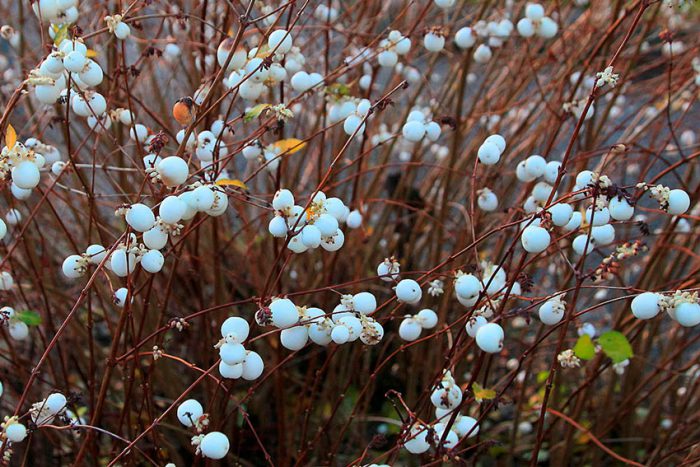
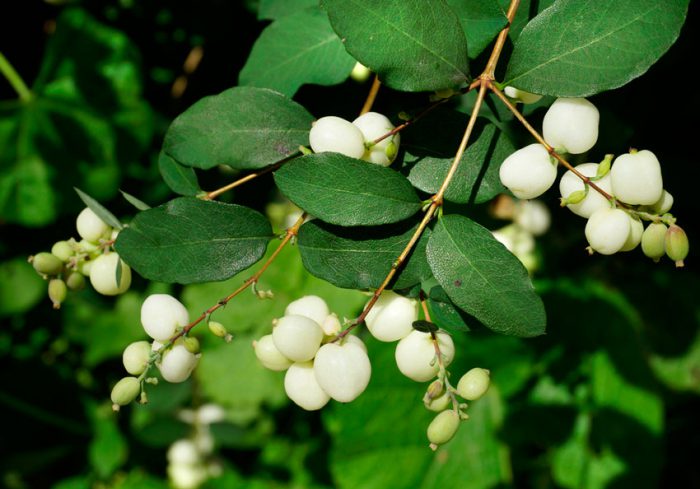
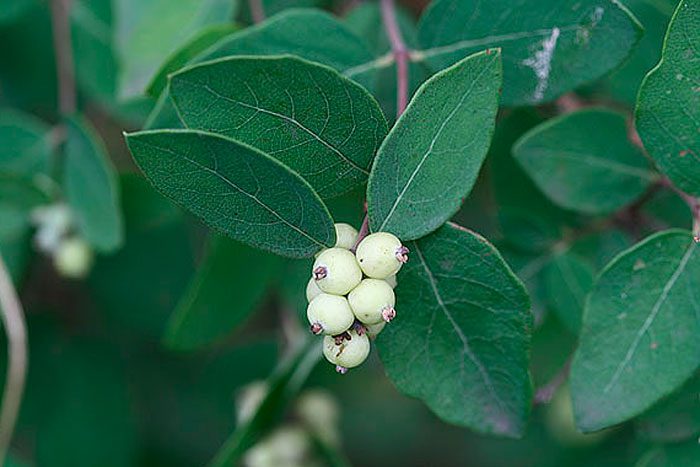
The deciduous shrub snowberry (Symphoricarpos), or wolfberry or snowberry, is a member of the honeysuckle family. This plant has been cultivated for at least 200 years, while it is used to decorate squares and parks. This genus unites about 15 species in the wild, native to North and Central America. However, 1 species occurs naturally in China - this is Symphoricarpos sinensis. The name Snowberry is made up of 2 Greek words meaning "to gather together" and "fruit". So this shrub was named because its fruits are very tightly pressed against each other. The snowberry has one distinctive feature - its fruits, they do not fall off throughout almost the entire winter period, and the seeds of these berries are eaten with pleasure by quails, hazel grouses, waxwings and pheasants.
