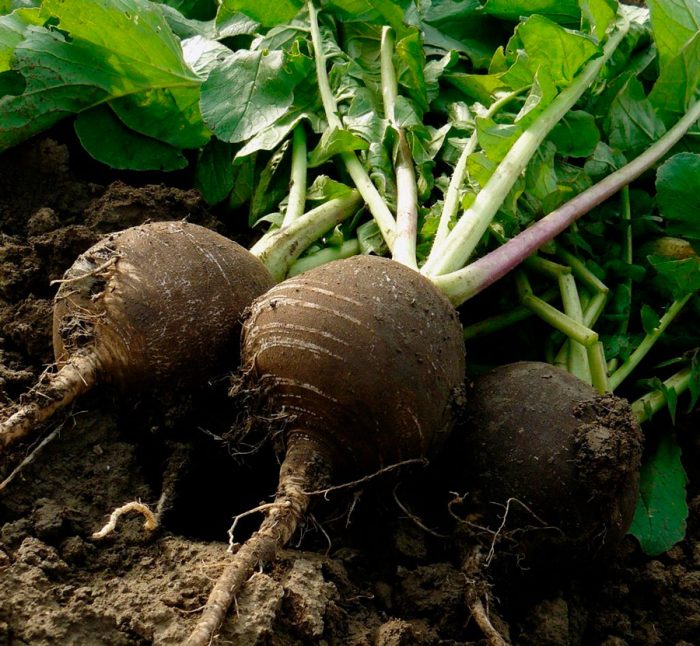
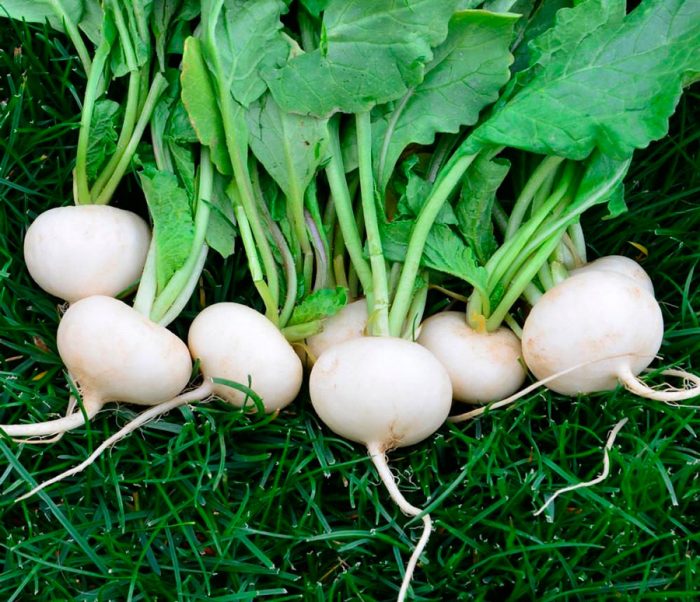
The annual or perennial herb radish (Raphanus) is not a very large genus of the Cruciferous or Cabbage family. Under natural conditions, it is found in Asian regions with a temperate climate, as well as in Europe. As a vegetable plant, radish began to be cultivated a long time ago. Today, gardeners grow a species called sowing radish (Raphanus sativus), it does not occur in natural conditions.
Content
Brief description of cultivation
- Sowing... Early maturing varieties are sown in open soil after April 25. Late varieties are sown in mid-June.
- Priming... We need a moist nutritious loam saturated with humus, it must be neutral or slightly alkaline. If the soil is acidic, then liming can be corrected.
- Watering... Water the radish systematically. Watering of early maturing varieties is carried out 1 time in 7 days, while late maturing - 3 or 4 times during the entire growing season. For 1 square meter of the garden, they take from 10 to 12 liters of water.
- Fertilizer... Top dressing of early ripening varieties is carried out only if necessary, using nitrogen fertilizers for this: the first time - during the unfolding of the cotyledon leaf plates, and the second - 7 days after the first. Late-ripening varieties need to be fed once a week; for this, complex mineral and nitrogen fertilizers are used in turn. All fertilizing must be stopped 20 days before harvesting.
- Reproduction... Seeds.
