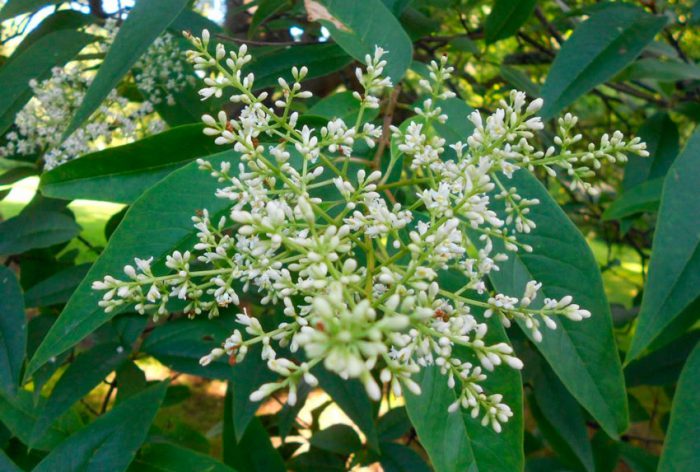
The genus privet (Ligustrum) is represented by deciduous, evergreen and semi-evergreen shrubs, as well as small trees, and it is directly related to the olive family. This genus unites more than 50 species of various plants. In natural conditions, they can be found in Asia, North Africa, Europe, and also in Australia. A large number of different types of privet can be found in nature in Japan, Taiwan, China and the Himalayas. The name privet comes from the Latin word "ligare", which translates as "to bind". The fact is that the bark of a plant has astringent properties. The privet shrub is very similar to lilac, as it is its close relative. The foliage and bark of these two plants are very similar, but the lilac is somewhat larger than privet and its flowering is more splendid and showy. If you do not take care of this shrub, then it will acquire an extremely unattractive and sloppy look. However, if you cut it, then it will instantly transform, in addition, it can be given various attractive shapes.
