The carrot (Daucus) is a member of the Umbrella family. The name "carrot" comes from the Proto-Slavic language. In the wild, this plant is found in New Zealand, America, Africa, Australia and the Mediterranean. In agriculture, cultivated carrots, or cultivated carrots (Daucus sativus), are grown, and they distinguish between table and fodder varieties. Such a culture has been cultivated for about 4 thousand years, and over such a long period, a large number of various varieties of this plant have appeared. It is believed that this culture comes from Afghanistan, since to this day most of the carrot species are found in nature there. At first, carrots were grown for seeds and scented foliage, not as a root vegetable. On the territory of Europe, this plant appeared in the 10-13th century AD. In "Domostroy" there is a mention of carrots, and this suggests that in the 16th century it was already cultivated in Russia.
Content
Features of carrots
Carrots are herbaceous plants that can be annual, biennial or perennial. During the first year of growth, only a rosette is formed, consisting of pinnately dissected leaf plates, as well as a root crop, and seeds are formed only in the second year of growth. The shape of the fleshy root vegetable is fusiform, truncated-conical or cylindrical, and its weight varies from 0.03 to 0.5 kg or more. 10–15-ray complex umbellate inflorescence consists of small flowers of light yellow, white or pale red color, with a red flower in the middle. The fruit is a small elliptical two-seed, reaching about 40 mm in length. Root vegetables contain carotenes, lycopene, B vitamins, flavonoids, anthocyanidins, sugars, ascorbic and pantothenic acids and other useful substances necessary for the human body.
Planting carrots in open ground
What time to plant
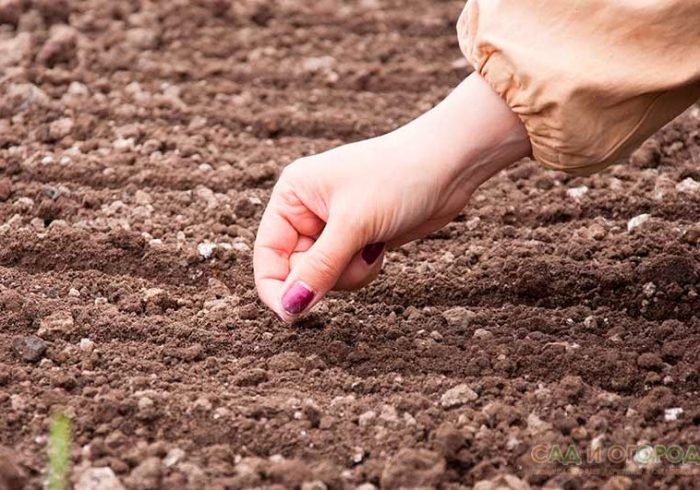
In carrots, seed germination begins at a soil temperature of 4 to 6 degrees. In this regard, sowing can be done when the soil warms up to the specified temperature, as a rule, this happens already in the last days of April. Mid-season as well as late-season varieties can be sown from April 20 to May 7. If the soil is medium, then carrots can be sown in the second week of May, and on light soil - until the last days of spring.The seeds that are in the ground can withstand frosts down to minus 4 degrees. It is very good if after sowing it rains for several days in a row. It is not necessary to sow the seeds too late, as in this case the sprouts will not appear for a relatively long time.
Suitable soil
The area for carrots should be sunny and even. However, for such a culture, a site with a slight slope is also suitable. Bad predecessors for this culture are: fennel, parsnips, beans, caraway seeds, parsley and carrots, since these plants quite actively absorb the nutrients they need from the soil, thereby depleting it. Such areas are suitable for planting carrots after at least 3 years. And the best predecessors are: cucumbers, cabbage, garlic, potatoes, zucchini, tomatoes and onions.
After a suitable site is found, you should start preparing it. Its digging must be carried out in advance, or rather, in the autumn time, then before the onset of spring it will have time to settle. You need to dig up the soil by 1.5 bayonets of the shovel, the fact is that if the root crop begins to grow actively, then resting on a solid layer of soil, it will change its direction, as a result of which the vegetable will be crooked. It is relatively difficult to extract a crooked root crop from the ground. Before starting planting, fertilizer must be applied to the soil, this is done during the autumn digging, for example, 15 grams of potash fertilizer, from 2 to 3 kilograms of humus, 25–30 grams of superphosphate and 15–20 grams of nitrogen fertilizer are taken per 1 square meter of the plot. fertilizers. In spring, the site must be leveled using a rake.
