The herbaceous perennial plant meadow parsnip, either sowing or common (Pastinaca sativa) is a species of the genus Parsnip of the family Celery or Umbrella. The name of this species was formed from the Latin word "pastus", which means "feed, food, nutrition". In the people, such a plant is also called a white root, white carrot or field borscht. This species comes from the Mediterranean. Parsnip has been known to man for a very long time, while the first mentions of him were found in the works of Dioscorides and Pliny, which date back to the 1st century BC. The seeds of this culture were found in Switzerland during the Neolithic excavations. The ancient Romans, as well as the Greeks, knew such a plant under the name "pastinaka", it was eaten, and also used as a medicinal plant, and was also used as feed for livestock. By the middle of the 16th century, this culture has become very popular and available in Europe, as, for example, potatoes at a later time, it is he who will eventually displace ordinary parsnips from the gardens of European countries. This plant first appeared on the territory of Russia in the 17th century, and then it was called "field borscht". Today, in natural conditions, it is found in weedy places among the bushes in Turkey, Western Siberia, the Caucasus and Europe. Parsnips are cultivated in almost all countries.
Content
Features of parsnip
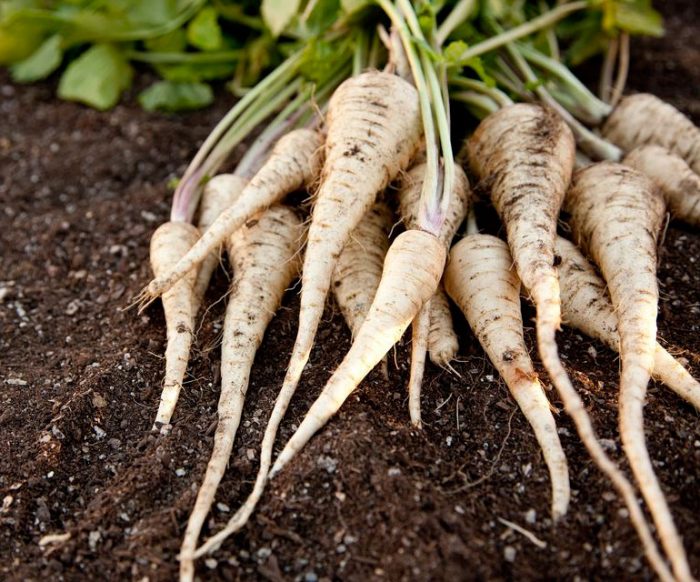
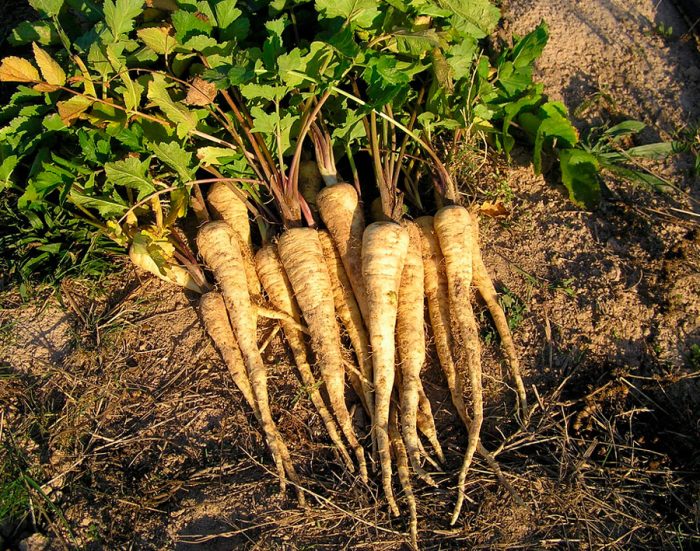
The height of a rough, furrowed, erect stem can vary from 0.3 to 2 meters, it has a faceted sharp-ribbed shape, and there is pubescence on its surface. The upper part of the stem is branched. The composition of unpaired leaf plates includes from 2 to 7 pairs of more or less pubescent leaves of large-toed oval or lobed shape, in the upper part they are sessile, and in the lower part they have short petioles. Ripening of the root crop is observed in the first year of growth. It is thick, fragrant white, has a sweetish taste, the root can be cone-shaped (like a carrot) or rounded (like a turnip). The color of the fruit in the context of dirty yellow.The composition of complex umbrellas includes from 5 to 15 rays, which in turn consist of bisexual, regular small flowers with a yellow corolla. The flowering of parsnips is observed in the second year of growth. The shape of the fruit is rounded-oval, this flattened droplet is painted in a dirty yellow shade. The common parsnip is considered the closest relative of the following garden crops: carrots, parsley, fennel, dill, celery, coriander and lovage.
