The cabbage plant (Brassica) is a member of the Cruciferous (Cabbage) family, which also includes turnips, radishes, rutabagas, cabbage, radishes, turnips and mustard. This genus includes about 50 species. In natural conditions, they are found in the Mediterranean, Central Europe, Central and East Asia. Only those species that were exported from Europe grow on the territory of America. People began to cultivate cabbage about 4 thousand years ago, the ancient Greeks, Egyptians and Romans did it. This culture came to the territory of modern Russia thanks to merchants, and it was introduced in the 13th century from Western Europe during the heyday of Kievan Rus. At the same time, by the 18th century, it had already very firmly entered Russian life, it was at this time that the tradition appeared, after the Orthodox holiday of the Exaltation (September 27), to start collective harvesting of cabbage for the winter, for this it was chopped and salted. At the same time, for 14 days, cheerful folk games called skits were organized everywhere. In the 19th century, the famous Russian scientist and vegetable grower Rytov described already 22 varieties of cabbage.
Content
Features of cabbage
Cabbage (Brassica oleracea) is a crop. This biennial has a leafy tall stem and bare leaf plates of green-gray or gray-green color. The lower large fleshy leaf plates have petioles and a lyre-pinnately dissected shape, they adjoin each other, as a result of which a rosette is formed (a head of cabbage around the stem). The upper sessile leaf plates have an oblong shape. The multi-flowered racemose inflorescence consists of large flowers. Large dark brown seeds are spherical in shape, they reach about 0.2 cm in length.
The composition of this plant includes mineral salts of calcium, potassium, sulfur and phosphorus, fiber, enzymes, phytoncides, fats, vitamins A, B1, B6, K, C, P, U, etc.Scientists have a version that the homeland of this culture is the Colchis lowland, and there to this day in nature you can meet many similar plants, which the locals call "kezhera". The type of garden cabbage includes red and white cabbage, as well as cabbage of Savoy, Portuguese, broccoli, Chinese, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, kohlrabi, Peking and kale.
Growing cabbage from seeds
Sowing
The quality of the cabbage crop is strongly influenced by the seeds used. In this regard, when starting the selection of seeds, you should decide whether you need an early harvest for preparing various dishes and salads, or you can use later varieties, with large, very dense heads of cabbage, which are ideal for salting and long-term storage. It is extremely important to decide what you are growing cabbage for, as this affects the choice of cabbage variety, and also at the time of sowing. Among gardeners, white cabbage is especially popular, which is used to prepare delicious borscht and not only. In this type of cabbage, varieties are divided into early-ripening - their heads can be eaten only in summer, medium-ripening - they are used for cooking in the summer, and are also salted for the winter, as well as late-ripening ones - they are great for long-term storage.
Early ripening varieties are sown on seedlings from the beginning to the twentieth of March, mid-ripening varieties are sown from April 25, seeds of late-ripening varieties are sown from the first days of April to the third decade of the month. As a rule, it takes approximately 45-50 days from the day of sowing to transplanting seedlings into open soil.
Before you start sowing seeds, you should prepare a suitable substrate for this. Experienced gardeners are advised to stock up all the necessary components of the substrate in the autumn, since it will be extremely difficult to get them in winter. It is necessary to combine the sod land and humus in a 1: 1 ratio, then for every kilogram of the resulting soil mixture, 1 tbsp. l. wood ash. Everything needs to be mixed well. Ash in this case will act as an antiseptic agent, as well as a source of micro- and macroelements, and it will also prevent the development of black leg on cabbage seedlings. The soil mixture may have a different composition, so it can be made on the basis of peat, the main thing to remember is that it must be nutritious and well letting in air. For seedlings, you cannot take the garden soil in which representatives of the Cabbage family previously grew, since pathogens that can infect seedlings may be present in it.
Cabbage seeds need pre-sowing preparation. To do this, they are immersed in hot (about 50 degrees) water for a third of an hour, then they are kept in very cold water for five minutes. This will increase the seed resistance to fungal diseases. After that, the seed is kept in a solution of a growth-stimulating agent for several hours, for example, Epin, Gumat, Silk, etc. But it should be noted that there are varieties whose seeds are prohibited to wet, therefore, be sure to study the instructions available on packaging. Sowing is carried out in a well-watered substrate, while it is impossible to water it more until the seedlings appear. During sowing, the seeds are buried 10 mm into the substrate, after which the container should be covered from above with a paper sheet or foil, which will prevent rapid evaporation of moisture from the surface of the substrate. The container with crops must be placed in a relatively warm place (about 20 degrees).
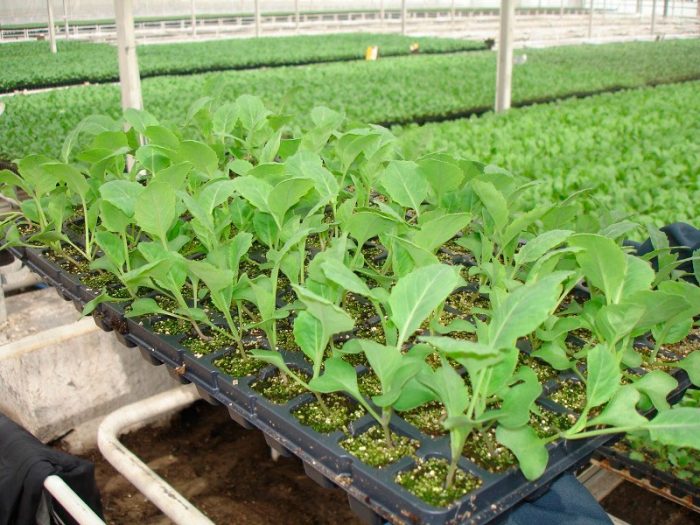
Growing cabbage seedlings
The first seedlings should appear within 4–5 days after sowing.When this happens, the cover must be removed from the container, and it must be removed to a cooler place (about 6-10 degrees), there the cabbage will be there until one real leaf plate is formed. If there is such an opportunity, then the seedlings can be transferred to the glazed loggia, while the first leaf usually grows after 7 days. When this happens, the seedlings should be provided with the following temperature regime: on a cloudy day, the air temperature should be about 14-16 degrees, on a sunny day - about 14-18 degrees, and at night - from 6 to 10 degrees. At this stage of growing cabbage seedlings, they will need access to fresh air, but it should be noted that this plant reacts extremely negatively to a draft. In addition, seedlings at this time need a long day of light (at least 12-15 hours a day), so they need additional lighting, you can use a phytolamp or a fluorescent lamp for this. The substrate should not dry out, but also moisture stagnation should not be allowed in it. Systematic loosening of the soil mixture will help in this, this should be done immediately after watering. After the seedlings appear, after 7 days they should be spilled with a weak solution of manganese potassium (3 grams of substance for 1 bucket of water) or with a weak solution of copper sulfate.
