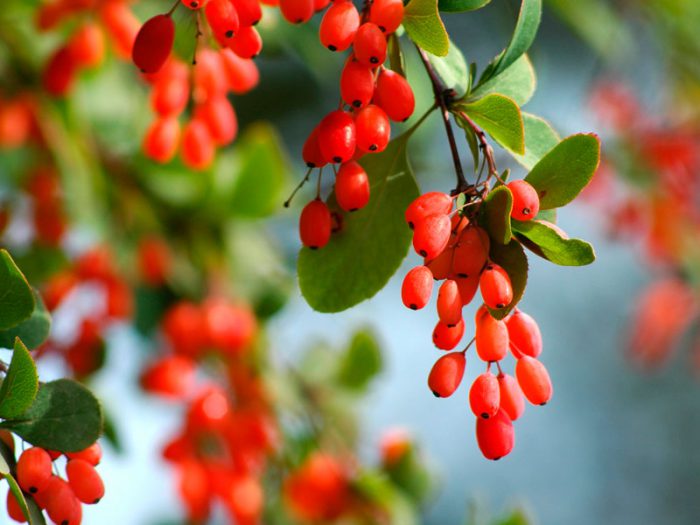
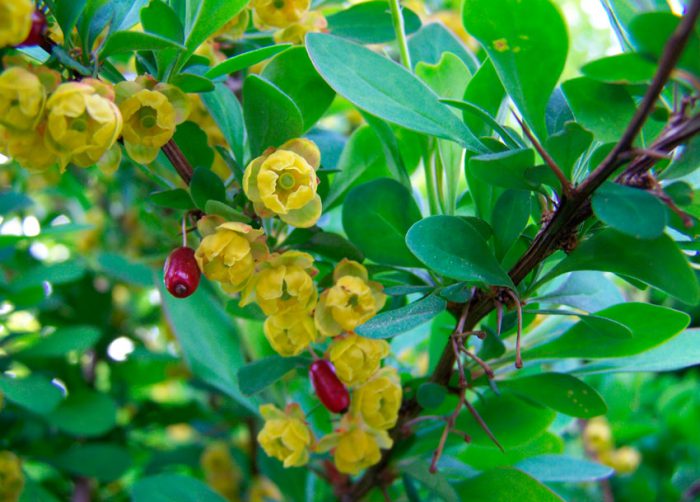
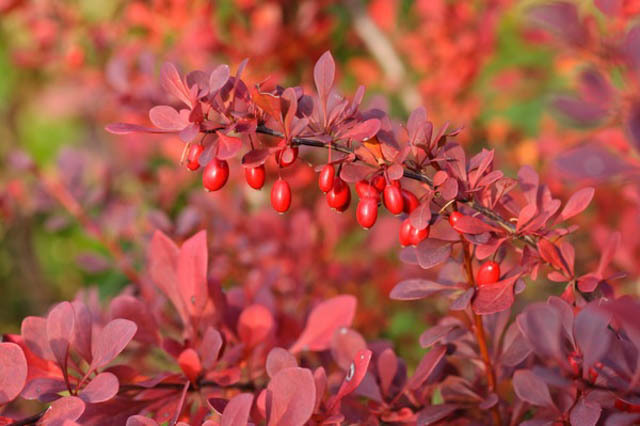
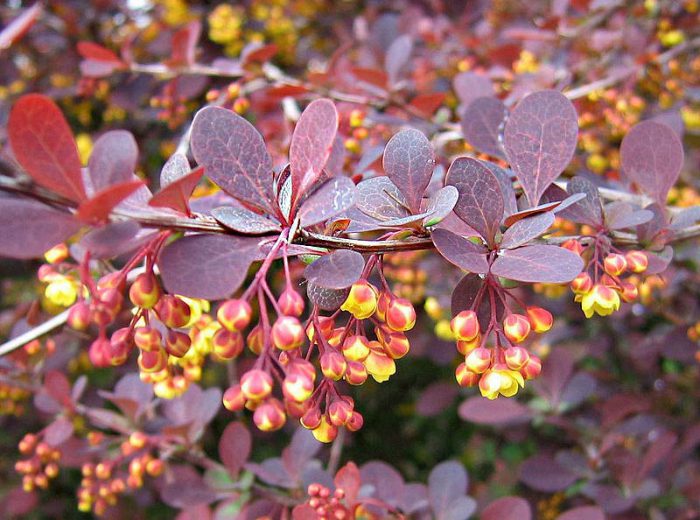
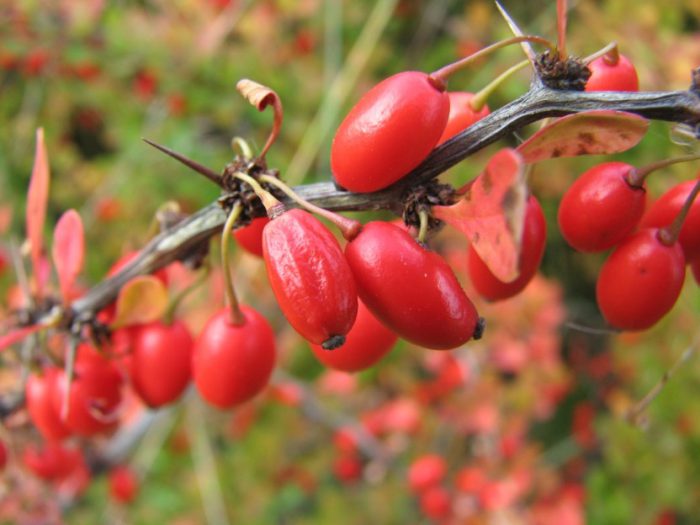
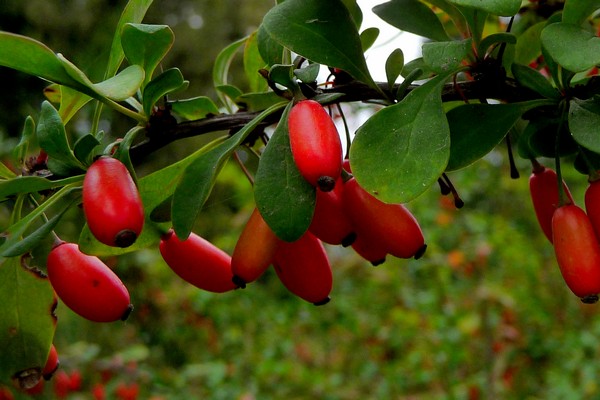
A genus of plants such as barberry (Berberis) is directly related to the barberry family, and it is represented by shrubs and trees. The name barberry comes from the Arabic word "beiberi", which translates as "shell-shaped." The greatest prevalence of barberry in natural conditions is observed in the mountainous regions of the Northern Hemisphere. This genus unites 170 species of various plants, some of which are cultivated by gardeners. Delicious jams, drinks are prepared from the fruits of barberry, and the plant is also used for the manufacture of medicines at home. And also such a plant has a rather spectacular appearance. The leaves of varietal barberries can be painted in different colors, for example, green, purple, yellow, and they can also be variegated, spotted, or have a border. Still different species and varieties can differ in the height of the bush, which varies from 30 to 300 centimeters.
