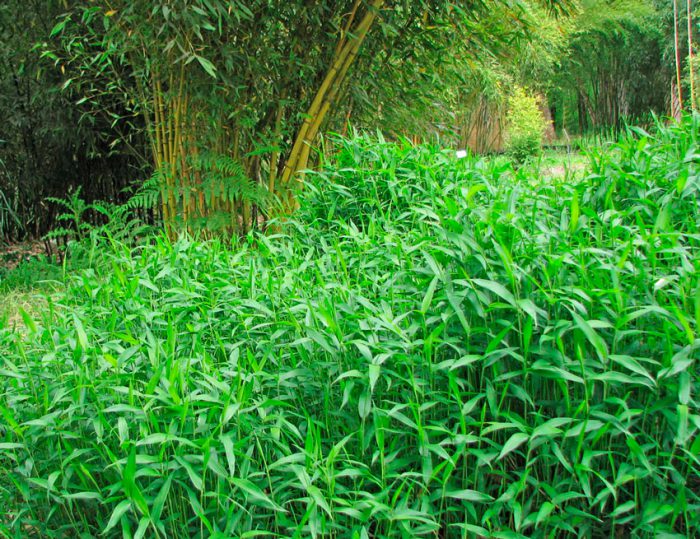
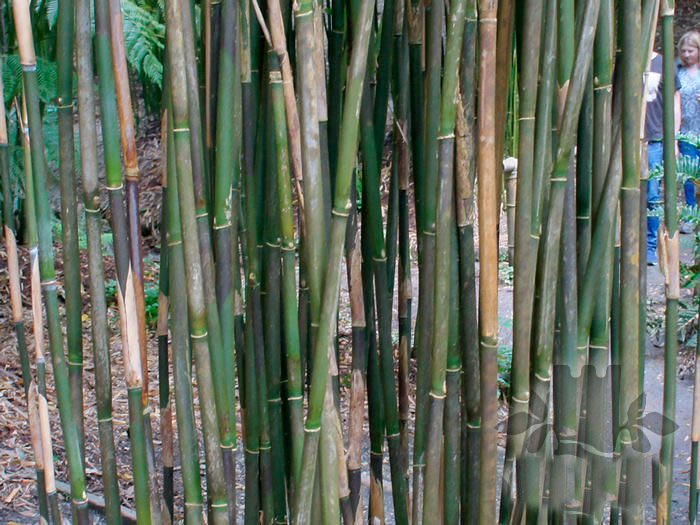
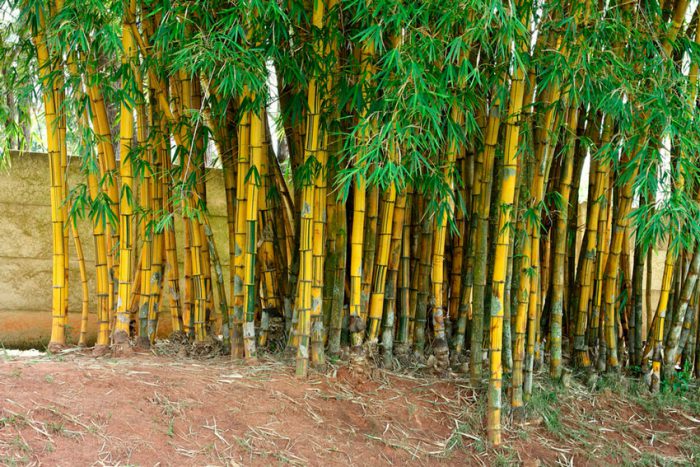
The evergreen perennial bamboo (Bambusa) is a member of the subfamily bamboo of the cereals family, or bluegrass. Gardeners cultivate both plants that are representatives of the bamboo genus and those that belong to other genera of the bamboo subfamily. For simplicity, gardeners call all these plants bamboos. And in this article they will be called in exactly the same way, but in the section on species and varieties, it will be described in detail to which genus and subfamily this or that plant belongs.