Seedling picking
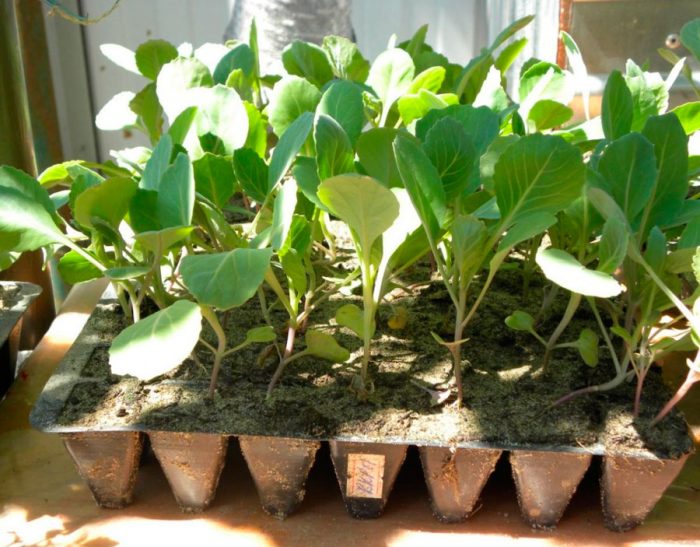
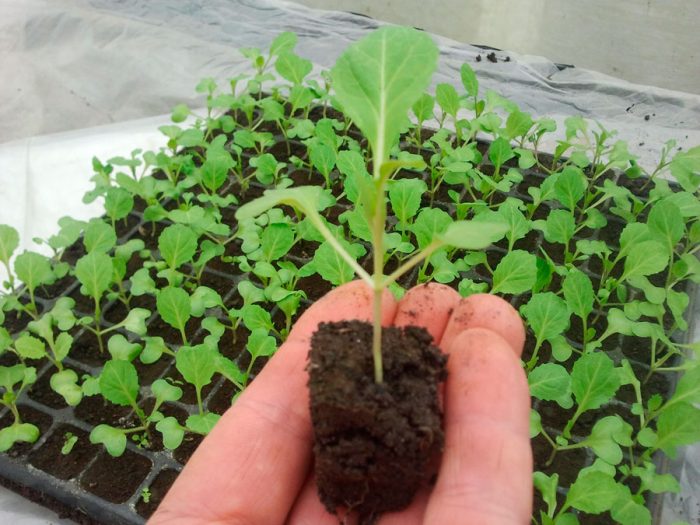
When 10-15 days have passed from the moment the seedlings appear and the first true leaf plate is formed, they will need a pick, which will allow the plants to significantly increase the feeding area. In 60 minutes before picking, the seedlings should be watered very well. After that, each plant must be pulled out of the box along with a lump of earth and put in separate cups (it is recommended to use peat-humus), it is first necessary to shorten the root by 1/3 of the length. At the same time, it is necessary to deepen the cabbage during the dive in cotyledonous leaves. If the sowing of seeds is carried out immediately in separate pots or cups, then the plants will not have to dive. During planting of plants in open soil, if they are removed from separate cups, then their root system is not damaged as much as when transplanted from a common container. The fact is that the root system of plants by this time will have impressive dimensions. For growing cabbage, it is best to use peat-humus pots, since when planting in the ground, the plant can not be removed from the containers, but planted in the soil with them.
Before you start planting seedlings in open soil, they must be hardened, which will allow the plants to adapt to new conditions of existence. To do this, for the first two or three days in the room where the seedlings are standing, you need to open the window for 3-4 hours, and do not forget to protect the plant from a draft. Then, for several days, you need to regularly transfer the plants to the balcony, loggia or street so that they can get used to the direct rays of the sun, while at first the cabbage should be protected from them by covering it with gauze. After 7 days, you need to significantly reduce watering and transfer the seedlings to the balcony, where they will be located before planting in open soil.
Planting cabbage in open ground
What time to plant
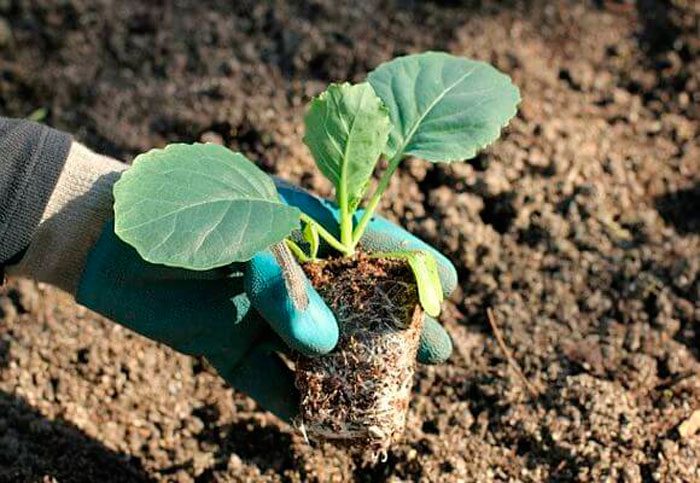
Seedlings of early-maturing cabbage varieties should be transplanted into open soil after 5 to 7 true leaf plates have formed in the plants, while their height should be about 12–20 centimeters. And cabbage seedlings of late and mid-season varieties should be planted in the soil when their height is 15–20 centimeters, and 4–6 true leaf plates should be formed in them. As a rule, plants of early ripening varieties are planted in the first days of May, varieties of medium ripening in the second half of May, and late ones - from the last days of May to mid-June.
