Such a shrubby perennial vine, such as cultivated grape (Vitis vinifera), is related to the genus of grapes of the grape family. This plant is grown in regions with temperate and subtropical climates in almost every country. This species cannot be found in the wild. It was born in ancient times from wild-growing forest grapes, which were distributed from the southern coast of the Caspian Sea to the northern coast of the Mediterranean Sea.
Grapes are among the plants that man began to cultivate first. Bas-reliefs and frescoes in the tombs of the pharaohs say that this plant has really been familiar to man since ancient times. There are also written documents from which one can understand that grapes were grown already 7 thousand years ago, while wine was made from its fruits. 4 thousand years ago, there was a prosperity of viticulture in Mesopotamia (Babylon and Assyria). Also, this plant was cultivated by the ancient Greeks, while they conducted a lively trade with India and Central Asia. Until the beginning of the 17th century, there was only imported wine from grapes in Russia. The first vineyard was planted in Astrakhan, and this happened in 1613, it was at this time that this crop began to be grown on the territory of Russia. The best grape varieties from Hungary were ordered by Peter the Great himself, while he invited winemakers and breeders from France. Today, this culture is still very popular as it was thousands of years ago. The fruits of such a plant are used to make juice, compote, wine, raisins, jam, vinegar, marinade, and they can also be eaten fresh. A valuable oil is extracted from grape seeds, which is widely used in the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. Dolma, cabbage rolls, etc. are prepared from grape leaves.
Content
Features of grapes
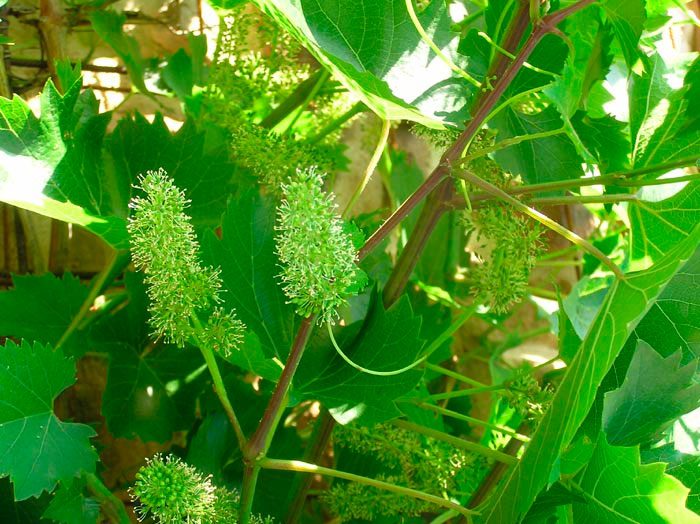
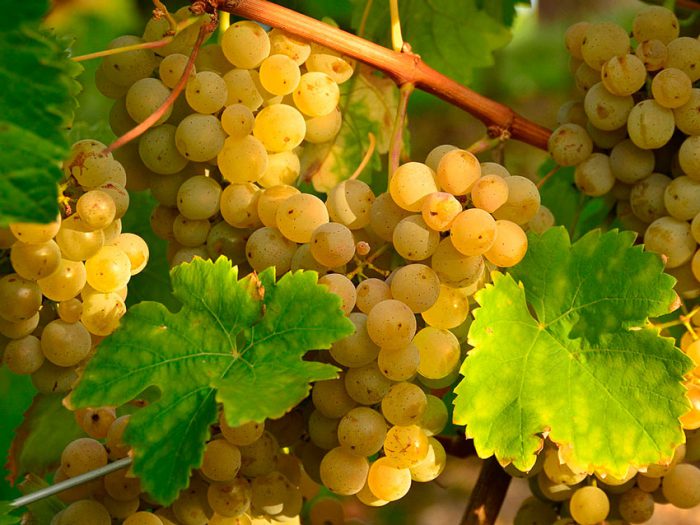
In the southern regions, cultivated grapes in length can reach from 30 to 40 meters, while in middle latitudes it does not exceed 3 meters. The branch of such a plant clings to the support with antennae. Old trunks are covered with deeply furrowed brown bark. The color of young stems is pale yellow or light red. Alternate solid leaf plates consist of 3 or 5 lobes and have petioles. Loose or dense panicle inflorescence consists of small pale green bisexual flowers. This culture blooms in May-June, while the ripening of the fruits is noted in August or September (in some varieties in October). Bunches of various forms consist of juicy fruits, inside of which there are 1–4 seeds; there are varieties without seeds at all. The color of the fruits is different, for example: green, purple-black, yellow, pink and dark red. As a rule, there is a waxy bloom on the surface of the fruit. Such a plant lives for a very long time, namely, 130–150 years.
Planting grapes in open ground
What time to plant
Grape planting can be done in the spring, namely, from the end of March to the last days of June. Or you can postpone it for the fall. Lignified seedlings are planted from the last days of March to mid-May. Planting growing green seedlings should be done from mid-May to the last days of June. As a rule, grape seedlings are sold in the autumn, and after purchasing them, it is recommended to immediately plant them in open ground, and not store until spring, because during the winter they can dry out or become moldy, and rodents can also harm them. In this regard, in the autumn, planting grapes is not only possible, but also necessary. If you buy healthy seedlings and when planting follow all the rules of agricultural technology, then grapes will definitely be accepted. Tips for choosing a healthy seedling:
- The root cut should not be colored brown, but white.
- If the one-year shoot has matured well, then it should be rich green on the cut.
- If you touch the peephole, then it should stay in place, and not fall off.
- The seedling should not be overdried.
In order for the planted seedlings to take root well and quickly, they must be prepared. Immediately before planting, the root system of the grapes should be placed in clean water for 12-24 hours. The one-year shoot should be pruned to a height of 3-4 eyes. On the upper nodes, all the roots must be removed, while on the lower ones they are only slightly shortened.
The site for planting grapes should be located on the west, south and southwest side of a building or other structure. The fact is that a plant needs a lot of light and heat for normal growth and development. Experts recommend cultivating such a vine in the middle of the slope, since there is a high probability of freezing in the lower part. A distance of at least 5-6 m should be kept between any tree and grapes.