- Harmful insects... Cruciferous fleas, cabbage and garden moths, cabbage flies, cabbage moths and whiteworms, stem nematodes and wireworms.
- Diseases... Black leg, keela, felt disease, powdery mildew, downy mildew, white rot, leucorrhoea.
Features of the radish
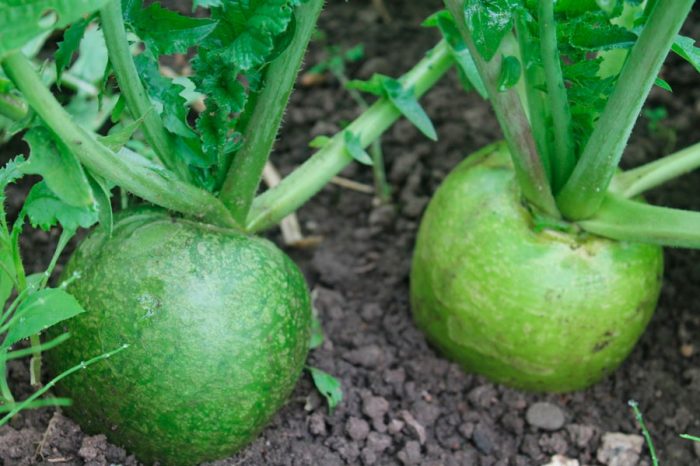
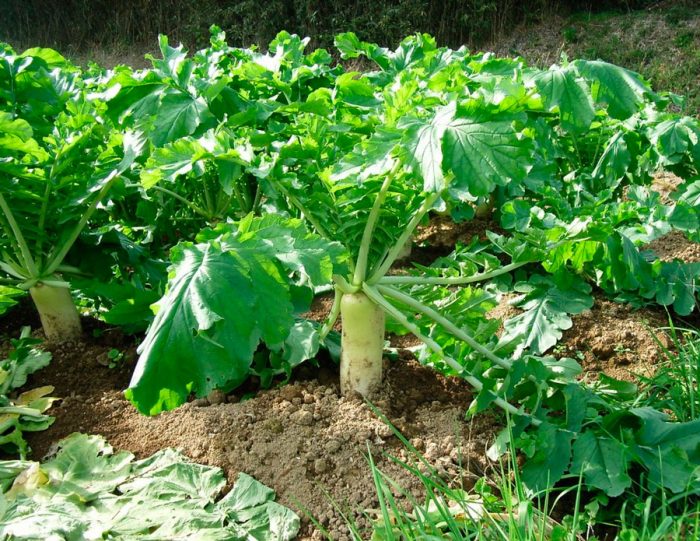
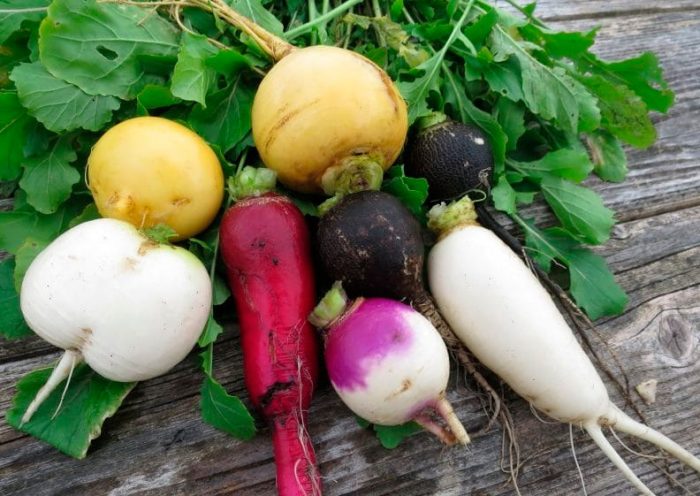
The radish has a thickened root, but it is also thin, like the oilseed variety. The root, which is formed in the first year of growth, can be colored pink, green, black, white, red or purple, but its flesh is always white. Lyrate leaf plates can be pinnately separate or whole with a large upper lobe, as well as 2–6 pairs of lateral lobes. The color of the flowers can be purple, pink or white. Swollen, wide pod fruits can be bare or covered with stiff bristles.