Growing parsnips from seeds
Sowing
If you decide to grow parsnips on your plot, then the first step is to sow it. Of all the root plants, parsnips are the most hardy, and it would seem that its seeds can be sown directly into open soil in early spring, as soon as it warms up a little. However, gardeners prefer to grow this crop through seedlings, since the seeds contain a very large amount of essential oils, which is why they sprout for a long time.
Large seeds of this plant require pre-sowing preparation. To begin with, they are immersed in lukewarm water for 24 hours, it must be replaced immediately after it has cooled down. After that, they are treated with a growth stimulating agent, for example: Epin, Heteroauxin or Zircon. The prepared seeds are sown in peat pots, which are filled with a peat-based substrate. You can buy a soil mixture ready-made in a special store or make it yourself, for this you need to combine peat, perlite, garden soil and sand. Remember that the substrate must be loose and light. Before proceeding with sowing, the soil mixture is disinfected, for this it is sieved and spilled with freshly boiled water or steamed in an oven.
Fill the pots with moistened soil mixture, which is tamped so that it is at least 10 mm below the edge of the container, then 2 or 3 seeds are placed on its surface. From above they must be covered with a thin layer of the same soil mixture. Then the containers must be placed on a pallet, and they are covered with foil on top.
Seedling care
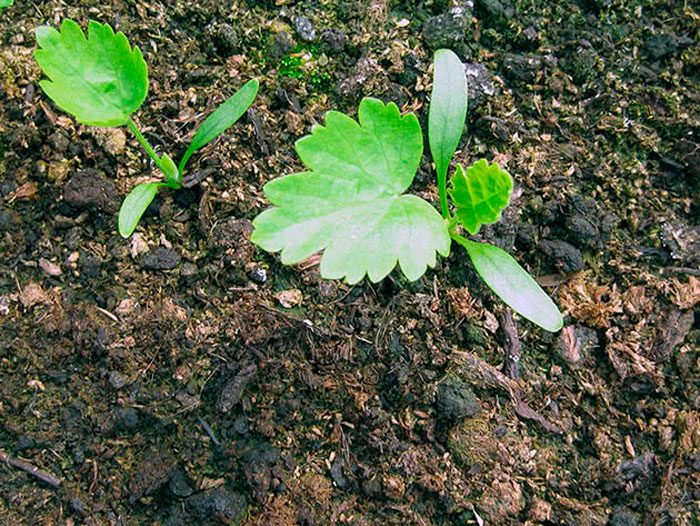
Until the seedlings appear, the crops should be regularly ventilated, for this, the shelter should be raised for 7–10 minutes once a day. It has already been mentioned above that the seeds of this culture germinate rather poorly, because they contain a lot of essential oil, in this regard, the first seedlings should appear no earlier than half a month after sowing. When the first shoots appear, the shelter is removed, and the pots are moved to a well-lit place.
The seedlings of this culture need a sufficiently long daylight hours (about 14 hours) in this regard, if necessary, it should organize additional illumination. Water the seedlings as the top layer of the substrate dries out in containers. Remember that the water should not stagnate in the pots, because this can cause the plants to hurt or even die.