Content
Features of barberry
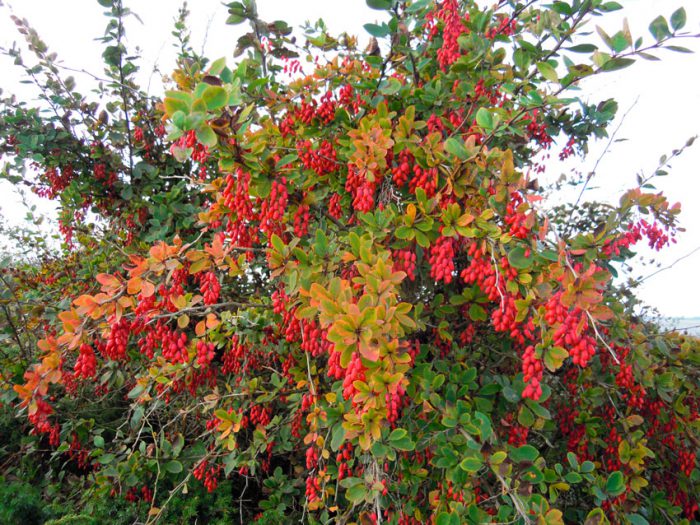
Such a shrub can be evergreen, deciduous and semi-evergreen. There are thorns on it, as well as leathery or simple alternate leaf plates. The thorns are modified leaves, with only the central vein left of them. In the axils of the thorns, short stems develop, because of this, the leaf plates are collected in a kind of bunches. On the stems of this year, the leaf plates are arranged singly in a spiral. Small fragrant flowers of golden yellow or orange color interspersed with red. As a rule, flowers are part of racemose or corymbose inflorescences, but in some cases there are also single ones. Each petal has a pair of nectaries. During the flowering of barberry, bees flock to the scent of flowers, such a plant is considered a good honey plant. Depending on the species and variety, fruits can have different shapes and colors. This plant grows well in the city, as it is distinguished by its unpretentiousness, drought resistance.And also barberry grows and develops excellently in any soil. This plant is excellent for creating hedges.