Watch this video on YouTube
Planting grapes in spring
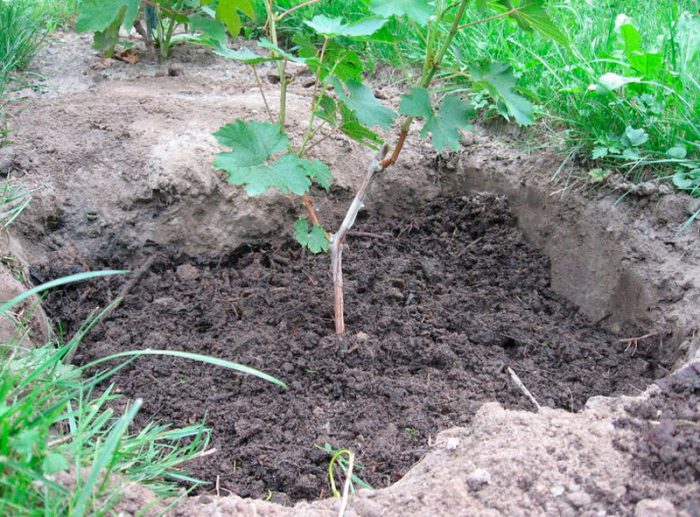
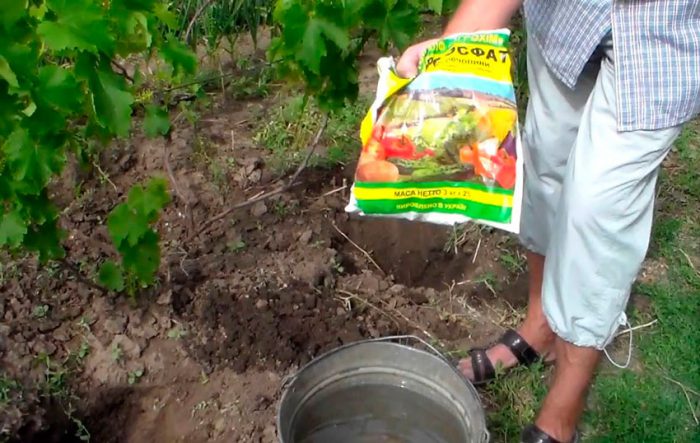
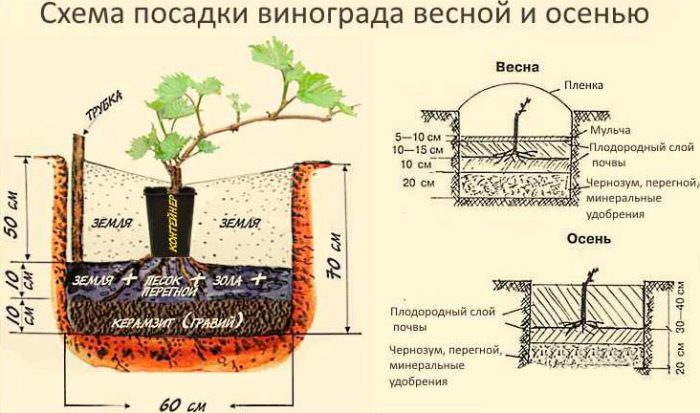
When planting this plant in clay or black soil, the size of the planting hole should be 0.8x0.8x0.8 m.In the event that the soil is sandy, then the depth of the planting hole should be at least 1 m, while its preparation should be done in autumn so that the soil has time to settle during the winter months. The advantages of deep planting are that the rooting of the plant will occur relatively quickly, and its roots will be reliably protected from severe winter frosts. The bottom of the pit must be covered with rubble, while the layer thickness should be from 10 to 15 centimeters. A plastic pipe with a diameter of 50 mm should be inserted into this layer, 10 centimeters from the pit wall. The pipe will need a long one, it should rise by 10-15 centimeters above the surface of the site.Then, at the bottom of the pit, a layer of chernozem is made fifteen centimeters thick, 200 grams of superphosphate and 150 grams of potassium fertilizer (potassium magnesium sulfate, potassium sulfate or potassium sulfate) are poured over it. Then the fertilizer must be evenly distributed over the bottom. If desired, instead of mineral fertilizers, you can take wood ash, a full can of 3 liters. A layer of nutritious soil should be poured over the fertilizer, the thickness of which should be 15 centimeters. Everything is leveled, and fertilizers are distributed from above, which should be taken in the same amount. Top it up with a layer of nutritious soil again. Then everything is well compacted and 50-60 liters of water is poured into the pit. The pit must be left until spring.
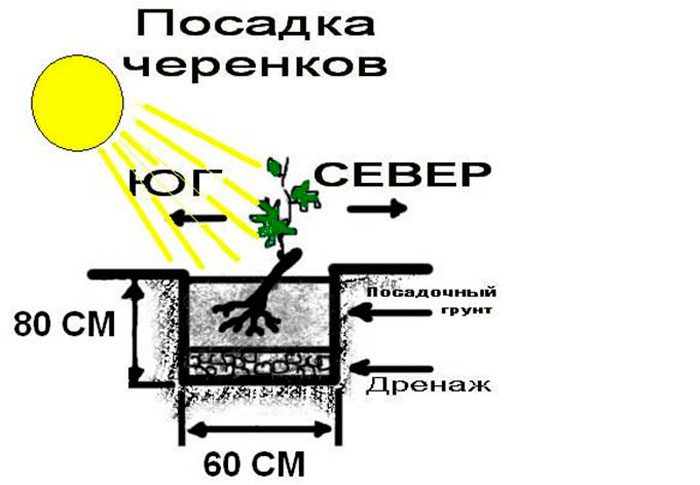
When in spring time you start planting grapes, then first, at the bottom of the hole, right in the center, you should pour a mound of nutrient soil. Immediately before planting, the root system of the plant is dipped into a chatterbox, which must be prepared as follows: 1 small spoonful of humate must be poured into 1 bucket of water and everything is well mixed, then such an amount of clay is poured so that the resulting mass is similar in consistency to store sour cream. Then the grapes are placed in a pit, they are placed on a mound with their root heel to the south, and buds to the north. The roots must be carefully straightened and covered with a layer of fertile soil ten centimeters thick. You need to fill the hole to the top with a mixture consisting of equal parts of sand and black soil. Tamp the soil around the plant. The surface of the pit must be covered with a black garden film, while holes must be cut out for the grapes and for the pipe. The seedling should be covered with a 5 or 6 liter plastic bottle with a cut throat. It will be necessary to water the seedling through a dug-in pipe (drainage hole).
A shortened seedling is planted in the above way. If it exceeds 25 centimeters in length, then it is planted in the same way, but the seedling is placed at an angle.
Planting grapes in autumn
You can plant such a liana in the fall from the first days of October until the soil freezes. The very procedure for planting a seedling is no different from the spring one, except that it will need to be prepared for wintering. To do this, it is necessary to produce a high hilling of the grapes and cover it with needles. In this case, the surface of the trunk circle must be covered with a layer of peat or sawdust. It is not recommended to plant a seedling in a just made hole, so it should be prepared 14–20 days before planting. The fact is that when the soil begins to settle, it injures the root system of the seedling, and will drag it away with it.
There are gardeners who recommend using an easier method of planting grape seedlings in open soil. For this you need a crowbar. It needs to be driven into the ground 50 cm deep, and then shaking it from side to side to widen the hole so that its diameter is about 10–12 centimeters. After that, it remains only to place a seedling in the resulting hole and bury it. However, this method is untested and does not give a 100% guarantee of the survival rate of the planting material, therefore it is up to you to use it for planting grapes or not.