Such a plant is cultivated for consumption at a time when the body lacks vitamins, such a vegetable helps to stimulate appetite, accelerate metabolic processes and improve digestion. It is also widely used in complementary medicine.
Planting radishes in open ground
What time to plant
The radish is frost-resistant. Seedlings appear already at temperatures from 3 to 5 degrees. Plants can withstand temperatures as low as 3-4 degrees. Adult bushes are able to withstand temperatures as low as minus 5-6 degrees.
Sowing seeds in open soil, depending on the type of plant, is carried out in summer or spring. Sowing of early varieties is carried out immediately after April 25. And varieties grown for storage in the winter are sown in mid-June.
Suitable soil
Such a culture grows best on moist nutritious loam saturated with humus, it should be slightly alkaline or neutral. If the soil is acidic, then it must be limed before planting the radish.
It is recommended to grow radish next to turnips and radishes. Legumes (peas, beans, soybeans, lentils, peanuts and beans) are good predecessors, as well as cucumber, tomatoes, pumpkin, onions, lettuce, squash, squash, dill, eggplant, corn, and peppers. At the same time, experts advise adding organic matter to the soil when planting radish predecessors. Bad predecessors are horseradish, cabbage, watercress, turnips, carrots, beets, turnips, radishes and radishes.
The preparation of the site should be done in the autumn. To begin with, the soil needs to be cultivated to a not very great depth. After a little time, to remove the weeds that have appeared, the soil is dug to the depth of the shovel bayonet, at the same time 0.5 liters of wood ash and 1 bucket of humus or compost are added to it per 1 square meter of the plot.
Landing rules
Seeds require pre-sowing preparation, which is carried out immediately before planting. To do this, the seeds must be calibrated by size and weight, for this use a saline solution (for 1 liter of water 50 grams of salt) and a sieve with holes of 0.2 cm. The seeds that remain in the sieve must be very well rinsed with water, then on 24 hours are placed in a solution of potassium manganese (for 1 liter of water 0.2 grams of the substance).
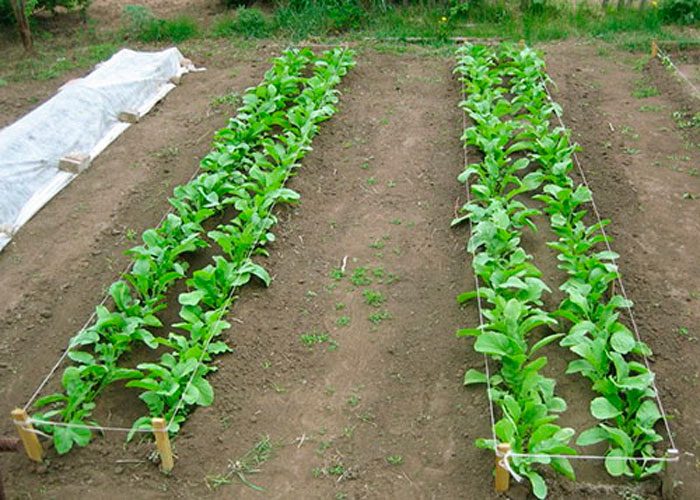
In the prepared beds, grooves must be made, reaching a depth of 20 mm, the width between them should be about 35 centimeters, while 3 seeds are laid in them, and a distance of 80 mm should be observed between the nests. Then the grooves are filled with soil, which is well compacted. If the soil is too dry, then after planting it must be watered. The first seedlings may appear after 7 days.


Watch this video on YouTube
Planting winter radish varieties
Late radish varieties are sown in the same way as earlier ones (see above). But in this case, the site must be prepared not in autumn, but in spring, while a distance of about 15 centimeters must be maintained between the nests.
Radish care
Radish is distinguished by its unpretentiousness, in this regard, it is quite simple to grow it in open soil. She should ensure timely watering, weeding, feeding, thinning and loosening of the soil surface. The first time you need to thin out the seedlings is when they have 1 or 2 true leaf plates, while the distance between them should be at least 60–70 mm. It will be necessary to thin out the seedlings again 20-30 days after the first thinning.
The soil surface between the rows must be loosened 3 or 4 times during the season. The first loosening is carried out to a depth of about 40 mm, the second - by 80 mm, the third and fourth - by 100–120 mm.
