Sweet cherry (Prunus avium), also called bird cherry, is a member of the pink family. Such a tree reaches an average of 10 meters in height, but there are also taller plants (up to 30 meters). Under natural conditions, this plant can be found in Western Asia, Europe and North America. Sweet cherry is quite popular among gardeners. Sweet cherry is the most ancient form of cherry, already 8 thousand years BC. e. they knew about it on the territory of modern Denmark and Switzerland, in Europe and Anatolia. The name of this plant comes from the toponym of the city of Kerasunta, located between Pharnacia and Trebizond. This city was famous for the fact that on its outskirts there were plantings of incredibly tasty cherries. From Kerasunt comes the Latin name for the cherry cerasi, Turkish kiraz, English cherry, Neapolitan cerasa, French cerise, Spanish cereza. The Russian name sweet cherry also comes from this word. It is interesting that in a large number of languages, cherry and cherry mean the same thing, in this regard, the famous Chekhov's play in various countries is called "The Cherry Orchard" and there is no mistake, since these cultures are considered closest relatives.
Content
Features of cherries
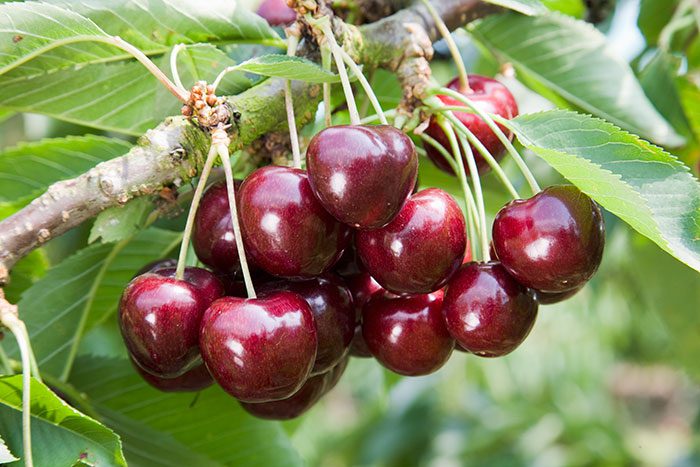
Sweet cherry is a fairly large tree. Young sweet cherry is a fast growing plant. Often its root system is placed horizontally, but when exposed to certain factors, the tree can develop very strong vertical roots. During the first two years of life, sweet cherry grows a taproot. After a while, it begins to branch out. The shape of the crown is ovoid, but under the influence of certain factors, it can become conical. The bark is colored in silver, brown or light red, in some cases its peeling with transverse films is observed.In such a tree, shoots are divided into 2 types: auxiblasts are long, strong shoots, and brachyblasts are shortened shoots with one internode. There are 3 types of buds on the shoots: generative, vegetative and mixed. Elongated obovate leaf plates are short-pointed and serrated along the edge. The length of the leaf petioles reaches 16 centimeters, glands are located at the base of the plate. Sessile few-flowered umbellate inflorescences consist of white flowers. The plant blooms in the last days of March or the first - in April, the foliage opens a little later. The fruit is an oval, spherical or heart-shaped drupe, it has a fleshy juicy pericarp of red, almost black, yellowish or dark red color. There are varieties with a blush on the fruits, while you should know that the berries in cultivated plants are somewhat larger than in wild cherries. The diameter of the berries is about 20 mm, in the pericarp there is a smooth spherical or slightly elongated seed with a seed, which includes the embryo, endosperm and a brown-yellow peel with a light red tint. The lifespan of such a culture is about a century. Fruiting of cherries begins at the age of four or five.
Planting cherries in open ground
What time to plant
If the region has a warm climate, then planting cherries in open ground is carried out in the autumn, while doing this several weeks before the ground freezes. In cooler regions, this procedure is carried out in the spring before the buds swell. For planting a seedling, it is recommended to choose a southeast, south or southwest slope or other areas that should be sunny and warm, and they should also be protected from the east and north wind. The groundwater on the site should not be located too high, because the vertically located roots can reach 200 cm in length. The sites located in the lowlands also cannot be used for planting this crop, since there is stagnant melt water there in spring.
Nutritious loam or sandy loam soil is best suited for planting cherries. If there is clay, sand or peat soil on the site, then it is not suitable for planting such a plant.
Such a tree needs cross-pollination, so pollinators should grow nearby. To do this, several cherries of 2 or 3 different varieties are planted next to each other. Several cherries can also act as pollinators, while varieties should be chosen whose flowering coincides with the cherry blossom time.
Planting cherries in autumn
If the planting of cherries is planned for the fall, then the preparation of the site should be done in advance. 15–20 days before the day of planting, it is necessary to dig the site, while 180 grams of superphosphate, 10 kilograms of compost and 100 grams of potash fertilizer per 1 square meter of the site must be added to the soil. You can replace them with a complex fertilizer for cherries and cherries (200 grams per 1 square meter of plot). Sour soil needs liming, for this you need to add lime, from 0.6 to 0.8 kg is taken per 1 square meter of heavy loam, and sandy loam soil - from 0.4 to 0.5 kg. Liming the soil should be carried out 7 days before fertilization. The fact is that lime and fertilizers are not applied to the soil at the same time. When planting this crop in clay or sandy soil, the site should be prepared over several years. To do this, sand is added to the clay soil for digging, and clay is added to the sandy soil, after which, for several years, fertilizers must be added to the soil every year.Only if the sandy or clay soil is properly prepared, cherries will grow and develop well in such a site.
