The fruit tree common apricot (Prunus armeniaca) is part of the genus plum, which belongs to the pink family. To date, scientists have not established where this plant came from. So, some of them believe that the apricot comes from Armenia, while the rest of the scientists are sure that it is from the Tien Shan region in China. Such a tree was brought to Europe from Armenia. There is a version that the apricot got to Greece thanks to A. Macedon, and from there it was transported to Italy. But there is no documentary evidence for this version. In the 17th century, this fruit tree from Western Europe came to the territory of Russia. At the same time, this plant came to the Caucasus and Ukraine from the Near and Middle East. The fact that this plant of Persian origin indicates that it was called "pole" in those days in Ukraine. In Russia, such a tree was also sometimes called "zherdel", it was also called "morel" and "yellow leaves".
Content
Features of apricot
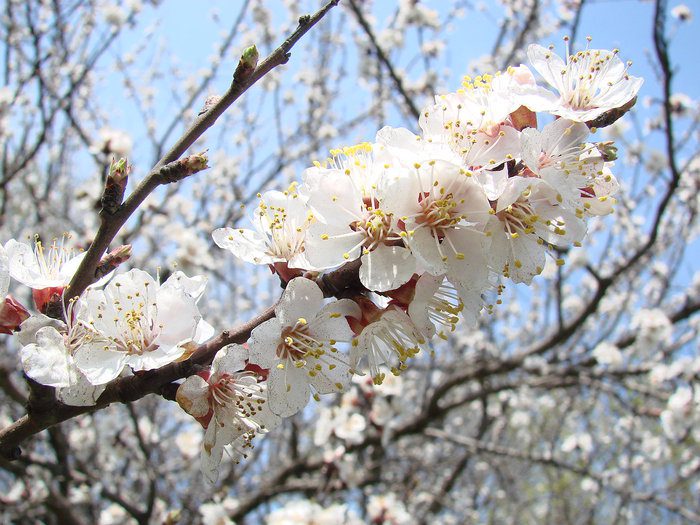
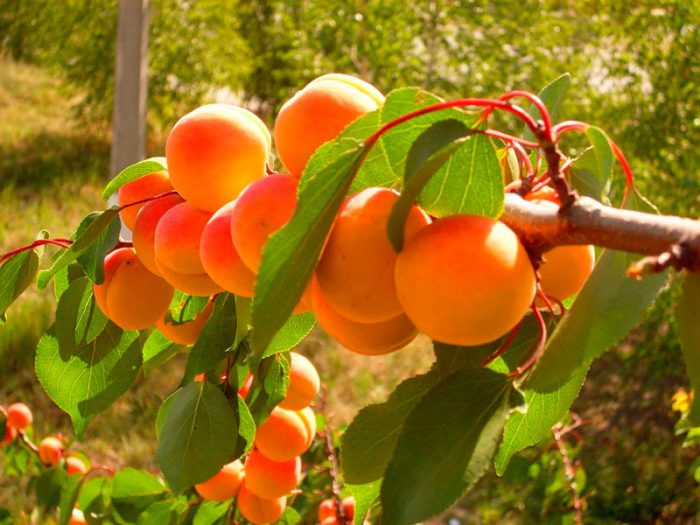
The apricot is a deciduous fruit tree with a height ranging from 5 to 8 meters. The color of the bark is brown-gray; on old trunks it is cracking. Young glossy brownish-red stems glabrous. Alternately arranged leaf plates have petioles and an ovoid-rounded shape, they are drawn at the apex and have a fine-toothed edge (sometimes double-toothed). The leaves reach 9 centimeters in length. The diameter of sessile single flowers is from 2.5 to 3 centimeters, they are white with pink veins and are located on very short pedicels. Flowering begins in March or April before the appearance of leaf blades. Such a fruit tree looks very impressive during flowering, like a pear, cherry, apple or sweet cherry.The fruit is an orange-yellow succulent elliptical, rounded or obovate monocotyledon, with a longitudinally located groove on the surface. The thick-walled bone is smooth or rough and is located inside the fetus.
Such a tree can live for about 100 years. After the apricot turns 3 years old, it begins to bear fruit, its duration is 30-40 years. The root system of the tree penetrates deep into the soil, making the plant drought tolerant. Most varieties are not afraid of a temperature drop to minus 25 degrees. The most frost-resistant varieties can withstand frost no more than minus 30 degrees. Such a fruit tree is related to plum, mountain ash, quince, wild rose, pear, peach, irga, chokeberry, medlar and apple.
Planting apricots in open ground
What time to plant
It is necessary to plant an apricot in open soil in northern latitudes at the beginning of the spring period, or rather, in the second half of April, while you need to be in time before the buds begin to open. In southern latitudes, it is recommended to plant such a plant in the autumn in the first days of October, while it should be borne in mind that the seedling must take root before the onset of the winter period. In mid-latitudes, apricots are planted in open soil in both spring and autumn. Apricot is a very warm and light-loving plant, therefore, for planting it, it is recommended to choose a sunny area on a hill that has reliable protection from strong gusts of wind, while cold air must necessarily flow to lower places. Such a plant cannot be grown on acidic soil, in this regard, it will need to be limed before planting. This tree grows best on light loam.