How to water
Radish, which was sown in spring, needs more frequent watering, carried out systematically 1 time in 7 days.Varieties that are sown in summer need to be watered only 3 or 4 times during the season. Such a culture is moisture-loving, therefore, during irrigation, 10 to 12 liters of water are taken for each square meter of the garden.
It is important to keep in mind that you should water the radish regularly. For example, watering it abundantly after a long dry period will cause the roots to crack. If the bushes feel a lack of water, then the fruits will become wooden and almost inedible. To reduce the number of waterings, it is recommended to cover the surface of the garden with a layer of mulch.
Fertilizing radish
If this is necessary, then the early varieties of radish are fed 2 times. The first feeding is carried out after the cotyledonous leaf plates have developed near the seedlings, and the second - 7 days after the first. Since spring varieties ripen relatively quickly, only nitrogen fertilizers are used for feeding, for example, calcium-ammonium or sodium nitrate at a concentration of 0.2 percent.
Late-ripening varieties should be fertilized systematically 1 time in 7 days, for this use a solution of complete mineral fertilizer, which consists of 10 liters of water, 20 grams of urea, 60 grams of superphosphate and 15 grams of calcium chloride. 10 liters of this solution is enough for a row up to 20 meters long. Radish needs a lot of nitrogen, so it must be fed alternately with nitrogen and complex mineral fertilizers. When 20 days are left before harvesting, it will be necessary to stop all feeding. Such a culture cannot be fed with manure, otherwise the root crops will grow branched.
Diseases and pests of radish with photos and names
Diseases
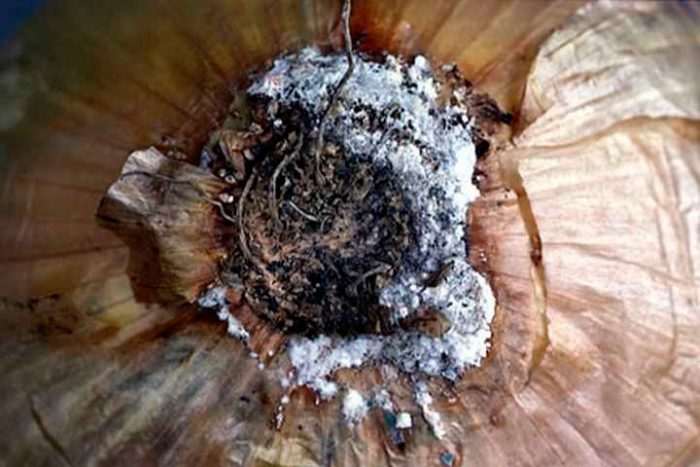
Most often, radish is affected by keel, cabbage mosaic, felt disease, powdery mildew, peronosporosis, white rot, black leg and linen.
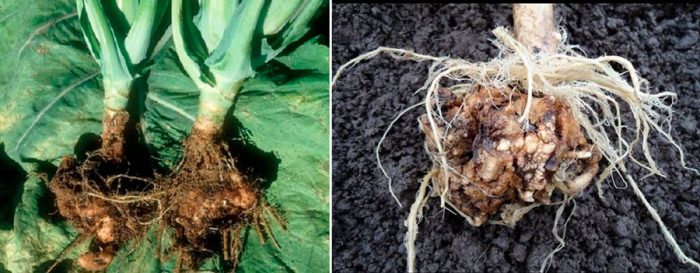
Keela
Keela is a fungal disease, in diseased specimens, spherical or spindle-shaped growths form on the surface of the roots, after a while they become brown and begin to rot. Then, the bushes experience growth retardation and wilting.