Suitable soil
The area where the cabbage will grow needs careful preparation.It should be borne in mind that it must be sunny. In this case, sunlight should fall on it from early morning until evening. It is recommended to plant early maturing cabbage in sandy soil or loam, and late and mid-maturing varieties - in clay soil or loam. For sandy soil, the pH should be within 6.0, while for clay and sandy-clay - pH 7.0. This crop should not be grown on acidic soil. Those areas that are infected with bacteriosis cannot be used for cultivating such a plant for 8 years. Bad predecessors of cabbage are other members of the cruciferous family, for example: radishes, turnips, rutabagas, turnips, radishes, mustard or cabbage. Only after 3 years on the site where these plants were grown, it will be possible to plant cabbage.
The preparation of the soil in the area intended for planting this crop should be done at the beginning of autumn. To do this, on a sunny day, you should dig the site to the depth of the shovel bayonet. After that, it is not necessary to level the surface of the site, because due to the large number of irregularities, the soil will be able to absorb more moisture in winter and spring. Leveling the surface of the site will need to be done in spring, when the snow cover melts, this procedure is called "moisture closure", because thanks to it, water from the soil will not evaporate very quickly. As soon as weeds appear on the site, they must be pulled out immediately.
Open ground planting rules
An approximate scheme for planting cabbage seedlings in open soil:
- for early-ripening and hybrid varieties of red and white cabbage - 30x40 centimeters, for medium-ripening varieties - 50x60 centimeters and late-ripening - 60x70 centimeters;
- for kohlrabi - 30x40 centimeters;
- for cauliflower - 25x50 centimeters;
- for Brussels sprouts - 60x70 centimeters;
- for savoy cabbage - 40x60 centimeters;
- for broccoli ―30x50 centimeters.
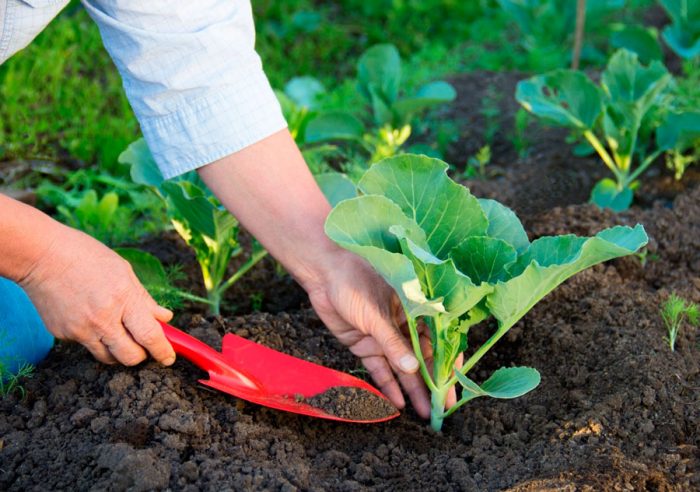
This culture needs a lot of light and space, in this regard, planting should not be thickened. Prepare planting holes on the site, they should be only slightly larger than the plant's root system, taken with a lump of earth or a peat-humus pot. In each hole should be poured one handful of peat and sand, 50 grams of wood ash, 2 handfuls of humus and ½ tsp. nitrophosphate. Mix the additives well together and sprinkle with plenty of water. The plant, taken together with the root system and a lump of earth, must be placed in the resulting slurry, after which the hole is sprinkled with wet soil, which is tamped a little, and on top it must be covered with a layer of dry soil. If the seedlings are overly elongated, then they must be planted in such a way that the first pair of true leaf plates are flush with the surface of the plot.
Cabbage care
In the first days, it is necessary to carry out a systematic examination of the cabbage seedlings transplanted to the garden bed, this will allow timely planting of the fallen plants. On fine days, the planted plants will need protection from the scorching direct rays of the sun, for this you can use a non-woven material or newspaper. For 7 days, every day in the evening, you need to water the cabbage from a watering can with a divider. After a week, the shelter must be removed, but only if frost is not expected at night.
After the seedlings have taken root, it is very easy to care for them. To do this, you need to water it in a timely manner, remove weeds, loosen the soil surface, feed and, if necessary, treat the bushes from diseases and harmful insects. After 20 days after planting, the cabbage will need hilling, and after 1.5 weeks, re-hilling is carried out.
How to water
When cultivating cabbage in open soil, special attention should be paid to the watering regime.The fact is that this culture is among the moisture-loving ones. The bushes are watered in the evening, in hot weather the frequency of abundant watering should be 1 time in 2 or 3 days, and on rainy days, one watering in 5 or 6 days is enough. After the plants are watered, the surface of the garden bed must be loosened thoroughly, while the bushes have been huddled. To reduce the amount of watering, experienced gardeners recommend covering the surface of the plot with a five-centimeter layer of peat, which will also become a source of nutrients for cabbage.
Fertilizer
7-9 days after the seedlings are cut, they should be fed, for this use a nutrient mixture consisting of 1 liter of water, 4 grams of superphosphate, 2 grams of potassium fertilizer and 2 grams of ammonium nitrate. One liter of this mixture is enough for feeding from 50 to 60 seedlings. To prevent the seedlings from getting burns, they should be fed after preliminary watering. The plants should be fed the second time after 15 days, for this they use the same nutrient mixture, but the amount of fertilizer should be doubled. Slightly yellowed seedlings need feeding with a liquid solution of fermented manure (1:10). The third top dressing is called hardening, it is carried out a couple of days before the cabbage is transplanted into open soil, for this a nutrient solution is used, consisting of 1 liter of water, 8 grams of potassium fertilizer, 3 grams of ammonium nitrate and 5 grams of superphosphate. In order for the seedlings to take root better after planting in open soil, a relatively large amount of potash fertilizer is used to feed it. The nutrient mixture described above can be replaced with the ready-made liquid complex fertilizer Kemira Lux.