How to plant barberry
What time to plant
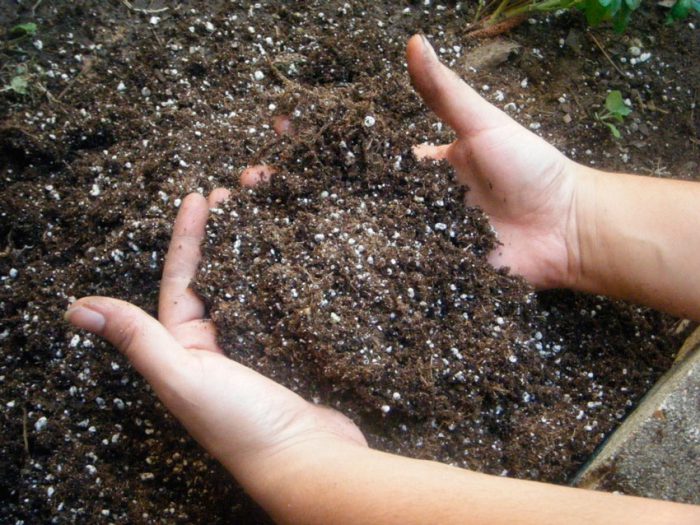
As a rule, planting of barberry seedlings is carried out in the spring after the soil has completely thawed. However, the landing must be made before the buds open. However, in some cases, planting can be done in the fall. Or rather, at a time when there is a massive leaf fall. Such an undemanding plant in care can be grown in a semi-shaded place, as well as in an open area, since it is not afraid of gusts of wind and drafts. It should be remembered that species and varieties with purple leaf plates look much more spectacular if they grow in a sunny area. The most suitable soil is neutral, but barberry grows and develops quite normally in soil with a pH of less than 7. In the event that the soil is excessively acidic, then lime will need to be added to it. You can apply the necessary fertilizers both a few months before planting the seedling, and immediately before planting. So, 100 grams of superphosphate, 200 grams of wood ash, 400 grams of slaked lime and from 8 to 10 kilograms of garden soil mixed with compost or humus must be added to the hole.
Landing features
If you plant the bushes alone, then between them you should maintain a distance of 150 to 200 centimeters. In the event that such a shrub is used to create a hedge, then no more than 2 bushes are planted per 1 running meter. Planting holes must be prepared 14–20 days before planting. The size of such a pit should be 40x40 centimeters, while the depth of the hedge trench is 0.4 meters. To improve aeration of the root system, cover the bottom of the hole or trench with a layer of sand. In the event that the soil is neutral or slightly acidic, then before planting the barberry, the fertilizers indicated above should be added to it, but you do not need to add ash and lime. After the hole is prepared, a seedling is placed in it and the required amount of soil is poured, which is then tamped. After that, the plant should be watered with plenty of water, and the surface of the trunk circle should be sprinkled with a layer of mulch (compost or peat). After the barberry is planted, it is necessary to cut off that part of it that is located above the soil surface. However, it should be borne in mind that the remaining part should have from 3 to 5 well-developed kidneys.
Barberry care
Growing
Even a person who is a beginner in gardening can grow barberry. The fact is that it is extremely unpretentious and undemanding to care for, while all species and varieties must be looked after in exactly the same way. So, for example, caring for the Thunberg barberry, which is most often grown as an ornamental shrub, is completely identical to that used for growing varieties with edible fruits. In this regard, it is enough just once to thoroughly study how to properly grow such a shrub, and then it will be possible to grow its various species and varieties.
Caring for barberry consists in watering, pruning, loosening the soil, removing weeds and timely feeding. If the summer period is characterized by long dry periods, then during them watering should be carried out once every 7 days, while using cool water, which should be poured directly under the root, trying to prevent the liquid from ending up on the surface of the leaf plates. If there is a sufficient amount of rain in the summer, then watering this shrub is not necessary. Newly planted plants should be watered the same way once a week until they get sick and start growing.If the summer turned out to be excessively rainy and damp, then this can cause rotting of the root system of the barberry, since it reacts extremely negatively to the accumulation of liquid in the soil. Do not forget to timely pull up all the weeds, as well as the growth that grows around the bush in large quantities. Also, be sure to loosen the surface of the soil. To reduce the number of weeding, soil loosening and watering, it is necessary to sprinkle the soil surface with a layer of mulch (sawdust, peat or nutshells).
