The phalinopsis orchid (Phalaenopsis) is a herbaceous plant of the Vendian tribe of the Orchid family. Her homeland is the humid forests of Southeast Asia, Australia and the Philippines. Most of these orchids are epiphytes, as they grow on trees, but in some cases they can be found growing on rocks. Georg Rumph, a German naturalist, was the first to find such a plant while on one of the Moluccas. Karl Blum, director of the Leiden Botanical Garden, called this orchid phalaenopsis, once he examined this plant through binoculars and decided that its flowers are real butterflies, and phalaenopsis just means "like a moth." Today this flower is sometimes referred to as “butterfly orchids”. This genus unites about 70 species. Such a plant is very popular with flower growers, because it is distinguished by its sophistication and showiness, and this is also due to the fact that this orchid is relatively easy to care for.
Content
Brief description of cultivation
- Bloom... Can bloom at any time, flowering time 2-6 months.
- Illumination... Needs diffused bright light (east, west and north-east windows are suitable) or a little partial shade.
- Temperature... The maximum allowable temperature is about 42 degrees, and the minimum is 12 degrees. And the flower is comfortable at a temperature of 15 to 25 degrees.
- Watering... This procedure is carried out after the substrate in the pot is completely dry.
- Air humidity... From 30 to 40 percent, while the room should be well ventilated.
- Fertilizer... 1 time a week with a solution of complete mineral fertilizer.
- Dormant period... Not very pronounced.
- Transfer... When the soil mixture turns sour and cakes, as a rule, once every 2–4 years.
- Reproduction... Vegetatively (side shoots).
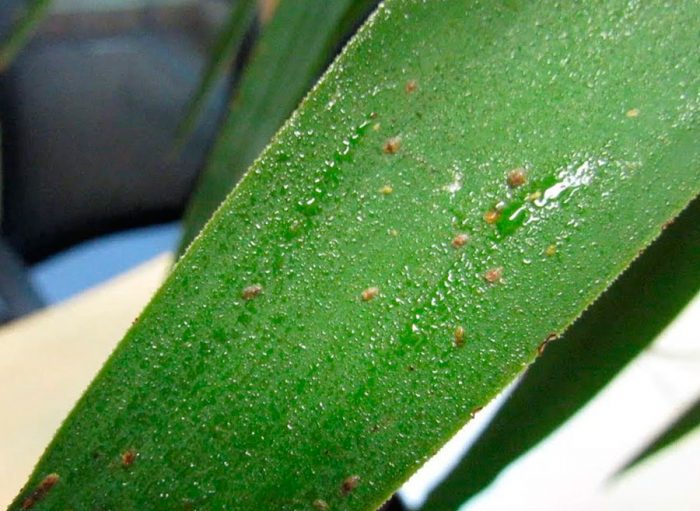
- Harmful insects... Mealybugs, spider mites, thrips, scale insects, slugs.
- Diseases... Fusarium, rust, anthracnose, blotches, black, brown, gray and root rot.
Features of the phalaenopsis orchid
To grow the Phalaenopsis orchid in indoor conditions, you need to know some features, because such a plant is unusual to middle latitudes.In the wild, such a flower prefers to grow in humid plain and mountain forests, while it grows on trees, in this regard, it needs a special microclimate, and it will need to be created artificially in the room. The most important features of such an orchid:
- The substrate and container in which the orchid is located is needed only for support.
- The root system needs to be exposed to air and needs light.
- The roots of such a plant are green, in the wild they extract rainwater and moisture from the atmosphere, and they take nutrients from the tree bark. They are directly involved in photosynthesis, and therefore they need a sufficient amount of light.
- Such a plant also has aerial roots, they branch out and seek nutrients. In this regard, it is necessary to constantly monitor so that they do not fall into a nearby flower pot.