Content
- 1 Features:
- 2 Planting privet
- 3 Privet care
- 4 Reproduction of privet
- 5 The main types and varieties with photos and names
- 5.1 Common privet (Ligustrum vulgare)
- 5.2 Shiny privet (Ligustrum lucidum)
- 5.3 Japanese privet (Ligustrum japonicum)
- 5.4 Oval-leaved privet (Ligustrum ovalifolium)
- 5.5 Privet Ibota (Ligustrum ibota)
- 5.6 Jester privet (Ligustrum yezoense)
- 5.7 Spicy Privet (Ligustrum acutissumum)
- 5.8 Dense privet (Ligustrum compactum)
- 5.9 Privet Kvihoui (Ligustrum quihoui)
Features:
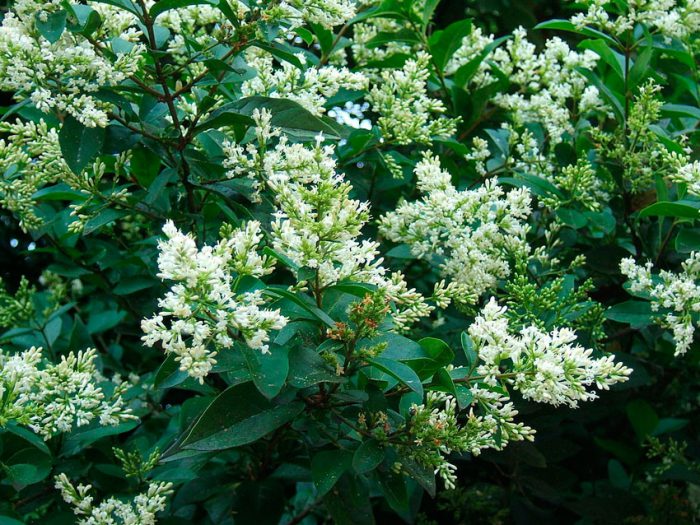
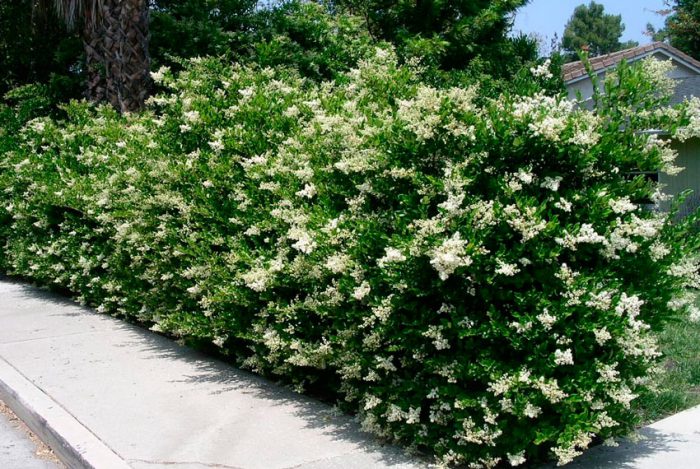
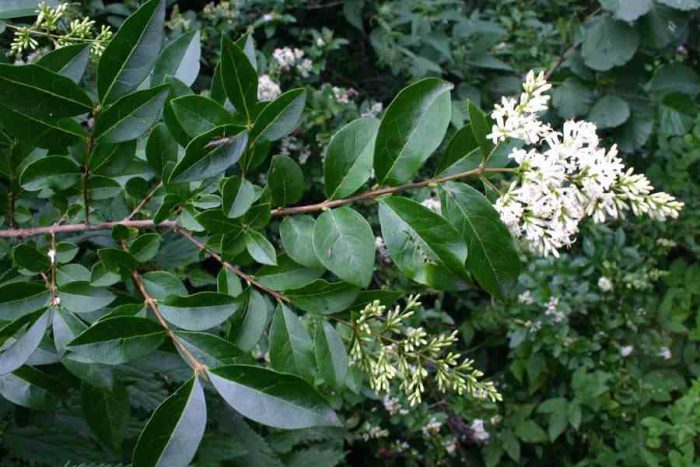
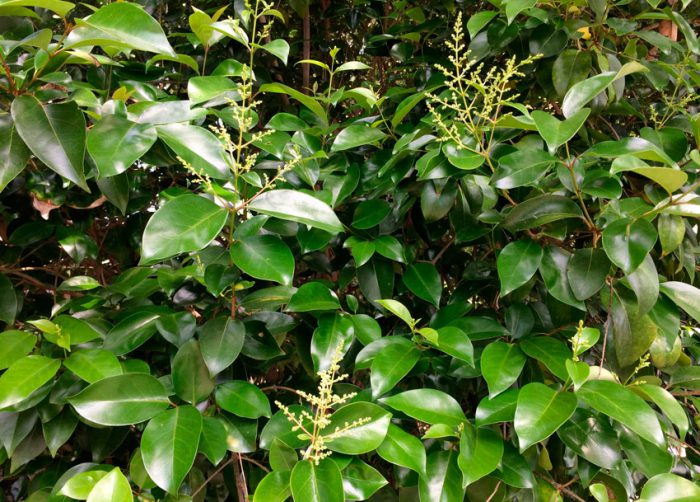
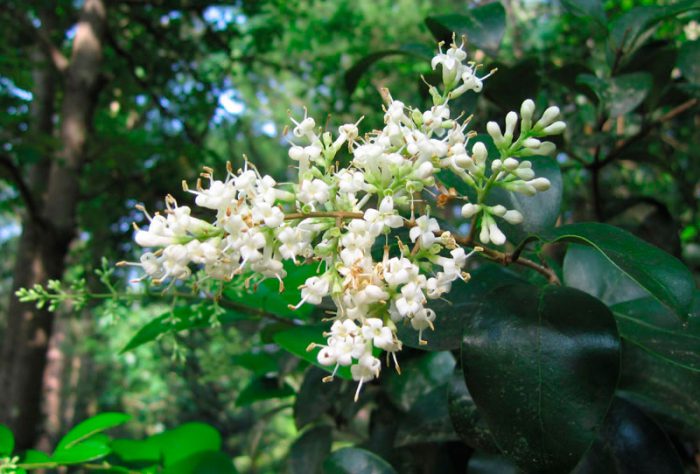
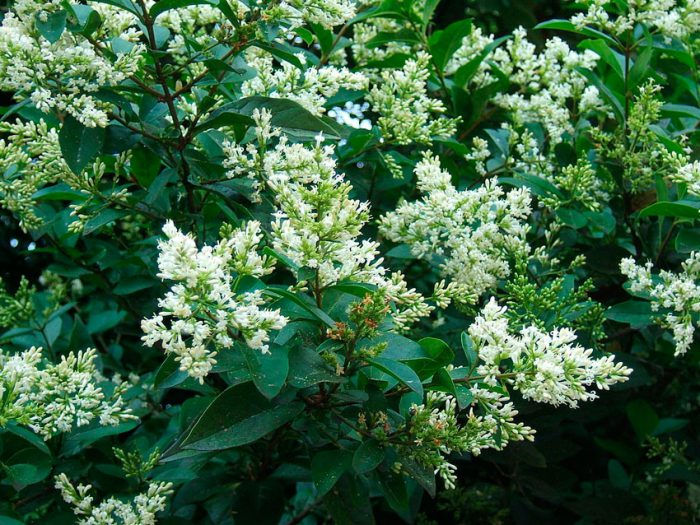
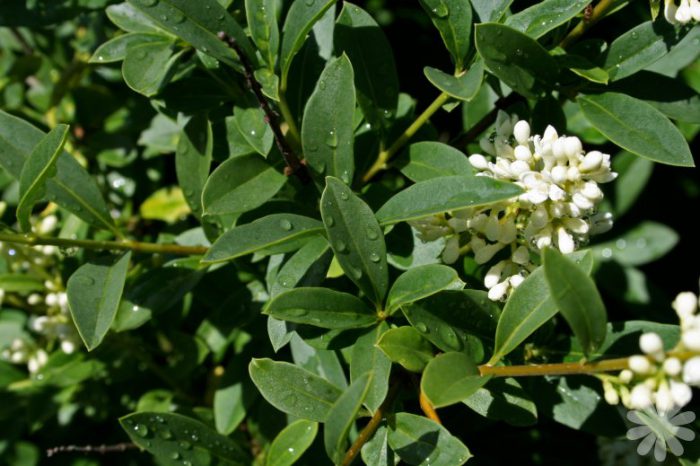
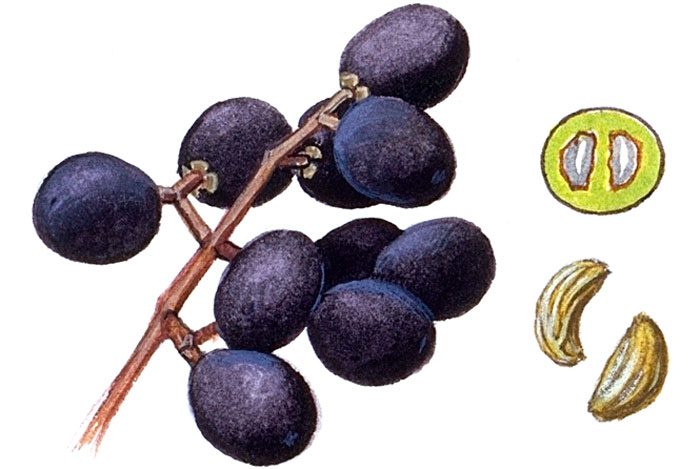
The height of the shrub reaches 200 centimeters, and its width is about 100 centimeters. Also privet is found in the form of small trees, which have a spreading crown and a height of about 6 meters. Leathery, whole-edged leaf plates have an elongated ovoid shape, they are oppositely located. Their front side is painted in dark green, and the back side is painted in pale green. White fragrant little flowers are practically sessile. They are collected in apical loose inflorescences with a paniculate shape. Their length varies from 6 to 18 centimeters. Flowering lasts 3 months, and it starts in June or July. The fruits are berry-like small rounded drupes, which are colored black or dark blue. Each fruit contains 1 to 4 seeds. Privet is a fast-growing plant. In the middle lane, common privet is most often cultivated, because this species is the most winter-hardy.Below will be described how to plant, care for and propagate this particular type of privet. Most often, such a shrub is used to form a hedge, but it is also grown as a single plant and in small groups. Privet bonsai are becoming more and more popular.
