of the skeletal branches. Those annual growths that have reached 0.8 m in length should be cut into a couple of buds, which contributes to the formation of the fruit link. Shorten the bottom shoot to half a meter. The growths located on the branches that were shortened last season by 2 buds, and growing upwards should be shortened for fruiting, while the lower ones are cut into 2 buds. In the coming season, they will be used to form fruit links.
In a tree of the fourth year of life, on the branching of the second order of skeletal branches, one should find a pair of successful branching of the third order, they must be cut off by 1/3 of the original length. Complete the formation of fruit links on the second-order forks. The growths located on the branches of the third order need to be thinned out, while some of them are shortened by 2 buds, while the rest should be used as fruiting non-permanent branches, so they should not be cut off. Cut out all non-bearing parts located on the first-order fruit links. The branches of the lower growth, strongly shortened last season, are cut into 2 buds, which are located below. To stimulate future fruiting, 7 or 8 groups of buds must be cut off on the upper growths.


Watch this video on YouTube
Spring peach pruning
The formative pruning described above is carried out in the spring. As a result, the crown will acquire a cupped shape, which will make it easier to care for the tree, as well as simplify the collection of fruits. This crop also needs sanitary pruning. To do this, cut out all injured, frost-damaged or disease-damaged branches and stems. Places of cuts must be treated with garden varnish.
Peach pruning in autumn
In the fall, you need to start preparing the peach for wintering.Carefully cut off all dried, injured, old and disease-damaged fruit branches, as well as those growing inside the crown and contributing to its thickening. Only completely healthy branches and stems should remain on the plant, which will bear fruit in the next season. In the autumn, they are not engaged in crown formation.
In the summertime, a fruiting tree is cut only when absolutely necessary.
Peach propagation
This culture can be propagated by seeds, cuttings and grafting. The cultivation of own-rooted plants from cuttings is carried out only by specialists in the conditions of horticultural farms, because it is extremely difficult for a simple gardener to create the conditions that are necessary for their rooting.
There are several significant disadvantages to peach seed propagation. Thus, a seedling obtained from a seed does not always retain all the varietal characteristics of the parent plant. It is quite difficult to find high-quality peach seeds, those fruits that are sold on the market or in the supermarket are undesirable to use for this purpose, moreover, they rarely meet the necessary requirements. The best option would be a peach from a tree growing in your area.
The method of reproduction by grafting is also not ideal. It is difficult enough to find and buy the right stock, but you can grow it yourself, but this process will take at least 1 year. In order for the scion and rootstock to grow together, it is necessary that their tissues be compatible. You should also strictly adhere to the instructions, because even a small mistake can lead to a disastrous result.
Peach propagation by seeds
Growing a peach from seeds has both disadvantages and undoubted advantages:
- the lifespan of self-rooted peaches grown from seeds is 2 times longer than that of grafted plants;
- such plants have greater drought and frost resistance, as well as resistance to gum flow and other diseases;
- it happens that self-rooted trees have better characteristics than the parent plants.
First of all, you need to find the most suitable area for the peach. It should be borne in mind that the distance between the future seedling and any other shrub, tree or structure must be at least 300-400 cm. It must be well lit and have reliable protection from cold winds in winter. Winter sowing is preferred. Seeds are sown in October or November, in this case, in the winter months, the seeds will be able to undergo natural stratification.
Before sowing, the seeds should be dried by placing them in a shaded place. After they are carefully opened, the kernels should be removed from them. On a site selected in advance, you need to make a trench into which nutritious loose soil is poured. The removed kernels should be planted in this trench, the distance between them should be from 25 to 30 centimeters, and they need to be buried in the soil by 50–60 mm. At the very end, cover the seeds and water the area. Seedlings may not show for a long time. The fact is that at the beginning of the seedling a root is formed, and only then a sprout. In this regard, very loose and soft soil should be used for backfilling the trench. At first, crops need daily watering. After the seedlings appear in the spring, they will need feeding with a weak solution of humus. And their leaves are sprayed with a solution of Tiovit or Ridomil, while it should be borne in mind that it must be of a very weak concentration.