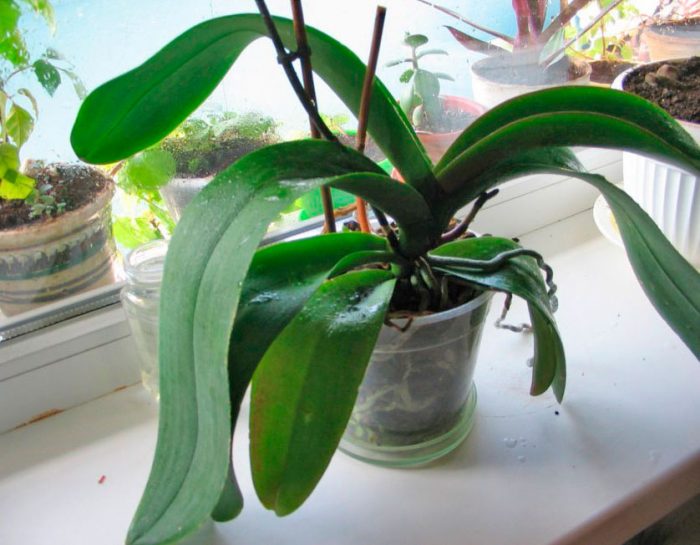
The root rosette consists of juicy leaf plates arranged in two rows. The curved peduncles are quite long. The racemose inflorescences are composed of butterfly flowers. Flowers can be painted in a variety of colors, for example: lilac, yellow, red, purple, white, green, brown, etc. Often the lip of the flower is clearly visible against the background of tiger, striped, monochromatic or mesh petals, as it has a contrasting color ... This type of orchid is monopodial, which means that it does not form a bulb. Such a flower does not differ in a pronounced dormant period. They bloom twice a year (in spring and autumn), but with very good care they can bloom 3 times in 1 year.
Caring for the phalaenopsis orchid at home
To grow a phalaenopsis orchid in indoor conditions, you need to find the most suitable place for it, choose the right mode of feeding, watering and temperature, and you also need to protect the flower from various diseases and harmful insects.
Illumination
To place a flower pot, it is recommended to choose an east, west or northeast orientation window. In the event that it needs to be placed on a windowsill located in the southern part of the room, then the pot is placed on a table that stands near a window closed with a curtain, due to which a slight shading is created. If the direct rays of the sun fall on the phalaenopsis, then burns will appear on the surface of the flowers and foliage, which are outwardly similar to spots. To prevent the bush from growing tilted to one side, it should be turned 180 degrees every 15–20 days. However, during the formation of buds, the bush does not need to be disturbed.
Temperature regime
The plant blooms in a shaded place at a temperature of 18 to 25 degrees, while the bush can stand for a short time in the heat (up to 42 degrees) or in the cool (at least 12 degrees). However, this should not be abused, it is better if the bush is at a temperature favorable for it (from 15 to 25 degrees).
Air humidity
The humidity should not be too high (30 to 40 percent), while the room should be well ventilated. If the humidity is lower, the foliage will lose its turgor, and the flowers will begin to fly around. To prevent this, the orchid pot must be placed on a tray filled with moistened pebbles. With excessively high humidity, rot may appear on the roots, and specks on the foliage. Experts do not advise moistening the orchid from the sprayer even in very intense heat, since the liquid flows into the leaf sinuses and into the core, and because of this, rot may appear on it. And even when liquid evaporates from the surface of the bush, burns can form on it.
Fertilizer
The plant should be fed during watering, while the complete complex fertilizer Kemira-Lux is added to the liquid (1 gram per liter of water). The frequency of dressings is 1 time per fortnight. Top dressing can be carried out once every 7 days, but in this case, the concentration of the nutrient mixture should be less weak. It is imperative to feed the plant after watering.
Watering rules
It is necessary to water the flower only after the substrate is completely dry, but it should not be dry for a long time. When growing a plant in a transparent pot, the disappearance of moisture from the walls is a signal for watering. If the plant does not have enough water, then the color of the green roots becomes paler. In the event that the pot is opaque, it will be necessary to rake out the soil mixture to check how dry it is. During watering, it is impossible for water to fall on the foliage, so it must be poured directly into the soil mixture or use the bottom irrigation method, for this the pot is immersed in a container filled with water, while the substrate must be saturated with liquid through the holes intended for drainage.
Irrigation water should be soft and clean, it should be passed through a filter and then boiled. Distilled water is also suitable for this purpose. Once every 4 weeks, the plant will need to take a shower, or it can be rinsed under the tap instead. Then the bush is wiped very well. It is impossible to overmoisten the flower, as its foliage will begin to fade, while the growth point is likely to rot. This can lead to regrowth of a lateral shoot, but in the worst case it will lead to the death of the bush.