Content
- 1 Features of the snowberry
- 2 Planting a snowberry in open ground
- 3 Caring for a snowberry in the garden
- 4 Snowberry breeding
- 5 Snowberry after flowering
- 6 Types and varieties of snowberry with photos and names
- 6.1 Snowberry white (Symphoricarpos albus)
- 6.2 Common snowberry (Symphoricarpos orbiculatus)
- 6.3 Western snowberry (Symphoricarpos occidentalis)
- 6.4 Mountain-loving snowberry (Symphoricarpos oreophilus)
- 6.5 Chenot's Snowberry (Symphoricarpos x chenaultii)
- 6.6 Chenaultii Snowberry (Symphoricarpos x chenaultii)
- 6.7 Dorenboz's Snowberry (Symphoricarpos doorenbosii)
Features of the snowberry
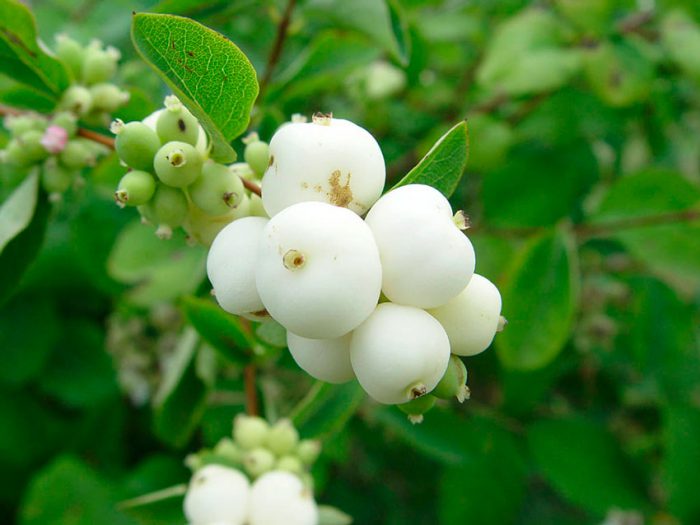
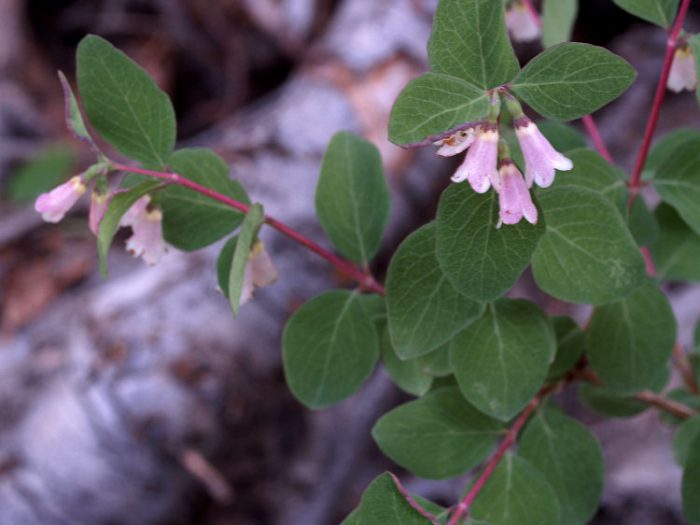
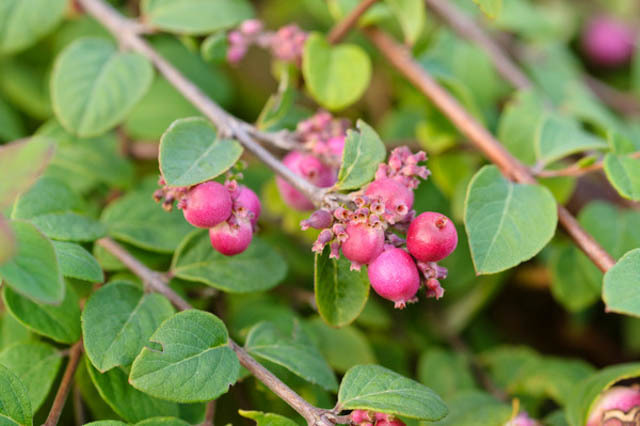
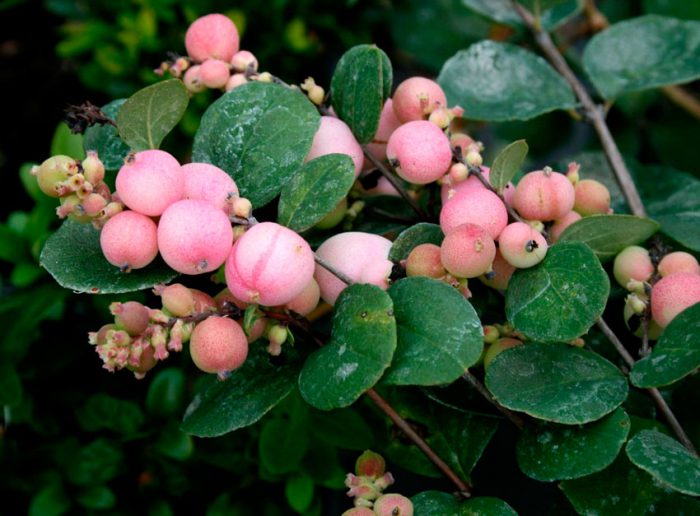
The height of the snowberry can vary from 0.2 to 3 meters. Its entire, oppositely positioned leaf plates have a rounded shape and a short petiole, they reach 10–15 mm in length, and there are 1 or 2 lobes at the base. Branches in winter do not break under the weight of snow, as they are very flexible. Terminal or axillary racemose inflorescences consist of 5-15 pieces of regular red, white-green or pink flowers. This shrub blooms in July or August. The fruit is a juicy drupe of spherical or ellipsoidal shape, which reaches 10–20 mm in diameter. The fruit can be colored purple-black, red, but often white, the inside of the stone is oval, compressed from the sides. The flesh of these berries looks like shiny grainy snow. These berries should not be eaten. This shrub is a good honey plant.
White (brushy) snowberry is very popular among gardeners, as it is highly resistant to gas and smoke. A hedge from such a shrub looks especially impressive.This plant with pink berries prefers to grow in regions with mild winters and black soil, while it develops worse in cool climates.
Planting a snowberry in open ground
What time to plant
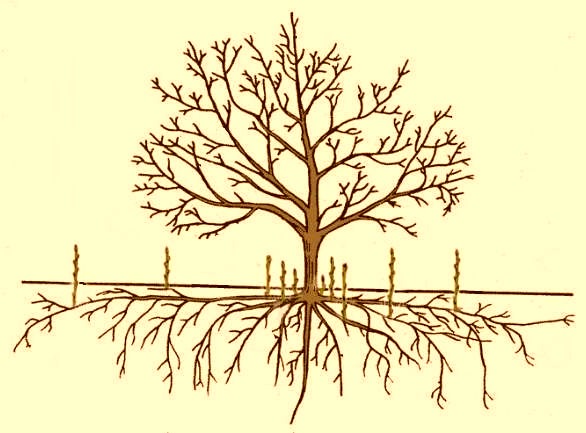