Seedlings will need 3 transplants. After the plant grows from 8 to 10 true leaf plates, it will need to be removed from the soil along with a lump of earth. The central root of the plant must be carefully trimmed 60 mm below the root collar. After that, the plant is planted in the same place, the soil near it should be well tamped. Then the seedlings are watered.
When the height of the plants is 0.9–1 m, they should be transplanted a second time. This procedure is carried out in the spring before sap flow begins. The plant must be dug around the perimeter, departing from the stem 0.25–0.3 m. Then the peaches are pulled out together with a lump of earth and transplanted, for this they must be swapped with each other.
Strengthened and grown seedlings should be transplanted a third time to a permanent place.


Watch this video on YouTube
Peach grafting
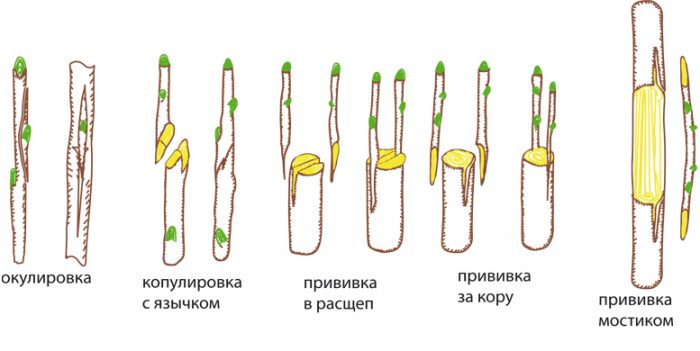
This crop does not have good frost resistance, but it is drought tolerant. For grafting a varietal peach, it is recommended to choose one of the following rootstocks: plum, quince, apricot or almond seedling. Whichever stock you choose, the vaccination rules are the same. First, prepare a stalk of the peach variety you need, after which it is grafted onto a one or two year old seedling (stock).
Cuttings are harvested in late autumn before the frost sets in. For storage, they are placed directly in the garden or removed to the cellar. From above, the cuttings are covered with any warm material, which is covered with a thick (about 20 centimeters) layer of sawdust. After it gets warmer outside, the cuttings should be placed in the refrigerator on the vegetable shelf. The vaccination procedure itself is carried out in the spring, while you need to wait for the start of sap flow.
As a stock, you can use a peach seedling, which was grown from a stone, or wild crops listed above. The rootstock thickness should not be less than 15 mm. The rootstock is shortened to the required height, while inspecting the bark, it should be smooth and not have buds. Which grafting method is most suitable in a particular case directly depends on the thickness of the scion and rootstock, or rather, whether they coincide or not. Possible methods of grafting: cuttings, buds or splits.


Watch this video on YouTube
Peach disease
Peach differs in that it can get sick with a countless number of various diseases. Below, only those of them will be described in detail, which are the most common, and also pose a rather great danger to this culture.
Clasterosporium disease
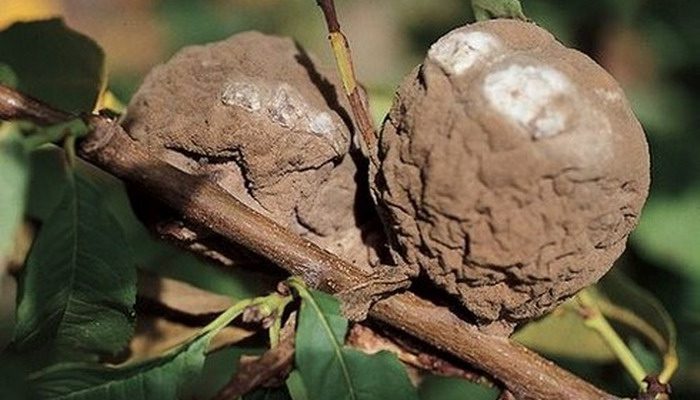
Clasterosporium - this very dangerous disease is fungal, it is also susceptible to nectarine. This disease affects all parts of the plant that are located above the ground. On the surface of the leaf plates, specks of a pale brown color are formed with a dirty red or crimson edging. Over time, the tissue inside the spots dries up, then it dies off and falls out. As a result, holes appear on the foliage, which is why this disease is also called perforated spotting. In annual seedlings, on the bark covering young shoots, varnished orange specks appear, spreading along the fibers in length. The bark itself cracks, and gum flows out of the cracks that appear. Dying off of the affected shoots is observed, the tree begins to dry out.