Transfer
When is such an orchid transplanted? This is done if it has been growing in the same soil mixture and container for 2 or 3 years. As a rule, during this time, the soil mixture is caking, its souring, as a result, it becomes unsuitable for growing, so the substrate must be replaced. Another transplant may be required in the event that the root system begins to branch very strongly and grows through the drainage holes. This procedure is carried out when the bush has faded.
If the phalaenopsis is completely healthy and is grown in a coarse substrate, then it is carefully transferred into a larger new pot, at the bottom of which there is a good drainage layer. The voids in the pot are filled with a new substrate, while it should include the bark of the medium and fine fractions, and sphagnum should also be added to it. The store has a ready-made substrate for orchids, but you can do it yourself, for this, a good drainage layer is made at the bottom of the container from small pieces of foam or expanded clay, then the bark of the middle fraction is poured, and then the fine fraction, which must be combined with crushed sphagnum ... It should be borne in mind that while the bark is dry, it passes liquid relatively quickly. In this regard, before starting the preparation of the substrate, the bark should be thoroughly rinsed, then it is left for 2 days in water in order for it to swell. Then the bark should be washed again with clean water.


Watch this video on YouTube
Pruning
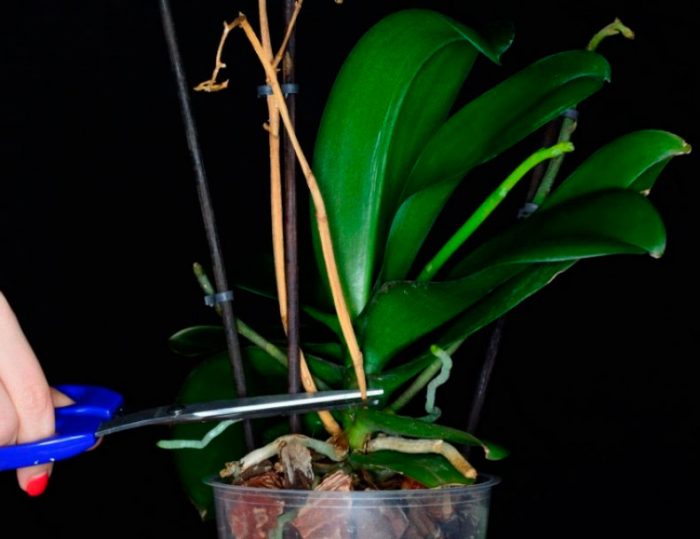
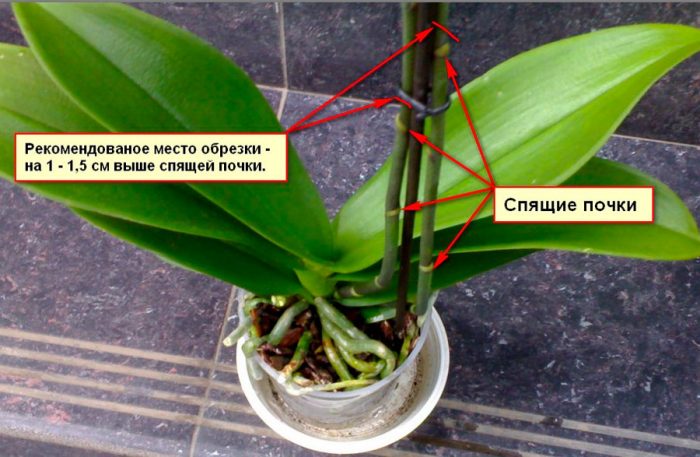
After the bush has faded, you need to watch the old arrow for some time. If the arrow becomes faded and yellow, then it must be cut off. However, if the arrow is juicy and green, then it is highly likely that after a couple of months of rest, flower buds will form on it. It should be borne in mind that a new arrow, before the budding of flower buds occurs on it, will have to grow. In the event that the old arrow is excessively long, it must be shortened, while cutting it off 10 mm higher than the developed kidney. It should be borne in mind that the higher the peduncle is cut, the fewer flowers will form on the side arrow. However, the peduncle cannot be cut below the third bud, otherwise the plant will not bloom for a relatively long time.