Watch this video on YouTube
Grape care
Spring grape care
Taking care of grapes is difficult, but over time, as you gain experience, it will be much easier. Moreover, the reward for your labors will be a rich harvest of delicious fruits.
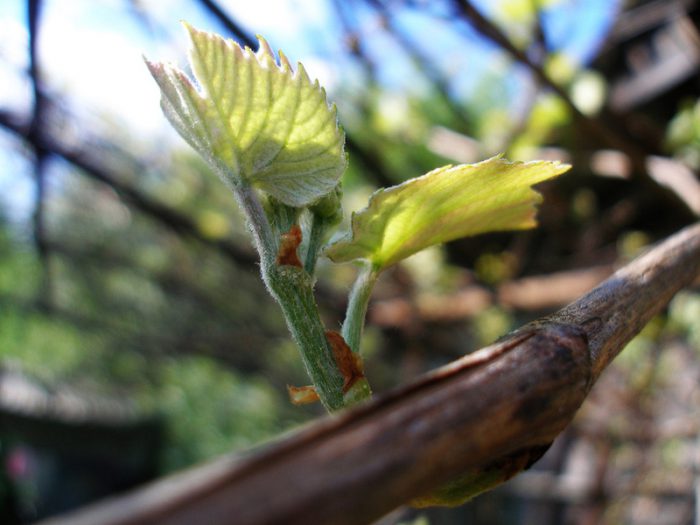
After the air temperature outside in the spring is above minus 5 degrees, it will be possible to remove the shelter from the grapes. In the event that there is a high probability of return frosts, then it is not necessary to completely remove the shelter, only several holes are made in it for ventilation. After the threat of frost is left behind, and bud germination begins, then the shelter must be removed.If you want to protect the plant from frost, then treat it with Epin dissolved in cold water. It will be necessary to spray the vine 1 or 2 days before frost, while it should be borne in mind that the protective effect of Epin lasts up to one and a half weeks.
In the event that a puddle has formed near the bush during the melting of the snow, then it is necessary to scoop it out, or you can make several grooves in the soil along which the liquid will drain itself. In order to avoid stagnant water near the bush, it should be planted on a slope or a mound of soil should be made for it. The grapes will need sanitary pruning, during which all injured and frost-damaged stems should be removed. Then you need to tie the vine to the lower wire in an inclined or vertical position. Next, a thorough examination of the plant is carried out, if any diseases are found, then you must definitely take all the necessary measures to treat it. In the event that the bush is absolutely healthy, then it will need to be sprayed with a solution of Nitrafen (200 grams of the product for 1 bucket of water), this will help protect the grapes from various diseases and pests.
Grapes, if desired, can be propagated by grafting and it is best to carry out this procedure in the spring before the sap flow begins. At the same time, a complex fertilizer should be added to the soil, which does not include trace elements (Kemiru or Nitrofosku). Then you need to dig up the soil in the near-stem circle and shed it in order to increase the temperature in the soil layers in which the plant's root system is located.
Spring is the time to plant new seedlings. At the same time, they begin to form the bushes. To do this, break off all unnecessary stems, and this procedure is repeated several times until the length of the required shoots is 0.4 m.All root shoots and extra buds should also be cut out. After 2 pairs of leaf plates grow on the pagons, the young bushes will need to be treated with a fungicide. In the first days of May, young shoots should be tied to the trellis. Top dressing of grapes with complex fertilizer is carried out 1.5 weeks before it blooms. After the appearance of inflorescences, their number must be normalized, this will avoid overloading the plant.


Watch this video on YouTube
Summer grape care
In the summer, special attention should be paid to the timely pinching of the vine, because it should not grow longer than 1.7 m. Until the middle of the summer period, such a vine needs to be fed 2 times. Also, in time, remove all stepchildren that form grapes so that he does not waste his energy on them, because he needs them for the formation of stems and ripening of fruits. In mid-July, it will be necessary to cut out those leaf plates that cover the berries from sunlight.
Every day it is necessary to inspect the bushes in order to timely detect pests or a developing disease. In the first summer weeks, for preventive purposes, the grapes should be sprayed with Ridomil to protect them from a disease called mildew, while a dose of Fufanon (a drug for spider mites) should be added to the solution prepared according to the instructions. Please note that you need to mix ready-made solutions. In the first days of July, you will need to spray the plant with this product again.


Watch this video on YouTube
Grape care in autumn
What is the maintenance of the grapes when all the fruits have been harvested? The most important thing to do in the fall is to prepare the plant for the coming winter. The liana at this time greatly weakens, because it spends a lot of energy on fruiting, in this regard, it must be fed with organic fertilizer, which is combined with wood ash. Also, the plant should be treated from pests and pathogenic microorganisms that can greatly harm weakened grapes.After all the leaf plates have fallen from the bush, it will be possible to proceed with the formative pruning. But at the same time, remember that it is impossible to delay this procedure too much, because during frost the wood will be extremely fragile and pruning the shoots at this time will cause serious harm to the vine.
If you are growing a variety with low winter hardiness, then such bushes must be covered for the winter. Without exception, all grape varieties will need shelter for the winter if such a plant is cultivated in a region with frosty winters. To do this, it is necessary to spud the base of the grapes with soil, and the vines should also be shortened so that they can be easily bent to the surface of the site. Spruce branches are used to shelter this culture. In the event that the winter is frosty, then the shelter must be covered from above with a layer of snow.
Treatment
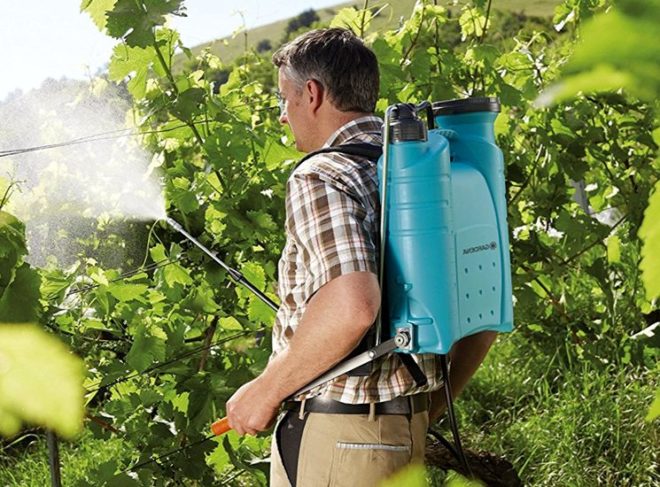
Many gardeners are sure that chemicals can restore health to all affected plant stems and branches, but this is a misconception. The fact is that any such drug can only destroy pathogenic microorganisms that are the cause of diseases, but it cannot heal the affected tissues. Therefore, the importance of preventive treatments for grapes can hardly be overestimated. They will be able to protect the plant from various dangerous pests and diseases. In the spring, after the length of the green shoots is 10 centimeters, the plant must be sprayed with a solution of colloidal sulfur (1%), Bordeaux liquid (3%) or copper oxychloride. This will improve the immune system of the grapes against felt mites and various fungi. In addition to these rather popular means among gardeners, you can use a solution of Ridomil (for 1 bucket of water from 50 to 60 grams) or Polychoma (for 1 bucket of water 80 grams). The prophylactic solution can be combined with a foliar application, such as Plantafol. Spraying grapes at this time is called "on the fifth leaf".
Then you will need to spray the plant before it blooms or over the buds. Remember that during flowering, all treatments are strictly prohibited. For this spraying, you should take a systemic fungicide, for example, Strobi. When the grapes have faded, they will need to be sprayed with a systemic fungicide again. After the berries are similar in size to peas, the bushes will need to be sprayed with one of those preparations that were used in the spring, namely: copper chloride, Bordeaux liquid, colloidal sulfur, Ridomil or Polychom. The last time in the season to spray the vine against oidium and mildew should be at the end of July, while it is necessary to use means of a short waiting period, for example: Tiovit Jet and Quadris or Tiovit Jet and Strobi, or colloidal sulfur and Strobi.
This treatment scheme is approximate. Remember, that pathogens and pests cannot develop resistance to a particular drug, they must be replaced every year.