Planting privet
What time to plant
Since this shrub in natural conditions prefers to grow in the underbrush, it can be grown in the garden in a shaded place. And also such a plant is drought and gas resistant, and it also does not require any special soil. However, it is not recommended to grow privet on dry, acidic sandy soils. But if you want your shrub to be as decorative as possible, then it will need to provide the most favorable conditions. So, it is recommended to plant it in a well-lit place, while it is necessary to retreat from buildings or trees not less than 0.7-1 meter. The soil should be well-drained, moderately moist, rich in nutrients. It should also be slightly alkaline or neutral. The soil should be composed of humus, turf and sand (2: 3: 1). A transplant of such a plant can be carried out during the entire growing season. However, it tolerates this procedure best of all in the spring, and it must be in time before the buds open. But some gardeners believe that this procedure is best done in September or October.
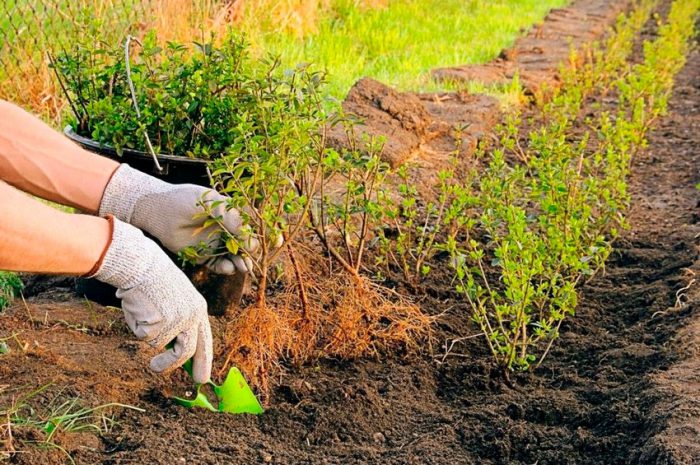
How to plant privet
Before planting privet, you need to dig up the site. Then you need to make a landing hole, the width of which will be 65 centimeters. The depth of such a hole should be 30 centimeters higher than the size of the root system of the shrub. Then you need to pour water into the hole and wait until it is completely absorbed into the soil. At the bottom of the hole, rubble should be poured, while the layer thickness should be 10–20 centimeters. In a not very large amount of soil mixture (the composition is described above), you need to pour 130 grams of nitroammophoska. Then it is poured into the planting hole with a mound, on which the seedling is placed. Its roots are straightened, and the hole is filled with earth mixture (without fertilization). For 4 weeks, care must be taken to ensure that the trunk circle does not dry out. Then its surface will need to be sprinkled with a layer of mulch (peat), the thickness of which should be 5-8 centimeters.
If this shrub is planted to create a hedge, then a trench is made for this, the depth of which should be 60 centimeters, and the width - 50 centimeters. When planting between plants, you must maintain a distance of 30-40 centimeters. You need to plant in the same way as for a single planting. The trench must be filled with earth mixture, which must be compacted. Then the plants must be well watered at the root.