Cabbage mosaic
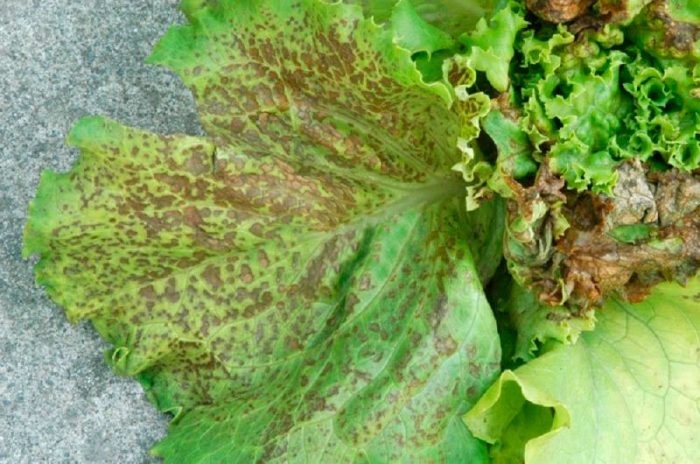
In plants sick with cabbage mosaic, a pattern is formed on the leaves, the veins become taut, and the plates are deformed. As the disease progresses, a dark green border forms around the main veins, and necrotic whitish specks appear on the surface of the foliage.
Felt disease
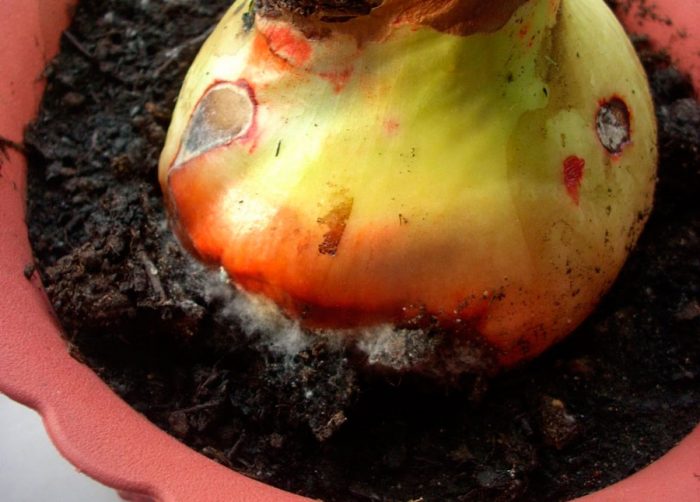
In radishes affected by red rot or felt disease, specks of lilac and brown color appear on the surface of root crops, after which dark-colored sclerotia of the fungus form in these places. The disease develops most intensively at excessively high humidity and air temperature.
Powdery mildew
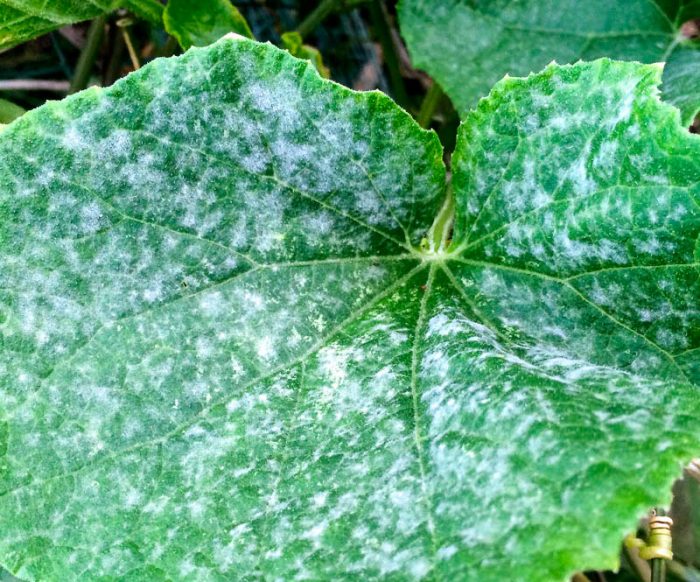
The bushes affected by powdery mildew are covered with a whitish-gray bloom, which, as the disease progresses, changes its color to brown. Deformation and drying of the affected leaf plates is observed, the bushes begin to lag behind in development.