Watch this video on YouTube
Watering the grapes
For the first time in a season, water the plant immediately after the winter shelter is removed, and the vine is tied to the lower horizontal guide of the trellis. Young plants (up to 3 years old) should be watered through a dug-in plastic pipe. For 1 vine, 40 liters of lukewarm water mixed with 0.5 liters of wood ash is taken. The second watering is carried out 7 days before flowering, and the third - when the plant fades. After the green fruits begin to change their color to the color characteristic of the variety, you should stop watering the grapes. However, 7 days before the plant is sheltered for the winter, it will need a sub-winter water-charging watering. Young specimens of wine varieties and table varieties must be watered 4 times per season. Ripe specimens of wine grapes need to be watered only 1 time for the whole season, and this watering will be water-charging in winter.
Top dressing of grapes
If during the planting of the seedling all the necessary fertilizers were introduced into the soil, then their grapes should be enough for 3-4 years. Most often, by this time, the vine has already fully formed and begins to bear fruit, in this regard, it will need additional nutrients. What do experts advise to use for feeding this plant so that it develops better and gives a rich harvest? For fertilizing, both mineral and organic fertilizers are used. Most often, manure is used as organic matter, since it contains all the nutrients that such a vine needs. If desired, manure can be replaced with compost, bird droppings or peat. Grapes also need mineral fertilizers. It is fed with such simple nitrogen-containing fertilizers as urea or ammonium nitrate. A simple or double granular superphosphate is used as a phosphorus-containing fertilizer. From potash fertilizers, potash salt, Ecoplant, sulfate or potassium chloride are recommended. The following complex mineral fertilizers are best suited for such a plant: Florovit, Master, Solution or Kemira.
The first time you need to feed the plant with dry fertilizer is after the winter shelter has been removed. To do this, use a nutrient mixture consisting of 45 grams of nitrogen and 30 grams of potash fertilizer, as well as 40 grams of superphosphate (calculated for 1 bush). A groove is made around the plant, into which the nutrient mixture is poured, then it is covered with a layer of soil.
For the second time in a season, the grapes need to be fed 7-10 days before they bloom, for this they use an aqueous solution. To prepare it, you need to combine 10 liters of chicken manure or slurry and 20 liters of water. The container with the mixture is tightly closed, it will be ready after it has been fermenting for 10-12 days. Then the mixture is diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 5 or 1: 6. In 10 liters of the finished solution, add 25 grams of superphosphate and 15 grams of potassium fertilizer. For 1 bush, 10 liters of ready-made nutrient mixture is taken.
When the berries are just starting to ripen, the vines should be fed with superphosphate (50 grams per bush) and potassium fertilizer (20 grams per bush).
Also, foliar dressing has a positive effect on the growth and development of the plant; it is recommended to carry them out in conjunction with spraying the bushes with a fungicide against mildew disease. The nutrient mixture used for this type of feeding may contain both basic nutrients (phosphorus, nitrogen and potassium) and additional elements that grapes need, namely: zinc, copper, manganese, boron, molybdenum and cobalt. Experienced gardeners recommend choosing ready-made preparations for such dressings, for example: Novofert, Plantafol, Kemira or Aquarin.
Nitrogen-containing fertilizers, as well as mullein and poultry droppings, grapes can be fed only until the middle of the summer period. Otherwise, it may delay the ripening of the fruit. And remember to feed the grapes in moderation. An overfed plant will not bear fruit.


Watch this video on YouTube
Tying grapes
By tying this liana to the support, you can form a bush that will be very easy to care for. In the event that the garter is not produced, the grapes will begin to cling to the supports that are in its path, in this case you will no longer be able to control its growth, the collection of fruits will be much more difficult, while their quantity and quality may disappoint the gardener.
Such a plant should be tied up in 2 stages:
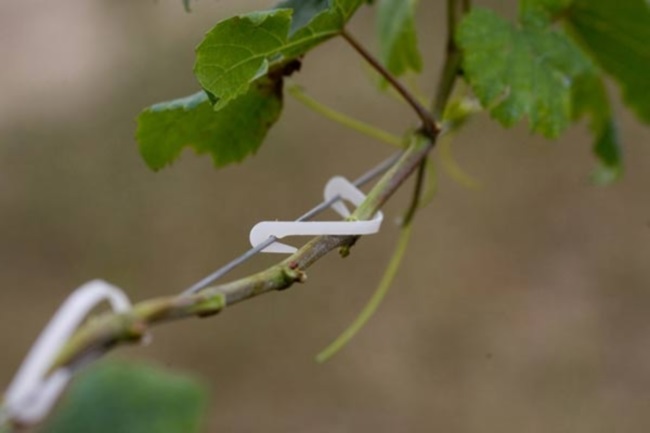
- A dry garter is produced at the beginning of the spring period, after removing the winter shelter, but before the buds open. To do this, you need to bend all the existing branches to the lower horizontal guide of the trellis and tie them to it. Try to keep the branches to be tied bent smoothly, in this case the conducting system will not be disturbed, and the necessary nutrients will be supplied to the eyes.
- A green garter is produced after the green shoots begin to grow, and their length will be at least 0.4 m. Young shoots should be gartered at an angle, in this case they will be evenly lit and will not break from gusts of wind. After the shoots grow to the next horizontal guide, they will need to be tied to it. During the growing season, young stems will need to be tied to the support 3 or 4 times. Green shoots are not tied for the upper internode. Try to pull them with a wire between the third and second buds from the end of the stem.
Experts advise using a horizontal tilting method for tying vines, because it is very convenient. However, there are growers who prefer a garter with a ring, an arc or strictly vertical. For the garter, it is recommended to use a washcloth soaked in water or a special rope (wire wrapped in paper). To prevent the abrasion of the shoots on the wire, it is necessary to fix the rope or a washcloth with a "eight", for this they are passed between the metal and the stem.


Watch this video on YouTube
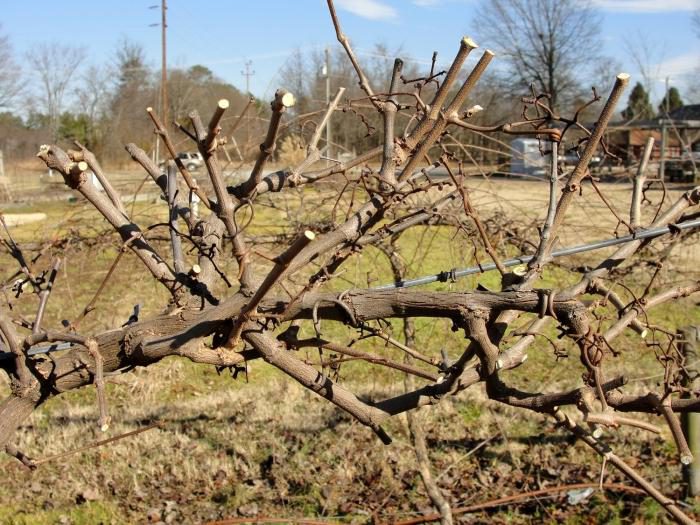
Pruning grapes
The grapes are pruned in autumn. The fact is that if this procedure is carried out in the spring, then the wounds will heal for a long time, flowing "tears". If the eyes are flooded with soda, this will lead to their acidification and death. It can even lead to the death of an entire bush.