The snowberry is distinguished by its unpretentiousness. A shaded or well-lit place, with dry or moist soil, is suitable for growing it. If this shrub is planted on a crumbling slope, then it is able to stop further destruction and erosion, thanks to its dense root system. You can plant it in open soil in autumn or spring, and at the same time it must be remembered that the soil on the site should be prepared in advance.
Landing features
In the event that you want to create a hedge, then seedlings that are 2-4 years old are suitable for you. Along the line of the designated fence, you need to pull the twine and already along it it is necessary to dig a trench 0.6 m deep and 0.4 m wide. 4 or 5 seedlings should be planted per 1 running meter of the trench. You can also plant a shrub solo or create a group planting, while a distance of 1.2 to 1.5 m should be kept between the plants.With such a planting, the size of the planting pit is 0.65x0.65 m.
A planting hole or trench should be made in advance. If planting is carried out in the fall, then it will be necessary to prepare the landing site 4 weeks before the day of disembarkation. For planting in the spring, the place is prepared in the autumn. If the soil on the site is clay or loamy, then special attention should be paid to the preparation of the site for planting, the fact is that before the day of disembarkation, the earth in the pit should settle. A layer of rubble should be laid at the bottom of the pit, and a nutritious soil mixture consisting of peat, river coarse sand and compost (humus) should be laid on it, while fertilizers should be added to it, so 0.6 kg of wood ash is taken per 1 bush, 0 , 2 kg of dolomite flour and the same amount of superphosphate. It is necessary to plant a seedling so that after compaction of the soil and its subsidence after abundant watering, the root collar of the plant is at the level of the soil surface. However, before proceeding with the direct planting, the seedling itself should be prepared; for this, its root system is immersed in a clay chatterbox for 30 minutes. The planted plant must be watered daily during the first 4 or 5 days.