Top dressing
The amount of fertilizer that is applied to the soil during planting is enough for him for about 12 months. With the onset of the next spring period, the barberry should be fed with a nitrogen-containing fertilizer, so a urea solution is used for this (for 10 liters of water from 20 to 30 grams of substance). In subsequent years, it will be necessary to feed the barberry with nitrogen-containing fertilizer at a frequency of 1 time in 3 or 4 years. However, if this shrub is grown for fruit, then when the flowering ends and at the end of the season, potassium and phosphorus will need to be added to the soil (15 grams of superphosphate and 10 grams of potassium fertilizer are taken for 1 bush). For feeding, you can use such a complex fertilizer as Kemira-wagon. It is necessary to apply such fertilizer to the soil in the first days of July, while 15 grams of the substance is taken for 10 liters of water.
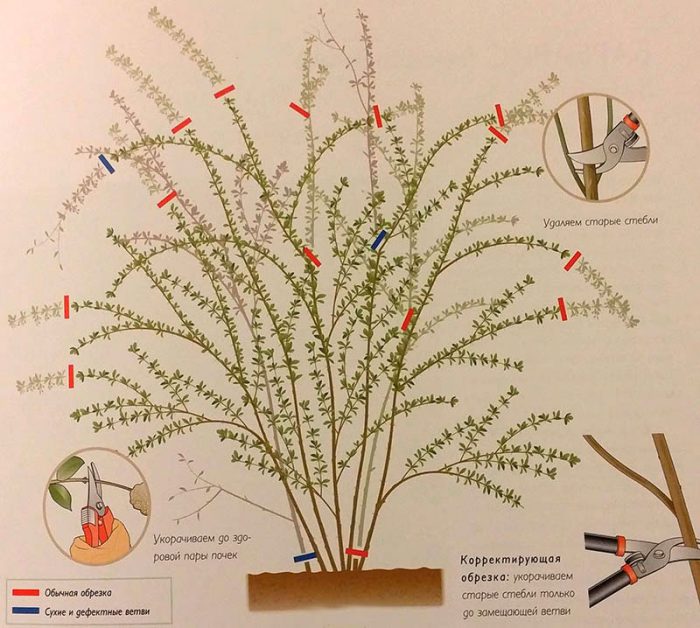
Pruning
During pruning, it will be necessary to cut off those shoots that are affected by any disease or pests, as well as weakened, dried, and also those that contribute to thickening. If the species is decorative, then the first time it needs to be cut in the spring when it reaches the age of one year. In this case, you need to cut off 1/3 or 2/3 of the shoot. In subsequent years, the bush is pruned 2 times a year, namely, in the first days of June and early August. Such pruning is both sanitary and formative. Those species and varieties that are undersized may not be pruned.
Diseases and harmful insects
Pests such as barberry sawfly, barberry aphid, or flower moth can harm this shrub. In a bush infected with aphids, the leaf plates begin to shrink and dry out. The moth is a great danger to those species that have edible fruits, because it feeds on them. To exterminate aphids, use a solution of laundry soap (300 grams of substance per bucket of water). To destroy the sawfly caterpillars, as well as the moth, it is necessary to treat the bush with 1–3% chlorophos solution.