Watch this video on YouTube
How to dive
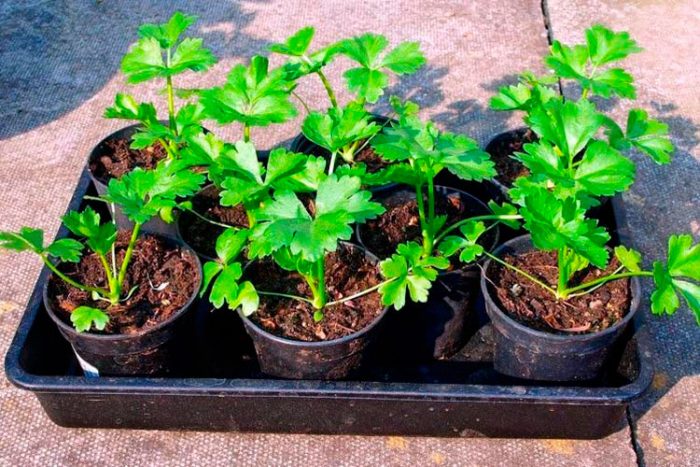
It should be remembered that root crops react extremely negatively to picking, in this regard, it is recommended to sow them in individual containers, and not in common boxes. After the plants have 2 true leaf plates, it is necessary to choose the most powerful of all in the pot, and gently pinch off the rest of the seedlings above the surface of the substrate. It is not recommended to pull out extra seedlings, as this can cause injury to the root system of a strong plant. About 1.5 weeks before transplanting parsnips into open soil, you should start hardening them. For this, the seedlings must be taken out into fresh air every day, while the duration of such a procedure is gradually increased.
Planting parsnips outdoors
What time to plant
It is recommended to plant parsnip seedlings in open soil in mid-May, after the plants are 28 to 30 days old. Most often at this time, returnable spring frosts are already left behind, and the soil is pretty well warmed up. It is necessary to plant seedlings in the Moscow Region at about the same time, adjusted for the weather.
Suitable soil
For planting seedlings, you must choose a sunny area, but such a plant can also be grown in a shaded place. It grows best on neutral moist sandy loam, peat or loamy soil. Such a culture does not grow on acidic soil; it can be corrected by liming. Areas where crops such as carrots, parsley, celery, parsnips and other root crops were grown a year earlier are not suitable for planting parsnips, since these plants suffer from the same diseases, and they also have common pests. It is best to grow such a crop in the area where cabbage, potatoes, onions or beets previously grew, especially if fertilizers were introduced into the soil during their cultivation. The fact is that parsnips grow well on the soil that was fertilized in advance, in this regard, it is recommended to prepare the parsnip plot in advance. This should be done in autumn, the site should be cleared of weeds, and if organic fertilizers were not applied to the soil in the current season, then rotted manure should be added to the soil (1/2 bucket of fertilizer is taken per 1 square meter). In spring, before planting seedlings in open soil, the site should be re-dug up, its surface is leveled, and then high beds are formed.
Seedling planting rules
Make several holes in the garden, keeping the distance between them from 10 to 12 centimeters, and the width between the rows should be at least 0.4 m.The depth of the planting holes should be made such that the plant can fit freely in them along with the peat pot. In the case when the seedlings were grown in plastic cups, they should be watered very well before planting. Carefully remove the plant along with a clod of earth and transfer it into the planting hole. The planted plants must be watered abundantly.
Planting parsnips before winter
This crop can be grown using sub-winter sowing. Sowing seeds is carried out in autumn until the second half of October, for this you should use a site that is best prepared in advance and is recommended in spring. Since the seeds are quite large, they are sown in one hole in 3 pieces, they are buried in the soil by 30–40 mm. The distance between the holes should be from 10 to 12 centimeters, while the width between the rows is about 0.4–0.45 m. The advantage of winter sowing is that seedlings appear very amicably in spring. After the seedlings grow a little, they will need thinning, while the most powerful plant should be chosen, and the remaining ones should be carefully plucked out.