Caring for a snowberry in the garden
The snowberry is distinguished by its unpretentiousness and does not require special attention from the gardener. However, if you take care of him even a little, then he will have a very neat and attractive appearance. After the seedling is planted, its near-stem circle must be covered with a five-centimeter layer of mulch (peat). It is necessary to systematically loosen the soil, remove weeds in time, feed, cut, water. Also, do not forget to pay attention to protecting the snowberry from pests. The shrub should be watered only during prolonged drought. Watering is carried out in the evening, while 15–20 liters of water are poured under 1 bush. In the event that it rains regularly in summer, then this plant will not need watering. It is best to loosen the soil or weed after watering or rain. In autumn, the soil near the bush should be dug up.
In spring, the snowberry should be fed by adding 5 to 6 kilograms of humus (compost) to its near-stem circle, as well as 0.1 kilograms of potassium salt and superphosphate. If this is necessary, then the second feeding is arranged in the middle of the season; for this, a nutrient solution is used, consisting of 1 bucket of water and 50 grams of Agricola.
Transfer
If there is a need to transplant a snowberry, then you should hurry up. After the bush has a powerful root system, it will be very difficult to carry out this procedure.Such a shrub quickly and easily adapts to a new place. The transplant is carried out in the same way as the initial landing and at the same time. In order for this procedure to end successfully, it is necessary to dig up the shrub so that its roots are injured to a minimum. The radius of the root system in an adult snowberry is on average 0.7 to 1 meter. Therefore, you should dig in the bush, stepping back at least 0.7 m from it.
Pruning
Pruning does not harm the snowberry. It is best to carry out this procedure at the very beginning of the spring period, while sap flow has not yet begun. All injured, dried out, damaged by frost, disease or pest, thickening and too old branches should be removed. Those branches that remain should be cut by ½ or ¼ part. You should not be afraid to prune, since the laying of flower buds occurs on the shoots of this year. It should also be noted that after a shearing, the snowberry recovers very quickly. If the cuts on the branches exceed 0.7 cm in size, then do not forget to process them with garden pitch. A shrub that is more than 8 years old needs rejuvenating pruning, as its foliage and flowers become smaller, and the stems grow short and weak. Such pruning is carried out "on a stump" at a height of 0.5 to 0.6 m. During the summer period, new powerful stems will grow from dormant buds on the remains of the stems.
Diseases and pests
Such a plant is highly resistant to diseases and pests. And this is most likely due to the fact that this plant is poisonous. Very rarely, powdery mildew can disturb this shrub, and sometimes rot appears on the berries. For preventive purposes, in early spring, before the buds swell, it is necessary to process the bushes with a solution of Bordeaux liquid (3%). In order to cure an infected plant, it should be treated with a fungicide, for example: Fundazol, Skor, Topsin, Titovit Jet, Topaz, Quadris, etc.
Snowberry breeding
Such a shrub can be propagated in a generative (seed) way and vegetatively: by layering, cuttings, dividing the bush and root shoots.
How to grow from seeds
Growing a snowberry from seeds is a rather laborious and lengthy process. But if you want, you can try. First you need to separate the seeds from the pulp of the berries, then they are folded into a nylon stocking and squeezed well. After that, the seeds must be poured into a not very large container filled with water. The mixture is thoroughly mixed. Then you need to wait until the seeds settle to the bottom, while the pieces of pulp should float. Remove the seeds and wait for them to dry well.
Seeds are sown before winter. This should not be done in open soil, since small seeds in spring can come off with the snow cover. For sowing, boxes should be used, which must be filled with a nutrient substrate, consisting of peat, river sand and humus, which must be taken in a 1: 1: 1 ratio. Seeds must be spread over the surface of the substrate, and then sprinkled with a thin layer of sand. The container must be covered with glass. In order not to wash the seeds, watering should be done through a sump or using a fine spray gun. The seedlings can be seen in the spring. It will be possible to pick the seedlings directly into open soil at the end of the season.