Phalaenopsis bloom
Phalaenopsis orchid is able to bloom at any time of the year, this is significantly influenced by the condition of the bush, as well as the conditions for its cultivation. The flowering period varies from 2 to 6 months. As a rule, the bush blooms twice in 1 year, but sometimes it blooms a third time in 1 year. In diameter, the flowers reach 2-15 centimeters, while on 1 peduncle there can be 3-40 pieces.The number of flowers formed is influenced by the degree of branching of the peduncle and how favorable the growing conditions are for such a plant. Sometimes the length of the peduncle can reach about 100 cm, while about 100 pieces of fairly large flowers can be placed on it. The flowers have a delicate scent and varied color: from a solid yellow, red, white or purple color to a wide variety of specks, specks and veins on the main background.
Lack of flowering
3 months after the end of flowering, the orchid should bloom again. However, in some cases, the bush can actively grow, but not flowering. What to do to make Phalaenopsis bloom? First you need to understand why the bush does not bloom. Possible reasons:
- Very poor lighting... Provide the plant with adequate lighting and it should bloom.
- The orchid is overfed with nitrogen... We must wait until all the nitrogen is processed by the orchid, while at this time it should be fed only with phosphorus.
- The bush is very tired, and it will take more time for him to regain his strength. It is necessary to wait a while, and then stimulate the flowering of the orchid.
In order to stimulate flowering, use the method of insufficient watering using the means "Ovary" or "Bud". It is also recommended to lower the night temperature, as a result, the difference between the temperatures during the day and at night should be at least 6-8 degrees. Due to the sharp change in temperature, flowering is stimulated.
After flowering
As a rule, at the end of flowering, the old arrow begins to dry, and therefore it is removed. However, in some cases, the arrows do not dry out, and their color remains green, in which case it will be necessary to decide what to do:
- leave a peduncle:
- cut the peduncle to the height of the branch;
- remove the peduncle completely.
In the case when the peduncle was cut off, it can be lowered into the water if desired, and after a while a baby can form on it. If the old arrow was left on the bush, then after a while lateral branches form on it, and then flowers form on them, however, it should be borne in mind that in this case the flowering will not be very lush compared to what is observed on the new peduncles.


Watch this video on YouTube
Reproduction of phalaenopsis
Reproduction of phalaenopsis by children
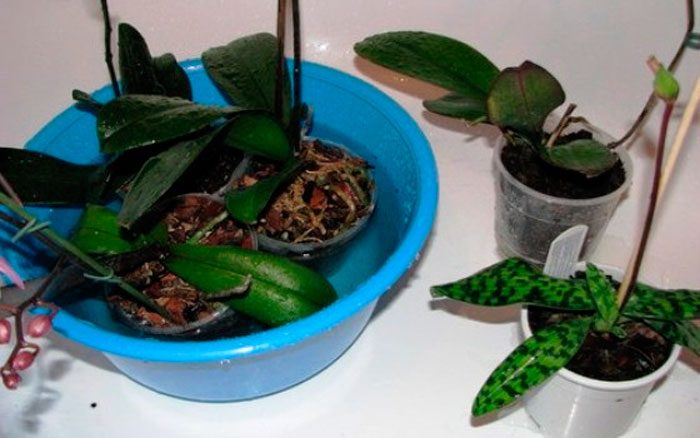
There are such orchids, for the reproduction of which they use the method of dividing the rhizome, but this method is not suitable for phalaenopsis. In the wild, the reproduction of such a plant occurs with new shoots and seeds. However, it cannot be propagated by seeds in room conditions.