If the cabbage seedlings received all the necessary fertilizing on time, then it will delight the gardener with its rapid growth and intensive development. However, after this culture is planted in the garden, it needs to continue to be fed. When foliage begins to actively grow in the bushes, they should be fertilized with a solution consisting of 1 bucket of water and 10 grams of ammonium nitrate, this volume is designed for feeding 5 or 6 copies. After the formation of foliage in the head of cabbage begins, the plants need to be fed again, but this time the following composition is used: for 1 bucket of water 5 grams of double superphosphate, 4 grams of urea and 8 grams of potassium sulfate. This amount of solution is enough for 5-6 bushes.
Cabbage processing
After the cabbage is planted in the beds, at first it will need dusting with wood ash, which must be combined with tobacco dust. This will scare off fleas and slugs from immature young bushes. This plant is a food product, in this regard, experts advise using chemical preparations for its processing only in the most extreme cases. But what is better to use in this case? There are quite a few folk remedies that can protect this crop from pests such as caterpillars, aphids, slugs, snails and larvae.
In order to get rid of caterpillars and aphids, you can use the following infusion: to prepare it, you need to combine half a bucket of water and 2 kilograms of tomato tops, after 3-4 hours the infusion is boiled for 3 hours, and when it cools down, filter and dilute with water in ratio 1: 2. It is also recommended to add to the infusion from 20 to 30 grams of tar soap crushed on a grater, in this case it will "stick" to the foliage and not drain onto the soil. Also, to combat these pests, an infusion of onion peels is sometimes used. For its preparation, a liter jar of onion husks is taken, which must be combined with 2 liters of freshly boiled water and 1 tbsp. l. dishwashing detergents or liquid soap.
To get rid of the larvae of the May beetle, cabbage fly or scoops, ants must be attracted to the cabbage garden.To do this, on the site, you need to dig into the ground a small container filled with water, in which honey or jam is previously dissolved. Black ants are very fond of sweets, and they also feed on the larvae of harmful insects.
In order to prevent harmful insects from appearing in the garden, it is recommended to plant mint, cilantro, rosemary, marigolds, sage, basil or other spicy herb around it. Butterflies, fleas, aphids and slugs do not tolerate the pungent smell of these plants, but it attracts enemies of these pests, for example: lacewings, ladybugs, horse beetles, etc.
Diseases of cabbage with a photo
Cabbage can be affected by such a disease, which is characterized by rapid development. If the gardener in this case, in the shortest possible time, does not take all the necessary measures to combat it, then he may even be left without a crop.
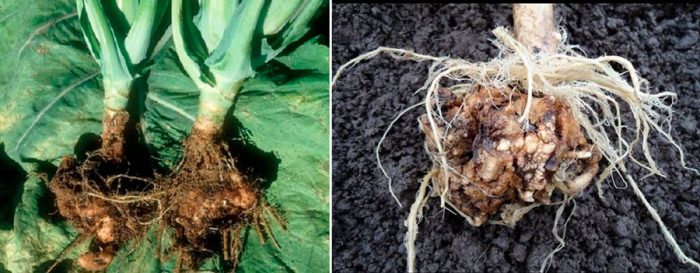
Keela
This fungal disease poses the greatest danger to this crop. It affects early ripe varieties of cauliflower and white cabbage, while plant infection occurs even at the seedling stage. In affected plants, growths appear on the root system, which contribute to a violation of their nutrition. Because of this, the seedlings are lagging behind in development, while they do not form ovaries. Diseased bushes need to be dug up and destroyed along with an earthen lump, and the resulting hole must be sprinkled with a layer of lime. This disease affects only representatives of the Cabbage family, so other crops can be safely grown in this area.
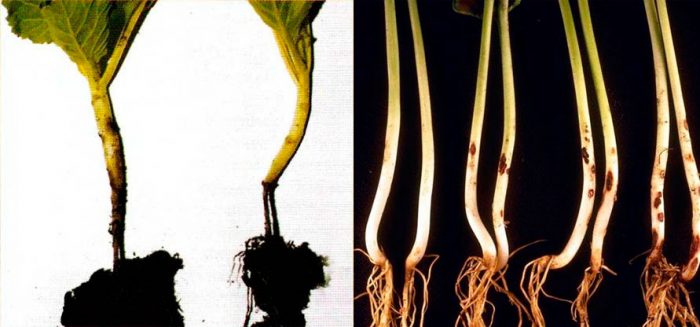
Blackleg
Very often, cabbage seedlings or young bushes planted in open soil are affected by a black leg. This fungal disease affects the root collar at the base of the stem. With the development of the disease, the affected parts of the plant turn black, they become thinner and rot, the growth of cabbage becomes slower and, in the end, it dies. Affected seedlings will die in any case, so there is no point in planting them in the garden. If diseased plants died from a black leg when growing in a garden, then the land on it must be replaced, since it can no longer be used for growing cabbage. As a preventive measure, before sowing, the seed material and soil should be treated. Garnosan is used to process the seed (follow the instructions), while in order to process 100 seeds, 0.4 grams of the product will be enough, and Tiram (TMTD) (50%) should be added to the soil, 50 is taken per 1 square meter of the plot gram.