Caring for parsnips
Growing parsnips in your garden is easy enough. For this, the plant must be watered, weeded, fed and loosened in a timely manner between the rows. The fact that this plant is distinguished by its unpretentiousness makes it easier to care for parsnips.
The first time it will be necessary to loosen the soil surface after the seedlings appear or when the seedlings planted in the open ground are accepted. Subsequently, loosening of the soil is carried out every time after the rain has passed or watering is carried out.
How to water
This plant is hygrophilous, especially it needs water during the formation of root crops. If the parsnip lacks moisture, then the color of its foliage will become lighter, the growth of the bush will be slower, and it may have an arrow. Also, because of this, the plant's roots can become tough, fibrous and dry, and cracks appear on their surface.If water stagnation is observed in the soil, this can cause the development of a fungal disease.
If parsnips are grown in moist soil, then during the season it will need to be watered abundantly only 4 or 5 times, and then only during prolonged drought. If it rains regularly in the summer, then you will not have to water this crop at all. When the bed is watered, it is recommended to weed and loosen its surface.
It should be remembered that in dry and hot weather, the foliage of such a plant emits a rather caustic essential oil that can cause burns. In this regard, try to work with such plants early in the morning or in the evening when the sun goes down.
Fertilizer
During the growing season, such a plant will need to be fed 3 or 4 times. For feeding, you need to use exclusively liquid fertilizers, for example: mullein solution (1:10), mineral fertilizers or infusion of wood ash.
When 7-15 days have passed after transplanting the parsnips to the garden, it will need to be fed with nitrogen-containing fertilizer. After 20 days, re-feeding with the same fertilizer is carried out. From mid-July, the bushes begin to be fed with fertilizers containing phosphorus and potassium. If, on the site where parsnips grow, the soil is nutritious, then the bushes can not be fed at all, especially if fertilizers were introduced into the soil earlier.
Pests and diseases of parsnips with photos and names
Parsnip disease
Parsnips can contract the same diseases as other crops belonging to the Umbrella family. For example, it can suffer from septoria, cercosporosis, wet bacterial rot, black rot (or Alternaria), and white and gray rot of root crops.
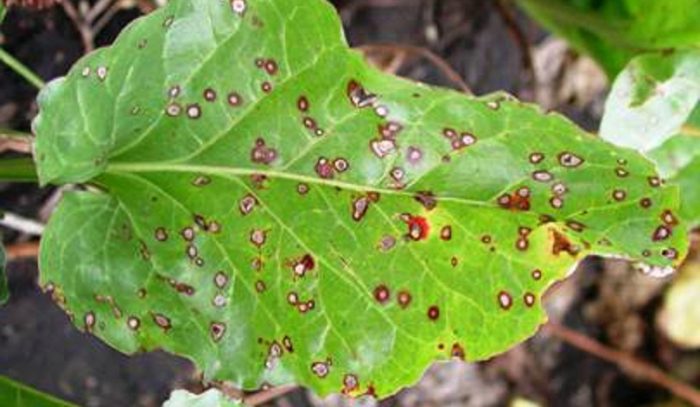
Septoriasis
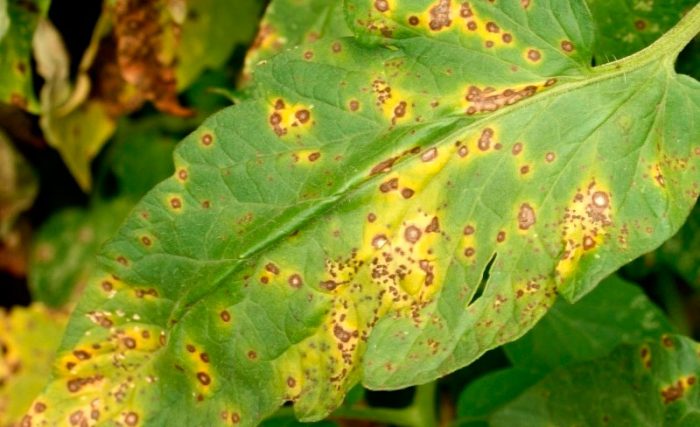
On the foliage of specimens affected by septoria, a lot of medium-sized specks appear that do not have clear boundaries; they become darker over time and eventually turn brownish-brown. Sick bushes turn yellow and dry out. This disease develops rapidly in cool weather, if there is high humidity. The infection enters plants through the stomata.