Spring planting
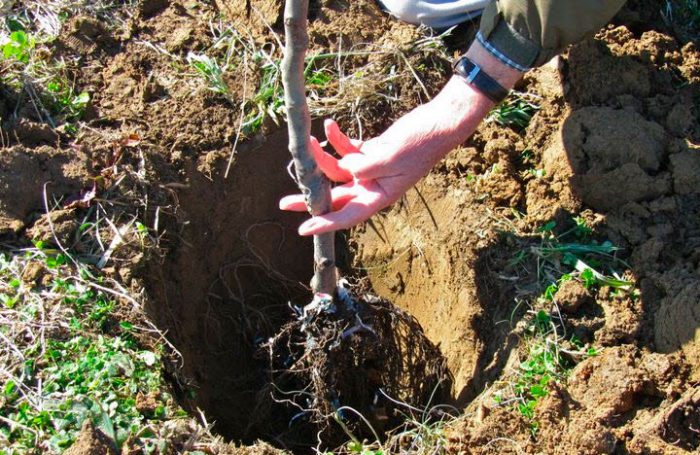
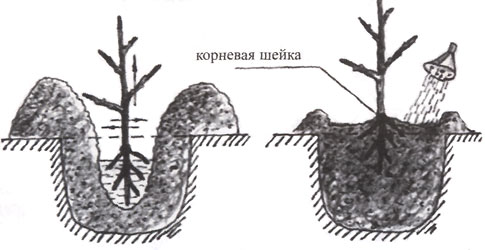
For planting, the pit must be prepared in advance and this should be done in the autumn, regardless of when exactly you are going to plant the apricot. The approximate size of the pit is 0.8x0.8x0.8 meters, but its final size is influenced by the size of the root system of the planted plant. First, you need to determine the middle of the excavated pit and drive a peg into it, which should rise 50 centimeters above the surface of the site. After that, a drainage layer is made at the bottom of the pit and crushed stone is used for this. The soil taken out of the pit during its preparation must be combined with humus or peat in a ratio of 2: 1, and 2 kilograms of wood ash and half a kilogram of superphosphate must be added to it. The resulting soil mixture must be thoroughly mixed and poured into the pit in such a way that a hill is obtained above the surface of the soil. Then the planting hole is left to settle.
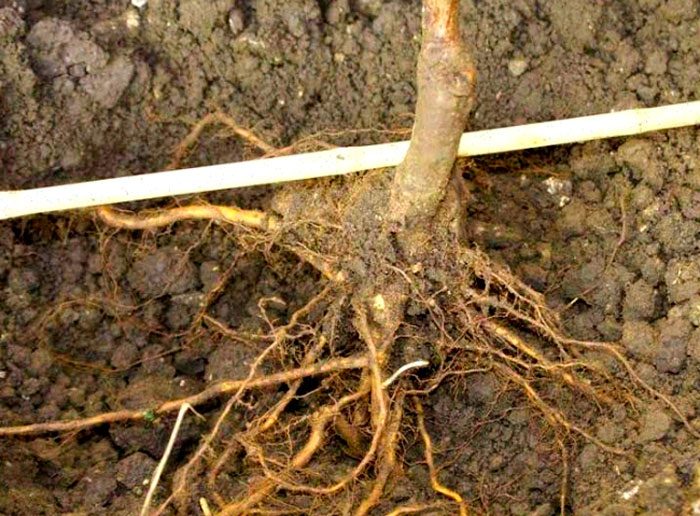
Experienced gardeners recommend using one-year-old apricot seedlings for planting. The fact is that they take root relatively quickly, and their crown lends itself well to shaping. If you want to buy a good varietal seedling, then you should go to a nursery or a specialized store that has a good reputation for this, otherwise there is a high probability that you will buy wild. If the seedling belongs to cultivated varieties, then its annual branches will be thick and devoid of thorns, while there should be a thorn at the base of the graft. Take a close look at the plant's root system. If a seedling has dry or frozen roots, then it is better not to buy it, as it most likely will not be able to take root.
With the onset of spring, a hole should be dug in a prepared pit, while its size should be equal to the size of the seedling root system. Inspect the roots of the plant and cut out any injured, decayed or dried out, and the rest need to be shortened slightly.The root system must be immersed for a while in a clay mash with the addition of a mullein, then it is placed in a planting hole. The seedling must be placed in such a way that the root collar rises above the surface of the plot by 50–60 mm. The hole should be buried with soil mixture, which must be well compacted. The planted plant needs to be watered well, for example, 20-30 liters of water are poured under one bush. After the water is completely absorbed into the soil, the root collar of the plant should be at the level of the surface of the plot. Only after that, the plant will need to be tied to a pre-installed peg.
Autumn planting
Planting an apricot in open ground in autumn should be the same as in spring. You need to prepare the pit 14–20 days before planting. In this case, the clay talker must be made very thick, because it must remain on the surface of the roots of the seedling, and the thickness of such a layer must be 0.3 cm.When planting several seedlings, it should be noted that an adult tree needs an area of at least 5 square meters ...


Watch this video on YouTube
Apricot care
How to groom in spring
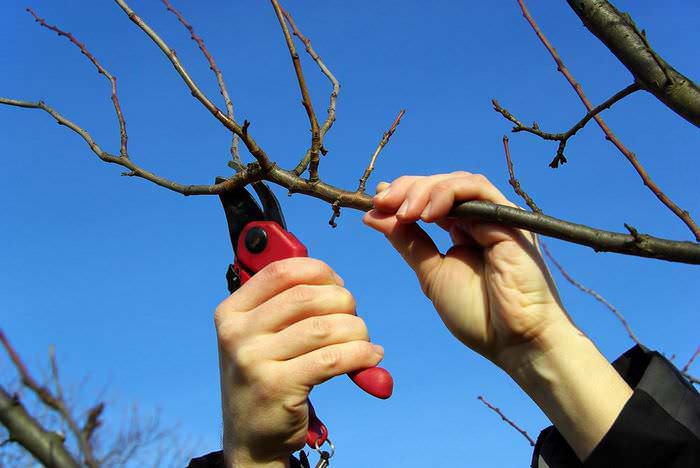
In the spring, before the start of sap flow in apricots, it is necessary to carry out a shaping and sanitary pruning, while it is necessary to cut out all injured branches and stems damaged by frost and disease. The base of the skeletal branches and the trunk of the tree should be painted with a lime solution.
In springtime, this fruit tree must be fed. What is the best use for feeding apricots? The first plant feeding in the spring, which is also a treatment, is carried out using a urea solution. This tool is capable of destroying pests and pathogens of various diseases that hibernated in the bark or in the soil of the trunk circle, and it is also a source of nitrogen, which is necessary for apricot in spring. But this kind of processing must be done before the buds on the apricot branches swell, otherwise they may burn out.