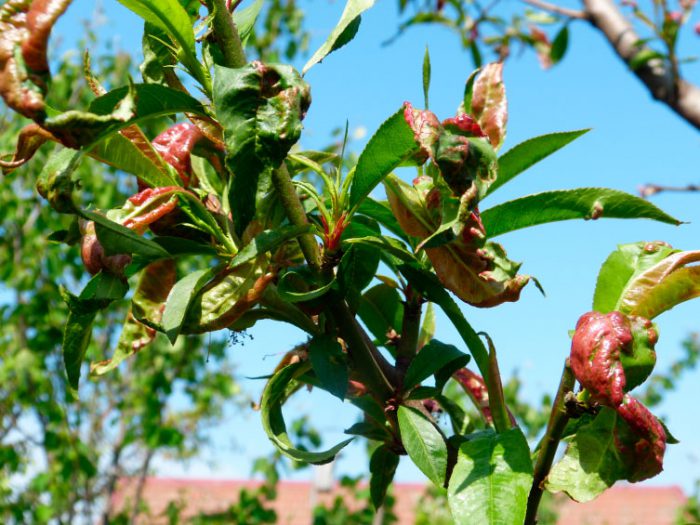
Curly leaves
The greatest danger to this culture is a disease called leaf curl. Often it appears when the spring is long and damp. On the surface of the leaf plates of an infected plant, swellings of a pale red color are formed, it becomes wavy, uneven. The swellings gradually swell, a white bloom appears on the seamy surface of the leaves. The foliage becomes brown and flies around. There is a gradual exposure of the stems, they become similar to a lion's tail, because a bunch of foliage remains on their tops instead of tips. Curvature, thickening and yellowing of the shoots are observed. If you do not take any measures to combat this disease, then the tree will have a developmental delay, which will lead to its death.
Powdery mildew
If a white felt bloom has formed on the seamy surface of the leaf plates, on the fruits and on the upper part of the stems of the current season, this means that the peach is affected by powdery mildew. Deformation, growth retardation and partial death of the stems are observed. The first signs of powdery mildew on the plant can be seen from the last days of April to the second half of May. In the hottest time in the middle of the summer period, this disease reaches its maximum development.
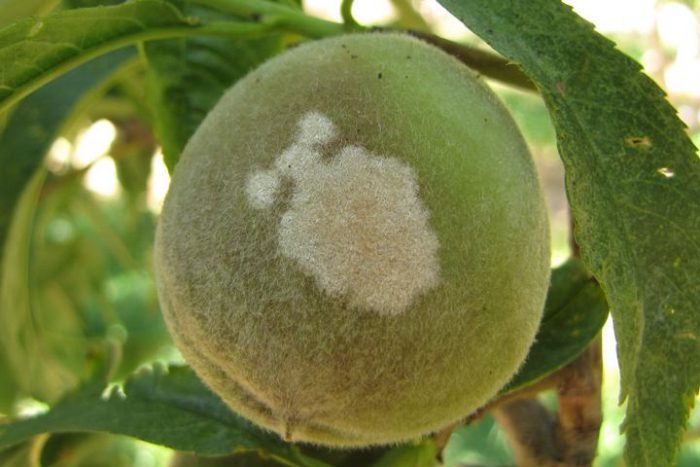
Moniliosis
Quite often the peach gets sick with stone fruit moniliosis. In the affected specimen, drying of the stems and individual branches is observed, specks of a dark color are formed on the fruits, which gradually increase. The color of the pulp of the affected fruit changes its color to brown, rotten peaches wrinkle and dry out. The affected fetus can infect healthy people with this disease.