Privet care
It is very simple to care for privet. It needs to be watered, cut off, loosened on time, while removing weeds. In order to reduce the number of watering and weeding, you can sprinkle the circle with a layer of mulch. However, it is necessary to mulch the soil only after it has warmed up properly. Watering should be done only during a long dry period. In a moderate summer period, the plants will have enough rainfall. It should be borne in mind that watering should be rare, but abundant enough, since the soil needs to be soaked about half a meter deep. So, one bush should take 3-4 buckets of water. During the growing season, watering on average will need to be done 3 or 4 times.
In spring, it is recommended to feed the plants with organic fertilizers; for this, under each bush you need to add 1 bucket of compost or humus. If this is a hedge, then organic fertilizer is distributed along the bushes, then granular superphosphate is scattered over it (1 m2 10 grams of substance). After this, fertilizer must be embedded in the soil at a shallow depth, and then watered.
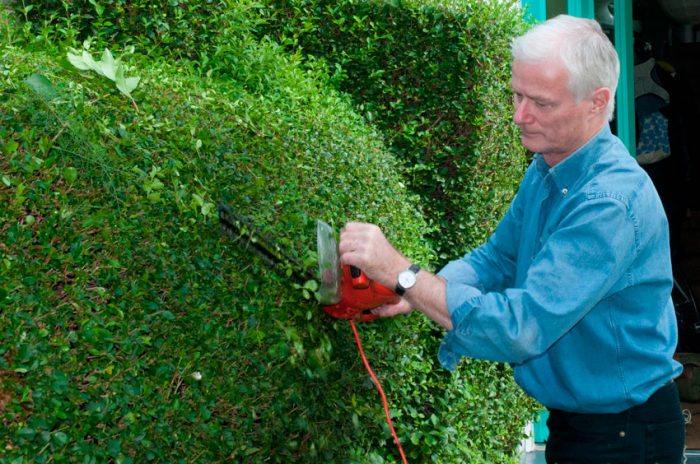
Pruning privet
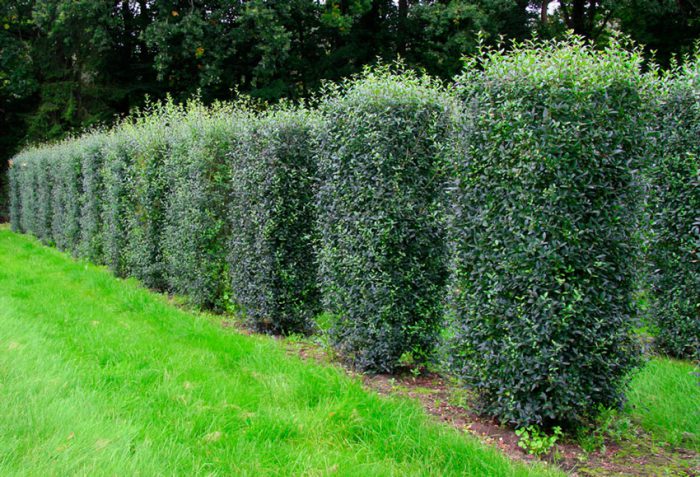
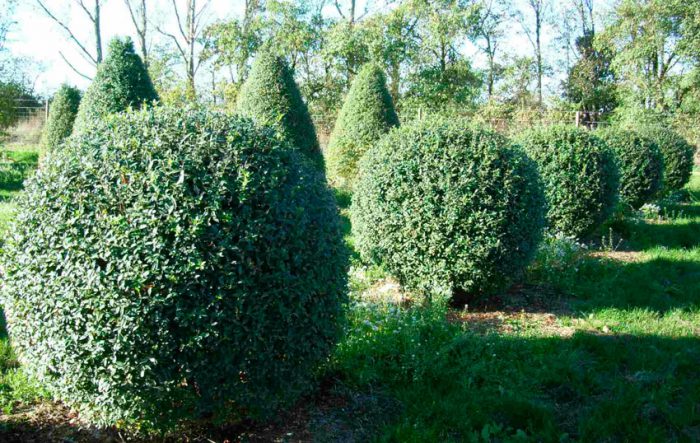
Privet is a plant that needs regular formative pruning. Since such a shrub is fast-growing, it will quickly hide all the flaws that were made during pruning. You need to start pruning almost immediately, as the plant is planted in the ground. When the established seedling begins to grow, it will need to slightly shorten the tops of the shoots. As a result, the plant will become more bushy. After the stems have grown by 10-15 centimeters, they will again need to be slightly shortened. This procedure should be carried out regularly during the first two years of the privet's life, as a result the bush will become thick and lush. After the specimen has built up a green mass, formative pruning can be done. Currently, an increasing number of gardeners prefer to cut this shrub in the form of dense cushions (karikomi). This haircut comes from Japan.