Watch this video on YouTube
Pruning grapes in spring
In early spring, this vine is pruned only when absolutely necessary and only after the air warms up to 5 degrees. In this case, the injured or diseased branches should be removed on young bushes or bushes planted in the autumn.
Summer pruning
In the summer, as such, pruning is not carried out. At this time, pinching, pinching, minting of grapes, as well as breaking out excess branches and removing foliage, which obscures the berries from the sun, are performed. All these procedures are necessary in order to improve the ventilation of the plant, as well as to evenly distribute lighting and nutrition. And the main goal of such procedures is a rich harvest.
Pruning grapes in autumn
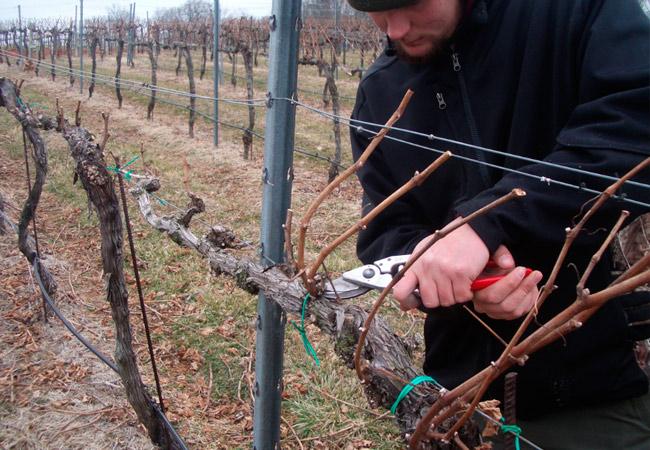
In autumn, the plant is pruned in 2 stages. After the bushes are freed from fruits, it is necessary to clean the branches from the fruiting links, as well as from tops and weak shoots. Half a month after the leaf fall ends, it is necessary to proceed to the second stage of pruning. Do not worry that the branches will be damaged by frost. The fact is that the first frost will only temper the grapes. But it should be borne in mind that pruning can be carried out at an air temperature of at least minus 3 degrees, otherwise the stems will be too fragile.
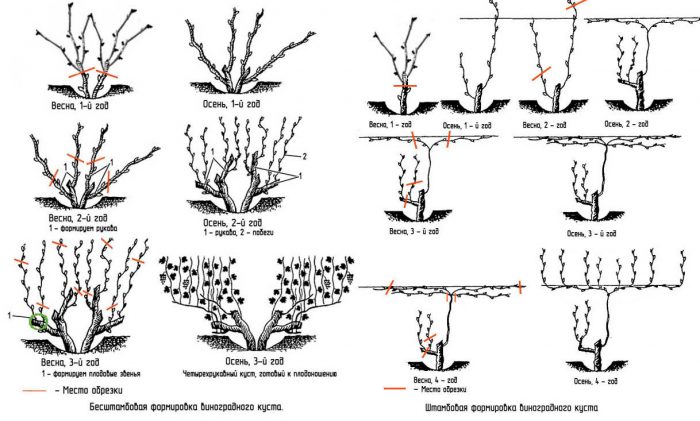
Pruning a seedling is easy enough. To do this, you need to cut off all the extra stems, while on the bush there should be 3–8 sleeves that grow at an angle from the ground.
Pruning adult grapes is more difficult:
- From the beginning to mid-September, all young stems should be cut from the bottom of the perennial sleeves. In this case, it is necessary to cut out those of them that are located below the first wire, which is located at a height of 0.5 m from the ground surface. Then, young stems are trimmed that have grown on the sleeve above the second wire, located at a height of 0.8 m from the surface of the site. All the side stepsons must be cut off from them, and the tops must be minted, while it is necessary to capture segments, the length of which is 10 percent of the length of the entire stem.
- When the leaf fall is over, you will need to select 2 developed stems located at the height of the first 2 wires. It will be necessary to form the replacement knot from the lower stem, which has grown from the outer part of the sleeve. To do this, this shoot must be cut to a height of 3 or 4 eyes.Then a fruit arrow is formed, for this the second stem, which is slightly higher than the first one on the opposite side of the sleeve, must be cut to a height of 7 to 12 eyes.
As a result, the bush will contain only perennial stems that grow perpendicular to the soil, as well as sleeves with buds, it is they who will give young brushes and vines next year.


Watch this video on YouTube
Propagation of grapes
It is quite possible to grow grapes from seeds, but the seedlings obtained in this way retain only part of the varietal characteristics of the mother plant. In this regard, for the reproduction of this plant, it is recommended to resort to vegetative methods: grafting, layering and cuttings. These methods will allow the plants to preserve all the varietal characteristics of the parent bush. An important component of the biological complex of such a plant is its ability to regenerate, which allows the plant to recover after freezing, severe injury, and it is also necessary for the healing of wounds.
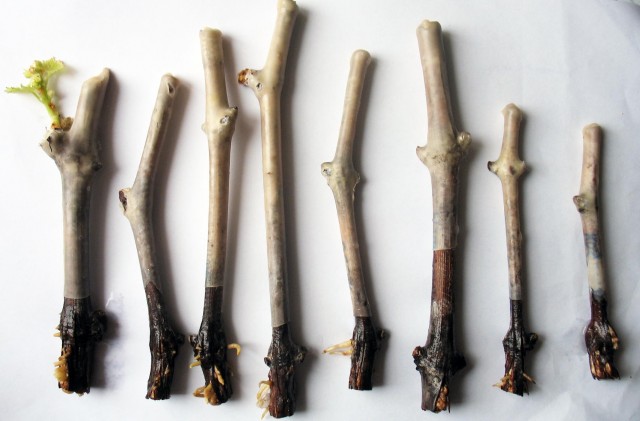
Propagation of grapes by cuttings
The easiest and fastest way to propagate grapes is cuttings. In the fall, when pruning plants, you should harvest lignified cuttings. To do this, use a ripe vine, which should not be thinner than a pencil. At the same time, internodes should be evenly distributed along its entire length, and also there should be 2 or 3 eyes on it. Please note that longer shanks are stored much better. The lower cut must be made at an angle of 45 degrees, while 30–40 mm must be retreated from the kidney downward. It is best to store such cuttings in a room with high humidity and an air temperature of 0-5 degrees. So, the best place to store them is a potato storage. Cut cuttings cannot be kept in the sun for a long time. Make a solution of ferrous sulfate (1%) and immerse the cuttings in it for 5-10 minutes. Wait until the surface of the cuttings is dry, and then wrap them in a paper sheet, fold them into a plastic bag and store them.
In the last days of February or the first days of March, deep rest in the cuttings ends, and it is replaced by a state of forced dormancy. At this time, it is recommended to start rooting the cuttings. The removed cuttings will need a thorough inspection. The brown bark should not have any specks or mold. And the peephole and the cut of the cutting should be painted in a deep green color. The shanks selected for rooting should be immersed in a solution of light pink potassium manganese for a few minutes. Then they are placed in a glass jar, which should be filled with clean water to a height of 50–60 mm, while it is mixed with one drop of honey. A plastic bag must be put on the shanks. When the cuttings are saturated with liquid, a lower cut should be made on each of them, which should be located under the lower node.
For rooting, cuttings are planted in plastic cups, which must be filled with a mixture of humus, sand and peat (1: 1: 1). It is necessary to make a depression of 50-60 mm in the substrate, then a pillow should be made at its bottom by pouring a small amount of sand, then a cutting is placed in it, and the resulting void is covered with sand. The upper cut of the shank should be coated with garden varnish, the upper bud should be only slightly covered with sand, and the lower cut should be 5–7 centimeters higher than the bottom of the glass. In order for the cuttings to give roots as soon as possible, it is necessary that their upper part be at a temperature of 15 to 18 degrees, while the lower one should be warm (from 23 to 28 degrees). To do this, the cups with cuttings must be placed on a pallet; they need bottom heating for 4 weeks. At this time, it will be necessary to water the cuttings, if necessary, using lukewarm water for this, the surface of the substrate is gently loosened, the excess stems are pinched, while all the growing inflorescences must be removed.Then the plants will need hardening, for this they begin to be transferred daily to the terrace or balcony in the last days of April or the first - in May. Hardened cuttings can be planted in open soil.