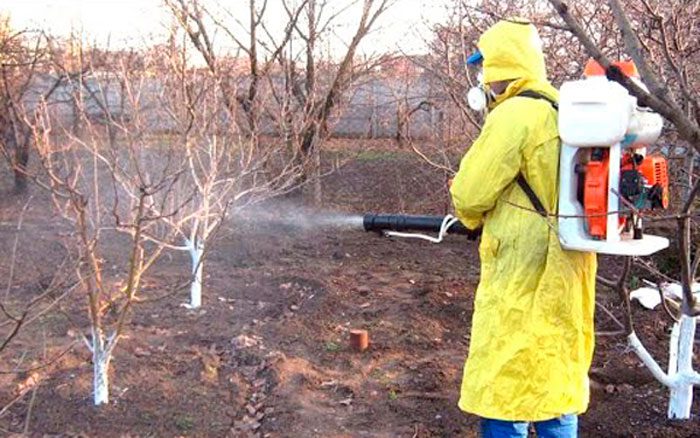
Peach processing
To cure the plant from clasterosporium disease, the first spraying must be done before the buds swell (necessarily before they open) and the drug Meteor or copper oxychloride is used for this. Then the plant is sprayed before flowering and after it ends, while using Topsin M or Horus (follow the attached instructions). In spring, before the peach blooms, you need to cut off all infected stems and branches, while the places of the cuts should be treated with a solution of lime (8%), to which a solution of copper or iron sulfate (2%) is added. Then the places of the cuts must be smeared with garden varnish.
A tree affected by curl should be treated with Meteor or copper oxychloride. This spraying is carried out after the entire crop has been harvested and the leaves begin to fall. The same treatment should be carried out in early spring and at the beginning of the appearance of pink buds, while instead of these funds containing copper, you can take Horus or Skor with the addition of Delan. Infected stems and foliage must be cut and destroyed before sporulation begins.
To protect the tree from powdery mildew, it should be sprayed at the end of flowering with Topsin M, Vectra, Topaz, Skor or Strobi. For prophylaxis, in spring and autumn, you need to cut and destroy the infected stems, also collect and burn all fallen fruits and loose leaves. The soil in the near-trunk circles must be dug up.
A plant infected with moniliosis will need 3 treatments. Before the plant blooms in the pink bud phase, it should be sprayed with Horus. The second treatment is carried out with Topaz at the end of flowering. The third time the peach is treated half a month after the second spraying and Topsin is used for this. Infected areas of the plant must be cut out and burned.
Also, this culture often suffers from coccomycosis, scab, fruit or gray rot, cytosporosis, milky shine, gum decay, verticillosis, homoz or fungal burn.


Watch this video on YouTube
Peach pests
As a rule, all stone fruit crops have common pests. However, there are such harmful insects that harm only peaches. Below will be described those pests that most often settle on the peach tree.
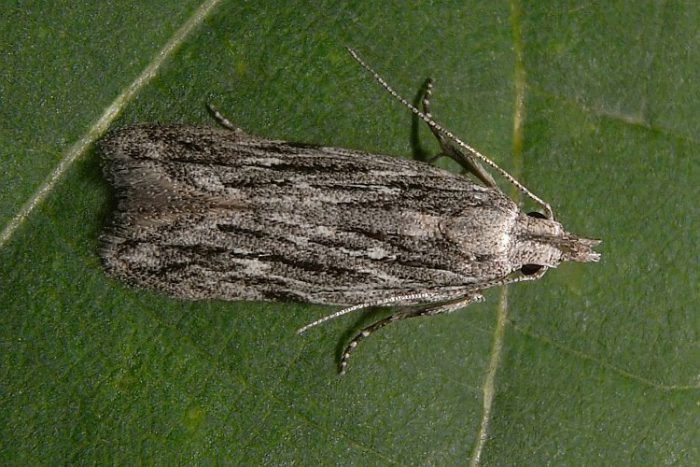
Plum moth
Plum and oriental moths are small butterflies. They need a peach to feed their offspring, and they also hide in it for the winter. Their caterpillars eat the young shoots of the plant, while the adults eat the seeds of the fruit. For the winter, such pests hide in cracks in the bark or under loose leaves in the trunk circle, while they hibernate in cocoons. To destroy the moth, the plant will need to be sprayed 3 times with an interval of half a month between treatments. To do this, use insecticidal agents such as Metaphos, Durban, Chlorophos and Karbofos.