In the event that for some reason the gardener did not manage to spray the plant with urea on time, it will need to be treated for preventive purposes from diseases and pests with a solution of Iskra-Bio, Healthy Garden, Agravertin or Akarin. In this case, fertilizing is applied to the soil of the trunk circle in a dry form, 50 grams of ammonium nitrate and 70 grams of nitrogen fertilizer are taken for 1 plant. During the second top dressing in the spring, organic matter must be added to the soil. However, such feeding is carried out no more than 1 time in 2 years.
If the winter period turned out to be little snow, and in the spring there was no rain, the tree should be well watered.
How to care in summer
In the summer, during the dry season, the apricot must be watered. If it was not watered in May, then be sure to do it in June.
In the summer, young fruit branches begin to grow, in this regard, it will be necessary to make mandatory pruning. Otherwise, the crown will become very dense, which will negatively affect the ripening of the fruit, and the tree will begin to grow actively and become a real giant, from which it will be rather difficult to harvest.
Treat the plant against seasonal diseases and pests if necessary.
It is in the summer that the collection and processing of apricot fruits takes place. Remember that the unripe fruits collected will not be able to ripen, in this regard, they need to be picked in a timely manner. Fruit picking starts from the lower branches.
When all the fruits are harvested, the tree will need to be well watered, usually in August. This watering will be the last for the season, it is also called podzimnim, so the soil must be well saturated with water so that the plant can survive the winter.
How to care for the fall
In the fall, you need to prepare the apricot for the winter period. To do this, the first step is to make sanitary pruning.Cut out all injured as well as dried and damaged branches and stems.
When leaf fall ends, it is necessary to free the surface of the site from plant debris, and you should also dig up the soil in the trunk circle. Even in autumn, it is necessary to carry out preventive spraying of the plant stem and the surface of the trunk circle, since it is there that pests and pathogens take refuge for the winter.


Watch this video on YouTube
Apricot processing
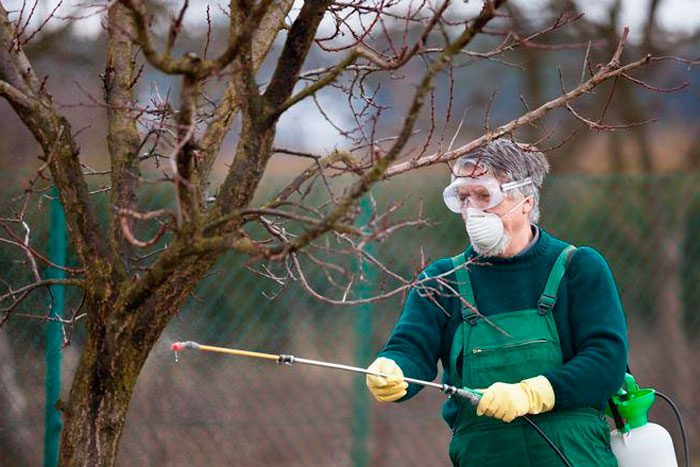
Apricot can suffer from various pests and diseases, but to prevent this from happening, you should resort to timely preventive treatments. To do this, the tree must be sprayed in spring and autumn with specially designed products. The first time you need to process the plant in early spring, while the buds are not yet swollen, for this, a urea solution is used (for 1 bucket of water, 0.7 liters of substance). However, if you did not have time to process the dormant kidneys, you cannot use urea, it should be replaced with Bordeaux liquid, copper sulfate or the means listed above. Together with such a preventive treatment, it is recommended to spray the plant with a solution of Ekoberin or Zircon, this will make the apricot more resistant to diseases and adverse environmental conditions.
The second treatment is carried out before flowering, while the air temperature should be at least 18 degrees. This treatment is aimed at destroying ticks, their larvae, as a rule, hibernate in the ground, for this they use Neoron or colloidal sulfur. You can get rid of leaf rollers and weevils with the help of Kinmix or Decis. When the plant fades, it must be treated with Ridomil or Oxychom for preventive purposes from moniliosis, and everything must be done according to the instructions.
While the fruits grow on the apricot, it will need to be treated with colloidal sulfur or Horus in order to protect it from powdery mildew and coccomycosis. Remember, however, that all treatments on the plant should be stopped 14 days before harvest.
In autumn, when leaf fall ends, the tree can be sprayed again with a urea solution.
Apricot feeding
Throughout the growing season, the apricot will need several dressings. In spring, such a tree needs nitrogen, while fertilizer is mainly applied to the soil. Before the onset of the summer period, you can feed the apricot with nitrogen 2 or 3 times, namely: in early spring, before the plant blooms and at the end of flowering. For feeding, slurry, saltpeter, urea or chicken droppings are used.
In the summer, the plant is fed on foliage. It is necessary to feed it at this time with fertilizers containing nitrogen, as well as solutions of those microelements that the apricot needs most during this period. Since the middle of summer, the tree is no longer fed with nitrogen, and instead, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are used for spraying.
When all the fruits are harvested (in the last days of August or in September), the apricot is fed with a mineral fertilizer that contains potassium and phosphorus. Both of these elements are found in wood ash. Even at this very time, it is recommended to add a small amount of calcium in the form of chalk to the soil.
Please note that you can feed apricots with manure only once every 2 or years, while 4 kilograms of organic matter is taken per 1 square meter. Compost must also be added to the soil (per 1 square meter from 5 to 6 kilograms), it should be mixed with mineral fertilizer. Potassium, nitrogen and phosphorus are part of chicken manure, it should also be applied to the soil (0.3 kilograms is taken per 1 square meter), but do not forget to combine it with compost first. Apricot is fed with organic matter only once every 2 or 3 years.It should be borne in mind that trees grown under turf do not need organic fertilizers.
Fertilizers containing nitrogen contribute to the fact that the shoots begin to grow more slowly, as a result of which their winter hardiness decreases. In this regard, it is not recommended to feed the plant with nitrogen from the middle of the summer period. During three spring dressings, nitrogen fertilizers are taken at the rate of 30 to 40 grams per 1 square meter.