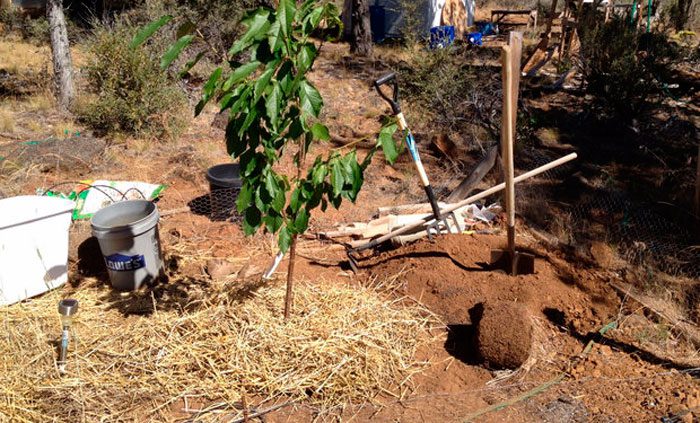
The planting pit should be prepared 15 days before the day of disembarkation. In diameter it should reach 100 centimeters, and in depth - from 60 to 80 centimeters. When preparing the pit, the upper nutrient layer of the soil must be thrown away separately from the lower one. A pre-prepared long wooden peg must be installed in the center of the bottom of the pit so that it rises 0.3-0.5 m above the surface of the site. The nutrient layer of soil must be combined with 200 grams of superphosphate, 500 grams of wood ash, aged compost and 60 grams sulfuric potassium. When planting cherries, lime and nitrogen-containing fertilizers must not be applied to the soil, otherwise burns may appear on the root system of the plant. Part of the topsoil, mixed with fertilizers, must be poured into the hole around the stake to form a mound, it is slightly tamped down, and then a layer of infertile soil is poured. Next, leveling and watering the soil in the pit are performed. The soil will settle within 15 days, after which you can start planting.
In addition to preparing the site and the pit, special attention should be paid to the choice of a seedling. It is necessary to choose one or two-year-old seedlings, while you need to make a thorough examination of its trunk. Remember that a trace of the vaccine must be visible on the trunk. The fact is that grafted cherries in most cases are varietal, and varietal plants have a number of advantages, for example, they begin to bear fruit earlier, and their fruits are much tastier. Also try to choose a seedling with many branches, in this case, the process of forming the correct crown will be much easier. Also, the plant must have a powerful guide. If the conductor is weak, then after the cherry starts to grow, it will have competitors from powerful branches. If the plant has a pair of conductors at once, then with a rich harvest there is a risk that the cherry will break between them, due to which it will die. Remember that the seedling should only have 1 powerful and straight guide. Also inspect the root system, it should not be injured or dry. Only seedlings with a strong, well-developed root system can be planted in open soil. When transporting, the plant's root system must be wrapped with a wet cloth, and then with polyethylene or oilcloth. If there is foliage on the seedling, then it must be removed, as it will contribute to the dehydration of the plant. Before planting, you need to cut out all dubious roots, as well as those that cannot fit in the hole. Then the root system of the plant must be placed in water for a couple of hours so that it can swell. Dried roots can be left in water for 10 hours.
Planting cherries in the garden can be done as long as the soil is not frozen. Make sure that after planting, the root collar of the plant rises 50–70 mm above the surface of the site. The root system of the plant must be carefully straightened by placing it on a hill of soil that was poured half a month ago. Then the hole is filled with soil from the lower infertile soil layer, while the plant needs to be shaken a little, as a result of which all existing voids will be filled. Then 10 liters of water is poured into the hole, and when the soil settles, you need to finish planting the cherries. The soil near the plant must be compacted. Then a five-centimeter deep groove is made around it, while 0.3 m must be retreated from the stem, from the outside it should be limited by an earthen rampart. Pour another 10 liters of water into this groove. After some time, the soil will settle in the pit, after which it will be necessary to add soil to it. When planting several seedlings, a distance of 4 to 5 m should be observed between them. Sweet cherry is a very large plant.


Watch this video on YouTube
Spring planting
Autumn and spring planting of sweet cherries in open soil have practically no differences. The pit for planting must be prepared in the autumn. It is dug up in October or November and humus or compost is added. In this form, it will have to stand until spring, as a result of which the soil in it will be able to settle well and settle. After the snow melts and the soil dries out slightly, it is necessary to start applying nitrogen-containing and mineral fertilizers into the pit. After 7 days after that, it will be possible to start planting cherries. At the very end, it will be necessary to cover the surface of the trunk circle with a layer of mulch (humus or peat).
Cherry care
Cherry care in spring
It is relatively easy to care for a sweet cherry grown in the garden. A seedling planted in the spring before the buds swell, needs formative crown pruning. To do this, you need to select several skeletal branches, and the remaining ones are cut into a ring, while there should be no stumps left. Places of cuts should be smeared with garden varnish. If you did not have time to carry out such a pruning before the sap flow begins, then it will need to be done only next spring. In older plants, formative and sanitary pruning is carried out in the spring, and it should be done before sap flow begins. After the outside air temperature rises to 18 degrees, it is necessary to carry out preventive treatment of cherries, as a result of which all pests and pathogens that have wintered in the surface of the trunk circle and in the bark of the tree will be destroyed.
If all the necessary fertilizers were applied during planting in the soil and in the pit, then feeding should begin only from the fourth year of plant growth. But this only applies to phosphorus and potash fertilizers, and those that contain nitrogen are introduced into the soil the next year after planting and do this annually. It is necessary to apply nitrogen-containing fertilizers in the spring after the establishment of warm weather, while the frosts should be left behind. The second feeding with liquid nitrogen fertilizers is carried out in the last days of May.
In the spring, they are also engaged in grafting of cherries. In this case, the old plant will act as a rootstock, on the roots of which you need to grow young cherries, which will be more productive.