Aphid
Aphids are able to settle on any crop, while they feed on plant sap.This sucking pest helps to weaken the plant's immune system. A sooty fungus almost always settles on the waste products of this insect, which covers the stems and leaf plates of the tree with a bloom of a dark color. You should also know that aphids are the main carrier of incurable viral diseases. In this regard, as soon as such insects are found on the plant, all necessary measures should be taken immediately to destroy them. This crop can accommodate green peach (greenhouse), black peach and large peach aphids. If there are very few aphids, then you can remove them from the plant mechanically, then the affected areas must be thoroughly washed with soapy water. In case of severe damage, the plant is sprayed with Aktellik, Karbofos or another means of similar action. If necessary, after 1.5–2 weeks, spraying is repeated. All treatments should be stopped 15–20 days before harvest.
Shield
The shield is capable of damaging any ground part of the peach. 24 hours after the scabbard adheres to the tree, red spots form on the surface of the fruits and bark. Pests settle on the tops of the shoots, on skeletal branches and bark, and contribute to the depletion of the plant. As a result of the vital activity of scale insects, cracking and dying off of the bark of a peach tree, drying out of growths, shrinking and deformation of fruits are observed, and leaves fly around ahead of time. To destroy such pests, the plant should be sprayed with Aktara, Inta-vir, Aktellik, Bankol or Mospilan (follow the instructions attached to the preparation). Onion water or pepper tincture is also often used, but such folk remedies are ineffective.
Striped moth
The striped moth also poses a particular danger to the plant. Caterpillars of such a pest, biting into young shoots and buds, eat away at their core, because of this they dry up and die off. If the caterpillars damage the fruits in the region of the stalk, then they begin to gum out. 1 caterpillar can harm 3-5 shoots. To get rid of moths, it is necessary to spray the tree with Chlorophos, Karbofos or Zolon during the period of bud opening. Inspect plants regularly and cut and destroy affected shoots.
Also on the peach tree, flower-eating weevils, fruit and miner moths, ticks and other pests very often settle.


Watch this video on YouTube
Peach varieties with description
Peach subspecies
The peach species is divided into several subspecies:
- Common peach... A description of this subspecies can be found at the beginning of the article.
- Peach (or almonds) Potanin. The height of such a low-growing plant is about 200 cm. The bark is pale red, the flowers are large, pink or white. The shape of the fruits is round, they contain an elongated stone. The fruits are inedible. This variety can be found in natural conditions only in China. This plant is not cultivated by gardeners because its fruits are not edible.
- Peach david... Such a tree reaches a height of 300 cm. Small fruits have a dry pericarp and low-juicy pulp of a sweet-sour taste. In this regard, this subspecies is cultivated, as a rule, as an ornamental plant.
- Gasuan peach... In natural conditions, it is found only in China. The height of such a medium-sized plant is from 300 to 400 cm. When a tree is covered with small flowers of white or pink color, it looks extremely impressive. Small, light yellow fruits are round in shape. The white flesh is comparatively tough and has a rather low taste. This subspecies is very often used in the breeding of valuable varieties of common peach. The fact is that it is able to endow the peach with frost and disease resistance.