Plants belonging to the genus bamboo and the bamboo subfamily can be found in the wild in the subtropical and tropical regions of Europe, Australia, Asia, Africa, America, and also in Oceania. Moreover, herbaceous bamboos are found exclusively in tropical areas. Every year, these plants are becoming more and more popular with gardeners. They are used to create spectacular hedges and to decorate patios and terraces.
Content
Features of bamboo
Bamboos growing in the wild are incredibly large. The stems (straws) are fast growing, they are woody and branch in the upper part. Their height can vary from 35 to 50 meters. Bamboo is one of the fastest growing plants on the entire earth. Short-petiolate leaf plates are lanceolate. On special branches with scaly leaf plates, multi-flowered spikelets are placed singly or in groups. Bisexual flowers bloom only once in several decades, while a massive and very lush flowering is noted. Interestingly, flowering begins almost at the same time on all plants in a given population. After the caryopses are fully ripe in the flower scales, they fall out, where they are carried by streams of water or animals. When fruiting is complete, the plant dies off entirely, but sometimes the roots may remain.
Bamboo has been used as a building material for a long time. Wind pipes or gutters are made from the dried stem.
Growing bamboo outdoors
Suitable conditions
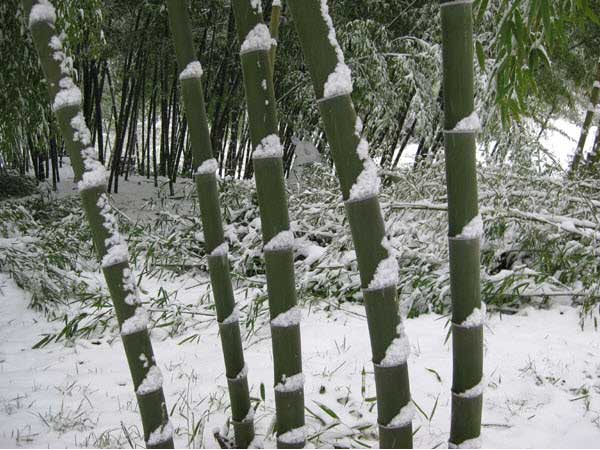
Bamboo has a high decorative value because it is evergreen.For example, it's January outside, it's cold, there is snow, and your garden is decorated with bamboo, which, like in summer, is covered with green foliage. But it should be borne in mind that most species are thermophilic. There are about 100 species that can withstand a drop in air temperature to minus 20 degrees, while only a few are able to withstand severe frosts (up to minus 32 degrees). Experienced gardeners say that if the bamboo survives the first winter, then in the next it will be able to calmly endure a decrease in air temperature to minus 20 degrees.
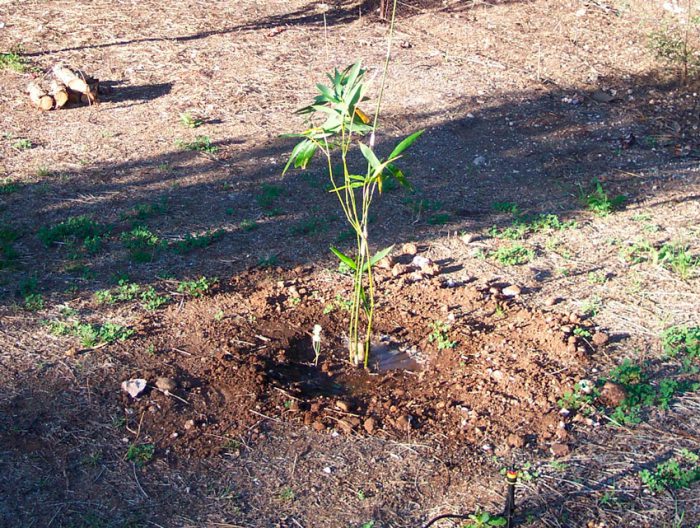
What conditions are needed for bamboo cultivation in mid-latitudes? To grow it, you should choose a well-lit or slightly shaded area, while it should be protected from cold and dry winds. A simple fence is able to protect the plant from the winter dry wind. You can grow bamboo on any soil except clay and heavy. The acidity of the soil should be 6.0–6.2. You can start planting such a plant in open soil in the spring, after the soil has warmed up well. In this case, planting can be carried out in spring, summer, and autumn (from March to September), but it is best to plant bamboo in April – June.