In European countries, where the climate is rather mild, privet in a hedge can reach a height of 200 centimeters. However, in mid-latitudes, such high bushes can be damaged by frost, therefore, in such areas, the optimum height of privet is about half a meter. In order to avoid frost damage to the shoots in winter, the bushes are covered with a layer of snow. The hedge is trimmed in May and then in August. Sanitary pruning should be carried out in early spring, while injured, frostbitten, dried and diseased branches should be removed. And those branches that remain must be shortened by 1/3 (if necessary).


Watch this video on YouTube
Autumn care
In middle latitudes, common privet is most often grown, since this species is resistant to frost. At the same time, the plant can withstand frost up to minus 30 degrees, but only if it is short-lived. In the event that the shrub is covered with a layer of snow, then it will be able to withstand a drop in temperature to minus 40 degrees. The tips of the stems, which have suffered during the winter cold, recover quickly enough in the spring. This type of privet should not be covered for the winter. In other species, for the winter, the trunk circle must be sprinkled with a layer of mulch, the bush itself must be bent to the surface of the soil and fixed in this position. From above, the plant must be covered with spruce branches.
Disease and pests
Privet is highly resistant to various types of diseases. However, if it grows in soil with high acidity, then it may develop powdery mildew or spotting. In this regard, it is necessary to monitor the acidity of the soil. It is very important to timely add a deoxidizer (dolomite flour, crushed limestone or fluff lime) to it.
Spider mites, thrips, worms, aphids and scale insects can settle on this shrub. They can be destroyed with Actellik or Fitoverm, and it may take from 1 to 4 treatments with a break of half a month. But if you provide the plant with proper care and optimal growth conditions, then the pests are unlikely to settle on the shrub.
Reproduction of privet
Privet can be propagated using seeds, cuttings, cuttings, shoots, or root suckers.
Growing privet from seeds
Growing privet from seeds is a very long and laborious process. Moreover, seed germination is low (about 65 percent). Privet begins to bear fruit only after she turns 6 years old. Thus, this plant is grown only in industrial conditions, in this regard, it is better not to collect seeds in the autumn, because there are ways that make it possible to propagate privet much easier and faster.
If you nevertheless decide to grow this shrub from seeds, then they must be selected from ripe fruits, and the largest ones should be left. Then they are placed in a container filled with water. After some time, some of the seeds will remain on the surface of the liquid, they can be collected and thrown away. Another part of the seeds will drown, it is they who need to be subjected to further stratification.To do this, they are sown in October in open soil, in winter they will undergo natural stratification. The first seedlings can be seen after 1 year. However, if you decide to sow in the spring, then the seeds should be poured into a box filled with sand and peat and kept in a place where the temperature is almost 0 degrees until spring.