When the fruit begins to ripen, the apricot needs potassium. Top dressing is done with potassium salt (40%) several times with an interval of 4 weeks. Fertilizer should be embedded in deep (depth from 0.2 to 0.3 m) grooves, which need to be made around the perimeter of the trunk circle, with 40 to 60 grams per 1 square meter.
During the growth, formation and ripening of apricot fruits, it needs phosphorus in the form of superphosphate. Such fertilization should be applied to the soil before the plant blooms, as well as at the end of flowering at the rate of 0.2 kilograms per 1 square meter.
Top dressing on foliage with boron and manganese is arranged in the summer. For example, you can feed the plant 2 or 3 times during the season with a solution consisting of 1 bucket of water and 1 large spoonful of boric acid. After opening the leaf plates, the apricot must be sprayed with a solution of manganese sulfate (1%). After 4–6 weeks, the tree needs to be sprayed again.
Wintering apricot
Apricot possesses the most winter-hardy root system of all stone fruit plants; therefore, winter in middle latitudes is not terrible for it. However, while the tree is young, it needs to be covered for the winter. To do this, for one-year and two-year-old seedlings, it is necessary to wrap the entire stem with spruce branches, and tie it with spunbond or lutrasil on top. Then the lower part of the trunk should be very high. The shelter needs to be removed in the last days of March.
Pruning apricot
What time is pruning
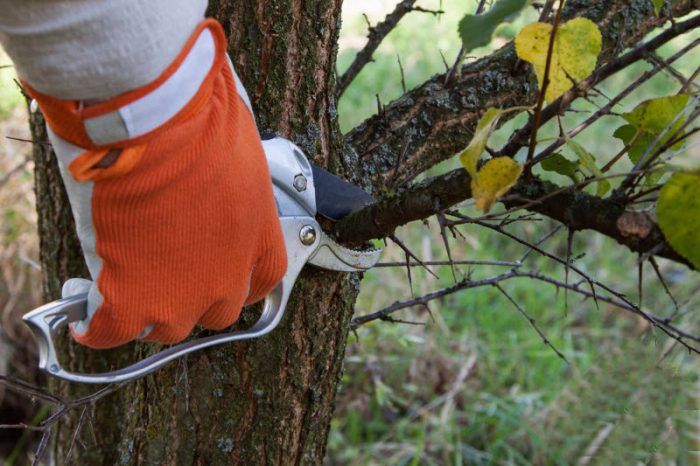
Apricot needs regular shaping, rejuvenating and sanitary pruning. The plant is pruned every year, and this is a very important point in plant care.
Apricot differs from other fruit trees in that it does not shed the ovaries. In this regard, the plant is often overloaded with fruits, which leads to injury to its branches. In mid-October, the apricot should be pruned, as a result of which it is necessary to form a crown, adjust the balance of branches, fruits and foliage, and this procedure is also performed for sanitary purposes.
Before the leaves open at the very beginning of the spring period, formative and sanitary pruning must be done, but at the same time it must be warm outside. All branches and stems injured or frost-damaged should be cut. You also need to prune the branches and the conductor to form the crown.
Once every 3 years in the summer, in mid-June, pruning should be done for sanitary and anti-aging purposes, this helps to stimulate the growth of new shoots by 0.3–0.5 m, as well as to lay fruitful buds on secondary shoots.
Already 12 months after planting a seedling in open soil, its first pruning should be done.
How to trim properly
Fruiting of apricot occurs on fruit branches, they are also called spurs, fruits, and bouquet branches. The spurs remain active for up to 3 years, then they must be replaced. In the event that the plant is not pruned, then its fruiting will become irregular, it will bear fruit once every 2-3 years. It should also be remembered that specimens with a thickened crown more often develop coccomycosis.
The crown shape of this tree can be different. So, traditionally, it is given the shape of a ball, the shape of a cypress, and there is also a form of palmette and its variety - Verrier's palmette. The last option for forming the crown is the best in terms of yield coefficient from 1 cubic meter of space.Below, it will be described in detail how to form a thin-tiered crown, which is quite common among trees grown by gardeners in mid-latitudes.
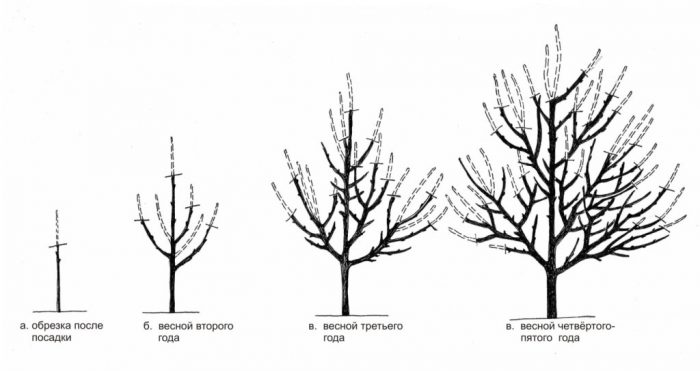
In the first year, the seedling will actively grow a conductor. In the first weeks of autumn, the conductor of the plant planted last fall must be shortened by ¼ part. Next year, the gardener will have to deal with the formation of skeletal branches. To do this, you will need to select the 2 most powerful branches that remain on the tree, cut them off by ½ part, while the remaining branches should be cut into a ring. The central conductor also needs to be shortened, and at the same time it should be 20-25 centimeters longer than the skeletal branches. From the branches you need to cut off shoots that grow at an acute angle.
Then, for the next years, it will be necessary to lay another 3 to 5 skeletal branches, while the formation of the second-order branching should begin on them, which should be at a distance of 0.3–0.4 m from each other. The shoots in the upper part of the crown should not be allowed to overtake the lower ones in growth. Unnecessary stems need to be cut. When the seventh and last skeletal branch is laid, with the onset of the next spring period, it will be necessary to cut the conductor flush with it, since it is no longer needed. After the crown is fully formed, you just have to maintain its shape, while preventing it from thickening. In highly branching varieties, the stems should be shortened by 1/3, and in those that are distinguished by poor branching - by only ½ part. If the tree is fast growing, then it should be pruned 3 times per season, while strong stems should be shortened by ½ part, and weak ones by ¼.