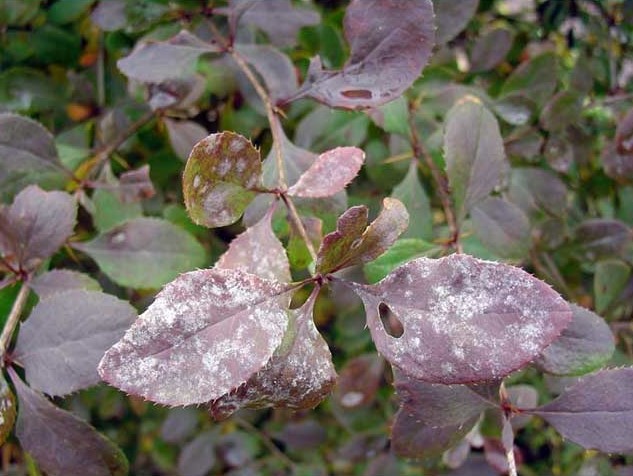
In most cases, these shrubs are susceptible to fungal infections, such as rust, leaf spot, powdery mildew, bacteriosis or wilting. In a bush infected with powdery mildew, a whitish powdery coating appears on the surface of leaf plates, berries and stems. Closer to autumn, cleistothecia appear in areas of the plant that are affected by the disease, and in them the fungus will tolerate wintering well. In order to get rid of such a disease, treatment with a solution of colloidal sulfur (1%) should be performed. Those stems that are very severely affected must be cut and destroyed. As a rule, rust appears on those bushes that grow near cereal plants. On the infected specimen, specks of orange color appear on the front side of the leaves, while red convex pads are formed on the seamy side. In case of severe infection, the leaf plates dry out and fall off. You can get rid of this disease by treating with a special solution, which is carried out 3 times. To do this, use a solution of Bordeaux liquid or colloidal sulfur (1%). The first processing is carried out immediately after all the buds open and the leaves grow, and the subsequent ones - with a break of 20 days.
When infected with spotting, specks of various shapes appear on the leaf plates, due to which the plant loses its decorative appearance. To get rid of the disease, a solution of copper oxychloride is used (for a bucket of water from 30 to 40 grams). Processing must be carried out before the barberry blooms, and after flowering ends. In a bush infected with wilting, the leaves and stems become lethargic and dry out. In this case, wilting begins from one side, and then gradually spreads throughout the plant. In order to prevent the disease from infecting the entire bush, it is necessary to cut off the infected stems in a timely manner. Also, at the initial stage of wilting development, copper oxychloride or Bordeaux liquid will help get rid of it. For preventive purposes, in the spring, the bushes need to be sprayed with Bordeaux liquid. When infected with bacteriosis (bacterial cancer), tumors and cracks appear on the bush, and it begins to grow. In the event that bacteriosis has affected only the upper part of the stem, then it must be cut off, while capturing healthy tissue. However, if the cancer appears on the lower part of the stem, which is located next to the trunk, then the entire bush will become infected. Infected areas must be cut off and destroyed, then the entire bush must be treated with Bordeaux liquid or another agent that contains copper.
Reproduction of barberry
Such a shrub can be propagated by seeds, as well as by dividing the bush, layering and cuttings. It should be borne in mind that each such method has both positive and negative sides.
Growing barberry from seeds
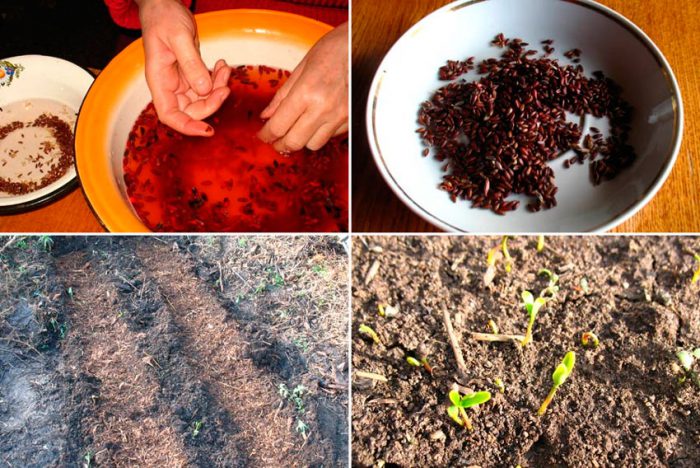
To collect the seeds, you need well-ripened barberry fruits. Separate the seeds from the pulp and immerse them in the potassium manganese solution, where they should sit for a few minutes. After that, the seeds must be dried. Sowing of seeds is carried out in the autumn time directly in the student's bed, while they need to be sealed to a centimeter depth. After a pair of true leaves appear at the seedlings in spring, thinning should be carried out, while taking into account that a distance of at least 3 centimeters must be kept between the plants. Barberries should grow on a training bed for a couple of years, after which they are planted in a permanent place. In the event that you have planned sowing in the spring, then the seeds will need to be stratified. To do this, they must be mixed with sand and placed on a refrigerator shelf (temperature 2–5 degrees), where they must spend from 2 to 5 months. Such seedlings, planted in a permanent place, will bear fruit for the first time 2 or 3 years after the emergence of shoots. However, it should be borne in mind that for the appearance of ovaries, several bushes are needed, located next to each other, since this plant needs cross-pollination.