Sowing
Before sowing carrots in open soil, the seed should be pre-sowed to improve germination. There are several ways to prepare seeds for sowing:
- For 1 day they should be immersed in lukewarm water (about 30 degrees), while the liquid must be replaced at least 6 times during this time. If desired, water can be replaced with a solution of wood ash (1 tbsp of substance is taken for 1 liter of lukewarm water). After 24 hours have passed, the seeds should be rinsed in clean water, and then they are placed in a cloth and put on the refrigerator shelf for several days.
- The seeds should be poured into a cloth bag, which is immersed in hot water (about 50 degrees) for a third of an hour. Then it immediately for 2-3 minutes. dipped in cold water.
- The seed is poured into a cloth bag, which must be instilled into the soil to the depth of the shovel bayonet. There he must lie for 1.5 weeks.
- You can sparge seed with a bubbler. For this, the seeds are immersed in a Silk or Epin solution saturated with oxygen, where they must stay for 18 to 20 hours.
Upon completion of pre-sowing preparation, you can proceed to direct sowing of carrots in open ground. If the soil on the site is light, then the seeds need to be buried in it by 20–30 mm, but if the soil is heavy, then the planting depth should be reduced to 15–20 mm. The row spacing is about 20 centimeters. A distance of 30 to 40 mm should be kept between seeds in a row. In order for the crops to be not thick, gardeners often resort to the following trick: toilet paper must be cut into thin strips, droplets of paste (from flour or starch) should be applied to them with an interval of 30-40 mm, after which the seeds are laid out in them. After the paste dries out, the paper needs to be bent in half along its entire length and wound into a roll. During sowing, the paper with the seeds is unfolded and placed in the grooves, which must first be well moistened. When the seeds are embedded in the soil, the surface of the bed should be covered with a 3 cm layer of mulch, this will prevent the appearance of a crust on it, which can make it difficult for the seedlings to germinate.
There is another method of sowing this crop.To do this, cut toilet paper or a paper napkin into small squares, and on each you need to drop a drop of paste, on which 1 or 2 seeds and 1 granule of complex mineral fertilizer are placed. The squares must be rolled up to make balls, when they dry out, they are removed for storage before sowing. During sowing, these balls are placed in the groove with a distance of 30–40 mm.
Planting carrots before winter
When sowing carrots in the winter, the gardener will be able to get a crop half a month earlier than in the spring. However, in autumn, only early-maturing varieties are sown, and such roots are not suitable for long-term storage. Sowing is carried out in the last days of October or the first - in November, while preparing the site for this crop should be 20 days before sowing. When sowing is done, the surface of the bed should be covered with a three-centimeter layer of peat. With the onset of spring, the bed must be covered with a film on top, it is removed immediately after the seedlings appear. It should be noted that only light soils are suitable for winter sowing of carrots.
Carrot care
To grow a carrot in your garden, you need to water it in a timely manner, thin out the seedlings if necessary, systematically loosen the surface of the garden bed, and also pull out all the weeds immediately after they appear, because because of them, such a plant can infect some diseases.
Thinning
For the first time, the seedlings should be thinned out when they have formed 2 true leaf plates, while a distance of 20–30 mm should be observed between the plants. After two more true leaf plates are formed at the seedlings, they must be thinned out again, while a distance of 40-60 mm must be maintained between the seedlings. In order not to thin out carrots, you need to sow them using balls or paper tape (see above). Weeds should be removed from the site at the same time when the seedlings are thinned out. Weeding is recommended after the garden is watered.
How to water
To harvest a high-quality crop of carrots, you need to water them correctly, then the roots will be sweet, large and juicy. If the plants do not have enough water, then because of this, the roots will become sluggish, and their taste will acquire a bitterness. It is necessary to water this crop correctly from the moment of sowing until the very harvest.