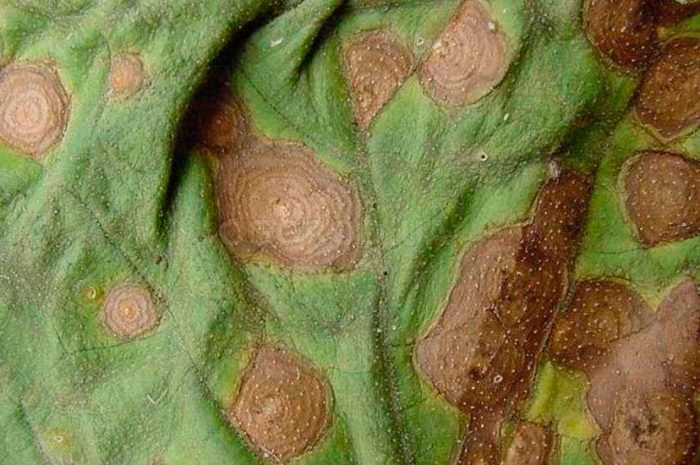
Cercosporosis
If the parsnip is affected by cercosporosis, then spots appear on the shoots and foliage, reaching 0.6 cm in diameter, of a dirty brown or light yellow color, which have an irregular shape. As the disease progresses, the spots in the center fade, while the border around them darkens. The edge of the affected leaf plates becomes raised and slightly curled. On the surface of the shoots, brownish-red specks of an elongated shape look like depressed ones. The affected bushes have a developmental delay, and the foliage turns yellow and dries up.
Wet bacterial rot
Wet bacterial rot is a widespread disease that develops intensively with high humidity and sudden changes in temperature. Root crops are affected by this disease both in the open field and during storage. The disease begins with the appearance of rot in the tail. Initially, oily-watery specks of a dark color are formed on the bush. Over time, depressions with a fetid rotting mass appear in these areas, it flows out of root crops like mucus, as a result of which the disease spreads to other bushes, and this happens quite rapidly.
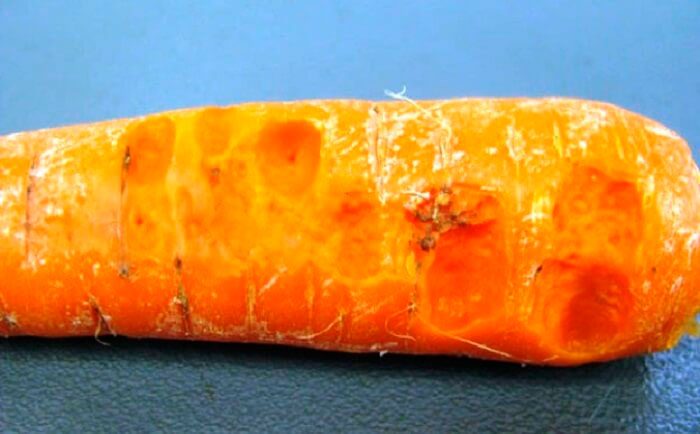
Alternaria
Black rot (Alternaria) - the development of this disease mainly occurs during storage. Slightly depressed spots of a dark color appear on the surface of root crops, and in damp weather they form a bloom of dark olive color. The diseased tissue in the section has a coal-black tint.
Sclerotinia
Sclerotinia (gray rot) and botrytis (white rot) - these diseases differ in the color of the plaque that forms on the surface of root crops.On root crops affected by gray rot, a fluffy bloom of gray appears, and on those that get sick with white rot, a white bloom is formed in the form of flakes with black sclerotia of the fungus. Such diseases develop most actively when the air humidity is high in warm weather.