Peronosporosis
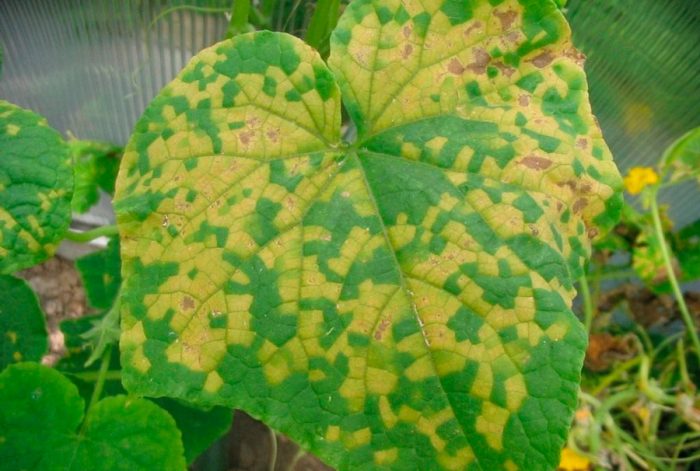
Downy mildew (peronosporosis) contributes to the formation of chlorotic spots on the front surface of the leaves, as the disease progresses, they turn yellow and become oily, and then turn brown. Later, on the lower surface of the plates under the dots, a bloom of a dirty purple color forms.
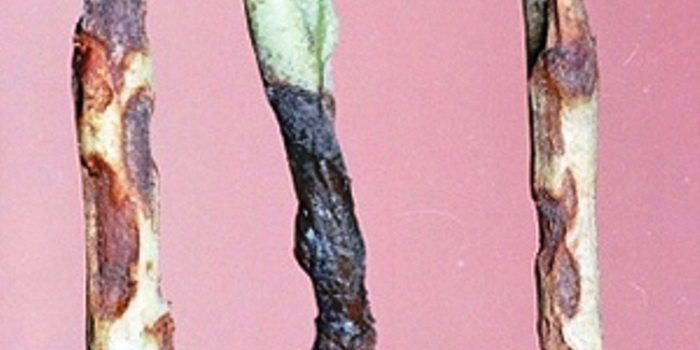
Blackleg
If the bushes are affected by a black leg, then the lower part of the leaf outlet and the upper part of the root crop thin out, become soft, and mycelium appears on their surface.
White rot
Due to white rot, the affected parts of the radish become colorless and watery, mycelium forms on their surface, which looks like cotton wool.
Belle
The aboveground part of the bushes of patients with linen seems to be covered with oil paint, after a while the affected tissues become brown and dry out.Clusters of fungal spores appear on the foliage, they become curved, and swellings appear on the surface.
Pests
Such a plant can be harmed by cruciferous flea beetles, garden and cabbage scoops, cabbage fly, cabbage whites, cabbage moths, wireworms and stem nematodes.
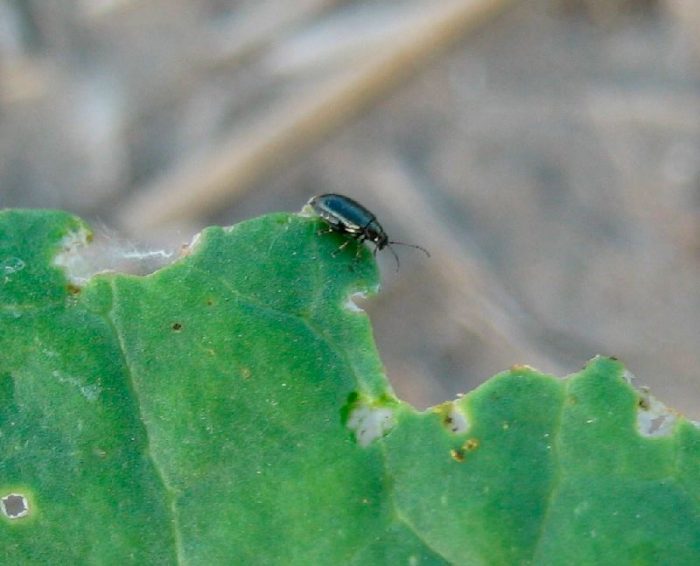
Cruciferous flea
The cruciferous flea is a very small leaf beetle that has hind hopping legs, like a grasshopper. This pest can destroy young radish seedlings, severely injuring their leaf plates.