When watering, the soil should be saturated with water to a depth of at least 0.3 m, which corresponds to the maximum size of root crops. If the bushes lack water, then their lateral roots grow, which are looking for additional sources of moisture, because of this, the roots lose their presentation, and their pulp becomes tough and coarse. If you water the carrots too abundantly, then root crops will crack, small growth will appear on their surface, and there is also an increased growth of tops. As a rule, watering the beds with carrots is carried out 1 time in 7 days, while adhering to the following scheme:
- after sowing, at first, for irrigation, 3 liters of water are used per 1 square meter of the garden;
- when the seedlings are thinned out for the second time, the abundance of irrigation must be increased, so, 1 bucket of water must now be consumed per 1 square meter of plot;
- after the bushes have built up a green mass, root crops begin to grow actively, and at this time the watering should become even more abundant (for 1 square meter of the plot there are 2 buckets of water);
- when 6–8 weeks remain before harvesting, the number of irrigations is reduced to 1 time in 10–15 days, while 1 bucket of water is taken per 1 square meter of the garden;
- and when 15–20 days remain before harvesting, watering the carrots should be stopped altogether.
Fertilizer
Throughout the entire growing season, the plants must be fed twice: the first feeding is carried out 4 weeks after the seedlings appear, and the second after 8 weeks.For feeding, liquid fertilizer is used, which should consist of 1 tbsp. l. nitrophoski, 2 tbsp. wood ash, 20 grams of potassium nitrate, 15 grams of urea and the same amount of superphosphate per 1 bucket of water. Top dressing is carried out only after the bed is watered.
Pests and diseases of carrots with photos
Diseases of carrots
Carrots can harm various harmful insects and diseases, so every gardener must know what to do in a particular case in order to preserve the harvest. For this culture, the greatest danger is posed by such diseases as: phomosis, bacteriosis, septoria, gray, white, red and black rot.
Bacteriosis
Bacteriosis - its spread occurs along with plant debris and seed. In this regard, after the harvest is harvested, the remains of the tops must be removed from the site, and the seed material must be pre-sowed before sowing, for this it is heated in hot water (about 52 degrees).
Gray and white rot
Gray and white rot - almost all vegetable crops are susceptible to these diseases. Their symptoms usually appear while vegetables are being stored. For prevention purposes, it is necessary to lime the acidic soil, not to overdo it with fertilizing with nitrogen-containing fertilizers, remove all the grass in a timely manner, and before laying the vegetables for storage, they are powdered with chalk. It is also very important that optimal storage conditions are created for root crops, while the storage must have good ventilation.
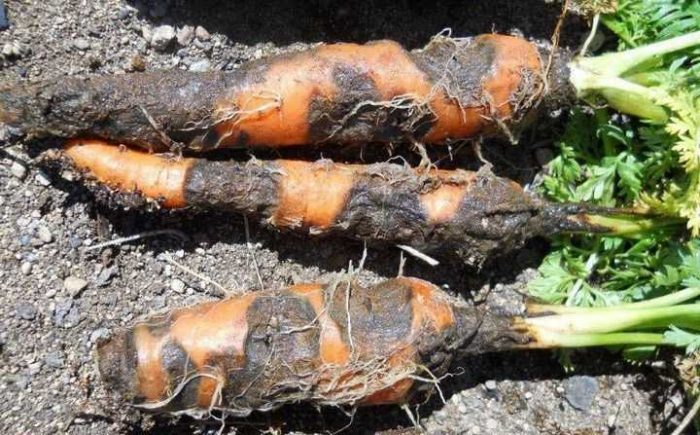
Felt disease (red rot)
Felt disease (red rot) - at first, purple or brown spots form on the affected root crops. As the disease progresses, they disappear, and in their place, black fungus sclerotia are formed. All root crops are susceptible to this disease: carrots, turnips, beets, rutabagas, parsley, etc. The reason for the development of this disease is the introduction of manure into the soil as an organic fertilizer. Affected root vegetables are stored separately from healthy ones.
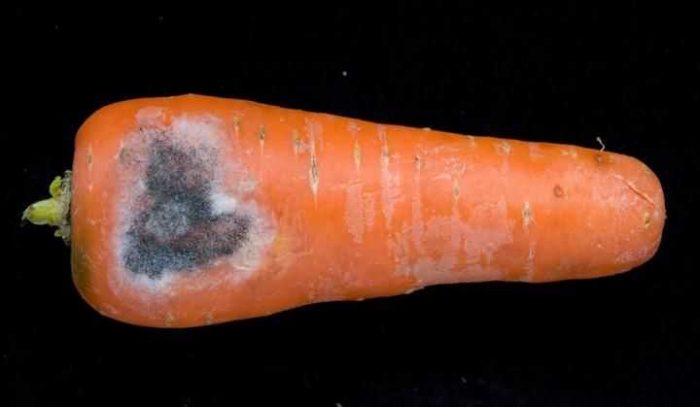
Black rot
Black rot - rotten areas of a coal black color appear on the affected root crop. This disease poses the greatest danger to the testes of carrots. Affected carrots should be removed and destroyed as soon as possible. In order to prevent the seeds before sowing, they are treated with Tigam's solution (0.5%).