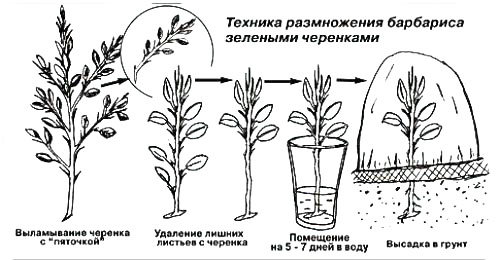
Propagation of barberry by cuttings
Cuttings are harvested in mid-June, while this procedure should be carried out early in the morning. The leaf plates located at the bottom of the cuttings must be removed, and those at the top are shortened by ½ part. Then the prepared cuttings must be immersed in a solution of an agent that stimulates root growth (heteroauxin, epin, or root), where they must stay for several hours. After that, they need to be thoroughly rinsed with clean water and planted in a greenhouse in a moist earth mixture consisting of fertile soil, humus, peat and sand (2: 2: 2: 1). For the greenhouse, you will need to make a removable dome, which must be transparent. The plants will stay in the greenhouse for about half a month. The dome must be systematically removed so that the cuttings can be ventilated. When they are completely rooted, the shelter should be removed permanently. The cuttings are planted on a training bed, where they should be grown for about 2 years, then they can be planted in a permanent place.
Propagation of barberry by layering
In springtime, on a bush among the lower branches, you need to choose a fairly strong annual stem. Then it must be pressed against the surface of the soil and placed in a shallow (about 20 centimeters) groove, which should be made in advance. Fix the stem, then fill the groove with soil, while only the upper part of the shoot should remain on the soil surface. In the autumn, the finished rooted layer must be separated from the parent plant and transplanted for growing.
Reproduction of barberry by dividing the bush
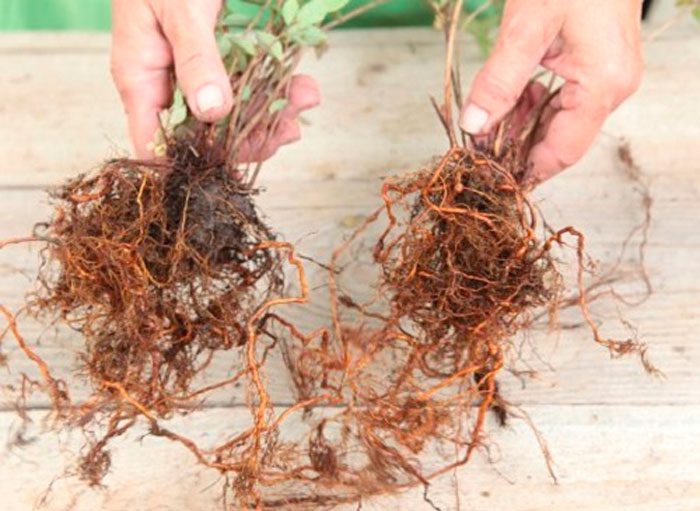
This method of reproduction is great for low-growing barberry species, while the plant must be at least 3-5 years old, and its root collar must be at a depth of at least 10 centimeters. In springtime, the bush needs to be dug up, and then it is divided into several divisions, which should be approximately the same in size. In order to divide the root itself, you may need not only a pruner, but also a garden saw. Proceed very carefully, trying to inflict as little damage as possible on the plant. When the bush is divided, all cuts must be smeared with chopped charcoal, after which the cuttings are planted in open ground. In the case when the stems of the specimen begin to branch above the surface of the soil, this propagation method is not used.
Barberry in winter
Barberry in autumn
After late autumn comes, the surface of the trunk circle must be sprinkled with a layer of mulch, while the material must be loose (compost, peat or dry foliage).
Wintering barberry
Young specimens that have not yet turned 5 years old should be covered with spruce branches for the winter, especially if the species is evergreen. In the event that the specimen is quite large, it should be covered for the winter in the same way as a hydrangea or a garden rose. To do this, twine (rope) must be tightly pulled together, after which a similarity of a cylinder of a metal mesh is built around the bush, while its height should exceed the bush by 10 centimeters. The existing voids inside the constructed structure must be filled with dry fallen leaves, and then the cylinder itself must be wrapped with a covering material.
Types and varieties of barberry with photos and names
There are a large number of types and varieties of barberry, and sometimes it is not so easy for a gardener to make a choice. When choosing a certain type or variety, you need to know exactly what goal you are pursuing and focus on it. In the event that you are going to grow barberries to get berries, then for this you should opt for special types. If you need to decorate your garden or create a hedge, then other varieties and types are suitable for this. However, it should be remembered that there are species that can not only become a wonderful decoration for the garden, but also give a rich harvest of delicious fruits.