Also, in spring time, cherries need to be watered, weeded, and weeds must be pulled out in time and the surface of the trunk circle must be loosened.
Summer cherry care
In the summer, the soil in the area where this crop grows must be loosened to a depth of 8 to 10 centimeters; for this, a hand cultivator or a garden hoe is used. Loosening is carried out the next day after the rain has passed or the plant has been watered. During the season, you need to water the cherries 3-5 times, while the final figure directly depends on the amount of rain. As soon as harmful insects or symptoms of disease are noticed on the plant, you should start processing it. Try to quickly determine what the problem is or how the plant is hurting, and fix it as soon as possible.
In the summer, formative pruning is also carried out, for this they pinch the shoots that grow incorrectly to weaken their growth. And also cut those branches and stems that contribute to the thickening of the crown. Root offspring should also be removed, otherwise they will begin to grow. Harvesting begins in the last days of May or the first in June. If the fruiting is abundant, then the branches may not withstand the severity of the fruit and break, therefore it is necessary to put props in the right places in a timely manner.
In the middle of the summer period, this crop needs feeding with phosphorus and potassium fertilizers with the addition of trace elements.In August, she is fed with organic fertilizers (solution of bird droppings or mullein). In order for the cherry to grow and develop normally, it is very important that its near-stem circle and aisles are always clean.
Cherry care in autumn
During the yellowing and falling of the foliage, as a rule, in September or October, you need to dig the site to a ten-centimeter depth while adding fertilization to the soil for the last time in the season. Before the mass fall of leaves begins, it is necessary to carry out a water-charging podzimny watering of cherries, this is especially important if the fruiting in the summer was abundant, and the autumn was dry. The flown leaves must be collected and destroyed, and then, for prevention purposes, treat the tree to destroy all pathogenic microorganisms and pests that prefer to winter in the bark of the plant, as well as in the upper layer of the trunk circle. In the last days of October, it is necessary to whitewash the base of the skeletal branches and the trunk.
After the onset of frost, you should start preparing the tree for wintering.
Cherry processing
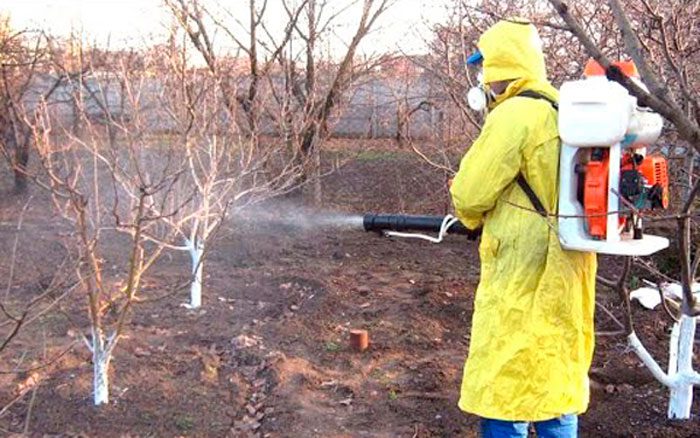
Preventive treatment against pests and pathogenic microorganisms is carried out twice a season: in spring before sap flow begins and in autumn, when mass leaf fall begins. What is used for processing? Treat the plant with a solution of urea (700 grams for 1 bucket of water), as a result, all pathogenic microorganisms and pests that hibernate in the bark or in the upper layer of the soil will die. However, this solution can be used for treatment only before the kidneys open, otherwise burns may appear on them. For migratory pests, the plant must be sprayed with Agravertin, Iskra-bio, Akarin or Fitoverm. To make the cherry more resistant to adverse conditions, it should be sprayed with Ecoberin or Zircon. This treatment is carried out at the same time as prophylactic.
Watering cherries
As a rule, during the season, cherries require 3 waterings:
- in the spring before the plant blooms, while for each year of its life, 15–20 liters of water are taken;
- in the middle of the summer period, even more so if there is a drought or rains are very rare;
- in the fall, they carry out podzimny watering together with feeding.
Before proceeding with watering, the trunk circle must be loosened. When the plant is watered and fed, the surface of the site must be covered with a layer of mulch. In autumn, when carrying out water-charging irrigation, try to soak the soil to a depth of 0.7 to 0.8 m.If you do everything correctly, the soil will freeze through in winter much more slowly, and the frost resistance of the tree will increase markedly.
Feeding cherries
What fertilizers should be used so that the tree grows quickly and gives rich yields? If the tree is more than four years old, then in the first days of May it is necessary to loosen the surface of the trunk circle, into which mineral fertilizers are then applied: from 15 to 25 grams of potassium sulfate, from 15 to 20 grams of urea and from 15 to 20 grams of superphosphate (per 1 square meter of the plot). In the last days of July, when all the fruits are collected, the plant that has begun to bear fruit will need foliar feeding, for this they use phosphorus and potassium fertilizers, and the necessary trace elements are also added to the nutrient mixture. Abundantly fruiting cherries should be fed with organic matter in August, for this you can use a solution of chicken manure (1:20) or mullein (1: 8).
When feeding cherries, it should be remembered that each plant has an individual need for nutrients. Therefore, when choosing suitable fertilizers, as well as the time for applying top dressing, it is necessary to take into account the weather conditions, the condition of the soil, and also pay attention to the appearance of the tree itself.


Watch this video on YouTube
Wintering cherries
Mature trees do not need shelter for the winter, but they must be prepared: paint the base of the skeletal branches and the stem with lime, and cover the surface of the trunk circle with a layer of mulch (peat). Young plants need shelter. To do this, they are tied with burlap or spruce branches. It is impossible to use lutrasil or other similar artificial materials for sheltering cherries, since under them the tree will rot.