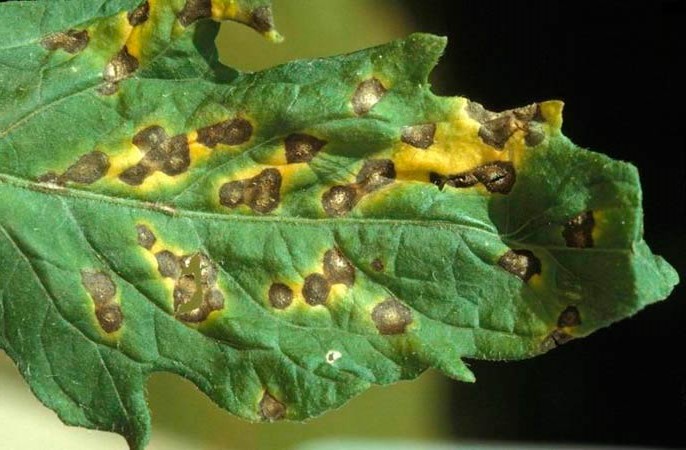
Septoriasis
Septoria - small chlorotic spots appear on the foliage of a diseased bush. As the disease progresses, they turn brown and have a red rim. High humidity contributes to the rapid spread of the disease. At the first symptoms of the disease, the bed is subjected to repeated treatment with a solution of Bordeaux mixture (1%) with an interval of honey in sessions of 1.5 weeks. Those bushes that are very badly affected must be dug up and destroyed. When the crop is harvested, plant residues are burned. In order to prevent the seed, before sowing, it is warmed up in hot water, and then immediately cooled in cold water. And also, preparing the site for sowing carrots, potassium-phosphorus fertilizers must be added to the soil for digging.
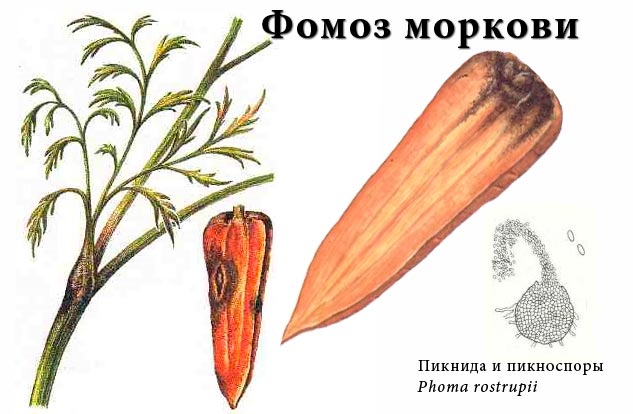
Fomoz
Phomosis - it damages the stems of the testes, as well as their inflorescences. Then brown spots appear in the upper part of the root, which deepen over time, and the entire root crop is affected. On light soil, this disease develops more rapidly. For preventive purposes, before sowing, the seed should be treated with Tigam's solution (0.5%), and the infected root crops should be immediately removed.