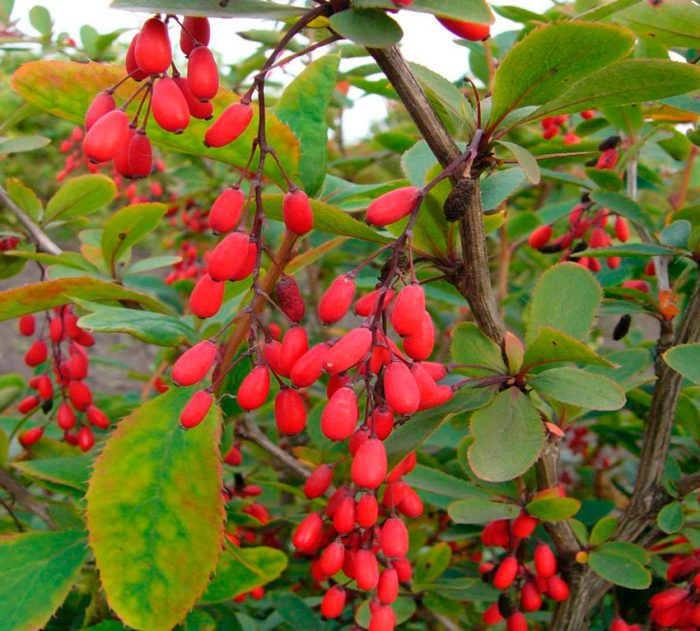
Common barberry (Berberis vulgaris)
This species is the main one in this genus. The height of such a shrub can reach 300 centimeters. The stems are brown-gray, with tripartite spines, two centimeters long, on them. Membranous, thin elliptical leaf plates have an ciliate-serrate edge. Their front side is painted dark green, and the back side is pale greenish gray. The length of racemose inflorescences reaches 6 centimeters, they consist of fragrant glossy yellow flowers. Flowering lasts 14–20 days. There are many rich red berries, which are about 15 mm long. This species has many varieties: albo-variegata - white-variegated leaf plates; aureo-marginata - the foliage has a golden border; atropurpurea - dark purple or red leaves. In the seedless form of the common asperm barberry, the fruits are very easy to process.
There are several species that have certain similarities to the common barberry, for example: Provencal barberries (a hybrid of common barberries and Siberian barberries), spinous - a species from the Himalayas, Canadian, Zimbold barberry, James barberry and Diels barberry.
Barberry Thunberg (Berberis thunbergii)
This is the most spectacular species among deciduous barberries, which stands out for its decorative effect. For this shrub, the height can vary from half a meter to a meter. There are horizontally located branches. Rich red or light yellow young stems are deflected arcuate, and they strongly branch. Over time, they turn brownish purple or brown. Elastic thin spines are one centimeter long. Graceful leaflets have an obovate or oblong shape, in length they reach no more than 30 mm. Their front side has a deep green color, and the back side is bluish, and in autumn they change their color to deep red. Flowers can be single or collected in bunches. The inner surface of the petals is yellow and the outer one is red. Flowering lasts 7-14 days. Centimeter glossy elliptical berries have a coral red color. They ripen in the first autumn days and become the main decoration of the shrub for several months. The fruits contain a large number of alkaloids, in this regard, they have a bitter taste, but on winter days they are eaten with pleasure by birds. Planting and growing this species is very simple. This shrub will be an excellent decoration for your garden area. This species has many decorative forms: multi-flowered (pluriflora), dark purple (atropurpurea), silvery-bordered (argenteo-marginata), etc.
The most popular varieties are:
- Golden Ring - reaches a height of 300 centimeters, has a rounded crown. The length of the ovate leaf plates is about 4 centimeters, they have a dark red-purple color, and a yellow border. In autumn, they change color to a deep red. Flowers with a centimeter diameter are collected in bunches (from 2 to 5 pieces), their outer surface is red, and the inner one is yellow. The glossy red-coral fruits ripen in October.
- Red Pilar - columnar shape. The bush reaches a height of 150 centimeters, and its crown is about 45 centimeters wide. The leaf plates are violet-red, and they turn deeply scarlet in autumn.