Landing in open ground
Plant bamboo outdoors in the same way as other plants in the garden. First, you need to prepare a planting pit, it should be noted that its size should be 2 times the volume of the seedling root system. Then its bottom is covered with a layer of nutritious garden soil, which is mixed with humus in advance, it must be compacted. The seedling should be immersed in a container filled with water, along with the container in which it grows, for several hours. You should remove the plant from the container only after air bubbles completely stop coming out to the surface. Then it is carefully lowered into a prepared hole, which is covered with a soil mixture consisting of nutritious garden soil and humus, which must be well compacted, trying to eliminate all voids. The top layer of soil (about 2–5 centimeters) does not need to be compacted. The planted plant must be watered very well, while all remaining voids must completely disappear.
How to water
When growing bamboo in mid-latitudes, you need to learn how to water it correctly, which is not difficult at all. Newly planted plants need very abundant watering at first, while the soil surface must be sprinkled with a layer of mulch (organic matter). After the plant begins to actively grow, watering will need to be reduced to 2 or 3 times every 7 days, while taking into account whether it rains often at this time of year. Bamboo is a moisture-loving plant, and if it feels a lack of water, then it will develop a very powerful and long root system that can take moisture from the deep layers of the soil.
Limiters
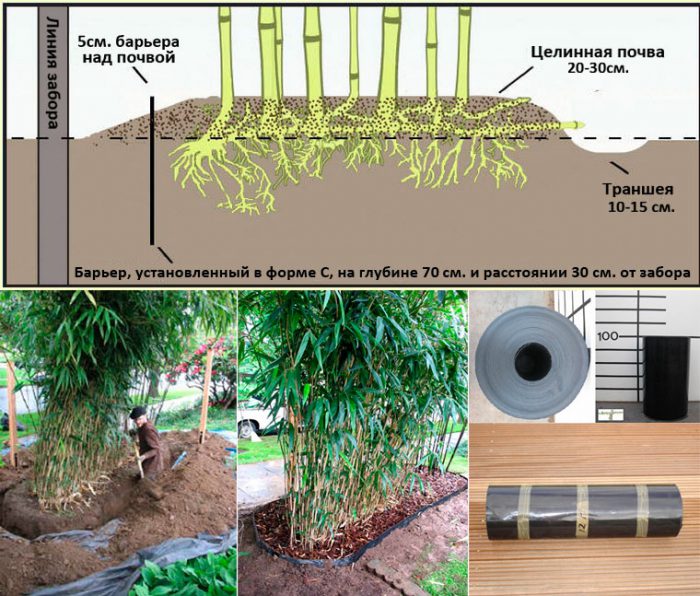
There are 2 main varieties of bamboo cultivated by gardeners, namely bushy and running. The peculiarity of bushy bamboo is that it grows in dense groups and at the same time does not spread over the site. But in running bamboo, the root system grows superficially, not sinking more than 5–20 centimeters into the soil, and sometimes they are located directly on its surface. Such a plant is capable of growing rapidly, capturing all new areas, if this is not included in your plans, then you will need to cut off the growing roots in a timely manner, and more than once a season. Those roots that you chopped off should be pulled out of the soil and disposed of, as they are able to continue their development further. You can limit the growth of running bamboo once and for all, for this, pieces of slate should be dug around the perimeter of the site, they must be buried 100-150 centimeters, and above the soil surface they should protrude 5-10 centimeters.You can also limit the growth of bamboo roots with a barrier film (root-barrier), which is a rigid and flexible plastic tape 0.5-1 m wide and 0.6 cm thick. This tape should be dug into the ground along the perimeter of the site at an angle ... In this case, the lower buried edge should be directed towards the site, and the upper one should be opposite from it. Sheets of slate, film or iron should be overlapped, not end-to-end, otherwise the powerful bamboo roots will break through them.