Parsnip processing
In order to prevent fungal diseases, a set of measures must be taken:
- Compliance with the rules of crop rotation. In the area where parsnips were grown, they can be re-grown only after 3 or 4 years.
- Agricultural engineering rules. It is necessary to strictly follow the agrotechnical rules of this crop.
- Site preparation. Before planting parsnips on the site, you need to properly prepare them. Do not forget to be sure to clean it from plant residues.
- Presowing seed preparation. Before sowing, the seeds must be warmed up in very warm (about 50 degrees) water for 30 minutes. Then they are quickly cooled and dried.
- Root crops must be stored correctly.
However, if, despite all the preventive measures taken, the first signs of rot appear in the store or on the garden bed, all affected specimens must be removed as soon as possible. Healthy ones should be necessarily sprayed with a solution of Bordeaux mixture (1%), Topsin-M or Fundazol.
Parsnip pests
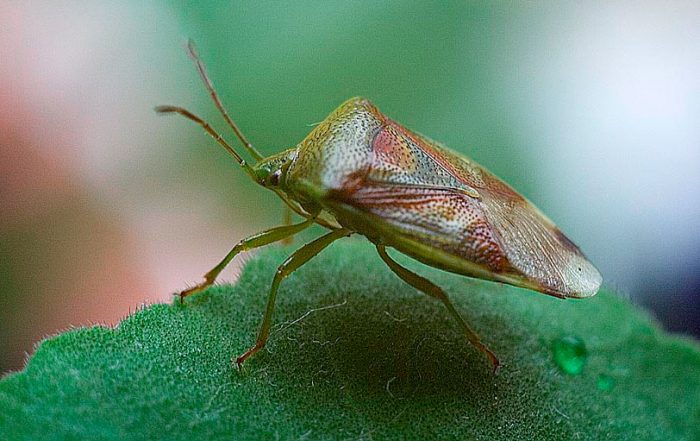
The greatest danger to such a plant is the caraway moth, the striped shield bug, the field bug and aphids.
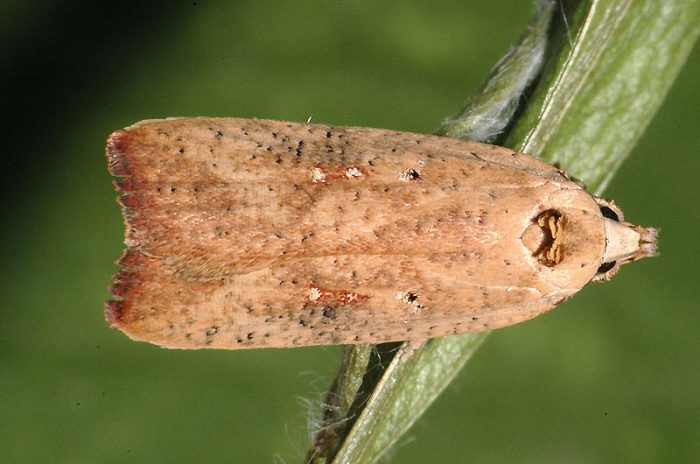
Caraway moth
Caraway moth contributes to the destruction of the testes of this culture. Caterpillars of such a harmful insect are able to penetrate the shoots, roots and foliage of parsnips, they feed on its tissues. After the bushes bloom, the caterpillars envelop the inflorescences with their cobwebs and eat the flowers, pedicels and seeds, and then hide in the shoot again. To get rid of such caterpillars, the bush must be treated with a decoction of tomato tops. For its preparation, 1 bucket of freshly boiled water and 3.5 kilograms of tomato tops are taken, the mixture must be left for a couple of days, after which the broth will be ready. It should be filtered and combined with 40 grams of household soap crushed on a grater.