Cherry pruning
What time to trim
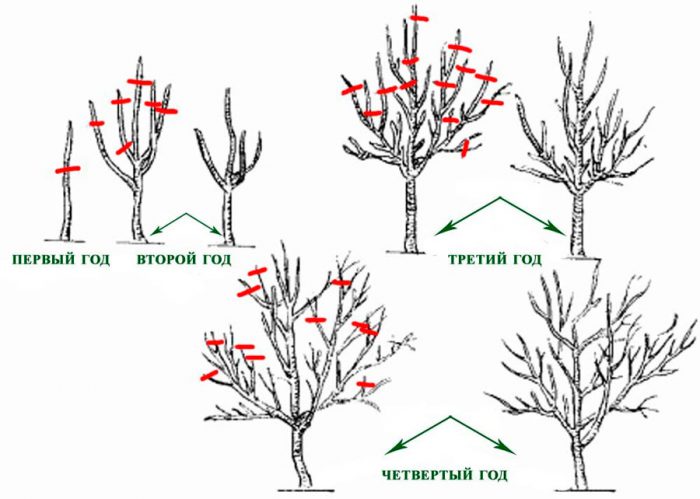
Taking care of cherries is not at all difficult, but this does not apply to plant pruning, which should be carried out correctly, regularly and with an understanding of the essence of this procedure. Pruning is carried out every year, while starting from the first year of the plant's life. If you cut cherries on time and correctly, then as a result, the quality of the fruits increases, as well as their quantity, the resistance to diseases improves, and the lifespan of the tree also increases. Pruning is recommended in the spring before sap flow begins, but at the same time there should be no frosts at night, and during the day it should be warm. There is an opinion among gardeners that it is possible to prune cherries only in spring, but this is far from the case. It is imperative to prune this crop every year, therefore, if pruning was not done in spring for some reason, this procedure is transferred to summer or autumn.
How to prune cherries
Pruning of seedlings is carried out after their height is equal to 0.5-0.7 m. Shorten the lateral lowest branch of the cherry to 0.5-0.6 m, while the remaining must be cut to the level of its cut. The conductor should not rise more than 15 centimeters above the skeletal branches. Those branches that are placed at an acute angle to the trunk must be cut. In the event that there are very few side branches (1 or 2), then they must be shortened by 4 or 5 buds from the base, the guide is cut 6 buds higher, and the laying of the lower tier is transferred to the next season.
Fruiting of this culture is observed on bouquet branches and annual shoots. It should be remembered that such a plant has an intensive growth of shoots, which, after pruning, grow back literally instantly, but it is not capable of branching. In this regard, the formation of the crown is carried out from skeletal branches in tiers. This process is long, because in 1 season in most cases it is not possible to lay even 1 tier. The formation of the first compact tier is made from branches that are located along the trunk at a distance of 10–20 centimeters from each other. On each of the next two tiers, there should be one fewer branches, while they should be placed asymmetrically and be relatively weaker. The distance between the tiers should be within 0.7–0.8 m. After the third tier is laid, in the same season on the first tier it is necessary to form 2 or 3 branches of the second order, which should be evenly spaced relative to the conductor, while the distance between them should be at least 0.6–0.8 m. In the next season, they are engaged in the formation of semi-skeletal branches on the second tier, and after another 1 year - on the third.
Starting from the fifth or sixth year of the cherry's life, during pruning, you need to try to maintain the height of the tree at a level of 300-350 cm, as well as the length of skeletal branches, which should not exceed 400 cm. Only those branches that are injured, grow incorrectly, or contribute to thickening should be cut crowns. Anti-aging pruning is carried out in the last days of February or the first of March. This procedure is necessary for those trees that have shrinking berries, while they grow exclusively in the peripheral areas of the crown.


Watch this video on YouTube
Spring pruning
Experienced gardeners recommend that sanitary and formative pruning be carried out in the spring, or rather, in mid-March or the first days of April.It is necessary to shorten the skeletal branches, as well as pruning the conductor to 300-350 cm. Those trees that give a bountiful harvest must be thinned out by cutting out all competing branches, as well as those that contribute to the thickening of the crown. All frost-damaged and injured branches and stems should also be cut. It should be remembered that the branches need to be formed in tiers, while the tier located at the very bottom should include from 7 to 9 skeletal branches.
Pruning cherries in summer
If there is a need to prune cherries in the summer, then this procedure is divided into 2 stages. The first stage occurs at the time when the plant finishes blooming, while its fruits should be in the stage of formation. The second stage is carried out after all the fruits have been collected. Shortening young shoots helps stimulate the formation of new horizontal branches. While the plant is young, it is subjected to pinching (the tips of non-lignified shoots are pinched), as a result, the cherry will be forced to form branches in the direction in which you need.
Pruning cherries in autumn
In the autumn, pruning is carried out after all the leaves have fallen from the tree. But experts advise to carry out this procedure before the end of September, otherwise the sections on the branches will heal much worse. If you cut out all the weak and injured branches, as well as those that grow incorrectly, cherries will more easily survive the winter. Shorten not skeletal branches to 0.3 m, but annual shoots by 1/3 part. In plants under 5 years old, the length of the branches should be no more than half a meter. In the autumn, it is recommended to cut the cherries with a saw, since such cuts will heal much faster than those that were left by the pruner.
One year old seedlings are still too weak for autumn pruning. If it is still carried out, then the plants will weaken so much that they will be damaged by frost. Such seedlings should be cut only in summer or spring time.