- Peach peace... This subspecies is oriental. The height of such a tall, wild-growing plant can reach up to 8 meters. The shape of the fruits is spherical, they have a low taste. Not cultivated by gardeners.
- Nectarine... Has a lot of similarities with a peach. The most important difference between nectarine and peach is that its fruit is covered with a slippery and smooth skin. They can be colored white, yellow or reddish yellow. The yellow juicy pulp is less sweet than the peach. However, the seeds found in the nectarine pits are very sweet and can be used like almond kernels if desired.
- Fergana peach, or fig... Only a part of scientists singles out such a plant as a separate subspecies. The tree can reach a height of about 5 meters. The crown is wide spreading. This subspecies is not associated with figs. Flattened, rounded fruits have a depressed top. The dense, slightly pubescent skin is greenish-yellow. The fibrous, pale yellow flesh is very fragrant and sweet. The bone is relatively small. This subspecies is resistant to freezing of buds and buds.
Peach varieties
Today, a large number of varieties of common peach are known. They differ in size, taste, shape, smell, color and texture of the pulp and skin.
Fruits are divided into 4 classes by type:
- real peaches - the skin of the fruit is velvety, the stone is well separated from the pulp;
- pavia - the skin is velvety, the bone does not separate from the pulp;
- nectarines - the skin is bare, the bone is well separated from the pulp;
- brunions - the skin is bare, the bone does not separate from the pulp.
Varieties are also divided by fruit color:
- green, for example: Grisboro, Juicy;
- red, for example: Sancrest, Harmony, Krasnodarets;
- yellow, for example: In memory of Rodionov, Solnechny, Donetsk yellow, Glo Haven and Bohun.
Some of the finest nectarines include: Bountiful, Princess Pink, Autumn Blush, Rylines, Skif, Lola. The best frost-resistant varieties of nectarine are: Skif, Krasnodarets, Fodor, Lyubimets 1 and Lyubimets 2.
Peach varieties are also divided into early ripening, mid-ripening and late-ripening varieties.
Early peach varieties
The most popular early maturing peach varieties:
- Morettini... This very early early-growing variety, created by breeders from Italy, is self-pollinating. It begins to bear fruit 2 or 3 years after it is planted in open ground. Up to 30 kilograms of fruits are harvested from 1 plant. The average fruit weighs about 115 grams. On the surface of the rich yellow skin, there is a gentle pubescence. On 60 percent of the surface of the fruit, there is a blush in the form of dots and specks of bright red color. Fragrant juicy pulp with delicate fibers is colored creamy yellow. A medium sized bone is difficult to separate from the pulp.
- Velvety... This medium-sized variety is distinguished by its yield. The fruits are large and medium in size and weigh about 140 grams. They are painted in a deep yellow color, have a rounded shape and a carmine blush that covers almost the entire fruit. On the surface of the skin there is a slight suede pubescence. The flesh, yellow-golden with delicate fibers, is very juicy and tasty. The bone, which is poorly separated from the pulp, is small in size.
- Kiev early... This Ukrainian early ripening variety is distinguished by its high yield and frost resistance, as well as undemanding to growing conditions. Medium-sized pale yellow fruits of an elongated-rounded shape weigh about 100 grams, in some cases they can be covered with a bright blush. Juicy and tasty pulp is colored white-green.
- Redhaven... This variety is resistant to curl and cold. On the surface of the yellow-orange large fruits there are specks and specks of red color, they weigh about 150 grams. Delicate yellow pulp is very fragrant.If the gardener does not follow the rules of agricultural technology of this culture, then the tree is easily affected by fungal diseases.
- Collins... This variety is distinguished by its yield and resistance to frost, curliness and powdery mildew. On the surface of the yellow-red fruits, there is pubescence, they weigh about 150 grams. The pulp is sweet with a pleasant sourness. Such plants need good care: they need to be watered frequently, fed and pruned on time.
The following varieties are also quite popular: Early Forest Steppe, Juicy, Early Fluffy, In Memory of Rodionov, Greensboro, Novoselovsky, May Flower, Arp, Early Rivers, Domestic, Excellent, Red Bird Kling, etc.