The tree will need rejuvenating pruning only after its annual growth is less than 0.4 m.To do this, it is necessary to prune skeletal branches for three or four years of wood, while the cuts should be made on strong branches that grow in the right direction.


Watch this video on YouTube
Spring pruning
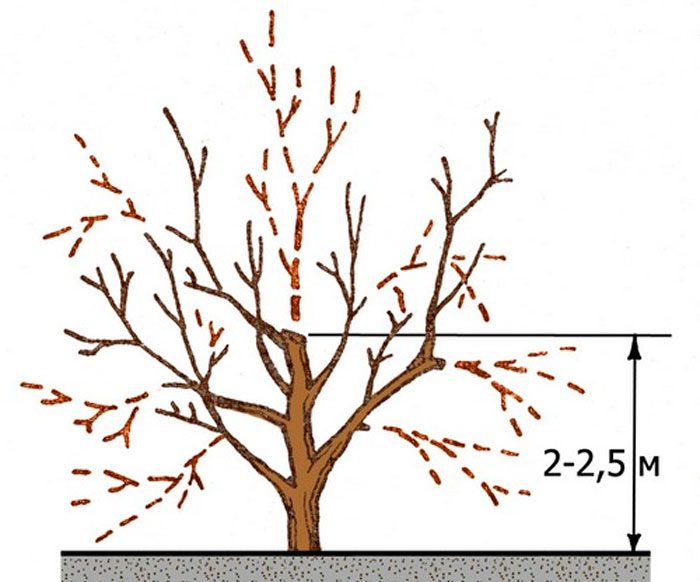
Since the fruits die off, there is a gradual exposure of the skeletal branches. Pruning a fruit-bearing tree helps to maintain its active growth, in this case, its annual growth will be not less than 0.4–0.5 m. After reducing the growth to 0.3 m, it is necessary to stamp the stems on two-year-old wood. Also, in the spring, the crown should be thinned. To do this, it is necessary to remove the weakened and starting to dry branches, you should also start transferring skeletal and semi-skeletal branches to the outer and lateral branches, which are located in free space. 2–4 blades-openings should be cut for 1 time, while their exact number depends on the density and size of the plant crown.
Summer pruning
If the apricot is grown in a region with a warm climate, then it will need pruning in the summer. It will be necessary to cut the stems, the length of which is from 0.3 to 0.4 m, in half. Pruning in the summer increases the abundance of growth even before the end of the current year. Until the end of the growing season, the plant has time to completely restore the leaves, and generative buds are laid on the shoots of the second wave. But in order for the apricot cut in summer to be able to fully recover, it will need a sufficient amount of moisture and nutrients. In the event that watering the plant in the summer is irregular, then it is better to refuse pruning.
Autumn pruning
In autumn, the apricot is pruned in order to prepare it for wintering. Weakened, dried out and disease-damaged branches should be cut off from young plants, and all cracks and wounds should be cleaned and treated with garden pitch. You should also cut out all branches directed inward, this will help brighten the crown.In order to avoid overloading during the period of fruiting and exposing the branches, it is necessary to prune strong shoots for two or three-year-old wood.
Pruning of branches on mature plants is carried out using a branch of the following order. Do not trim branches in the bare part. If the crown is strongly thickened, then thinning should be started from semi-skeletal (peripheral) branches. To begin with, you need to cut out all injured, shading and interfering branches, then, if necessary, you need to shorten from 15 to 20 percent of healthy branches to the lower branch. Then, all dried, injured and disease-damaged branches must be removed from the fertile fouling wood.
If this is very necessary, then cut out the skeletal branches of the first order.


Watch this video on YouTube
Propagation of apricot
Apricot can be propagated by generative (seed) and vegetative propagation. Since most apricot varieties are cross-pollinated, it is difficult to predict which plants will grow from these seeds. However, the Dwarf variety, unlike the others, can be safely propagated by seeds, since they completely inherit all the varietal characteristics of the parent plant.
If you want to be completely sure which kind of apricot you will grow, give preference to vegetative propagation methods. Often, gardeners propagate the apricot by grafting, but only when propagated by root suckers or by shoots, the grown tree will retain all the varietal characteristics of the parent plant.
Reproduction by root suckers or shoots
As a rule, the growth around the plant appears due to the fact that it was severely damaged by frost, animals, or too strong pruning. Moreover, the appearance of root suckers indicates that the root system has been injured. This method of reproduction of apricot, on the one hand, is very easy, but on the other hand, it is rather complicated, since neither root suckers nor shoots appear in a healthy, undamaged plant. If they do exist, then choose a one-year-old shoot that is located at a sufficiently large distance from the tree, since when digging up, the roots of an adult plant can be injured. Then the scion is dug up and planted in a new place. Remember that only self-rooted trees can be propagated in this way, since in grafted plants, the shoots appear from the stock, and not from the varietal scion.


Watch this video on YouTube
Seed propagation of apricot
If there is a great desire, then an apricot can be grown from a brush. The plant grown from the seed of a self-fertile apricot is highly resistant to climatic conditions.
The seeds are planted in the first half of autumn, but before that they should be thoroughly washed and soaked for 24 hours in water. The floating seeds need to be thrown away, those that remain should be planted wet in open soil, while they are buried in the ground by only 6 centimeters. If the seeds are sown later, then rodents can take them apart. Mulch the surface of the bed with a layer of humus and grass, and also make sure that the soil is always slightly damp. Sowing can be done in the middle of the spring period, but in this case, the bones will need preliminary stratification, for this they are put in a box filled with sand, which is put into the refrigerator, there it will stay until spring. The emerging seedlings should be covered from above with a plastic bottle, from which the neck must first be cut off. The emerging seedlings must be watered, weeded, fed and loosened in a timely manner. By September, the seedlings will grow up, and they can be planted in a permanent place.