Cherry propagation
For propagation of cherries, seeds are used, as well as grafting. Seedlings grown from seeds may not retain the varietal characteristics of the parent plant. In this regard, as a rule, this method of reproduction is used only for growing rootstocks, in the future they are grafted with a cultural scion.
Seed propagation of cherries
In areas with a mild climate, it is quite possible to use a seedling of a sweet cherry growing in the wild as a rootstock. However, if the climate in the region is cold enough, then such a rootstock cannot be used, because it is not sufficiently winter and drought resistant. If you decide to grow a stock with your own hands, then the seeds should be taken from ordinary cherries, which are distinguished by frost resistance and yield, and it also grows well in areas where the groundwater is high enough. This stock has only 1 drawback, it is a tendency to form abundant growth.
Cherry pits should be separated from the pulp, then washed and placed in a shaded area to dry. After that, the seeds must be combined with moistened sand in a 1: 3 ratio. Then they are placed in a cool place (from 2 to 5 degrees), where they will stratify for 6 months, while mixing and moistening the mixture must be periodically performed. Sowing in open soil is carried out at the beginning of the spring period. They should be sown thickly, while keeping a distance of 10 centimeters between the rows. If the soil is loamy or sandy loam, then the seeds should be buried 40–50 mm into the soil. When the seedlings appear, they should be thinned, while the distance between the plants should be from 30 to 40 mm. It is very simple to care for such seedlings, they need to be watered, weeded and loosened in time. You should also protect the plant from rodents.By autumn, the seedlings will have to get stronger and grow, after which they should be dug out and those in which the length of at least a slightly developed fibrous root system will reach 15 centimeters, and the thickness of the stem at the base will be at least 0.5–0.7 cm. Data the plant should be planted in the nursery, adhering to the 0.9x0.3 m scheme. At the beginning of the next season, in the spring, varietal cuttings will need to be grafted onto them.


Watch this video on YouTube
Cherry grafting
Grafting of varietal cherry cuttings should be carried out 7-15 days before sap flow begins. If this procedure is carried out later than this period, then the cut on the rootstock will oxidize, due to which the scion will take root much worse. Both seedlings and root shoots of ordinary cherry can be used as a stock. A one- or two-year-old basal shoot or a cherry seedling should be used as a stock, and the grafting should be done at a height of 15–20 centimeters from the soil surface. The preparation and carrying out of this procedure require special attention and accuracy, since it is extremely difficult for cherries to take root on a cherry stock. Experienced gardeners recommend choosing an improved copulation method for grafting. To begin with, both the scion and the rootstock should be cut obliquely, while the resulting oblique cuts in length should reach 30–40 mm. Then, an additional cut should be made on both cuts, the depth of which should not exceed 10 mm. The graft and rootstock must be folded in slices into a "lock" so that the joint is motionless. Then this place needs to be wrapped with tape or eyepiece tape. In order for the scion to take root faster and better, the stalk must be used short with only a couple of buds, but its diameter must be the same as that of the rootstock at the cut site. Cuttings are harvested in late autumn after the onset of the first frost, while the air temperature should be about 8-10 degrees. The cuttings should be tied together, moistened with water using a sprayer and wrapped in plastic wrap. For storage, they are placed on the shelf of the refrigerator or buried in the snow, where they will stay for about 6 months. Before starting grafting, the cuttings should be in the melt water for several hours. For vaccination, you need to take a very sharp instrument that is well sterilized. To speed up the fusion, the cuts must be accurate and even.
Diseases of cherries with photos and descriptions
Most of cherry and cherry diseases are common. Sweet cherry is most susceptible to fungal diseases such as moniliosis, coccomycosis and clotterosporia.
Clasterosporium disease
Hole spot, also called clasterosporium, damages stems, branches, leaf plates, flowers and buds of a plant. On the surface of the foliage, specks of a dark brown color appear with a border of a darker shade. In place of the spots, the leaf tissue is colored, and holes appear. Affected leaves fly around ahead of schedule. On the stems affected by the disease, tissue death, gum flow is observed, while the berries dry out. The infected parts of the plant must be removed, while the cut sites are cleaned and disinfected with a solution of copper sulfate (1%), then they are rubbed 3 times with sorrel foliage with a ten-minute break between sessions. And at the very end they are coated with garden varnish. Before the kidneys open, the area should be treated with Nitrafen or a solution of copper sulfate (1%). After the cherry blossoms, a second spraying is carried out with a solution of Bordeaux mixture (1%). The next treatment is carried out 15–20 days after the second, and the last time the area with cherries is sprayed no later than 20 days before harvesting.
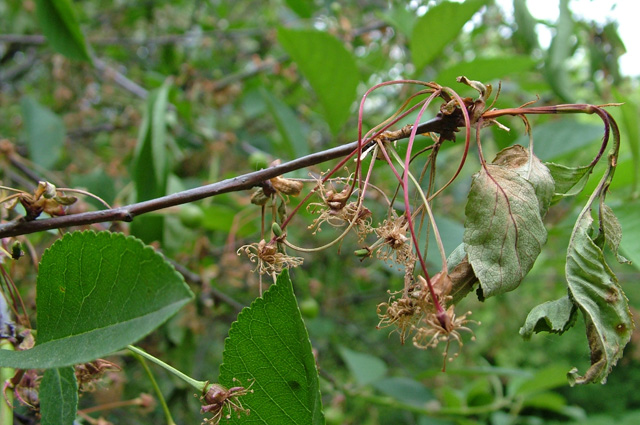
Moniliosis
Any stone fruit, for example, sweet cherry, cherry, cherry plum, apricot, peach or plum, can become infected with gray rot, either moniliosis, or monilial burn. The affected plant has rotting fruits, drying of flowers and branches. If the weather is damp, then gray pads will appear on the surface of the berries and ovaries, in which the spores of the fungus are located, as a result of which the fruits wrinkle and dry. As soon as the affected tree fades, it is sprayed with a Bordeaux mixture (1%), the second time this treatment is carried out after 15 days have passed after harvesting the fruits. During processing, you should pull out all infected ovaries and berries, as well as remove the affected shoots and rake loose leaves, and destroy everything. In the presence of gum removal, using a very sharp instrument, it is necessary to clean the wounds to healthy tissue, and then process them as if the plant is damaged by clasterosporium (copper sulfate, sorrel foliage and garden pitch).