Watch this video on YouTube
Propagation of grapes by grafting
To carry out the grafting, you will need a graft - this is a stalk of a cultivar that has only 1 bud, as well as a stock - this stalk must be taken from a variety that is resistant to phylloxera, while it must be 50 cm long. thicker than a pencil. In this case, the stock must be necessarily thicker than the scion. Cuttings are harvested in autumn days during pruning, while on all cuttings there should be at least 3-4 eyes. They should be saved until spring, as described in detail above. In autumn, you should also start preparing the stock bush. To do this, it is necessary to remove all unnecessary from it, only the vine for grafting should remain, then the bushes must be provided with a good shelter for the winter.
The vaccination itself should be carried out before the sap flow begins, while choosing a cloudy, windless day, because in order for the vaccination site to grow together, high humidity will be needed. This procedure can also be carried out in the summer. From storage placed there in the fall, cuttings must be removed in June. Refresh their lower cuts, which are immersed in a container with a little water (at the bottom). After the buds swell on them, the containers are moved to the refrigerator shelf, where the cuttings can be hardened. After a few days, remove the cuttings from the refrigerator and graft them to the stock. The rootstock bushes during the summer procedure must be cut off in the spring on last year's vine, it is on it that the cutting will be grafted. During the summer grafting, tissue fusion is noticeable better, because the rate of sap flow in the scion and rootstock is significantly different. You can vaccinate at an outdoor temperature of 15 to 35 degrees.
New cells begin to appear between the two parts, as a result of which they grow together. Take the scion, expanding it with the place of future vaccination from yourself, then you should trim it just above the upper bud. Then step back from this kidney down 40-50 mm, then make an incision on the handle on both sides in the direction away from you with a sharp wedge by 20-30 mm. At the same time, keep in mind that if the wedge is concave, then the stock and the scion will not grow together. To prevent the shank from drying out, wrap it with a damp cloth. Step back on the rootstock from the last bud upwards 40-50 mm and cut. The cut should follow the larger oval of the vine cut. The cut should be the same depth as the cutting wedge. A scion wedge should be placed in the rootstock cut so that their buds are directed in different directions. The vaccination site must be wrapped with an eyelid film, tape or electrical tape. After the start of sap flow, this place should be wrapped with a newspaper sheet or other material that does not allow light to pass through.
If the grafting is carried out in the summer, then after installing the scion wedge in the rootstock, the fusion should be wrapped with a damp cloth. Put on a polyethylene bag on top of the plant and fix it below the vaccination site. Then it should be wrapped in a thick paper sheet that protects the plant from direct sunlight. In the event that the appearance of condensation on the inner surface of the bag stops, then it should be removed. The tissue must be moistened again with water, then the bag is returned to its original place, fixing it below the vaccination site. After the grafting bud has opened, the paper should be removed. Then the bag is trimmed over the inoculation. The same package must be fixed on the handle above the graft site. After the formation of powerful stems on the scion, the package and tissue must be removed from the plant.During the first 12 months, be extremely careful with the grafted plant, as it can be broken very easily.