How to propagate by root shoots
Many root suckers grow near the shrub, they create large and fairly dense clumps. Therefore, this plant is able to actively grow and move from the planting site. Dig out the curtain you like and plant in a permanent place. By the way, this will help prevent thickening of the bush.
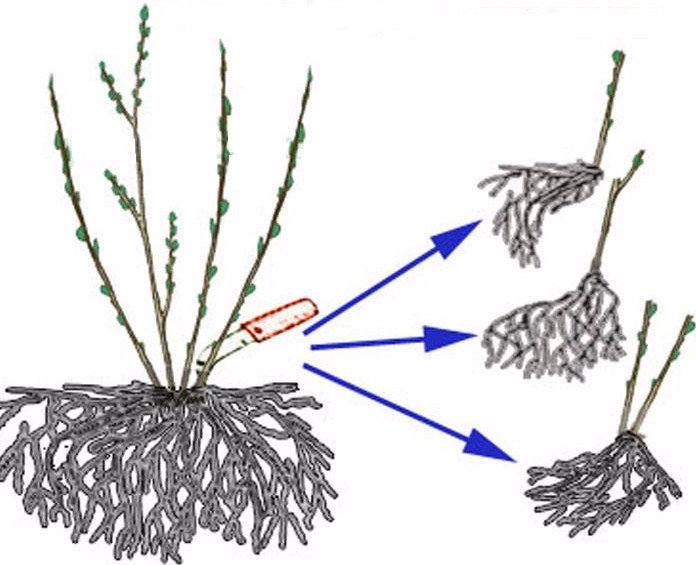
Reproduction by dividing the bush
The division of the bush can be done in early spring, before sap flow begins, or in autumn, when leaf fall ends.To do this, an overgrown shrub is chosen, dug up and divided into several parts. Then the delenki are planted in new permanent places, following the same rules that are used for the initial planting. You should pay attention to the fact that each delenka must have strong developed roots and young healthy branches. At the cuttings, it is also necessary to process the cut points on the root system with chopped charcoal.
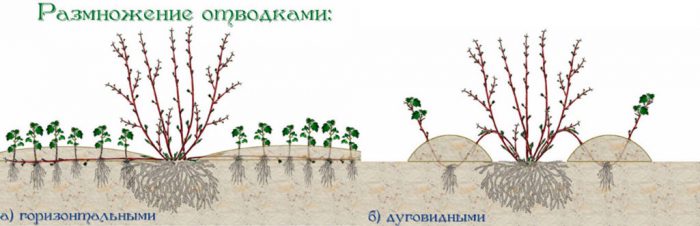
How to propagate by layering
At the very beginning of spring, you need to choose a young branch that grows near the surface of the soil. It is laid in a groove dug in the ground and fixed in this position, and then covered with a layer of earth, while the top of the layer should not be covered. During the season, the layering must be looked after, as well as the shrub itself, namely: water, feed and loosen the soil surface. By the fall, the cuttings will have to give roots, it is cut off from the parent bush with pruning shears and planted in a permanent place.
Cuttings
For reproduction of such a plant, it is recommended to use lignified or green cuttings. Harvesting of lignified cuttings is carried out at the end of the autumn or at the beginning of the spring. Their length can vary from 10 to 20 centimeters, with 3-5 buds on each cut. They are stored in the sand in the basement until spring. The upper cut is made over the kidney, and the lower cut obliquely.
The harvesting of green cuttings is carried out early in the morning at the beginning of the summer period, and this should be done almost immediately, as the shrub fades. Large, mature and well-developed shoots are suitable for cutting. To understand whether a certain shoot can be used as a cutting, a simple test is carried out, for this it is simply bent. In the event that the shoot breaks and a crunch is heard at the same time, this indicates its maturity. Prepared cuttings should be placed in water as soon as possible.
For rooting, both lignified and green cuttings are planted in containers filled with soil mixture (the composition is the same as when sowing seeds). They can be deepened by no more than 0.5 cm. Then the container is removed to a greenhouse or a greenhouse, since high air humidity and moderate soil moisture are required for the rooting of cuttings. By the onset of autumn, the cuttings should have developed a good root system, they can be planted in a permanent place, not forgetting to cover them for the winter with spruce branches or dry foliage.