Coccomycosis
Often, coccomycosis affects the foliage, in more rare cases, it damages the stems, berries and petioles. In wet weather, this disease develops most rapidly. In June, small specks of brown-red color appear on the surface of the leaf plates, over time they become larger until they merge with each other. In this case, almost the entire leaf plate is affected, because of which the foliage flies around ahead of time. If the tree is very strongly affected, then secondary growth of shoots is observed. This disease leads to a longer ripening of berries, the plant weakens, its frost resistance decreases, in some cases the gardener may completely lose the crop. Before the buds open, the diseased cherries should be treated with a preparation containing copper (for example: Bordeaux mixture, copper oxychloride or copper sulfate). During the formation of buds, the plant is sprayed with a solution of Horus (for 1 bucket of water 2-3 grams). The second time the plant is sprayed with Horus immediately after it has faded. After 15–20 days, the infected branches should be cut off, while it is necessary to capture healthy tissue. These branches must be destroyed.
In addition to these diseases, such a culture can get sick with diseases such as: brown spot, witch's broom, plum dwarfism, false or sulfur-yellow polypores, mosaic ringing, dying off of branches, scab, fruit rot, Steklenberg viros, etc. In some cases, cherries are affected by diseases completely unusual for such a culture. How to get rid of fungal diseases is described in great detail above. At the moment, no effective drugs have been found for viral diseases. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to strictly adhere to the rules of agricultural practices and properly care for the plant.


Watch this video on YouTube
Cherry pests with photos and names
Sweet cherries are affected by the same pests as other stone fruit plants. Below will be described those pests that are most common when growing cherries in the garden.
Black cherry
The most dangerous for cherries and cherries are apple-plantain and black cherry aphids. The larvae of such pests suck out the plant sap from the leaf plates, as a result of which the growth of the central vein stops, and the leaf itself is curled, dried and blackened. In young trees affected by aphids, deformation and a decrease in growth are observed, in those plants that have already begun to bear fruit, flower buds are not set, and the quality of berries is also noticeably reduced. A layer of honeydew (sweet and sticky excrement of pests) appears on the surface of the foliage, on which a sooty fungus prefers to settle.At the beginning of the spring period, the tree must be sprayed with Confidor along the sleeping buds, after half a month, re-processing is carried out. With such a pest, you can fight harmless herbal remedies that differ in insecticidal properties. For example, you can use the following solution: 200 grams of tobacco dust and a small amount of liquid soap are taken for 1 bucket of water.
Cherry fly
The cherry fly is also very dangerous for cherries and cherries. It can destroy about 90 percent of the entire crop. The larvae of such a pest eat the nectar from the flowers, and also suck the juice from the berries, as a result of which they are damaged. Such a pest is most dangerous for mid- and late-ripening varieties of sweet cherry. The berries damaged by the pest become dark, begin to rot and crumble. The larvae that emerged from the fallen fruits burrow into the soil. To catch such flies, special traps are used. For their manufacture, plywood or plastic is used, they are painted in a deep yellow color, and then coated with entomological glue or petroleum jelly. Ready-made traps are hung on cherries at a height of 150-200 cm. After 3 days, check the traps, if you find at least 5-7 flies on them, then sprinkle the cherries with Confidor or Aktellik. If the plant was sprayed with Confidor, then re-treatment with the same agent is carried out 20 days after the first, and if with Aktellik, then after 15 days. The last time the cherries can be processed no later than 20 days before harvesting the fruits of mid- and late-ripening varieties.
Leaf rollers
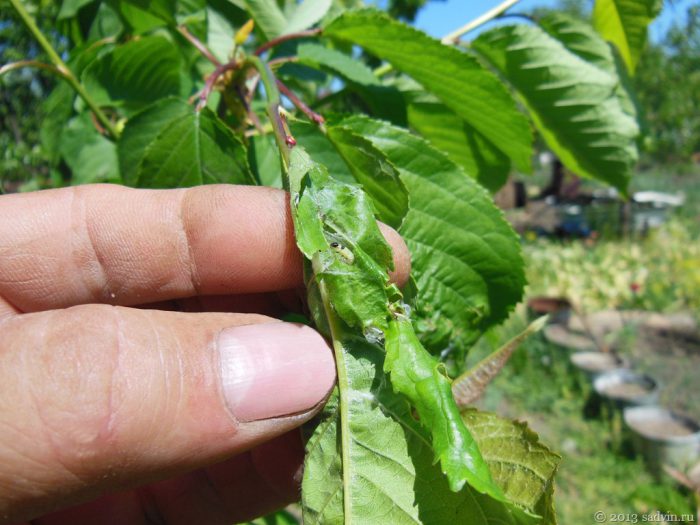
Leaf rollers are less dangerous, but their caterpillars destroy leaf plates. So, the caterpillars of the hawthorn and rose leafworm, eating the foliage, twist it and fix it with the help of a cobweb along the central vein. In this case, the caterpillars of the variegated-golden leafworm differ in that they twist the leaf plates across the median vein. All these caterpillars devour flower petals and buds, and also gnaw off leaf plates, while only a skeleton of veins remains of them. Older caterpillars gnaw at the fruit pulp and damage the ovaries. In the subcortical leafworm, the caterpillars injure the lower part of the tree trunk, they bite into the wood and make many moves there. When all the fruits are harvested, it is necessary to clean the affected areas on the trunk, and then process the wounds and the whole plant with a concentrated solution of Chlorophos. Re-processing is carried out in the spring before the buds open.