Watch this video on YouTube
Secrets of a successful vaccination:
- For the rootstock, you must choose a frost-resistant hybrid that is resistant to powdery mildew, mildew and phylloxera.
- Scion and rootstock varieties must have the same vigor.
- The cutting tool must be very sharp and well sanitized.
- The rootstock vine is pruned strictly perpendicular to the growth line.
- How to propagate by layering
Reproduction by layering is carried out in spring and autumn. To begin with, a deep (about 0.5 m) groove should be made in the soil near the bush, into which black earth is introduced, combined with humus. After that, a one-year low-growing shoot fits into it, and the groove must be filled with soil. In this case, the top with three leaf plates and a growth point should remain on the surface. The layering will need to be watered and for this they take 20 liters of water. During spring and summer, make sure that the ground above the cut is always slightly damp. In this case, each node will grow along a shoot with its own root system. This propagation method is often used to replace an old plant with a young one.
Diseases of grapes with photos
If you decide to grow grapes, then you should be prepared to fight many different diseases. And even if you strictly adhere to all the rules of agricultural technology, this will not guarantee that the vine will not get sick. Below will be described the diseases that growers encounter most often.
Anthracnose
In a bush infected with such a disease, inflorescences, berries, leaf plates and stems are damaged. On the affected grapes, specks of brown color are formed, which have a border of a lighter shade, over time they combine with each other. In these places, tissue death and loss occurs. On the surface of the stems, specks of a dark brown hue are first formed, after which pinkish-gray oval-shaped spots appear, which can spread to the entire internode. In these places, tissue cracking and ulcers appear. The inflorescences become dark and gradually dry out, and specks appear on the fruits. To cure the affected bush, it should be sprayed with a systemic and contact fungicidal agent, for example: Ridomil, Horus, Acrobat, Bordeaux mixture, Thanos or Antracol. In the event that in your region plants very often fall ill with such a disease, then experts recommend choosing grape varieties for growing that are resistant to anthracnose.
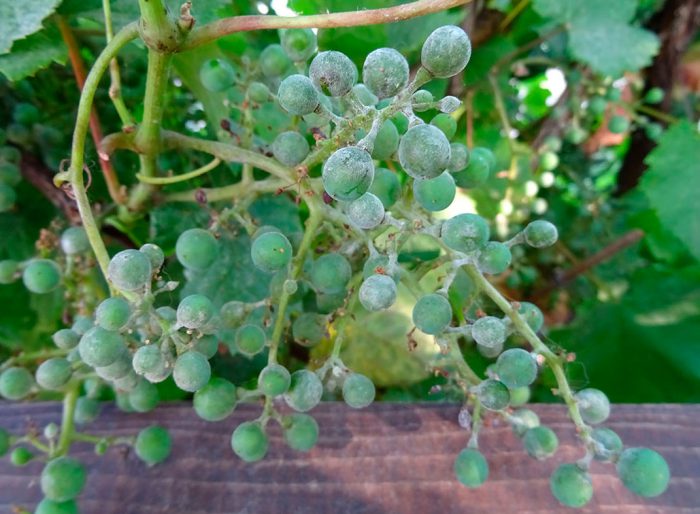
Oidium
This fungal disease is grape powdery mildew. A white-gray powdery bloom appears on the surface of the affected bush. As the disease progresses, the inflorescences begin to fall off, the leaf plates will become curly, and the fruits will burst or dry out. Most often, grapes get sick with this disease in damp and warm weather. There is a high probability of infection in highly leafy specimens that do not have very good ventilation. For the purpose of prevention, do not allow the bush to thicken, for this you need to tie up the branches, break out excess stems, and pull out weeds in time. You can spray grapes with Horus, Topaz, Thanos, Strobi or Tiovit.
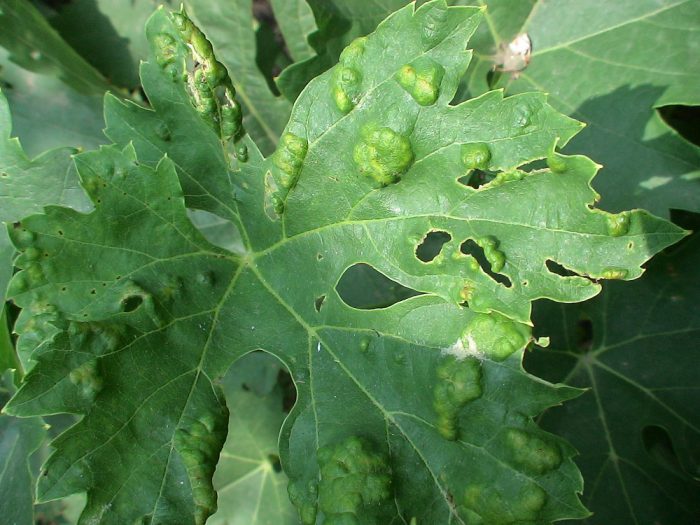
Downy mildew (mildew)
This fungal disease most often affects grapes, while it is also very dangerous. The disease affects all green parts of the bush. You can find out that grapes are affected by mildew by looking at the oily specks on the front surface of the leaf plate. In rainy weather, a powdery bloom of a light shade appears on the seamy surface of the leaf plate, and then necrosis forms in its place. So, at first, the affected tissue becomes yellow, then it has a brownish-red tint, and then dying off areas are formed.Affected leaf plates die off, as a result of which the stems are exposed, and the inflorescences are covered with a bloom of white. Flowers and buds dry out and die off. If you decide to start growing grapes, then the variety you choose must be highly resistant to fungal diseases. For prevention purposes, mulch the surface of the trunk circle, feed the plant with potassium and phosphorus in time, cut off the stepsons. Spray the bushes with fungicides. The first spraying is carried out at a time when the length of young shoots reaches 15–20 centimeters, the second - before the plant blooms, the third - when the fruits are similar in size to peas. The grapes should be sprayed with Cuproxat, Thanos, Ridomil, Strobi, Antracol, Horus, copper oxychloride and Bordeaux mixture.
Gray rot
All green parts of the bush and annual wood, as well as grafting sites, are affected by this disease. A plaque appears on the surface of the opening eyes and young shoots. Fruits affected by such rot are covered with a dense bloom of gray, while the clusters become like mushy lumps. Dampness is necessary for the development of such a disease. With the onset of dry weather, the symptoms of the disease can almost completely disappear, however, pathogens will remain on the bush. The affected bush should be sprayed with the same fungicide that is used for grape disease with mildew or powdery mildew.
Black spot (phomopsis, death of shoots or escoriasis)
This harmful disease can harm both the green and lignified parts of the bush. Because of it, the bark loses its color. If the temperature rises above 10 degrees, then pycnidia of the fungus will appear on these discolored areas. In the event that the fungus penetrates deep enough into the wood, this will lead to the appearance of rotten areas. At first, the growth of the sleeve will slow down, and then it will die. On leaf plates, necrotic spots have a border that is denser and lighter than leaf tissue. The affected foliage turns yellow, the diseased bush stops developing, it rots and dries up. Since the mycelium of the fungus is able to penetrate into the deep layers of the wood, spraying the bush with a fungicidal agent will be ineffective. In this regard, one should deal with the spores and bodies of the fungus. So, in the autumn, when the leaf fall ends, and the plant is cut off, it should be sprayed with a agent containing copper, for example: Bordeaux liquid, Horus, copper oxychloride or Cuproxat. Remove any sleeves that have started to dry out. When 2 or 3 leaf plates appear in the spring, the bush should be sprayed with a fungicide. The following prophylactic treatments for grapes from this disease will be carried out at the same time with spraying the plant from oidium and mildew. Remember that it is not so easy to get rid of such spotting, and you will have to fight it for several years.
In addition to those diseases that were listed above, grapes can suffer from alternaria, bacterial cancer, apoplexy, verticillosis, armillariasis, white, black, sour and root rot, diplodiosis, various kinds of necrosis, fusarium, penicillosis, bacteriosis, cercosporiosis, chlorosis, etc. It should be borne in mind that some diseases are incurable. If the grapes are well-groomed and strong, then it will be extremely rare to be affected by various diseases.