Snowberry after flowering
When grown in mid-latitudes, the snowberry does not need shelter. Even its hybrid varieties, which are highly decorative, can withstand frost down to minus 34 degrees. However, if the winter is very frosty, then the plant may suffer, but during the growing season it must recover. If the bush is young, then for wintering it should be highlighted with soil.
Types and varieties of snowberry with photos and names
Snowberry white (Symphoricarpos albus)
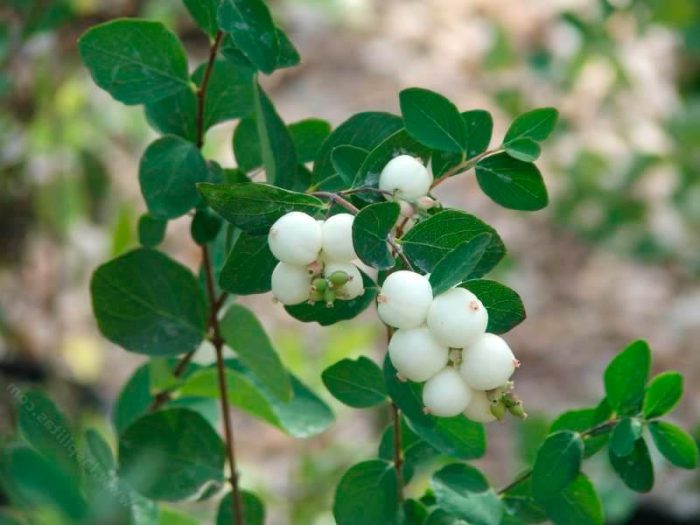
This type is considered the most popular, and it has several names, namely: the snowberry is white, or brush, or carp. It occurs naturally in North America from Pennsylvania to the west coast, with a preference for growing on riverbanks, open slopes, and mountain forests. The bush can be about 150 centimeters high. This deciduous shrub has a rounded crown and slender stems. The leaf plate has a round or ovoid shape, it is simple, whole-edged or notched-lobed. The length of the leaves is about 6 centimeters, their front surface is green, and the back is gray. Lush, brush-shaped inflorescences are placed along the length of the entire stem, they consist of small light pink flowers. The shrub blooms magnificently and for a very long time. Therefore, at the same time, you can admire beautiful flowers and spectacular white fruits, which are a juicy ball-shaped berry with a centimeter diameter. The fruits do not fall from the bush for a very long time.
This plant is very unpretentious and has a high frost resistance. It has been cultivated since 1879. Often hedges and curbs are created from such a snowberry, and it is also used for group plantings. The berries of this plant cannot be eaten, they contain substances that, getting inside the human body, cause weakness, dizziness and vomiting. This species has a variety that is quite popular among gardeners - a white, slightly shiny snowberry (Symphoricarpos albus var.laevigatus).
Common snowberry (Symphoricarpos orbiculatus)
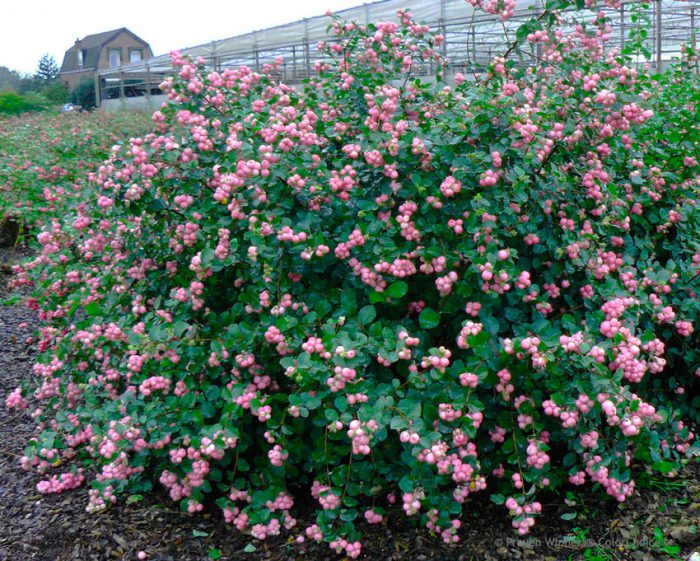
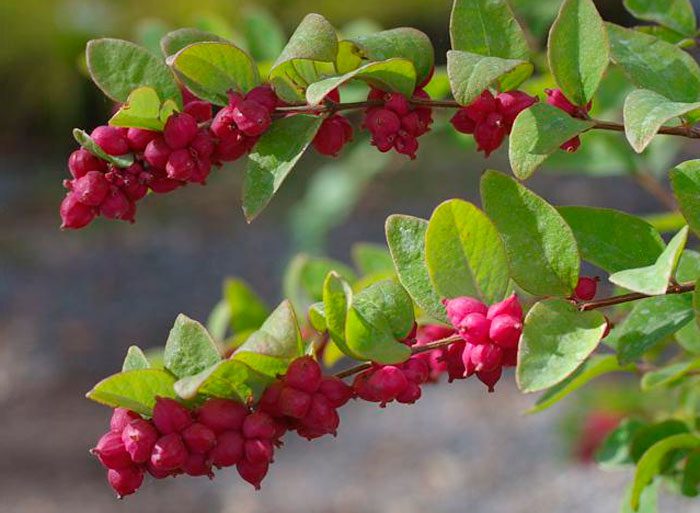
This species is also called pink, or round, or coral. And where this species comes from, it is called "Indian currant". In nature, this shrub grows in North America on river banks and in meadows. Such a snowberry has a large bush with thin stems and small dark green leaves, which have a bluish seamy surface. Short lush inflorescences consist of pink flowers. Quite spectacularly, such a shrub will overcame in the autumn, it is at this time that red-purple or coral berries of a hemispherical shape begin to ripen on the stems, which are covered with a bluish bloom, while the leaf plates turn purple.
The common snowberry does not have high frost resistance compared to the previous species. But at the same time, it overwinters quite normally when grown in the middle lane. This plant has gained high popularity in Western Europe, the Taffs Silver Age variety, which has a white edging on the leaf plates, is in special demand here, as well as Variegatus - an uneven pale yellow strip runs along the edge of the leaves.