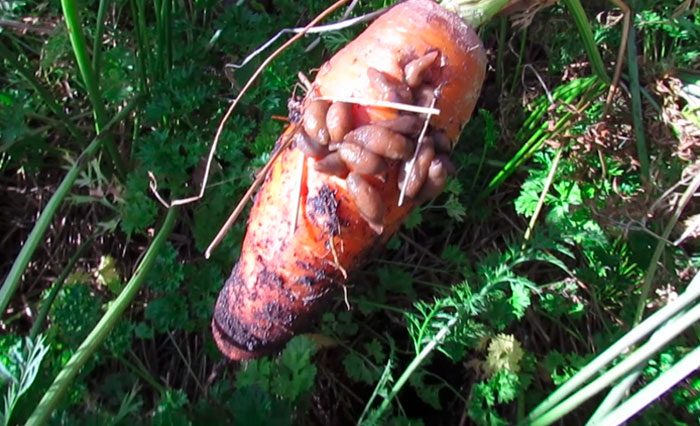
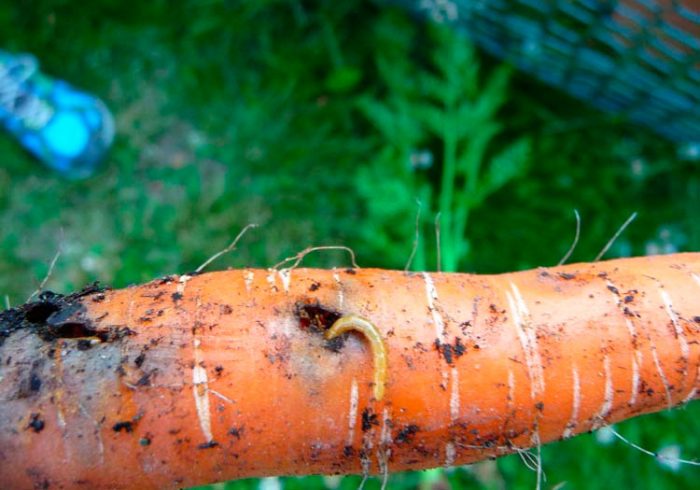
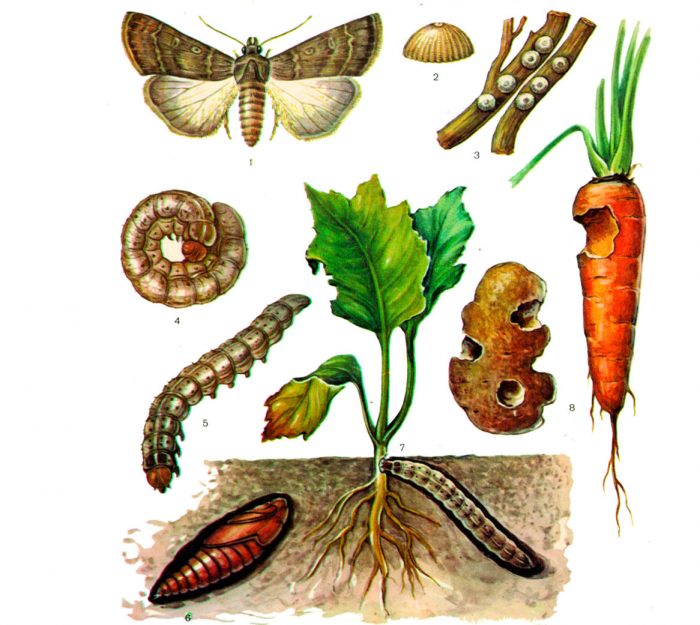
Carrot pests
Winter moths, slugs, carrot flies and wireworms can harm this crop.
Slugs
Slugs - if there are few of them, then you can collect them by hand. If gastropods have flooded the site, then you will have to fight them with the help of homemade traps.To do this, in several places on the site, small cans should be dug in, which are filled with beer, its aroma will attract a large number of slugs to the traps. If there is a watermelon or pumpkin available, then it needs to be cut into pieces that are laid out on the surface of the site, in the morning it will only be necessary to collect the pests that have crawled to feast on the "treats" left by you. You can also cover the surface of the site with a layer of wood ash, pulverized superphosphate or needles.
Wireworms
Wireworms are actually dark nutcracker larvae. They can harm not only carrots, but also such crops as: cucumbers, celery, strawberries, cabbage, tomatoes and potatoes. The length of an adult beetle is about 10 mm, it has a brown-black color, and its elytra are light red. The female clicker lays the eggs, in which there are about 200 eggs. They hatch brownish-yellow cylindrical larvae, they reach a length of about 40 mm, their development is observed for 3-5 years. In order to clear the area of the wireworm, traps are also required. To do this, on the site, you need to make several not very deep pits, in which pieces of any root crop (potatoes, carrots, beets, etc.) or half-over-ripe grass are placed. Then the hole is covered with earth and a peg is placed so as not to forget where it is. After a few days, the hole must be dug up, and the bait, with the pests gathered in it, must be destroyed.
Winter moth caterpillars
Caterpillars of the winter scoop - they injure the aerial parts of the bush, and also damage the shoots and roots, gnawing them. These caterpillars also harm tomatoes, parsley, onions, kohlrabi, beets, cucumbers and potatoes. To get rid of the caterpillars, the garden is sprayed with an insecticidal preparation, following the instructions attached to it, for example, you can use Cyanox, Revikurt, Ambush, Anometrin or Etaphos.