Propagation of privet by cuttings
It is better to choose summer cuttings, since the percentage of their rooting is 90-100%. Cutting should be done when flowering is almost over, while choosing the most mature and developed shoots. Cuttings should be 10–12 centimeters long. Cuttings are planted in sod soil, the surface of which must be covered with a layer of washed coarse sand. They are planted at an angle of 45 degrees, while deepening 5 centimeters into the substrate. Cuttings root most quickly at temperatures from 20 to 25 degrees, while constant humidity is needed. To provide the cuttings with optimal conditions, each of them should be put on a 1.5-liter plastic bottle, in which you need to cut off the neck, and make several holes in the bottom. The first roots will grow in half a month, and after 3 months the plants will already have a well-developed root system. After complete rooting, the cuttings will need to be grown for about a year, while, if necessary, they are transplanted into larger containers. Planting in open soil can be done only after the height of the cuttings is 50-60 centimeters.
Reproduction of privet by layering
In springtime, you will need to choose a sturdy branch that grows close to the ground. It should be tilted to the surface of the soil and fixed in this position, having previously made a not very large shallow incision on the lower surface of the part of the branch that will be immersed in the soil. Then part of the branch, bent to the ground, must be covered with soil, on top of which sphagnum is laid. It is important to keep the moss moist at all times. At the same time, remember that you do not need to drop in the top of the branch. If the cuttings are successfully rooted, they will start growing. It will be necessary to separate the layers and plant in a permanent place only after the next spring comes.
Also, layering can be obtained without digging. To do this, take a sewing needle and use it to make a few scratches on the surface of the branch. Then you need to pour moistened soil into a bag of polyethylene. After that, it must be fixed on the branch so that part of the branch with scratches is in the soil. Then seal the bag hermetically using tape. This method allows you to get several layers from one bush at once. After the bag is filled with roots, the layers must be carefully sawed off. Then carefully remove the bag and plant the cuttings in open soil.
The main types and varieties with photos and names
Below are the types and varieties that are most popular with gardeners.
Common privet (Ligustrum vulgare)
Under natural conditions, this species can be found in the southwestern and southern regions of Ukraine, in the Caucasus, in the northern part of Moldova and Africa, in Central and Southern Europe and in Asia Minor. At the same time, such shrubs prefer to grow in oak undergrowth. This deciduous, branchy shrub grows well in the shade and can reach a height of about 5 meters. Leathery plates are oblong-ovate or lanceolate, their seamy side is light green, and the front side is dark green. White fragrant little flowers are part of standing panicles, which can be up to 6 centimeters long. Flowering can start from June to mid-July and last 20 days. Black fruits do not fall until January. This species is the most winter-hardy, therefore it is widely cultivated in the middle lane.In addition to the original species, 10 more of its decorative forms are cultivated: pyramidal, weeping, evergreen, gray-gray, gray-white-bordered, golden, yellowish, golden-motley, silver-motley, sterile and yellow-fruited.
The most popular varieties are:
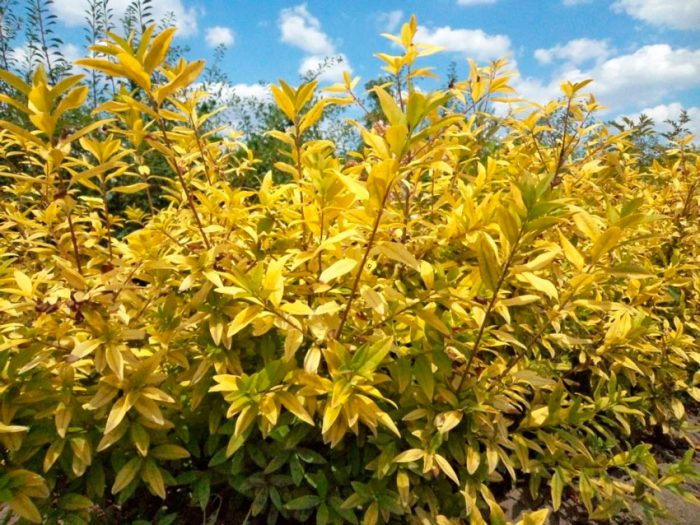
- Aureum... In height, such a semi-evergreen plant reaches about 100 centimeters. This slow-growing, non-flowering plant has golden leaves. If the winter is not frosty, then some of the leaves remain on the bush until spring.