Pruning
Pruning is carried out once a year in the spring. In this case, you should remove frost-damaged or old ugly bamboo trunks. In order for the rays of the sun to penetrate deep into the thickets, it is recommended to carry out systematic thinning. It should be borne in mind that if the trunk is chopped off above the node, then the plant can continue to grow and develop further.
Top dressing
In the springtime, the plant needs feeding with a nutrient mixture consisting of phosphate, nitrogen and potassium (3: 4: 2). In the fall, bamboo is fed with the same mixture, which includes potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen, but their proportion this time should be 4: 4: 2. After the nutrient mixture is introduced into the soil, the old stems will need to be completely cut off to the surface of the site, which then must be covered with a ten-centimeter layer of mulch (pine bark or dried foliage).
In the event that you decide to feed the bamboo with organic fertilizers, then it should be noted that they should be applied to the soil 1 time in 4 weeks throughout the season. After the autumn period comes, such feeding should be stopped.
Wintering
The first wintering for bamboo is the most difficult. Its root system at temperatures below minus 17 degrees is capable of freezing, while at minus 20 degrees the trunk of the plant, located above the snow cover, dies. In the event that forecasters predict a frosty or little snowy winter, experienced gardeners recommend bending the trunks of plants to the surface of the mulch layer, and spruce branches should be thrown over them, which will save the plant from freezing. If the first wintering for the plant is successful, then in the next winters it will quite calmly endure frosts down to minus 20 degrees.
Bamboo propagation
How to grow from seeds
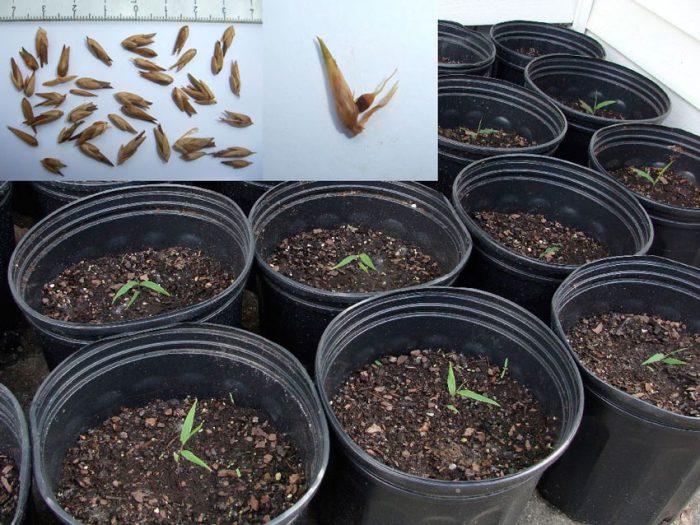
Before sowing seeds, they need to be immersed in clean water for 12 hours. For sowing, you need a soil mixture consisting of fine wood shavings, wood ash and topsoil (1: 1: 8). The resulting substrate must be sieved through a sieve and moistened. This mixture is used to fill the cells in the cassette, without the need to tamp it. Small holes should be made in the cells, the depth of which should be within the range of 0.4-0.5 centimeters. In each such hole, 1 seed is placed, which must be removed from the water a third of an hour before sowing and blotted with a clean cloth. The crops should be covered with a layer of substrate.
Then the cassettes are removed to a shaded place. Before the seedlings appear, the substrate should be moistened from the sprayer 2 times a day, so that it is constantly slightly damp. As a rule, the first seedlings appear on the soil surface 15–25 days after sowing. After 3-4 months have passed since the emergence of shoots, and the formation of shoots will begin in the plants, it will be necessary to pick them in individual containers, which are filled with high-moor peat. After that, watering must be reduced to 1 time per day, while it is best done in the evening. Transplanting seedlings into open ground is carried out after they reach a height of 0.4-0.5 m. But it should be borne in mind that it will be better if the seedlings stay indoors for the first winter, because there is a high probability of freezing out or death from lack of moisture. During the first winter, plants can be kept in a greenhouse or in another room that is not heated, but it must be protected from drafts and frost.After the soil warms up well in the spring, bamboo can be transplanted into open ground.