In order to prevent the appearance of a carrot fly, onions are planted between the rows with carrots.
Cleaning and storage of carrots
Harvesting carrots consists of several stages. First, the plantings are gradually thinned out; for this, carrots can be pulled out throughout the season for cooking. As a result, the remaining vegetables will receive much more nutrients, and their mass gain will be more active. In July, the early ripening varieties of this plant are harvested. Root crops of medium ripening varieties are dug up in August. And harvesting of late-ripening varieties, which can be stored for a long time, is carried out in the second half of September.
Harvesting takes place on a sunny, dry and warm day. If the soil is light, then the carrot can be pulled out by grasping the tops. And if the soil is heavy, then you need to remove the roots from it with a shovel. The dug up roots must be sorted, while all injured carrots are set aside for further processing. For those root crops that are suitable for storage, all foliage should be removed to the very head, after which they are laid out under a canopy and left to dry for several days. The crop can then be harvested to storage. A cellar or basement is ideal for storing such a vegetable, carrots are placed in boxes made of plastic or wood, while it should be sprinkled with dry sand so that the roots do not touch each other. If desired, replace the sand with moss. Some gardeners use crushed chalk and onion husks for this purpose, thanks to this overfilling, the crop will be protected from rot. There is another method of storing carrots, which is to glaze the carrots with clay. Clay is mixed with water to a creamy consistency, after which the roots are alternately immersed in this chatterbox and laid out on the grate. When they are dry, they are carefully removed to storage.Such a carrot, when stored in a dry cellar at a temperature of about 0 degrees, retains its juiciness and freshness until spring.
Types and varieties of carrots with photos and names
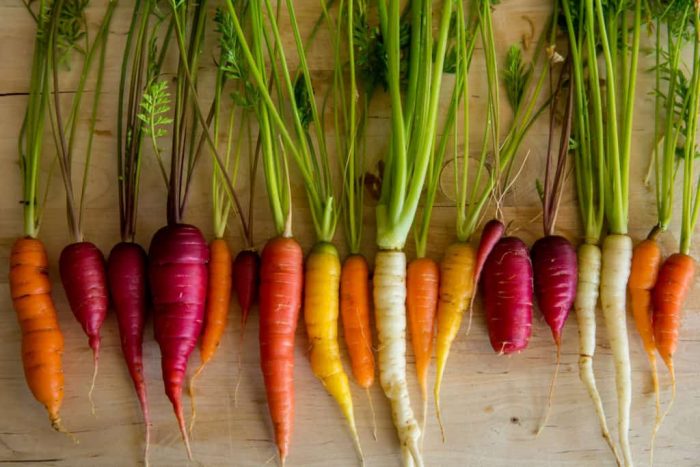
Most people believe that carrots must be orange-red in color and have a conical shape, but this is far from the case. The orange carrot became only in the 17th century, and before it was different, for example, in the Roman Empire such a vegetable was white, in some countries of Western Europe it was black, and in Ancient Egypt it was purple. In the Dutch artists' early canvases, you can see the image of yellow and purple carrots. When the first orange-colored carrots appeared, they were very light in color, since they contained a small amount of carotene (3-4 times less than modern varieties). In 2002, the purple carrot variety was recreated and is now available for free purchase. Purple pigments are anthocyanidins, in addition to such carrots, these substances are found in beets, purple basil and red cabbage, they help to improve the functioning of the brain and cardiovascular system, help cleanse the blood of fats and cholesterol. Breeding work is also carried out in the direction of changing the size and shape of root crops, so today there are varieties with an almost round, spindle-shaped, conical, pointed shape, and also with rounded tips.
Most varieties of this vegetable are divided into varieties. Main varieties:
- Parisian Carotel... This very early variety is high-yielding, even if it is grown on clay or poorly cultivated soil, the gardener will still not be left without a crop. Sweet and tender root vegetables have a rounded shape similar to radishes, they reach 40 mm in diameter.
- Amsterdam... This early maturing variety series is not intended for long-term storage. Sweet, juicy and tender roots have a small core and a cylindrical shape with a rounded end, their length is from 15 to 17 centimeters, and in diameter they reach 20–25 mm. However, it should be borne in mind that these vegetables are very fragile, and if they are handled carelessly during harvesting, they are easily injured.