- Vicar... This semi-evergreen plant can reach a height of 100 centimeters. Has a dense crown, consisting of broad-oval leaves of a yellow-golden color, and in the fall they are painted in a bronze-purple hue. Their length does not exceed 6 centimeters. Flowering occurs in mid-summer. Small white fragrant flowers. For wintering, the shrub must be covered.
- Aureo-variegatum... The height of this non-flowering plant is about 1 meter. Has variegated plates of golden color. The crown diameter is about 1.2 meters.
Shiny privet (Ligustrum lucidum)
In natural conditions, it is found in China, Japan and Korea. It is a large evergreen shrub or a compact tree. Dark green leaf plates have an elongated ovoid shape, their front side is glossy, and the length reaches 15 centimeters. The fragrant paniculate inflorescences are about 18 centimeters long and consist of small white flowers. Flowering lasts 3 months. This species can withstand temperatures down to minus 15 degrees, therefore, in order to survive the winter, it needs shelter. Decorative forms: golden-bordered, golden-motley, tricolor.
Japanese privet (Ligustrum japonicum)
In natural conditions, you can meet in Japan and South Korea. This type has many similarities with shiny privet, which is why they are often confused. Such an evergreen plant does not exceed 400 centimeters in height, has a compact crown and small leathery dark green leaf plates. The inflorescences of this species have a shorter length compared to the shiny privet, the flowering period is shorter, and this plant does not grow so quickly. However, this species is more resistant to frost and shade-loving. There are 2 decorative varieties: variegated and round-leaved.
Oval-leaved privet (Ligustrum ovalifolium)
The height of the bush is no more than 100 centimeters, and all because during cultivation in the middle lane it freezes over all the time in winter. In spring, the shrub is restored. Flowering is irregular. The scent of narrow flowers is not very pleasant.
Decorative forms:
- Variegatum (variegated). Such an evergreen shrub in areas with mild winters can reach a height of several meters. Green leaf blades have a cream-white border.
- Argentum (Silver). On medium-sized bushes, leaves flaunt with cream edging.
- Aureum (Golden). The leaf plates have a yellow-golden border. In the southern regions, it is grown without shelter, often used as a container culture.
Privet Ibota (Ligustrum ibota)
In natural conditions, it is found in Korea, China and Japan. This deciduous shrub can reach a height of 200 centimeters. The crown is spreading. Glossy leaf plates of an elongated ovoid shape are painted dark green on the front side, and bluish on the seamy side. Irregular flowering is observed in the summer. The length of fragrant white inflorescences is about 7 centimeters. This species loves warmth and reacts negatively to sudden changes in temperature. It must be covered for the winter.
Jester privet (Ligustrum yezoense)
It is a winter-hardy species, like common privet. His homeland is Sakhalin. The shade-loving shrub reaches a height of 150 centimeters. Has small wide sheet plates.
Spicy Privet (Ligustrum acutissumum)
Originally from the mountain slopes of southern China. The height of the bush is about 300 centimeters. Abundant flowering, lasts half a month, and begins in the first days of July. The fruits ripen fully in October. It is not winter hardy.
Dense privet (Ligustrum compactum)
Such a semi-evergreen shrub does not bloom. In natural conditions, it reaches 400 centimeters in height, and 200 centimeters in culture. The crown has a diameter of about 1.8 meters. Large leaf plates remain on the branches until the next growing season. Winter hardiness is low.
Privet Kvihoui (Ligustrum quihoui)
It occurs naturally in the provinces of China: Sichu-an, Shanxi, Yunnan. The height of such a semi-evergreen shrub is about 200 centimeters. The leaf plates are small and hard. The length of flower panicles consisting of small flowers is about 20 centimeters. Flowering begins in late summer. The species is characterized by pubescence of the seamy surface of leaf plates and young shoots. Varieties:
- Variegatum... The leaves have a white border.
- Vicar... Light yellow leaf plates turn bronze after frost.