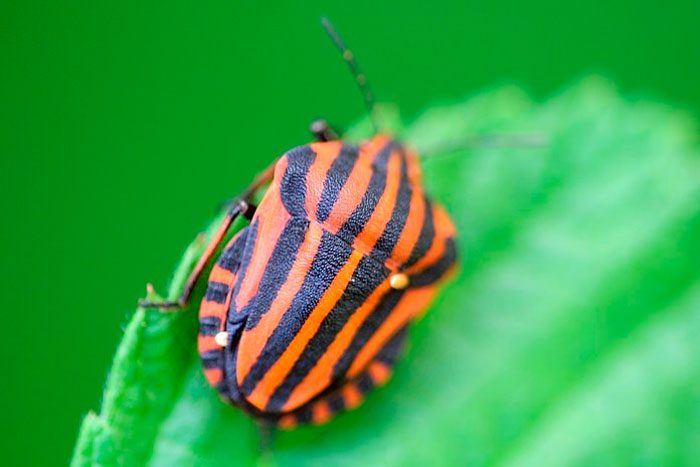
Striped bug
The striped bush bug feeds on the juice of young buds and ovaries, as a result of which they die.
Field bug
The field bug is a beetle of grayish-green color, which has a length of about 0.4 cm. In the tissues of the bush, females arrange egg-laying. The larvae are selected from the eggs, which suck the plant sap from the tops of the stems and foliage. In those areas where there are punctures, there is death, yellowing and drying of the tissue, and due to the toxic saliva of such an insect, the seeds become sterile. In regions with a warm climate, during one season, 3 or 4 generations of such a pest are formed. You can use Actellic or Karbofos to destroy the striped bugbug and the field bug.
Aphid
The greatest danger to such a plant is aphid, this pest is the most prolific of all. It sucks out the plant sap, as a result of which the bushes become frail, deformed, and their development stops. In addition, aphids are the main vector of viral diseases that are considered incurable. You can try to destroy aphids with folk remedies, or chemicals are used for this, for example, Biotlin or Antitlin, even in this case the same drugs can help as in the fight against aphids, for example, Confidor. For prevention purposes, all weeds must be removed from the site in a timely manner. And when the entire crop is harvested, the site must be cleared of plant residues, as well as deep digging.
Cleaning and storage of parsnips
It is necessary to harvest parsnips in the autumn, after the foliage begins to die off. Roots are removed from the soil with a pitchfork, while you need to try not to injure them.If necessary, the harvest can be postponed until the onset of winter, the fact is that from a low temperature the roots become much tastier.
It is necessary to work with such a plant, protecting your hands with gloves, since its tops can leave burns on the skin. Root vegetables for storage are placed in boxes filled with sand, the temperature in the storage should be from 0 to 2 degrees, while the humidity level should be from 80 to 85 percent. It should be noted that when stored in a cellar, the roots become soft, in this regard, in areas with a warm climate, where there is no severe frost in winter, they can not be removed from the soil.
Types and varieties of parsnips
There are not too many types and varieties of parsnips. All types of root crops are divided into long and round. The varieties that belong to the long species need a well-developed soil, and to the round ones they are distinguished by their unpretentiousness.
Also, all varieties are divided by ripening time into:
- early maturing - ripening lasts from 110 to 120 days from the day the seedlings appear;
- average ripening - they need 120-140 days;
- late maturing - they ripen in 140 days or more.
The most popular varieties are:
- Round... This variety is early maturing. The shape of the root crops is rounded-flattened, conical, they are painted in whitish-gray color, and weigh about 170 grams. The pulp is white, fragrant and has a whitish-gray core.
- Chef... This early ripening variety ripens in 95–105 days. The rosette of leaves is spreading and small. The conical-knotted root vegetable is colored in a light cream color, and it weighs about 140 grams, at the base it is rounded-flattened. The white flesh has a pale gray heart.
- White stork... This is an early maturing variety. The smooth roots are white and weigh between 90 and 110 grams. The tasty and juicy pulp is also white. The variety has good keeping quality.