Medium peach varieties
The most popular mid-season varieties:
- Veteran... This Canadian variety has a high yield and frost resistance. The yellow, rounded fruits are weakly pubescent, they weigh about 130 grams, most of their surface is covered with a red blush. Medium density fragrant juicy pulp has a yellow color and a sweet-sour taste. The pulp separates well from the stone. The plant is resistant to powdery mildew.
- Ambassador of Peace... Self-fertile variety, distinguished by yield and frost resistance. The carmine yellow fruits are very large, weighing about 220 grams. The fibrous yellow pulp is juicy and tasty. It is quite difficult to separate it from the bone. Fruit ripening occurs in mid-August.
- Nectarine Krasnodarets... Rounded small fruits weigh about 50 grams, have an almost invisible seam. They are colored yellow and have a deep red blush, presented in the form of stripes and dots. The smooth skin has no pubescence. Delicious juicy yellow flesh has delicate fibers.
- Soviet... This variety is zoned for the southern regions of Ukraine. The shape of the fruits is oval-obtuse, slightly compressed from the sides, they weigh about 170 grams. The medium velvety yellow skin has a carmine blush. Medium-fiber, fragrant, very juicy pulp is colored yellow. A medium-sized bone is well separated from it.
- friendship... This frost-resistant variety was obtained using Chinese material. Round-shaped fruits have a ribbed abdominal seam and weigh 140–250 grams. On the surface of the elastic tender skin there is a slight pubescence, it is painted in a yellow-cream color and has a red blush, consisting of streaks and dots. The sweet white-creamy very juicy pulp separates well from the stone.
Also quite popular are such varieties as: White Swan, Golden Jubilee, Champion, Dakota, Tuscany Kling, Double Mountain, New Yielding, Fine, Pineapple Nectarine, Salami, etc.
Late peach varieties
There are very few late-ripening varieties in comparison with early and middle ones. But since this culture is thermophilic, there is nothing strange in this. The most popular late-ripening varieties:
- Jaminat... This variety has a high yield. Elongated fruits are slightly compressed laterally. They are painted in a deep yellow color with marble red. Very juicy and sweet of medium density, the pulp has a rich orange color and barely noticeable acidity. The pulp can be easily separated from the seed.
- Irganai late... This cold-resistant variety can be easily affected by curliness or clasterosporium disease. Round-shaped fruits weigh about 160 grams. On the surface of the rich yellow skin there is a suede pubescence and beautiful red spots. The non-fibrous sweet pulp is orange-yellow in color. The small bone can be easily separated from the pulp.
- Kremlin... This variety, which is distinguished by its yield, is zoned for the southern regions of Ukraine and Crimea. The shape of the fruits is round, they weigh about 200 grams. Most of the orange-yellow skin with soft pubescence is occupied by a marble burgundy-carmine blush. The fragrant yellow-orange pulp of medium juiciness and density is very tasty. The stone is not very large and is easily separated from the pulp.
- Golden Moscow... This variety is distinguished by its high yield and frost resistance. The rich yellow fruits weigh about 180 grams, most of the skin surface is covered with a blurred red blush. The velvety pubescence on the skin is relatively weak. The fragrant, dense, medium juicy pulp of yellow color is easily separated from the stone.
- Tourist... The variety of medium frost resistance is zoned specifically for the southern part of Ukraine and for the Crimea. Wide-oval, rounded fruits weigh about 200 grams, they are painted in a creamy greenish shade and have a blurred burgundy blush that can cover about ½ of the skin surface, which has a slight suede pubescence. Medium density fibrous white-green pulp is fragrant, juicy and sweet, has a slight sourness. The pulp easily falls behind the large bone.
Still quite often cultivated are such late varieties as: Aidinovsky oblong, Champion late, Khudistavsky late yellow, Geokchaisky late, Oktyabrsky, etc.


Watch this video on YouTube