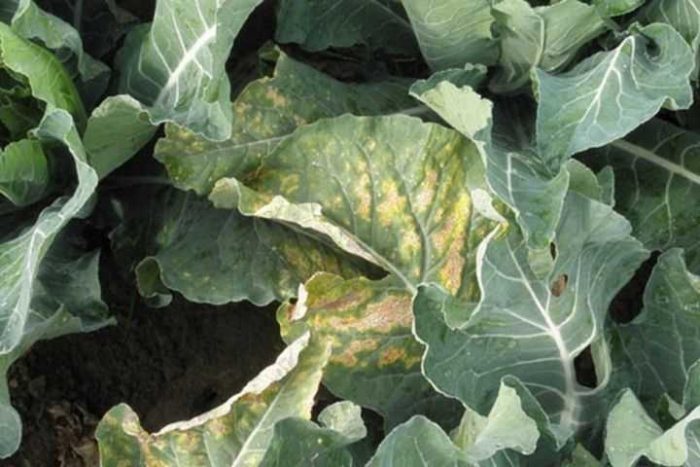
Downy mildew (downy mildew)
As a rule, the causative agents of this disease are present in the seed, therefore it is not recommended to neglect its pre-sowing preparation. The disease begins to develop actively in damp weather, specks of a pale yellow-red color appear on the outer foliage of the bushes. Over time, the leaf plates turn yellow, and they die off. In order to prevent the seed, before sowing, it is etched with Planriz or Tiram. Some gardeners instead immerse the seeds in hot (about 50 degrees) water, where they should stay for 20 to 25 minutes. If pre-sowing preparation was not carried out or it turned out to be ineffective, the bushes should be sprayed with a decoction of garlic. To prepare it, 1 bucket of water must be combined with 75 grams of chopped garlic, after 12 hours the mixture is heated over a fire to a boil, and then cooled, after which the broth will be ready for use. If this measure is also ineffective, the cabbage should be sprayed with a solution of Fitosporin-M (2-3%). Re-processing, if necessary, is carried out after 15-20 days. However, it should be remembered that spraying with a fungicidal preparation cannot be carried out after the head of cabbage has tied, otherwise there is a high probability that poison will accumulate in the foliage.
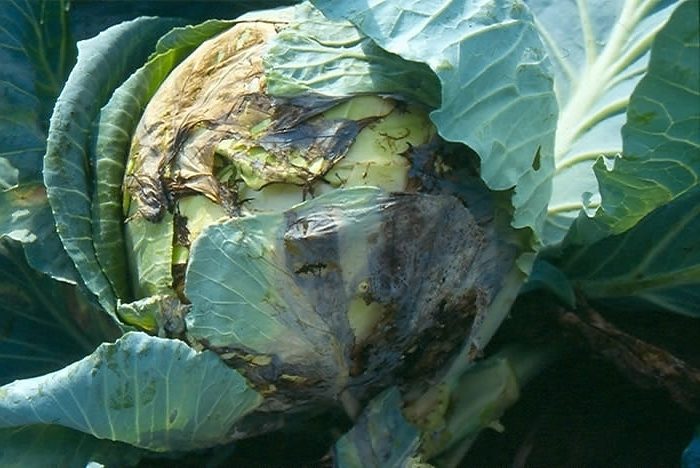
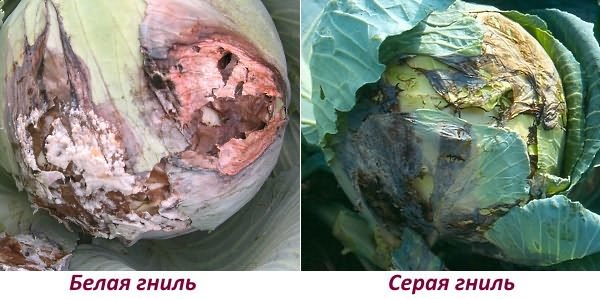
Gray and white rot
The development of white rot occurs when the weather is damp and cool outside. In the affected bushes, the mucousness of the outer leaf plates is observed, while between them a white cotton-like mycelium with black sclerotia is formed, the size of which is 1–30 millimeters. Infected forks in storage begins to rot, and the disease spreads to other heads of cabbage located nearby. During storage, symptoms of gray mold damage also appear. So, at the lower leaf plates on the surface of the petioles, a fluffy mold with beads of black dots forms. To protect cabbage from these diseases, it is necessary: before sowing, disinfect the seed, adhere to the agrotechnical rules of this crop, clean and disinfect the storage facilities before laying the heads of cabbage, store it correctly, conduct systematic inspections of the forks, and, if necessary, clean the affected areas.
Fusarium wilting (yellowness of cabbage)
This disease occurs due to the Fusarium fungus. The defeat of yellowness occurs even in the seedling period, while very often from 20 to 25 percent of all seedlings die. In affected plants, leaf plates lose turgor, and yellow foci appear on their surface. In places of yellowing, the leaves develop more slowly, while the affected foliage dies off. All diseased bushes should be removed from the soil and destroyed, and the earth should be replaced or steamed. In order to get rid of the fungus, it is necessary in autumn and spring to carry out preventive soil treatment on the site with a solution of copper sulfate (for 1 bucket of water, 5 grams of the product).
Rhizoctonia
The development of this fungal disease occurs with sharp changes in temperature (for example, from 4 to 24 degrees), air humidity (from 45 to 100 percent), soil acidity (pH 4.5-8). In a diseased plant, the root collar is affected, which turns yellow, dries up and dies. The root system of a diseased bush becomes like a washcloth. As the disease progresses, cabbage dies. Bushes become infected in open soil, while the development of the disease does not stop in storage. For preventive purposes, before planting seedlings in open soil, the site must be treated with copper oxychloride or with a product that contains it.
Cabbage pests with photo
Above, it was described in detail how to save cabbage from caterpillars, snails, slugs, aphids and larvae. However, other insects can also harm this plant.