- Nantes... The shape of juicy and sweet root crops is cylindrical with a rounded end, their length is about 22 centimeters, and in diameter they reach 30–40 mm. Suitable for food in the summer, and also for storage.
- Berlikum-Nantes... Cylindrical roots have sharp ends and are larger when compared with Nantes. Such root vegetables are well suited for long-term storage, but their taste is slightly lower than that of the variety series described above.
- Emperor... The length of the roots is about 25 centimeters, they have a conical shape with a sharp end. The varieties included in this series differ from each other in taste (there are sweet and not very sweet ones), fragility and the degree of keeping quality of root crops, in some varieties they can be easily injured if handled carelessly.
- Flakke... This series has the strongest and longest roots (about 0.3 m). The weight of the root crop can reach 0.5 kg or more. The growing season for such varieties is quite long, and these roots are suitable for long-term storage, but in terms of taste they are inferior to the Amsterdam and Nantes carrots.
Also, all varieties intended for open soil are divided depending on the purpose of cultivation. The following varieties are quite exotic:
- F1 Purple Elixir... From above, the roots have a purple color with a purple tint, and their flesh is orange. In length, they reach 20 centimeters. Such carrots are suitable for salads, and also for pickling.
- Russian size... This variety, which is a representative of the Imperator variety series, stands out among the rest for the size of its root crops. When grown in light soil, their length can reach 0.3 m, and their weight can be up to 1 kg.Such large roots have a very juicy and tasty pulp, rich orange color and a small core.
- Polar Cranberry... This variety belongs to the Parisian Carotel variety. Outwardly, root vegetables, which have an almost rounded shape, are similar to cranberries, they contain a large amount of sugars and dry substances. Suitable for long-term storage and canning.
- Minicore... This early ripening variety belongs to the Amsterdam variety series. The length of small juicy roots is from 13 to 15 centimeters, they have a cylindrical shape and a delicate taste. Such carrots are suitable for whole fruit preservation.
If the gardener is interested in the taste of root crops, as well as the amount of nutrients in them, then he should pay attention to the following varieties:
- Helzmaster... This variety, belonging to the Flakke variety, was created very recently and contains a large amount of beta-carotene. If compared with other varieties, then this substance in it is no less than 1/3. Red-raspberry smooth root crops have a brighter core, they average 22 centimeters in length.
- Sugar Gourmet... This hybrid belongs to the Emperor variety series. The length of dark orange roots is about 25 centimeters, their core is small, and the surface is smooth.
- Praline... The variety belongs to the Nantes variety series. Orange-red root vegetables contain a large amount of carotene, they have practically no core, and their length is about 20 centimeters. These carrots are delicious, tender, sweet and juicy.
- Losinoostrovskaya 13... Medium ripening variety, suitable for long storage. The length of the root crop is from 15 to 18 centimeters.
Some gardeners prefer varieties that are resistant to diseases, yield and good keeping quality. They should pay attention to varieties such as:
- Samson... A high-yielding variety of medium ripening, which is a representative of the Nantes variety series. The shape of the deep orange root vegetables is cylindrical, their flesh is sweet, juicy and crunchy.
- Moe... This late variety of the Imperator series has a high yield and good keeping quality. The shape of the rich orange juicy roots is conical, and they reach about 20 centimeters in length.
- Flakke... Medium ripening variety, it grows well even in heavy soil. The shape of the root crops is fusiform, they have barely noticeable eyes, and their length is about 30 centimeters.
- Forto... This mid-early variety belongs to the Nantes variety series. The shape of even tasty root vegetables is cylindrical, their length is from 18 to 20 centimeters. This variety has high yields and is suitable for long-term storage.
Also, the varieties of this culture are also divided according to the ripening period:
- early ripening or early - harvesting is carried out after 85-100 days;
- medium ripening - the roots are harvested after 105–120 days;
- late - roots ripen in about 125 days.
The best early ripening varieties: Alenka, Belgien White, Dragon, Zabava, Bangor, Kinby, Kolorit, Laguna and Touchon. Popular medium-ripening varieties: Vitamin, Altair, Viking, Callisto, Canada, Leander, Olympian and Chantenay Royal. The best late-ripening varieties: Queen of Autumn, Vita Longa, Yellowstone, Selecta, Perfection, Totem, Tinga, Olympus, Skarla.


Watch this video on YouTube