- Boris... This early variety has a high yield. The shape of the creamy root crops is conical, and the white fragrant pulp is very tasty.
- Hormone... In such an early variety, white roots have a conical shape, they reach about 22 centimeters in length, and up to 5 centimeters in diameter. The root crop is completely submerged in the ground, and it weighs from 110 to 130 grams. Boiled or fried root vegetables are used as a side dish or as a seasoning.
- Delicacy... Medium early variety. Root crops have a round shape and are very well stored, they weigh 200-350 grams, and reach 80 mm in length. The fragrant white flesh has specks of light yellow color.
- Best of all... This variety is medium early. The pointed conical root vegetable is white and weighs about 200 grams. The white pulp is delicious and fragrant.
- Petrik... Such a dietetic medium-ripening variety, a universal variety, has a high yield and resistance to diseases. The white conical root vegetable reaches 35 centimeters in length and 8 centimeters in diameter. The dense whitish-gray pulp is juicy and fragrant.
- Gladiator... This medium-ripening hybrid is very productive. Smooth white roots are tapered. The white pulp is sugary and fragrant.
- Guernsey... The late-ripening variety has a high yield. Root vegetables are very well stored, they weigh about 200 grams, and reach about 25 centimeters in length. Delicious white pulp is fragrant and sweet.
- Student... This late high-yielding variety is drought tolerant. White cone-shaped roots reach 30 centimeters in length and weigh about 160 grams. Delicious fragrant pulp is colored white.
Also quite popular among gardeners is the Serdechko variety and foreign varieties such as Hollow Crown, Contess, Javelin and Tender and Tru.


Watch this video on YouTube
Parsnip properties: benefits and harms
Medicinal properties of parsnips
The root vegetable of parsnip contains carotene, ascorbic acid, carbohydrates, essential oil, mineral salts, B vitamins (B1, B2, B3). The carbohydrates included in their composition are easily digestible, and they also contain a fairly large amount of potassium, and it improves blood circulation and digestion, and also has a positive effect on the state of the nervous system. The complex of macro- and microelements and vitamins contained in this plant is very similar in composition to that of spinach. The foliage contains a large amount of essential oils, and the root vegetable contains fructose and sucrose that are harmless to diabetic patients; parsnips contain 3 times more of them than carrots.
This plant is unique in that it contains substances that can relieve spasms. If you eat a root vegetable shredded on a grater in a timely manner and correctly, you can relieve renal or hepatic colic. This plant also has a tonic, expectorant and analgesic effect. Since ancient times, it has been used as a diuretic for edema, and also as a means of improving appetite, strengthening the walls of capillary vessels and stimulating sexual activity. At the moment, this plant is used in therapy, as well as for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Scientists have conducted many experiments that have made it possible to find out that the furocoumarins found in parsnips increase the sensitivity of the skin to ultraviolet rays. This property has been used to repigment discolored areas of the epidermis in people with vitiligo.
Root crops are used for the manufacture of drugs "Beroxan" and "Eupiglin", which are used during the treatment of alopecia areata and vitiligo. And they also extract furocoumarin of pastinacin, which is a vasodilator, it is used to prevent attacks of angina pectoris in cardiac neurosis and coronary insufficiency, as well as in other spastic phenomena.
Previously, to improve mood and appetite, it was recommended to take a root vegetable tincture of this plant on moonshine. At the same time, the infusion of root vegetables on water was used to restore strength in seriously ill patients. And also such infusions are distinguished by a sedative effect, in this regard, they are recommended for neuroses and insomnia.


Watch this video on YouTube
Contraindications
Parsnip and preparations made on its basis cannot be used by people with individual intolerance, and for patients with photodermatosis - inflammation of the epidermis due to high sensitivity to sunlight. The fact is that the substances contained in such a root vegetable contribute to the enhancement of this sensitivity. Parsnips are also not recommended for small children and the elderly.