Vegetative breeding method
In the springtime, it is necessary to dig out several shoots that are 3 years old, and then they are planted in a new place, which is in shade. They should be provided with abundant daily watering, but first they will need to be shortened by 1/3 part.
Diseases and pests of bamboo
This plant is highly resistant to both diseases and pests. However, there are certain types of bamboo that spider mites or worms like to settle on. To get rid of spider mites, the affected specimen is treated with an acaricide, and an insecticide will help with worms.
In some cases, bamboo is damaged by rust. In order to get rid of it, fungicides are used.
Yellowing bamboo
In the event that the foliage changes its usual color to yellow in the autumn, then this is a natural process. So, for example, in bamboos of the genus Fargesia, 10–30 percent of the leaf blades turn yellow and die off, while in representatives of the genus Phillostachis - no more than 15 percent. Some of the leaf blades die off in the fall, because bamboo thereby conserves the energy needed in the winter months. In winter, all the yellow foliage will fall off completely, and the plant will again return its fresh and very effective appearance.
The yellowing of the leaf plates in summer or spring suggests that not everything is in order with the plant. The foliage can turn yellow due to either chlorosis or flooding. In the event that the soil is oversaturated with moisture, then rot develops on the root system of the bamboo. Therefore, when planting seedlings in clay or heavy soil, it is recommended to make a very good drainage layer of sand or gravel at the bottom of the planting pit. Chlorosis can develop due to the fact that the plant lacks nutrients such as nitrogen, magnesium or iron. In some cases, it develops due to soil salinity. After you start caring for the bamboo properly, new green leaves will grow.
Types and varieties of bamboo with photos and names
Bamboos cultivated in the garden are conventionally divided into upright-stemmed species with a rigid trunk, as well as into not very large herbaceous plants. Considering that the homeland of such a plant is the subtropics and tropics, when choosing a particular species and variety, its frost resistance should be taken into account. Of the bamboo subfamily, plants of the genus Saza are distinguished by the greatest frost resistance. Fargesia (synarundinaria) are distinguished by their frost resistance and endurance. Plants belonging to the genus Pleioblastus stand out for their highly decorative appearance. In regions to the south, you can grow phyllostachis bamboos. Of the species belonging to the genus bamboo, ordinary bamboo is the most popular among gardeners. Ornamental (indoor) bamboo is not actually bamboo, the real name of this plant is Dracaena Sandler.
Sasa
This genus is a representative of the bamboo subfamily and it unites about 70 species of various plants. They are found naturally in East and Central Asia. Plants of this genus are distinguished by the fact that they form rather dense thickets, while they prefer to grow under tall trees or on the edges. The height of the shoots can vary from 0.3 to 2.5 m. Wide-oval leaf plates are painted in a deep green color in spring and summer. In autumn, the edge of the leaves dries up, which gives the impression of variegation.
The most popular of the representatives of this genus is the Kuril saza. Shoot height can vary from 0.25 to 2.5 m, and their thickness is 0.6 cm. The length of the pointed-ovate leaf plates is 13 centimeters, and their width is about 2.5 centimeters. Flowering in this species is observed only once, and then the plant dies off.The development of such a plant is very slow, while in the middle latitudes only its undersized forms are cultivated, they are used as ground cover plants or to decorate Japanese gardens. The Shimofuri variety is quite popular, which has yellow streaks on the surface of the green leaf plates. In addition to Kuril saza, spikelet saza, panicle, finger saza (the Nebulose variety has palm leaf plates), branched saza, Vichy, golden and reticulate are also cultivated.