Cruciferous bugs
These variegated beetles, reaching about 10 mm in length, which hibernate in the ground, are very dangerous for cabbage. In the last days of April, they begin to eat seedlings, then in the first summer weeks, the females arrange egg-laying, the larvae appear after half a month, and after 4 weeks they become adult insects. Bed bugs pierce the surface of the leaf plates and suck the sap from the plant. The tissue of the sheet where the puncture is located dies off. If there are a lot of punctures, then the leaf plates wither, dry up and die off. In the dry season, this pest is the greatest danger to cabbage. In order to prevent from the site, it is necessary to pull out all the weeds that belong to the Cruciferous family, for example, rape, sverbyga, field yarrow, shepherd's bag, beetroot and gristle. When the crop is harvested, all weeds should be removed from the site, which must be collected and destroyed. To get rid of this pest, seedlings should be sprayed with Phosbecid or Actellic, this must be done before the head of cabbage begins to form.
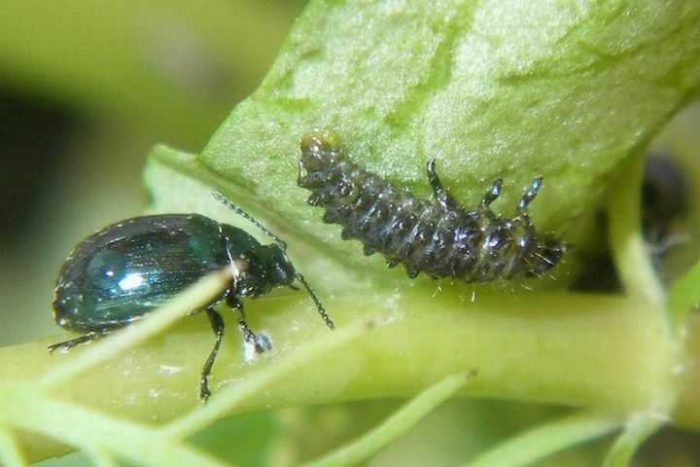
Cabbage leaf beetle
This small bug, up to 0.5 cm in length, has an ovoid shape. He injures the sheet plates, making holes in them or eating grooves along the edge.For wintering, leaf beetles settle in the ground, females arrange their egg-laying, after 10–12 days larvae hatch from the eggs, which feed by scraping the skin from the leaf plates. For preventive purposes, it is necessary to pull out all the weeds from the site, which belongs to the Cabbage family. To scare off this pest, it is necessary to treat the bushes through dew every morning with a mixture consisting of wood ash or slaked lime and tobacco dust (1: 1). Before the heads of cabbage begin to form, you can use Actellik's solution (2%) or the biological product Bankol, which is less toxic, to treat plants.
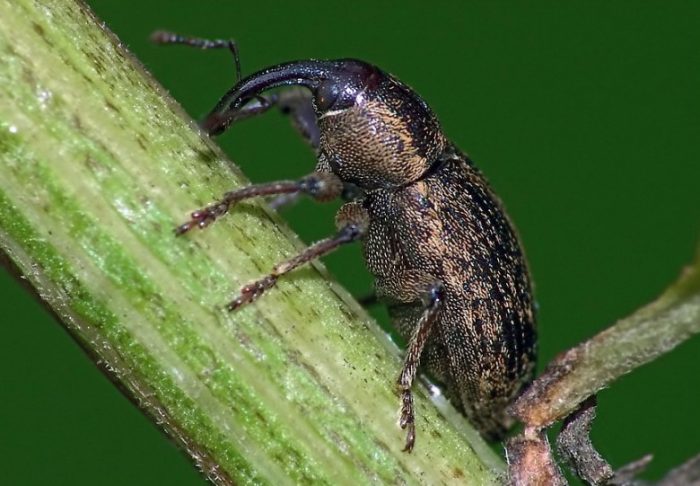
Stem Cabbage Lurker
It is a beetle, painted black and having a length of about 0.3 cm.The danger to the plant is its larvae, which gnaw holes in the petioles of the leaf plates, through which they penetrate into the stem, and along the tunnels made in it they descend into the root system of the bush ... As a result, damage to the conducting system occurs, the foliage turns yellow, the development of the plant stops and soon it dies. In order to exterminate this bug, in the autumn time it is necessary to remove all plant residues from the site, as well as to dig the soil. During the growing season, it is necessary to remove the weed from the garden in time, and also timely dig up and destroy the cabbage affected by the hidden proboscis. To exterminate this pest, you can use Phosbecid or Aktellik, but such treatment is permissible only at an early stage of seedling development in open soil.
Harvesting and storing cabbage
When there are about 20 days left before harvesting the cabbage, you will need to stop watering it. As a result, there is a relatively rapid accumulation of fiber in the heads of cabbage, due to which they will be better stored. After the temperature drops to minus 2 degrees at night, you can start harvesting cabbage forks. You should not pull with harvesting, since if the forks freeze, this will extremely badly affect their keeping quality.
The bushes should be dug together with the roots. Then they need to be sorted, for this, pest-damaged, small and rotting specimens are removed to the side, they can be used for food or for salting, but they are not suitable for storage. All forks that are suitable for storage must be placed under a canopy, where they will stay for 24 hours. During this time, the heads of cabbage will dry out and wind up a little. After that, the cabbage should be cut off the stalk 20 mm below the fork, while 3 or 4 green leaf cover plates should remain. Then the heads of cabbage are collected in storage.
A cellar is perfect for storing this vegetable, since the temperature in it does not fall below zero degrees, and the air humidity is high. If in winter it is not warmer than 4-6 degrees in the cellar, then this vegetable will be stored in it very well. The ideal conditions for storing cabbage are as follows: humidity is 90–98 percent, and temperature is from minus 1 to plus 1 degrees. Prepare the cabbage before placing it in storage. Despite the fact that the humidity in the cellar is very high, there should be no mold anywhere, and the floor should be thoroughly cleaned of debris. After the walls have been whitewashed with quicklime, it is necessary to fumigate the cellar with sulfur. Also, the storage should be well ventilated. In the absence of ventilation, experts recommend ventilating the storage at least once every 4 weeks. On the shelves, forks should be placed in 1 layer, they can also be wrapped in newspaper sheets and hung or laid in a pyramid on a wooden board.