Watch this video on YouTube
Pests of grapes with a photo
Grape bushes can damage a variety of pests, for example: grape flea, grape miner moth, grape cushion, grape gnat, gray and black beet weevils and large alfalfa, goldweed, odorous woodworm, grape spiderweb, grape felt and European red mites, grape itch , biennial and grape rolls, wasps, grape thrips, mealy and Comstock bugs, cicadas and phylloxera, etc.
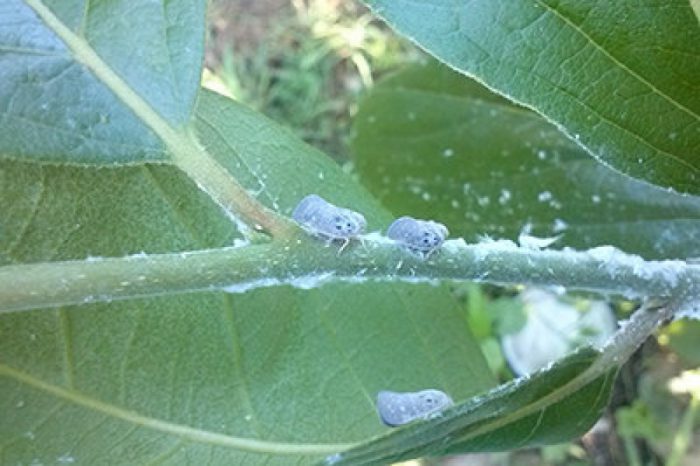
Phyloxera, or grape aphid
The greatest danger to the plant is represented by phylloxera (grape aphid). They have two forms: root and leaf (gallic). The spread of such a pest occurs with water used for irrigation, with planting material and with the wind (over a distance of about 15 kilometers). Due to the root form of such a pest, the bushes die, because punctures in the root system become infected and gradually destroyed. You should know that the fight against such a pest is not easy. Previously, the soil was treated with fumigants, but at the moment, gardeners have abandoned this method of struggle. To get rid of the leafy form of this pest, the bush is sprayed with Zolon, Confidor, Aktellik or another means of a similar action. You cannot get rid of the root form, therefore it is recommended to choose varieties that are resistant to it for growing.
Caterpillars of leaf rollers
The caterpillars of leaf rollers can damage the buds, leaf plates and berries of the plant. In some cases, they destroy about 80 percent of the fruit, as they are very voracious and prolific. When the winter shelter is removed from the grapes, it should be sprayed with Nitrafen solution (0.25 kg for 1 bucket of water). After the beginning of summer of butterflies, plants need to be sprayed with any insecticidal agent (for example: Karbofos or Aktellik), after half a month the bush is re-treated. When the caterpillars themselves appear, the grapes must be treated with a solution of Benzophosphate (6%) or Karbofos (10%).
Cicadas
Sucking pests such as cicadas are polyphagous. They multiply incredibly quickly. These pests carry viral and mycoplasma diseases that are incurable. If such pests were noticed on the plant, then it must be sprayed with Aktara's solution.
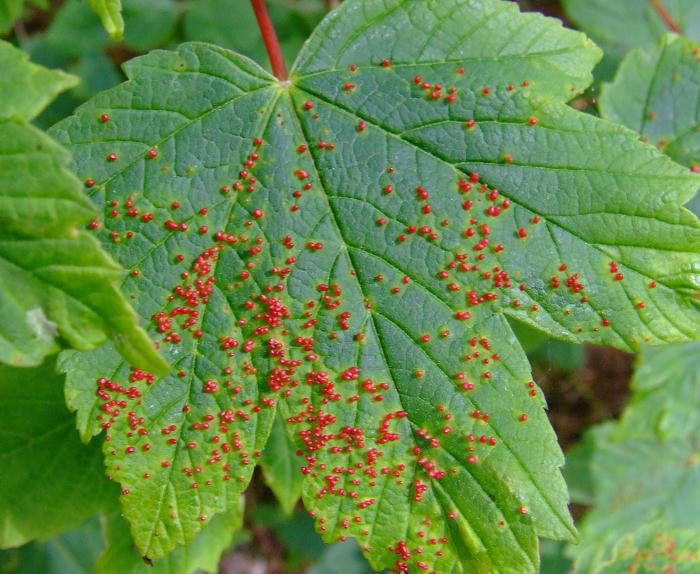
Mites
Mites that suck pests prefer to live on the seamy surface of the leaf plate. By puncturing the leaf, they suck out the juice and eat the tissue. Small spots appear in such places, after a while they begin to dry out. Within one season, up to 12 changes of tick generations occur. The affected plant must be treated with acaricide, for example: Fufanon, Omayt, Aktellik, Neoron, etc. You need to make 3 sprays with an interval of 1–1.5 weeks.
Zlatka
Zlatka is a grape beetle of green-olive color, reaching 2 cm in length. Because of the beetle, deformation of the leaf plates occurs, while its legless larva gnaws through winding passages in the stems, where it hibernates. At the affected bush, the leaf plates dry up, the stems wither, and the fruits become smaller. Affected leaf plates and stems must be cut out. The bush itself is sprayed with Aktellik or Karbofos. With timely preventive spraying from pests, such an insect will not settle on the bush, since it chooses weakened specimens.
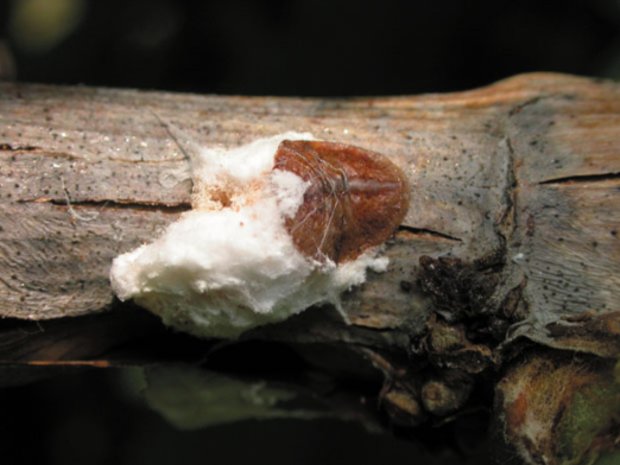
Pillowcase
The cushion is a sedentary sucking parasite belonging to the family of false scutes. It sucks the sap from the plant and is a carrier of viral diseases. Such a pest settles on stems and leaf plates. Having attached to the chosen place, he will remain there until his death. Such a pest produces a substance that protects it from the action of even strong drugs. In the spring, before the leaves open, the bushes must be sprayed with Preparation 30 or Nitrafen. During the growing season, process the grapes with BI-58. Try to remove insects by hand using a stiff glove to protect your hand.


Watch this video on YouTube
Types and varieties of grapes with photos and names
According to the ripening time, all varieties of such a plant are divided into super-early, early, early-medium, medium, mid-late, late and very late. And according to their purpose, they are divided into technical, canteen and universal. Table varieties are of the highest quality, their fruits are very beautiful and tasty. They are usually used for fresh food. The fruits of industrial varieties are used for the preparation of wines and juices.The versatile varieties can be eaten fresh and processed.
To date, mainly only varieties are grown that are hybrids of 3 species: Labrusca (homeland America), Amur (homeland of the Far East) and wine cultivated (growing in Europe and Asia). All varieties are conventionally divided into 3 groups:
- Eurasian varieties... The berries are the largest and most delicious. The best are Central Asian varieties, for example, Ladies' fingers and Husayne. However, these varieties have a number of disadvantages: low resistance to frost, susceptibility to phylloxera and fungi, and a long growing season. European varieties are more resistant to frost, but their fruits are not as tasty and attractive.
- American varieties... They are fast growing, drought, frost and phylloxera resistant. But the fruits are quite small, and they have Isabella's "fox taste". However, the Labrusca Isabella and Lydia hybrids are quite popular, as they are unpretentious and winter hardiness.
- Amur varieties... They are distinguished by high winter hardiness, they are able to withstand a temperature drop down to minus 42 degrees. They do not have the flavor that American varieties have and have a short growing season. The disadvantages of such varieties are demanding for watering and susceptibility to phylloxera.


Watch this video on YouTube
The most popular varieties:
- Cabernet Sauvignon (Lafite)... A technical French variety with a relative resistance to frost, but high - to gray rot, mildew and grape leafworm. High quality table and dessert red wines are made from the fruits. The fruits have a nightshade flavor.
- Aligote... A white grape variety from France, it is relatively frost resistant. Susceptible to diseases such as mildew, gray rot and powdery mildew. High quality wines and juices are prepared from the fruits.
- Flame Tokai (Cardinal)... This table variety belongs to the American group. Oval fruits are large purple-red, their flesh is fleshy, juicy and crispy, has a subtle nutmeg smell. Low resistance to frost. It is susceptible to disease with mildew, oidium and gray rot, the grape leafworm often settles.


- Hope (Dream)... This table variety from Ukraine is seedless, it was obtained as a result of crossing the Central Asian varieties Chaush Pink and Kishmish black. Medium oval fruits of pink-green color are covered with thin skin. The pulp is fleshy, juicy and quite tasty. This variety has low winter hardiness, and it is also prone to mildew and mildew disease.
- Muscat Ottonel... A versatile variety from France. Medium fruits are round, yellow-green in color, covered with firm skin. The fleshy flesh has a pungent nutmeg odor. The fruits are eaten fresh, and they are also used for preparing semi-sweet and blended wines, juices. Medium frost resistance. Susceptible to diseases of gray mold, oidium and mildew.
- Isabel... This grape is a hybrid of varieties such as Vitis Vinifera and Vitis Labrusca, which are native to North America. The berries are eaten fresh and made into juices and wines. Medium-sized, rounded, almost black fruits with a firm skin. The slimy pulp has a strong strawberry aroma.
Also popular are such varieties as: Agdai, Italy, White Kokur, Queen of Vineyards, Beauty Cegleda, Merlot, Moldova, White Muscat, Alexandria, Amber, Hamburg, and Yerevan, Odessa souvenir, Pinot noir, Riesling, Rkatsiteli, Green Sauvignon, Feteasca white, Chardonnay, etc.


Watch this video on YouTube