Fargesia
This plant is a Chinese mountain bamboo. This genus was discovered by French missionaries in the eighties of the 19th century. Today this genus includes about 40 species of evergreens, the height of which is not less than 0.5 m. Such plants form loose bushes with a large number of stems. Graceful deep green leaf plates have a lanceolate shape, they reach 10 centimeters in length and 1.5 centimeters in width. In autumn, their color changes to greenish yellow. The most popular types:
Fargesia brilliant (Fargesia nitida = Sinarundinaria nitida)
This species is distinguished by its winter hardiness. The height of its shiny shoots varies from 0.5 to 2 meters, they are painted in a rich dark brown-red, almost black. Narrow-lanceolate leaf plates reach about 12 centimeters in length. Popular varieties:
- Eisenach - small leaf plates have a dark green color;
- McClure is a tall variety;
- New collection - the color of the shoots is cherry-purple;
- Great Wall - this variety is used to create tall hedges, the color of the leaf plates is dark green;
- Nymphenburg - on arched branches there are narrow leaf plates.
Fargesia Murielae = Sinarundinaria Murielae
This species is frost-resistant. His homeland is Central China. There is a waxy bloom on the surface of the greenish-yellow smoothly curving shoots. Long-pointed leaf plates are bristly and pointed. This species blooms once every 100 years, after which the plants die off. The last flowering was observed in the late seventies of the last century, while its duration was equal to 20 years. At the moment, the following varieties are popular:
- Simba is a new compact Danish variety;
- Jumbo - delicate green leaf plates grow on a bushy plant;
- Bimbo - this variety is distinguished by its diminutiveness, the color of its leaf plates is greenish-yellow.
Also cultivated species such as Jiuzhaigou fargesia and pectoralis.
Phyllostachys
This genus is a representative of the bamboo subfamily. It unites 36 species of plants that have corrugated or flattened cylindrical shoots, painted in yellow, light blue, green or black. The stems have short internodes, green leafy plates and creeping rhizomes. The height of such a plant can vary from 350 to 550 centimeters. The most popular types:
Phyllostachis golden-grooved (Phyllostachys aureosulcata)
In height, the stem can reach 10 meters, while its diameter is 20-50 millimeters. Strongly convex nodes are colored dark purple, grooves are yellow-golden. The Spectabilis variety is very popular with gardeners, distinguished by its spectacular zigzag stems, this plant was awarded an RHS award. And very often such a variety is cultivated as Areokaulis with golden shoots, it was also awarded a prize.
Phyllostachis black (Phyllostachys nigra)
In height it can reach no more than 7 meters. After the plant is 2 years old, its stems turn almost black. Small leaf plates are dark green in color. This species is most popular in its homeland, namely, in China and Japan.Very often cultivated varieties such as Boryana (height about 450 cm, spots appear on the surface of the stems from sunlight) and Hemonis (the color of the stems is green, and their height is about 900 cm).
Phyllostachis edible, or moso (Phyllostachys edulis = Bambusa moso)
Originally from the southeastern regions of China. This species is considered the largest in this genus. The height of highly beaten shoots with smooth nodes can reach up to 20 meters. The tortoiseshell form is distinguished by its ugly appearance, because the arrangement of its nodes is oblique and alternating; in the wild, it is found in Batumi, Sukhi and Sochi.
Gardeners also cultivate phyllostachises such as: sweet, Simpson, pubescent, Meyer, soft, flexible, green-blue, reticulated (bamboo) and gold.
Pleioblastus
This genus is represented by low-growing long-rhizome bamboos, while it unites 20 different species. The homeland of such plants is China and Japan. Certain species are highly frost-resistant and therefore cultivated in mid-latitudes. These plants are distinguished by their shade-loving nature, but it should be borne in mind that variegated forms are best cultivated in a well-lit area. For cultivation in the garden, it is recommended to choose the following types:
Simon's Pleioblastus (Pleioblastus simonii)
The height of this plant can reach 800 cm. Strongly branched straight shoots have internodes, the length of which reaches 0.45 m. The nodes are convex. The length of the lanceolate leaf plates is 8–30 centimeters. When grown in mid-latitudes, the height of such a plant does not exceed 0.5–0.6 m, however, it is highly decorative, because it has dense bushes with well leafy stems. The variegated form of Variegat differs in that on the surface of the rich green leaf plates there are strips of various thicknesses of cream color.