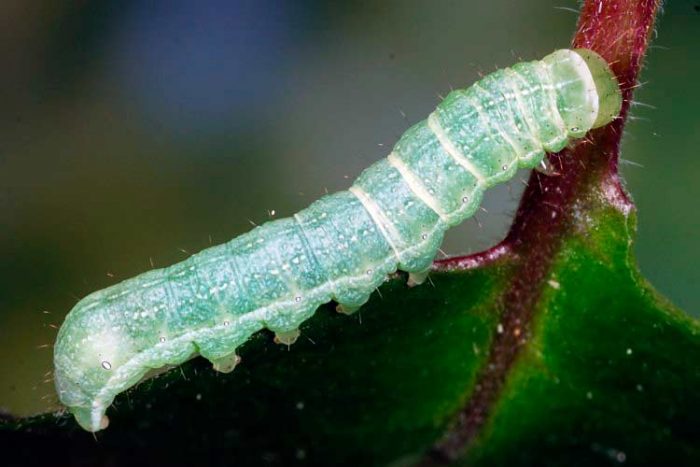
Caterpillar scoop
Caterpillars of cabbage whites and scoops gnaw out the flesh from the leaf plates. Cabbage fly larvae damage the fruit, causing it to rot. If nematode larvae, feeding on vegetable sap, settle on a bush, then they bend and begin to lag behind in growth. Wireworms use both the fruits and foliage of this plant as food.
Radish processing
If the radish is affected by fungal diseases (for example: keel, linen, rot, powdery mildew, black leg and peronosporosis), it should be sprayed with a product containing copper, namely: Bordeaux mixture, copper sulfate or copper oxychloride. To process the bushes, you must strictly follow the instructions on the package of the drug.
Mosaic is now considered an incurable disease. Plants affected by it must be removed from the ground and destroyed as soon as possible, otherwise neighboring bushes may also get sick.
In order to get rid of pests, insecticidal preparations are used to treat the radish; they can be bought in a specialized store.
But in order to protect this crop from both harmful insects and diseases, one must not forget to process seed material and soil before sowing, and also remember the rules of crop rotation and agricultural technology of this crop.
Cleaning and storage of radish
The harvesting of root crops of spring radish varieties must be carried out in the summer. This is done selectively after the fetus reaches 30–40 mm in diameter. These varieties are not suitable for long-term storage, they are grown exclusively for human consumption. These root vegetables should be stored on the refrigerator shelf, where they remain fresh for up to 20 days.
It is necessary to harvest the roots of winter radish varieties in the autumn. This is done from mid to late September, before the onset of the first frost. It is necessary to remove soil residues from the root crops extracted from the soil. Then small roots are torn off from them and the tops are carefully cut off at the very root crop, while trying not to injure it. Dried roots should be placed in a cool and dark place for several days. Radish intended for storage in winter should be placed in boxes with holes for ventilation, it should be sprinkled with sand, like beets or carrots. The thickness of each layer of sand should be about 40 mm. Such root vegetables are very well stored in a cold (about 2-3 degrees) cellar, the air humidity in it should be about 90 percent. If done correctly, winter radish varieties, such as Winter Round Black or Winter Round White, can stay fresh until spring.
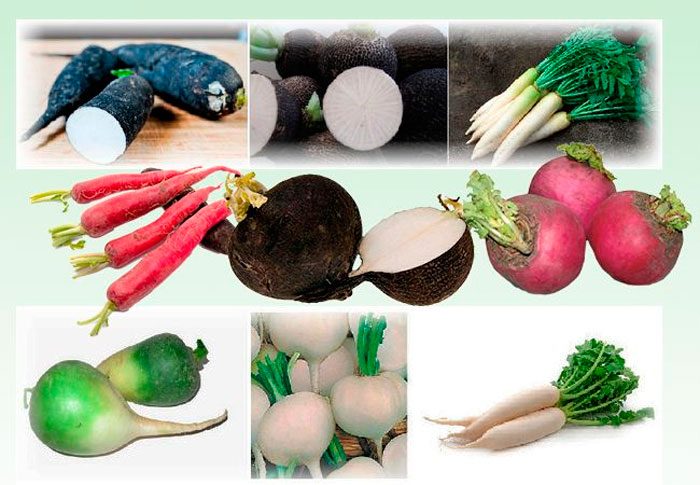
Types and varieties of radish
The radish species has the following varieties:
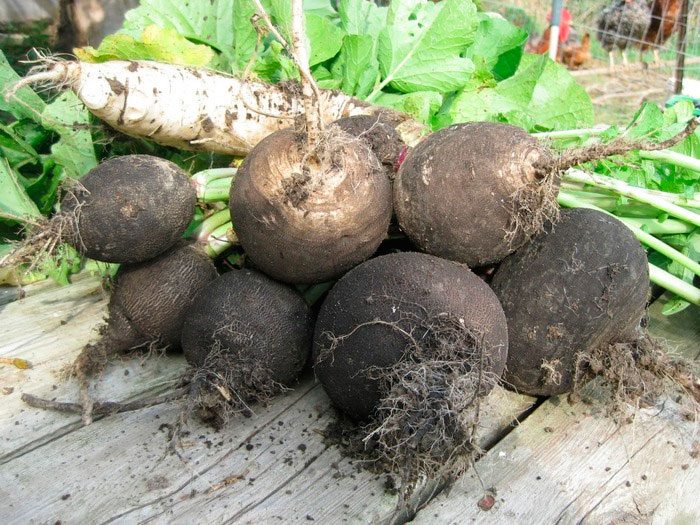
- Black radish... This subspecies has a lower taste compared to others, but it has the most powerful and valuable medicinal properties.