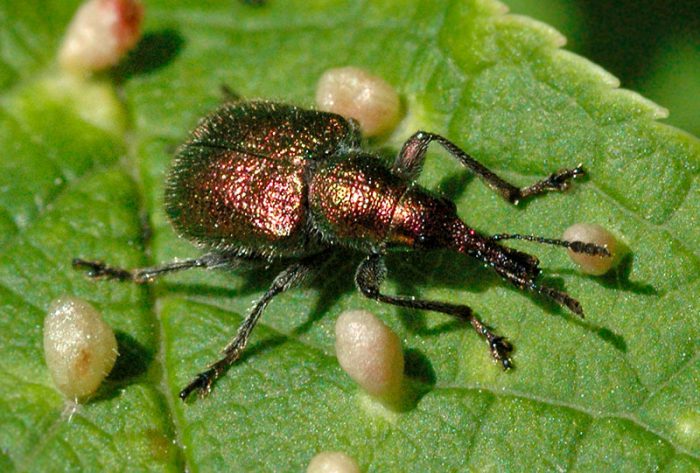
Cherry pipe runner
Cherry pipe worm can harm any stone fruit plants, including cherries and cherries. The larvae of this insect eat the kernels in the seeds, and the pulp of the berries is also damaged. To get rid of such a pest, you will have to process the tree 2 times. As soon as the plant fades, it needs to be sprayed with a solution of Aktara (for 1 bucket of water 1.5 grams), after half a month, another treatment is carried out using Karbofos, Ambush, Aktellik, Corsair or Metafox for this.
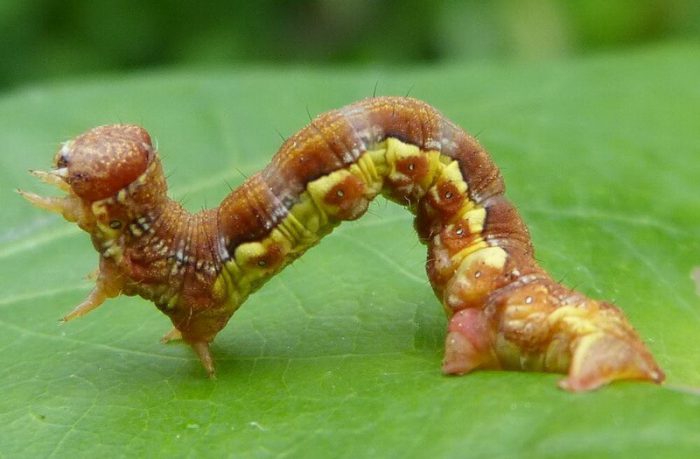
Moth-stripped
Also, often on cherries and cherries, winter moths and peppered moths live. The caterpillars of such insects feed on foliage, buds and flowers. They hide in sheet plates that are connected by a web. If there are a lot of pests, then only veins will remain from the foliage of the plant. Unlike other caterpillars, which have 8 pairs of legs, these have only 5, because of this, when moving, they bend their back in a loop. Before the plant blooms, it must be sprayed with Zolon, Phosphamide, Karbofos, Metaphos, Cyanox or another means of similar action. At the beginning of the spring, before the buds open, it is necessary to treat the area with Oleocubrite or Nitrafen.
Also, brown fruit and red apple mites, cherry shoot, mining and fruit striped moths, cherry, yellow plum and slimy sawflies, sapwood, unpaired bark beetle, ringed,downy and unpaired silkworms, apple glass, etc. But the problem with these pests can arise only in case of violation of the rules of agricultural technology or because of gross mistakes in care, because of which the tree weakens. To destroy such harmful insects, you need to choose one of the drugs that was described above.
Birds can also significantly reduce the number of fruits. The fact is that they love to feast on ripe berries. To save the crop on the plant, you should hang tapes made of rustling foil or unnecessary disks intended for a computer. If in this way it is not possible to scare off the birds, then a net will have to be thrown over the plant, the size of the cells of which should be 5x5 cm.


Watch this video on YouTube
Cherry varieties with photos and descriptions
Cherry varieties for the Moscow region
For the normal growth and development of cherries, a large amount of sunlight and heat is needed. Therefore, for many years it was believed that the rather cold climate of the Moscow region is simply not suitable for growing such a crop. But breeders were still able to get varieties that have high frost resistance. They can be cultivated both in the Moscow region and in colder regions. For instance:
- Bryansk pink... Self-fruitless late-ripening variety, distinguished by its productivity. Begins to bear fruit in the fourth or fifth year of life. The juicy pink berries reach 2–2.2 cm in diameter and weigh about 6 grams. The sweet flesh is light yellow, and the stone is brown.
- Iput... An early maturing, self-fertile variety with a high yield. The tree reaches a height of about 400 cm. The burgundy berries weigh about 5.5 grams, and their diameter is 2.2 cm. The juicy pulp is very sweet, the brown stone separates well from it.
- Fatezh... This self-fertile medium early variety has an average yield. The round, reddish-yellow fruits weigh about 5 grams. The sweet-sour pulp is very juicy.