Experienced gardeners have several secrets that help keep this vegetable fresh for a long time:
- The forks are tied by stumps in two pieces, after which they are suspended from the ceiling on the poles.Hanging heads of cabbage are very easy to inspect for damage, and in this position they will have good air access.
- The heads can be stored in trellises made of wood, which are placed on shelves or on stands. It is forbidden to put them on the floor.
- The forks are wrapped in paper and placed in a plastic bag, and you do not need to tie it. This bag can be placed on a shelf or hung from the ceiling.
- The cabbage should be placed in a 10 liter bucket, which is filled with soil; on top of the forks should also be covered with soil. In this form, cabbage is harvested to storage. The soil, if desired, can be replaced with sand.
There are other storage methods. To do this, in cabbage, it is necessary to cut off all the covering leaf plates, and the root should not be cut off. The forks must be hung by the roots in a draft, where they will have to wither a little. After the upper leaf plates have dried out a little, the cabbage is removed to the storage, for this it is tied in pairs, and then hung by the roots to the ceiling. You can also immerse the forks in a clay mash, the consistency of which should be similar to the dough for pancakes. The cabbage should be completely covered with clay, and the surface of the leaf plates should not be visible through it. Hang it up. After the clay is completely dry, the cabbage is hung from the ceiling in the storage.
In all the ways described above, you can store red and white cabbage. The cauliflower heads are wrapped in paper sheets and hung from the ceiling in the cellar, and they can only be stored in this way. You can also wrap the forks with a paper towel and place them in a plastic bag that should not be tied tightly. It is then removed to the vegetable shelf in the refrigerator. In this form, cabbage will be stored for about 8 weeks.
Types and varieties of cabbage with photos and names
Cabbage is grown both in vegetable gardens and on an industrial scale, since it, like potatoes, is the main vegetable crop. In this regard, there is a very large number of species and varieties of this vegetable. Below will be described the types and varieties of this crop intended for cultivation in the open field.
White cabbage
The most popular among gardeners in the middle latitudes is white cabbage. Its stem is not very high and thickened, it is covered with large leaf plates, and there is also a head of cabbage, which is a strongly overgrown apical bud. There are forks weighing about 16 kilograms, they are dense and have a rounded shape. This vegetable contains carotene, fiber, vitamin B and C. In alternative medicine, such cabbage is used for stomach diseases and edema, and externally it is used for boils and suppurations. The variety of cabbage affects the size of the head and the yield of the plant: the early varieties are the most productive - June and Gribovskaya, the middle ripening period - Slava and Podarok, as well as late-ripening - Amager and Moscow late.
Red cabbage
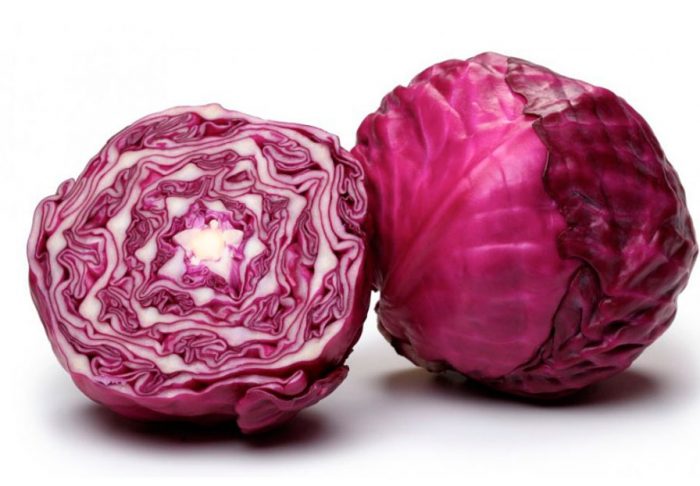
This species is very similar to white cabbage, but it is more frost-resistant. The leaf plates are purple, the forks weigh up to 5 kilograms, they are very dense and therefore have excellent keeping quality. This cabbage has 4 times more carotene and 2 times less fiber when compared to white cabbage. It also contains iodine, mineral salts, pantothenic acid, iron, cyanidin (strengthens the walls of blood vessels). The most popular varieties: Gako, Mikhailovskaya, Kamennaya Golovka.
Cauliflower
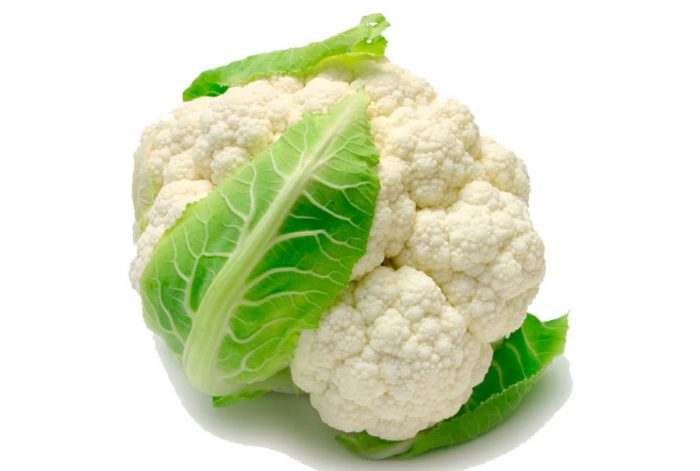
Such a dietary vegetable consists of a lumpy granular head of a pale cream color of a hemispherical shape, which is surrounded by green leaf plates.The mass of the head can reach up to 1.5 kg, and it includes rudimentary flowers on short branchy legs, which almost merged into a single whole. The most popular varieties are: early ripening - Movir, Early Gribovskaya, Garantia, middle ripening - Moskovskaya Konservnaya, Otechestvennaya, late ripening - Adlerskaya Zimnyaya.