- Daikon, or Japanese radish... The length of large white root crops reaches 0.6 m, while they reach 10 to 15 centimeters in diameter. This radish is very tasty and healthy, and it is also unpretentious. 100 grams of this radish contains about 40 percent of the daily value of vitamin C. This variety also contains a lot of beta-carotene, potassium, selenium, fiber, folic acid, iron and iodine.The most popular varieties are: Sasha, Dragon, Dubinushka, Japanese white long.
- Oil radish... Such a moisture-loving annual variety is distinguished by shade tolerance, frost resistance and productivity. The flowers are purple-white. This variety is recommended to be sown in June or July.
- Green uzbek radish... This variety has almost the same benefits as black radish, but tastes more pleasant and delicate. It is rich in carotene, vitamins, phytoncides, potassium, phosphorus, sodium, sulfur, calcium and essential oils.
- Margelan radish, or Chinese, or forehead... The shape of dense and juicy fruits is elongated or round, but they are stored somewhat worse than European varieties. Such a salad variety has varieties that differ in color, they are: red, dark or pale green, pink or purple-lilac, but the tops of their heads are all bright green. The pulp of such a radish is neither bitter nor spicy. The most popular varieties are: Ladushka, Khozyayushka, Severyanka, Zarevo.
However, in the conditions of middle latitudes, only European varieties grow well, below those that are most popular will be described. For outdoor cultivation, the following varieties are recommended:
- Winter round white... This medium-ripening variety is distinguished by its yield. White fruits have an oval-round or flat-round shape, their weight is about 0.4 kg. Firm and juicy white pulp has a medium-sharp taste.
- Winter round black... This variety is one of the most popular, it is distinguished by keeping quality and productivity. Very tasty fruits have a flat-round or oval shape. The variety has powerful medicinal properties. The juicy and white pulp has a mild taste.
- Sudarushka... The variety ripens in just 37 days. White oval fruits, immersed in the soil only ½ part, so the harvest of this type of radish is comparatively easy. Their pulp is very tasty.
- Gaivoronskaya... The medium-ripening variety is distinguished by its yield and excellent keeping quality. The hard white pulp has a pungent taste. Cylindrical root vegetables have a green head.
- Mayskaya... In such an early ripening variety, smooth white fruits have an oval-conical shape and white juicy flesh, which has a pleasant semi-sharp taste.
- Green goddess... The early variety has pale green fruits of a round shape with crispy juicy flesh, which is distinguished by a slightly spicy taste. This variety has good keeping quality.
- Elephant fang... The medium ripening variety differs in keeping quality and productivity. The length of the white fruits is about 25 centimeters.
- Healer... This late variety combines high medicinal and taste qualities. Smooth black roots have a rounded shape, juicy, dense and crunchy flesh is painted white. The variety is perfect for salads, and during storage, the fruits remain elastic for a long time and do not lose their qualities.
Also popular are such varieties as: Munich Beer, Chernavka, Negritanka, Delikates, Odessa 5.


Watch this video on YouTube