- Orange Rocket - columnar shape. The height of the bush is not more than 1.2 meters, and the width is 0.6 meters. Smooth little ovoid leaf blades on this year's stems are orange with yellow edging, while last year's shoots are purple-red. Against the background of greenery, such a bush looks very elegant. In autumn, the leaves are colored in various shades of red.
- Kornik - the height of this deciduous plant is about 150 centimeters. On the surface of the light green leaf plates, there are randomly arranged white-cream specks of various shapes. It seems that the leaves have been splattered with paint. In autumn, the green color of the leaves changes to scarlet red. This variety is recommended to be planted in the vicinity of conifers, roses or other varieties of barberry.
Ottawa barberry (Berberis x ottawensis)
Such a decorative hybrid was born as a result of crossing the Thunberg barberry and the atropurpurea of the common barberry. This species is one of the most beautiful representatives of its kind. The height of the bush varies from 150 to 200 centimeters. Outwardly, such a bush looks like an enlarged Thunberg barberry, but the color of the leaf plates is similar to the purple-leaved form of the common barberry. So, the leaves are painted in a dark purple-pink color, which looks almost black in the sun.In autumn, the leaves acquire a crimson color, while they decorate the plant for a long time. This species is distinguished by winter hardiness, unpretentiousness, and it also belongs to fast-growing plants.
The most popular varieties are:
- Auricoma - the bush reaches a height of 250 centimeters. Rounded leaves five centimeters long in spring and summer are rich red, and in autumn - orange. The length of racemose inflorescences is about 5 centimeters, they consist of yellow-red flowers with a centimeter diameter. Deep red berries.
- Superba - the bush can reach a height of 400 centimeters. The length of the rounded leaves is 3-5 centimeters, they have a dark red color with a bluish bloom. In autumn, they change their color to different shades of red and orange. The racemose inflorescences are composed of red-yellow flowers. The fruits are red.
- Silver Miles - such a variety does not look attractive when viewed up close, but when viewed from a distance, it is very effective. On the surface of the purple leaves, there are randomly located streaks of a dirty gray color. If you look at the bush from a distance, it seems that it is painted in lilac color.
Also quite popular are such barberries as: Juliana, Beana, Tishler, Morrison, Wilson, greenish, willow, multiflorous, oriental, Iberian, net-leaved, similar, bluish-white, box-leaved, notched or unbordered, large-spiked, provincial, spring monotonous, Korean, Tibetan, Siberian, transparent, circular-sawed, twisted, Amur, Turkmen, whole-edged, oblong, round, Asian, etc.
Barberry properties
Useful properties of barberry
Many types and varieties of barberry are grown as a garden decoration. However, common barberry, as a rule, is grown to obtain fruits, from which compotes, liqueurs, marinades, marshmallows, jelly, syrups, preserves and jellies are prepared. Pickled barberry fruits are used in Armenian cuisine, for example, they are served with lamb, fried vegetables or rice.
In edible species, the fruits contain tartaric, malic and citric acids, while the leaf plates contain vitamins E and C, as well as carotenoids and mineral salts. Fruits are able to lower blood pressure, fight psoriasis, tone the body, eliminate various infections in the intestines, stop bleeding, and prevent the growth of lamblia, yeast and other parasites.
All parts of the barberry have medicinal properties. Only ripe berries should be picked, because unripe ones contain poison. The berries are dried in a shaded place, while the temperature should not exceed 50 degrees. After that, they are poured into paper bags or cardboard boxes, where they are stored for no more than 3 years.
The plant has anti-inflammatory, choleretic, analgesic, antipyretic, antispasmodic, antitumor, hemostatic, antibacterial action. A decoction of the roots relieves inflammation of the gallbladder and promotes the outflow of bile. A decoction of leaf plates is used for various forms of hepatitis, digestive disorders, inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract, diseases of the liver, gallbladder and ducts. A decoction of the bark will help with chronic pancreatitis. Fruit juice has a mild laxative effect and improves appetite. Ripe fruits mixed with honey can improve the body's immune system after radiation exposure. Inflamed eyes, wounds, areas of the epidermis affected by eczema are washed with a decoction of the roots, and it is also used for lotions, compresses and rubbing with radiculitis, arthritis, rheumatism, leg muscle spasms and osteochondrosis.
Contraindications
Medicines prepared using barberry cannot be used to treat children under 12 years old, people with individual intolerance, as well as those suffering from a complex form of hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver and gallstone disease. And also during pregnancy, with postpartum or climacteric bleeding. Remember that unripe fruits contain poison!


Watch this video on YouTube