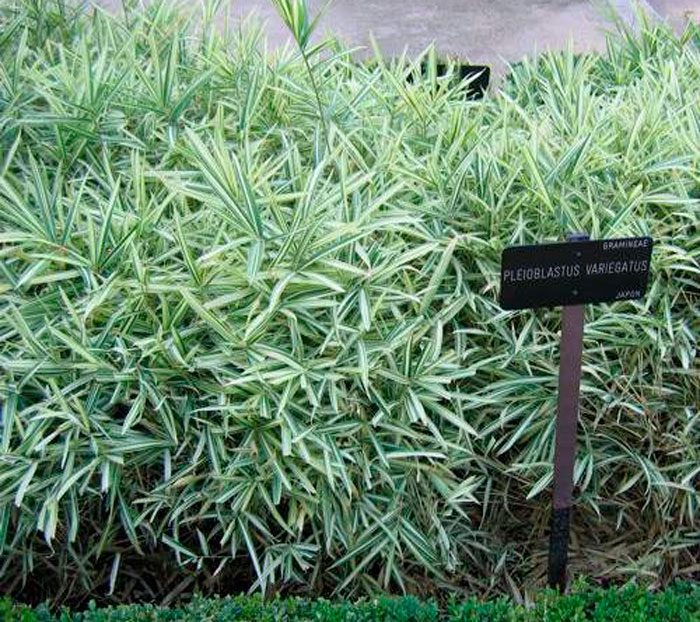
Pleioblastus variegated (Pleioblastus variegatus)
This species is cultivated in the Caucasus (Sukhumi, Batumi and Sochi). Plant height can vary from 0.3 to 0.9 m. Elbowed thin shoots have short internodes. The leaf plates are very beautiful, on their green surface there is a slight pubescence, as well as a strip of white. If there are severe frosts in winter, then the leaves of such a plant can fly around, but with the onset of the spring period they grow rather quickly. The development of this species is very fast, while it is able to form wide bushes.
It is also possible to cultivate pleioblastus narrow-leaved, short, dwarf, cereal, green-striped, two-row, Ginza, Shina and Fortune, but they are not very popular.
In the southern regions, other plants are also grown that are representatives of the bamboo subfamily, for example, some types of shibata and indocalamus. Gardeners cultivate only one member of the bamboo genus, namely, common bamboo.
Common bamboo (Bambusa vulgaris)
This herb is deciduous. Unbending, densely leafy woody shoots are painted in a deep yellow color. Their walls are thick, and there are green stripes on the surface. The height of the shoots can vary from 10 to 20 meters, while their thickness is 4-10 centimeters. The knees can reach 0.2–0.45 m in length. There is pubescence on the surface of the spear-shaped rich green leaf plates. Flowering is extremely rare, seeds are not formed. In this regard, for the reproduction of this bamboo, vegetative methods are used, for example, layering, division of the bush and rhizomes, shoots. There are 3 varieties: yellow-bore (gold), green-bore and variegated (up to 3 m in height, knee length about 10 centimeters). Most popular varieties:
- Striata... This variety is smaller than the main species. Deep yellow constrictions are located between the knees. On the surface of the stems, pale and dark green spots are randomly placed.
- Vamin... The bamboo is not very large. The constrictions located at the bottom are flattened and thickened.
- Vittata... Quite a popular variety that can reach a height of 12 meters. On the surface of the stem, there are a very large number of stripes that look like a barcode.
- Waste paper... On the surface of the green trunk, there are many black streaks and specks. From year to year, the stems turn black.
- Vamin striata... The height of the stems does not exceed 5 meters. On the surface of the pale green trunk, there are stripes of dark green color. The bridges located in the lower part of the trunk are enlarged.
- Aureovariety... Quite popular in culture. On the surface of thin golden trunks there are stripes of dark green color.
Kimmei. There are green stripes on the surface of the yellow stem.