Western snowberry (Symphoricarpos occidentalis)
This species is from the western, eastern and central regions of North America. It creates thickets along streams, rivers and rocky slopes. The bush is about 150 centimeters high. The front surface of the leaf plates is pale green, while on the seamy there is felt pubescence. The short and dense, brush-shaped inflorescences consist of light pink or white bell-shaped flowers. The shrub blooms from the first days of July to the last - August. Then soft fruits appear almost spherical in shape, which are painted in white or light pink.
Mountain-loving snowberry (Symphoricarpos oreophilus)
Originally from the western regions of North America. The bush can reach a height of 150 centimeters. The shape of the slightly pubescent leaf plates is round or oval. Single or paired bell-shaped flowers are painted white or pink. Inside the globular white berries there are 2 seeds. Possesses average frost resistance.
Chenot's Snowberry (Symphoricarpos x chenaultii)
This hybrid was created by crossing a small-leaved snowberry and an ordinary snowberry. A not very tall bush has dense pubescence. The length of the sharp leaf plates is about 25 mm. Fruits are pink with white cheeks. Has a relatively low frost resistance.
Chenaultii Snowberry (Symphoricarpos x chenaultii)
This hybrid plant has a height of one and a half meters, its crown diameter is also 1.5 m. The front surface of the leaf plates of a bright dark green color, while the wrong side is gray. Foliage grows very early, while it stays on the branches for a long time. The inflorescences consist of pink flowers. The berries are round in shape, they can have a color from purple to white, stay on the bush for a relatively long time. The most successful variety is the Hancock snowberry.
Dorenboz's Snowberry (Symphoricarpos doorenbosii)
This is a group of hybrid varieties that Dutch breeder Doorenbos has created. He got them by crossing a rounded snowberry with a white snowberry. Varieties differ among themselves by the abundance of fruiting and compactness:
- Mather of Pearl... Elliptical leaf plates are dark green in color. The berries are white with a slight blush.
- Magic Berry... The shrub bears fruit very abundantly. Its branches are covered with deep pink berries.
- White Hage... On an upright, dense bush, there are small white fruits.
- Amethyst... It has a very high frost resistance. The height of the shrub is about 1.5 m. The color of the leaf plates is dark green, and the nondescript flowers are light pink. The pink-white berries are rounded.
In addition to the species described here, the following are cultivated: round-leaved, small-leaved, Chinese, soft and Mexican snowberries.


Watch this video on YouTube