Grafting apricot
For the scion, you can choose a sapling of homemade plum, bitter almond, apricot, peach and cherry plum. Before you start grafting, decide exactly what the grown tree should be like. If you graft such a plant on a peach or almond, then you will get a heat-loving plant with low winter hardiness. If grafted onto the stock of apricot, cherry-plum or plum, then the grown tree will have an average winter hardiness. The height of the future tree also depends on the choice of the stock. So, if you choose a rootstock of cherry plum, mirabelle or peach, then the tree will grow tall, on the rootstock of Hungarian plums, not grafted apricots and almonds, the plant will turn out to be medium-sized. If you graft on a thorn, then you can get a dwarf or semi-dwarf tree, caring for it is relatively simple, as well as collecting fruits from it.
For the rootstock, two-year-old seedlings are chosen, the trunk of which has a thickness of at least 0.8 cm. It is best to plant in April or May, because it is at this time that the sap flow into the plant is as strong as possible. The easiest and fastest method of grafting is copulation, but it can only be used when the thickness of the rootstock and the scion are the same. The rootstock is trimmed at a height of 7 centimeters from the soil surface. Then, on the scion and rootstock, you need to make oblique cuts, which should be the same. After that, the sections must be attached to each other and well coated with garden varnish, then the connection is tightly wrapped with tape or electrical tape. In the case when the diameters of the rootstock and scion are only slightly different, then you can resort to the one-sided copulation method. And when the scion is much thinner than the rootstock, they resort to the bark grafting method.


Watch this video on YouTube
Apricot diseases
Apricot can get sick with the Vals fungus, clasternosporium, tape mosaic, moniliosis, verticillosis, smallpox, and viral wilting.
Moniliosis
When a tree is infected with moniliosis, the flowers first begin to fade, then the stems and foliage are affected, and then the branches. As the disease progresses, cracks appear on the surface of the branches. The plant begins to dry out. In the fight against moniliosis, you need to spray the apricot while the buds are still green with Bordeaux liquid (3%). During flowering, Teldor must be used for treatment. When the tree has faded, it will need to be sprayed with Horus. When the fruits begin to ripen, you will need 2 treatments of the affected plant with a break of 1.5 weeks and use the Switch's solution for this (for 1 bucket of water 5 grams of substance). In this case, the plant must be processed a second time half a month before harvesting the fruits.


Watch this video on YouTube
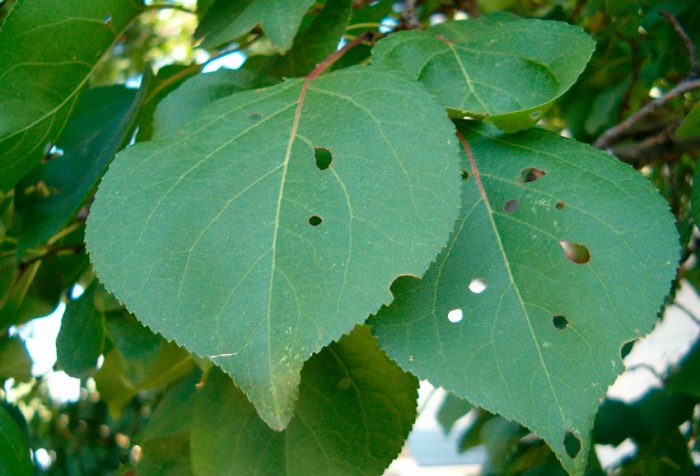
Clasterosporium disease, or perforated spot
If brown spots appear on the leaf plates, turning into holes over time, this means that the plant is infected with clasterosporium (perforated spot). Specks also form on the surface of the stems, and then cracks appear in their place, from which gum flows out. The affected parts of the plant become ugly. In order to get rid of this kind of spotting, you need to spray the tree with Bordeaux liquid (4%) or a solution of copper sulfate (1%) at the beginning of the spring period, as well as in the fall at the end of the leaf fall. If there is a large amount of rain in the summer, then the apricot will need to be processed 1 time in half a month. At a time when the green buds change their color to pink, instead of the listed drugs, you can process it with Horus.
Valsa mushroom
If orange ulcers appear on the tree, this means that it is infected with such an infectious disease as the Valsa mushroom. For prevention purposes, experts do not advise pruning apricots during the dormant period. It is also necessary that the soil surface of the trunk circle be loose during the growing season.Spray the infected plant with a solution of Switch (10 grams of substance for 1 bucket of water). It is necessary to carry out the processing several times with a break of 1-1.5 weeks. However, remember that half a month before harvesting, all processing must be stopped. You can also spray the plant with a fungicidal spray. For prevention purposes, do not forget to sterilize all garden tools before pruning.
Verticillary wilting
If in the lower part of the plant the foliage turns yellow, while the top has not changed its color, this is a sure sign of its infection with verticillium wilt. The accumulation of the fungus occurs in the veins and petioles of leaf plates, when they fall into the ground, which leads to infection of the rest, most often young plants. In order to prevent this disease, do not overmoisten the soil, and you should not grow strawberries and plants of the Solanaceae family near the apricot. Also, as a preventive measure, in spring and when leaf fall ends in autumn, spray the plant with a solution of Topsin-M, Fundazol, Bordeaux liquid, Previkur or Vitaros.