- Tyutchevka. This late-ripening self-fertile variety has a high yield. Wide-rounded berries have a dark red color and weight up to 7.5 grams, while their diameter reaches 2–2.3 cm. The dense juicy red pulp has excellent taste.
- Jealous... This is a late self-fertile variety. The berries of a dark red color have an average weight of about 5 grams, and their diameter does not exceed 2 cm. The sweet juicy pulp is very dense and colored in dark red.
Also, over time, varieties such as: Kid, Poetry, Orlovskaya pink, Sinyavskaya, Cheremashnaya, Krymskaya are becoming more and more popular.
Early varieties of cherries
In terms of ripening, all cherry varieties are divided into early ripening, medium and late ripening. Early maturing varieties:
- Valery Chkalov... It is recommended to use the following cherry varieties as pollinators for this large self-infertile plant: April, June early, Zhabule, Skorospelka. Such a plant begins to bear fruit in the fifth year. The red-black, wide-heart-shaped berries have a blunt apex and weigh 6 to 8 grams. In the dark color of the pulp, there are streaks of pink.
- Dunn... Partially self-fertile variety with high yield. Begins to bear fruit only in the fifth or sixth year. One-dimensional, rounded, dark red berries have a slightly conical shape and weigh an average of 4.5 grams. The sweet dark red flesh is very juicy and tender.
- Lesya... This variety is frost-resistant, it does not require a lot of heat, but it is susceptible to infection with coccomycosis. Begins to bear fruit in the fourth or fifth year. The dark red heart-shaped berries weigh 7 to 8 grams. The sweet-sour juicy pulp is quite dense.
- Ruby Nikitina... This partially self-fertile variety is distinguished by its resistance to diseases and pests, and by its yield. Begins to bear fruit in the fifth or sixth year.The berries weigh about 3.8 grams and are dark red in color. The sweet juicy pulp is quite tender.
- Early pink... This variety is resistant to frost and fungal diseases, as well as yield. Begins to bear fruit at 4 or 5 years. The pink berries are oval-rounded and have a red blush. The fruit weighs about 6–7 grams and tastes great. The following varieties should be used as pollinators: Ugolek, Annushka, Ethics, Donchanka, Valeria.
Also popular are such varieties as Recognition, Debut, Lasunya, Melitopol early, Skazka, Melitopol red, Elektra, Ruby early, Chance, Era, Priusadebnaya yellow, Ariadna, Cheremashnaya, Krasnaya Gorka, Ovstuzhenka, etc.
Medium ripening varieties
Popular mid-season varieties:
- Velvet... This dessert variety is resistant to fungal diseases. Fruiting begins at the age of five. Glossy large berries have a dark red color and excellent taste.
- Nectar... This variety, which is distinguished by its yield, begins to bear fruit in the fourth or fifth year. The glossy fruit is dark red in color. The sweet crunchy flesh is juicy enough.
- Coal... The yield of the variety is average. It begins to bear fruit in the fourth or fifth year. Dark red berries have a juicy and dense pulp, which has a mild wine-sweet taste.
- French black... It is a frost-resistant medium-yield variety that begins to bear fruit in the seventh year. The berries have an almost black color and a juicy dense flesh with a dessert taste.
- Backyard... A productive variety that begins to bear fruit in the sixth or seventh year. Glossy yellowish large heart-shaped berries have a red blush. Delicate juicy pulp has a wine-sweet taste.
The following varieties are also quite popular: Ruby, Franz Joseph, Kubanskaya, Black Daibera, Gedelfingen, Totem, Epos, Adeline, Dachnitsa, Dilemma, Prostor, Izyumnaya, Dniprovka, Vinka, Mirage, Rival, Tavrichanka, Talisman, In memory of Chernyshevsky, Raditsa , Veda, etc.
Late varieties of cherries
Popular late varieties:
- Bryanochka... A self-infertile variety with a high yield and resistance to frost and coccomycosis. Begins to bear fruit in the fifth year. The deep red berries are broad-hearted and weigh about 7 grams. The sweet, firm flesh is also dark red in color. It is recommended to use such varieties as Veda, Iput or Tyutchevka as pollinators.
- Michurinskaya late... A self-infertile variety with a high yield and frost resistance. Begins to bear fruit only in the fifth or sixth year. The varieties Pink Pearl and Michurinka are used as pollinators. The broad-hearted dark red berries weigh about 6.5 grams. The juicy red pulp has a sweet taste.
- Farewell... Self-fertile variety with high yield and drought tolerance. Begins to bear fruit from four or five years. Rounded, very large red berries weigh about 14 grams. The yellowish flesh is cartilaginous and dense. For pollination, it is recommended to use the following varieties: Annushka, Aelita, Donetsk coal, Sestrenka, Ethics, Valeria, Valery Chkalov, Yaroslavna, Donetsk beauty.
- Lena... A self-fertile variety that is resistant to frost and fungal diseases, as well as high yields. Begins to bear fruit in the fourth year. The red-black fruit is blunt-hearted and weighs about 8 grams. The pulp is firm. The following varieties are suitable for pollination: Ovstuzhenka, Revna, Tyutchevka, Iput.
- Amazon... A self-infertile variety with a high yield and resistance to frost and drought. The dark red, firm, meaty fruit separates well from the stem and weighs about 9 grams. The pink-red flesh is firm and gristly.For pollination it is recommended to use the following varieties: Donchanka, Yaroslavna, Annushka, Donetsk beauty, Early rozovinka.
The following varieties are also popular: Announcement, Iskra, Druzhba, Zodiac, Divnaya, Vekha, Large-fruited, Orion, Black Melitopol, Meotida, Prestige, Surprise, Romance, Temporion, Cosmic, Full house, etc.


Watch this video on YouTube