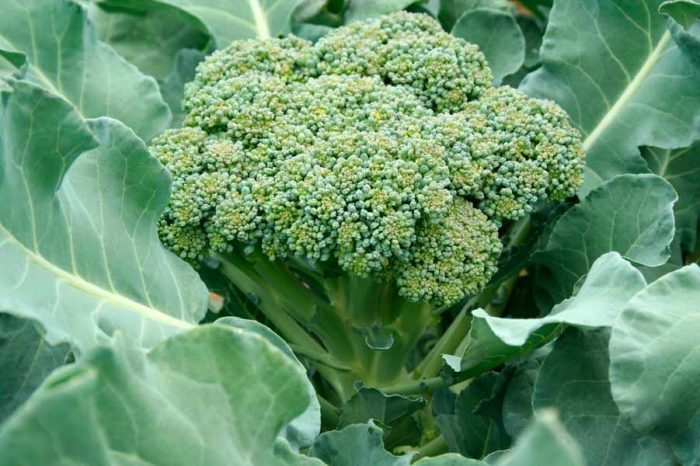
Broccoli
This is a type of cauliflower. The head includes inflorescences with a purple or green color. Such cabbage is rich in mineral salts of potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, calcium, vitamins C, A, B1, B2, PP. It has an antioxidant effect, it is recommended to use it in order to prevent cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
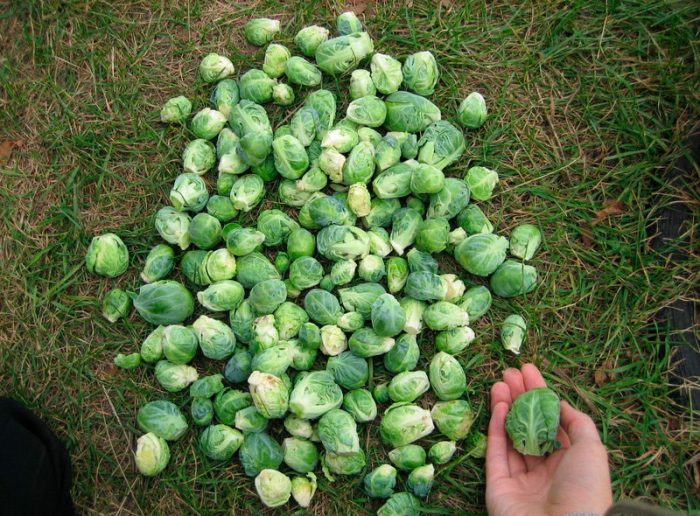
Brussels sprouts
This plant has a long stem, and there are many small heads of cabbage on it, which outwardly resemble the forks of white cabbage. This cabbage contains more vitamin C than citrus fruits, as well as a lot of protein and contains magnesium, phosphorus and folic acid. It helps to significantly improve mental performance, and also strengthens the immune system.
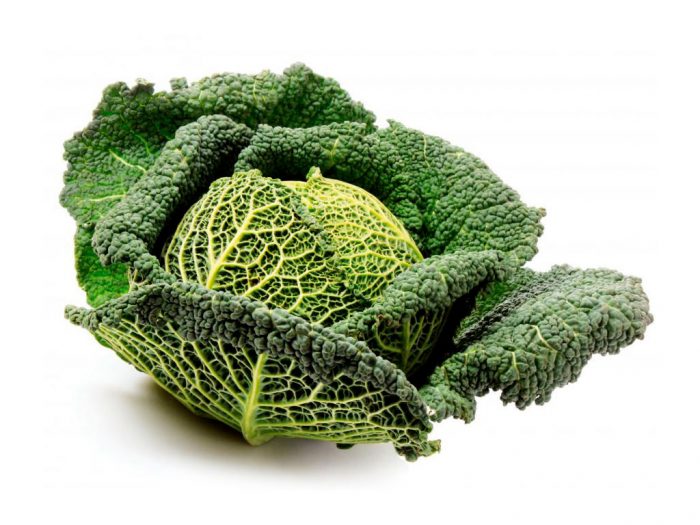
Savoy cabbage
It is similar in shape to white cabbage, but its head is loose and consists of strongly corrugated delicate leaf plates of a rich green color. Such cabbage, in comparison with white cabbage, contains more vitamins and proteins.
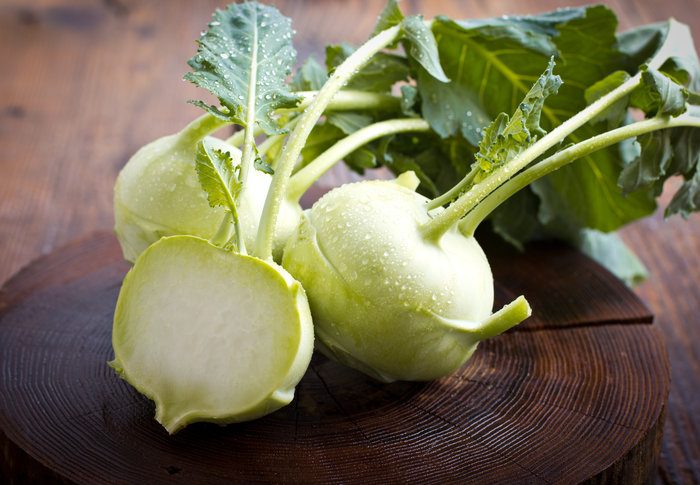
Kohlrabi
The bush is a spherical stem, on which there are long-stemmed leaf plates. This cabbage is rich in vitamin C, protein, calcium and glucose.
Chinese cabbage
Today this species is very popular in mid-latitudes. The slightly loose head has an oblong shape, the fiber is pleasant to the taste and delicate. It contains many useful substances. It is noteworthy that during storage, vitamin C does not disappear from the foliage.
Chinese cabbage
This leafy vegetable does not develop forks. Outwardly, it is similar to a salad, and in composition - to white cabbage. It contains the valuable amino acid lysine: it strengthens the immune system, and also removes toxins and toxins from the body. This type of cabbage is considered a source of longevity.