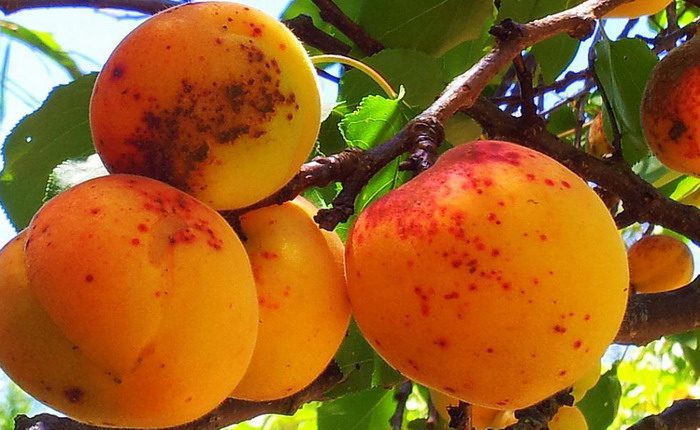
Smallpox
If sunken spots and brown stripes are formed on the surface of the fruit, this means that the plant is infected with a viral disease called smallpox. The pulp dries up near the spots. Fruit ripening occurs ahead of schedule, while their taste is significantly reduced.
Viral wilting
It is possible to understand that a tree is infected with viral wilting during the blooming of leaf plates during the flowering period. On the surface of the foliage, there are specks of a pale green color, while the plate itself becomes thicker and curls. The pulp near the stone in the fruits that appear becomes dark and gradually dies off. The transmission of such a disease occurs, as a rule, during the vaccination process.
Tape mosaic
The infection of an apricot with such a viral disease as a tape mosaic can be understood by the stripes of yellow color that appear on the leaf plates, which eventually form a lace pattern. The infected foliage dies off.
What are the ways to fight viral diseases? It should be remembered that today it is impossible to cure a plant from such a disease. In this regard, it is important to prevent apricot infestation by them. In this case, proper planting and tree care will be a good prevention. For planting in open ground, you should choose completely healthy seedlings, while taking the top of the plant as a scion. Make sure the area is always clean and all plants healthy. Start eliminating pests that carry dangerous diseases immediately. Be sure to sterilize the entire instrument before proceeding with pruning or grafting. Do not forget to process the surface of the plant trunk with lime mixed with copper sulfate.


Watch this video on YouTube
Apricot pests
Apricot is not very often affected by pests, but sometimes it does happen.
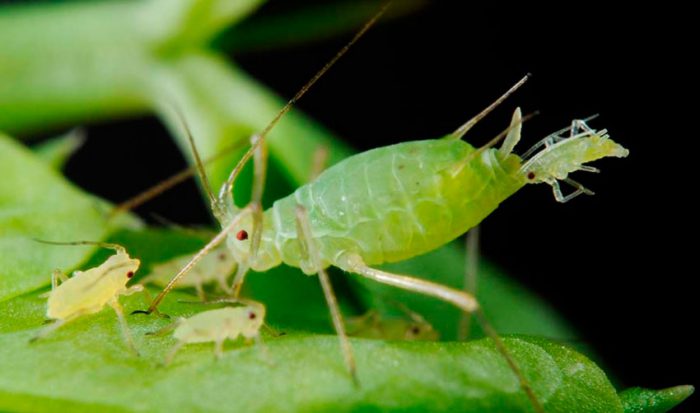
Aphid
Aphids are a fairly common pest; this sucking insect feeds on plant sap, which leads to their significant weakening. In the presence of aphids, a sooty fungus often settles on the foliage, which eats up the waste of such pests. Aphids are also considered the main vector of incurable viral diseases. To get rid of the plant from aphids, it must be sprayed with a soapy solution of ash or tobacco. In the event that not all insects die, the tree should be treated with Karbofos or Aktellik.
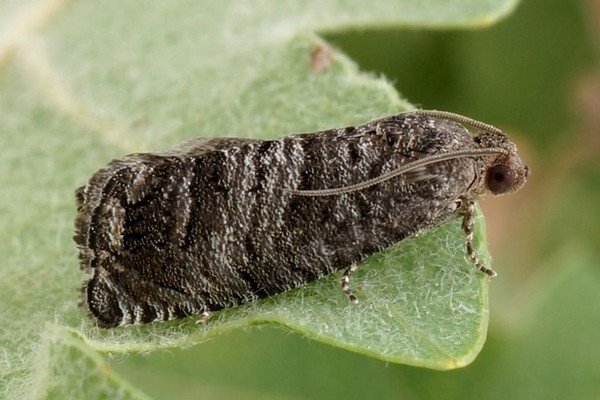
Fruit moth
The moth is a small butterfly that hibernates in a cocoon, hiding in cracks in the trunk or in the upper layer of soil. Moths hatch in early June, and they lay eggs in the fruit ovary and on leaf petioles.From the middle to the end of the summer period, a second generation of insects appears, which also lay eggs. In the fight against the moth, good results are observed with systematic preventive treatments in spring and autumn. You also need to constantly loosen the surface of the trunk circle. And you should also timely paint the base of the skeletal branches and the stem with lime mixed with copper sulfate.
Hawthorn butterfly caterpillar
Caterpillars of hawthorn butterflies gnaw holes in the buds and foliage of the plant. They are harvested by hand throughout the season. In the autumn, it is necessary to remove from the tree all the egg-laying of the pest, which are in the twisted sheet plates.
Leaf roll
Leafworm caterpillars overwinter in the upper soil layer or in the apricot bark. Upon awakening, they begin to devour the foliage and buds of the plant. Then they pupate, and in July butterflies appear, which start laying eggs on leaf plates and apricot stalks. In the fight against such a pest, the base of the skeletal branches and the stem should be treated with a solution of Chlorophos, which should be concentrated. Such spraying is carried out in the spring, when the air temperature rises to 15 degrees, and also after the harvesting of fruits is over.
In order for your tree to always remain healthy, it is necessary to carry out mandatory cleaning of the site in the autumn, while plant residues must be destroyed. Also, dig up the soil in the near-trunk circle and do not forget about preventive treatments in spring and autumn.
Apricot varieties
Apricot varieties for the Moscow region
Since Ukraine has a rather mild climate, apricots grow there almost everywhere, and they give a bountiful harvest, while often no one ever cuts or feeds them. The Moscow region has a colder climate, so not all varieties of apricot can be grown here, and besides, such a tree in this region needs good care. The best varieties for the Moscow region:
- Red-cheeked... This self-fertile variety is distinguished by its yield and resistance to disease and frost. The spreading crown has a rounded shape. Large fruits, round-flat or ovoid, weigh about 50 grams and have an orange-golden color with a bright blush. The fruits are covered with a thin skin, the fragrant pale orange pulp is sweet with a slight sourness. The fruits are eaten fresh, and they are also used to prepare jams, compotes and make dried fruits.
- Honey... This tall variety is productive and highly resistant to frost. Small yellow isosceles fruits are strewn with small red dots. Fruits are slightly pubescent. The fibrous, dense yellow flesh is quite sweet. The fruits are eaten fresh and used for the preparation of preparations.
- Northern triumph... The high-yielding variety is disease resistant. Large orange-yellow oval fruits weigh about 55 grams, there is a small green on the shady surface. There is pubescence on the middle thickness of the skin. The uniform orange pulp tastes good.
- Hardy... Such a self-fertile variety, resistant to diseases and pests, is distinguished by a stable and high yield. A large tree begins to bear fruit 5–6 years after planting in the garden. Medium flat-rounded fruits weigh about 45 grams, have an orange-golden color with a deep red blush. The skin is pubescent. The rich orange fragrant pulp is very sweet. The bone can be easily detached.
- Snegirek... The most winter-hardy variety, reaching a height of 150 cm. Such a self-fertile high-yielding variety is undemanding to the composition of the soil. However, it is easily affected by moniliosis and leaf spot. If stored properly, firm fruits will not deteriorate until mid-winter.
Early varieties of apricot
Today, there are more than 50 varieties that are bred both in Russia and abroad. They are divided into 3 groups according to the ripening time. Early apricots are the first group, the fruits ripen in early July. Early varieties:
- Melitopol early... The winter-resistant variety is resistant to diseases. Crohn's high pyramidal shape. Large yellow-orange oval, slightly flattened fruits weigh about 60 grams. The fruit is covered with a thin skin, and its dense, fragrant fiber-free pulp is sweet.
- Lescore... This early maturing variety was bred by Czech breeders. Crohn's high obrantopyramidal shape. Medium fragrant fruits weigh about 45 grams and taste good. Easily becomes infected with moniliosis.
- Alyosha... Winter-resistant fruitful variety. The deep yellow, rounded fruits are covered with small red dots, they weigh about 20 grams. The sweet-sour pulp is colored orange.
- Voronezh early... This hybrid variety was created using the Michurin variety Tovarish and the Central Asian variety Akhrori. This partially self-fertile dessert variety is the earliest, average winter hardiness, small fruits weigh about 20 grams. Sweet fruits have a slight sourness, the bone can be easily separated from the pulp.
- Early of Morden... Frost-resistant Canadian variety. The tree begins to bear fruit systematically and abundantly from the second year. Medium fruits weigh about 50 grams, not very sweet, but the pit can be quickly separated from the orange pulp.
Also early varieties are Samburskiy early, Tsarskiy, Iceberg, June, Alliance, Early Marusicha, Chervnevy, Veteran of Sevastopol.
Mid-season varieties
Fruit ripening occurs in the second half of July. Popular varieties:
- Polessky large-fruited... A fast-growing fruitful winter-hardy variety is resistant to fungi. The shape of the crown is round. Delicate fragrant sweet-sour fruits weigh about 55 grams, they are rich orange with a red blush. The tree is not too tall, but the fruit can only be reached with a stepladder.
- Pineapple... The early ripening unpretentious widespread variety has a high yield. The crown is not very dense. Delicious large fruits are quite sweet. Easily infested with spotting. The fruits are eaten fresh and used for the preparation of preparations.
- Rattle... The variety is partially self-fertile for universal use. The yellow-green oval fruits, slightly compressed from the sides, do not have a blush. The dense yellow-orange flesh is very sweet. The bone can be easily removed from the pulp.
- Kuibyshev jubilee... This variety is resistant to drought, cold and fungi. Orange fruits are slightly flattened, they have a slight blush on the surface turned towards the sun. They weigh about 25 grams. A thin skin covers the orange juicy slightly fibrous sweet-sour flesh.
- Dessert... The variety is fruitful, winter-hardy, has a dense crown. Medium, pale yellow sweet-sour fruits weigh about 30 grams. A thin skin covers the delicate pulp.
Also mid-season varieties are Botsadovsky, Zaporozhets, Shalamark, Sardonyx, Sheludko, Dessertny, Nadezhny, Michurinets, Yaltinets, Amursky, Aquarius, Monastyrsky, Molodezhny, Aviator, Burevestnik, Phelps, Olympus, Altair.
Late varieties of apricot
Fruit ripening is observed in August. Late varieties:
- Favorite... The variety is frost-resistant. Medium round, orange glossy fruits weigh about 30 grams. Juicy dense orange pulp has a very high taste.
- Spark... Such a fruitful variety is resistant to frost and some diseases. The tree begins to bear fruit early. The asymmetrical orange fruits are strewn with red dots and have a pink blush. They weigh about 45 grams. Juicy pulp is not very dense, sweet and sour.
- Krasin Kiev... Ripens in the second decade of August. Self-fertile winter-hardy variety. He needs pollinators.Large, rich yellow sweet-sour fruits of wide oval shape weigh about 55 grams. They are eaten fresh, canned and dried.
- Twinkle... The frost-resistant variety has a spreading crown. The rounded flat orange fruits are almost completely covered with a deep red blush. They weigh about 25 grams. The sweet dense orange-red pulp separates well from the stone.
- Success... This self-fertile hybrid has a very high frost resistance. It was bred using the Lewise, Comrade and Best Michurinsky varieties. The surface of the middle, round, yellow fruit is covered with light red dots on the sun-facing side, weighing about 30 grams. The amber-yellow sweet-sour pulp has medium juiciness and separates well from the stone.
Also late varieties are Sirena, Kostyuzhensky, Denisyuk's Special, Kompotny, Gift, Surprise and Joy.


Watch this video on YouTube