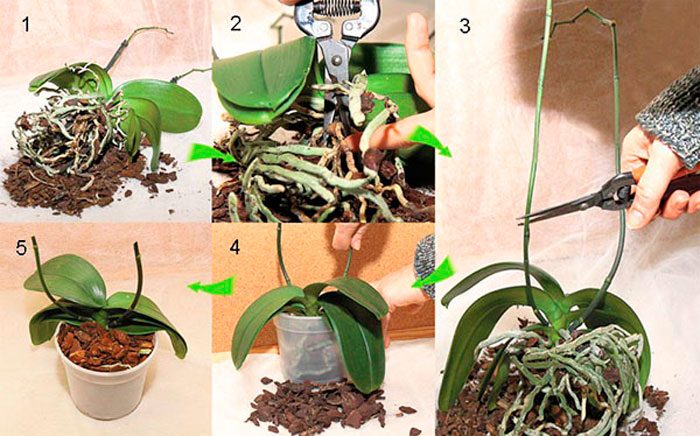
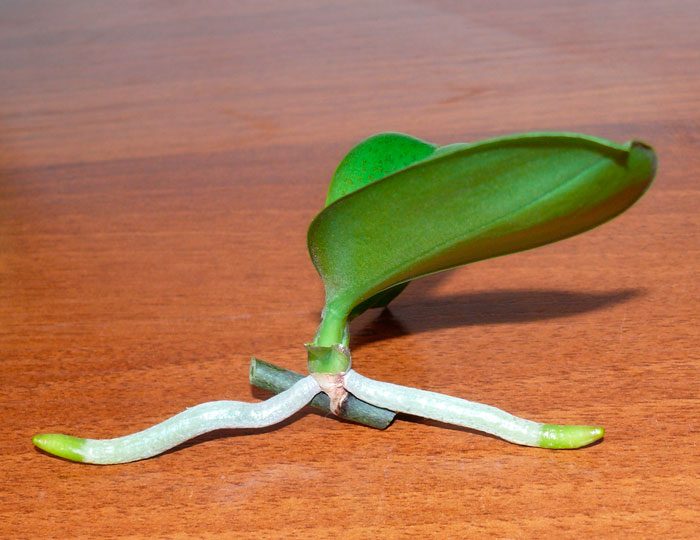
It is easiest to propagate such a flower in a vegetative way; for this, the lateral shoots are cut off, which have grown on the peduncle or at the base of the rosette of leaves. Cut off the shoot only after the flowering is over, and the bush will rest for 1-2 months. Jigging is carried out only for those shoots in which 2 leaf plates are formed, and the length of the air roots should be about 50 mm. However, children should not be allowed to outgrow, as this will negatively affect the state of the parental outlet. After separation, the baby must be left for 24 hours to dry, and then it is planted in a substrate consisting of bark of a fine fraction, while a mini-greenhouse must be made above the shoot, where the temperature should be from 22 to 25 degrees all the time.
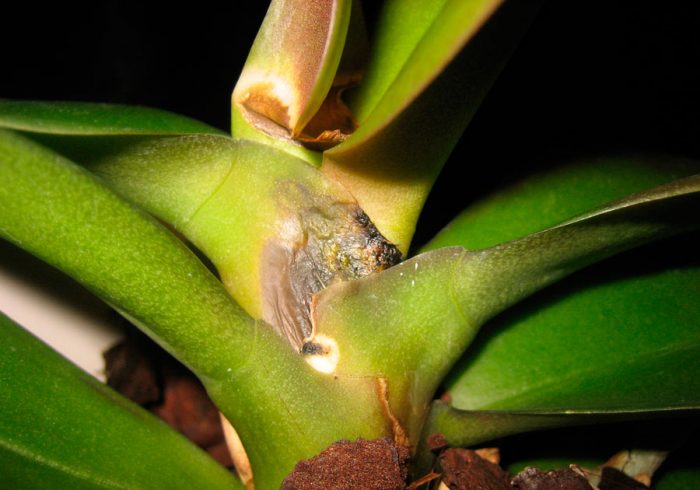
The lateral processes of the bush are formed very rarely and only when there are irregularities in flower care. In this regard, if the bush does not give children, then the awakening of the sleeping buds can be caused artificially. To do this, at the base of the peduncle, which has faded, you need to find a sleeping bud, with the help of a sharp blade you need to make a not very deep semicircular incision at the base of the covering scales, then it is removed with tweezers. Next, the kidney is treated with fresh birch sap or a solution of a growth stimulating agent. At the site of the incision, after 1–2 months, a leaf rosette should form, consisting of several plates, and after 3 months it will develop roots.To speed up this process, you need to put a plastic bag on the bush, the fact is that a humid and warm microclimate contributes to the faster growth of children.
You can get a baby using a trimmed peduncle. First, the scales must be removed from the bud (how to do this is described in detail above), then the peduncle is immersed 40–70 mm in a solution of complex mineral fertilizer (0.005%). The peduncle must be placed in a mini-greenhouse, and also provided with regular water changes.


Watch this video on YouTube
Phalaenopsis diseases and their treatment
The phalaenopsis orchid can get sick with both non-infectious and infectious diseases. It should be borne in mind that such a flower can only get sick if it is not properly looked after.
Fusarium
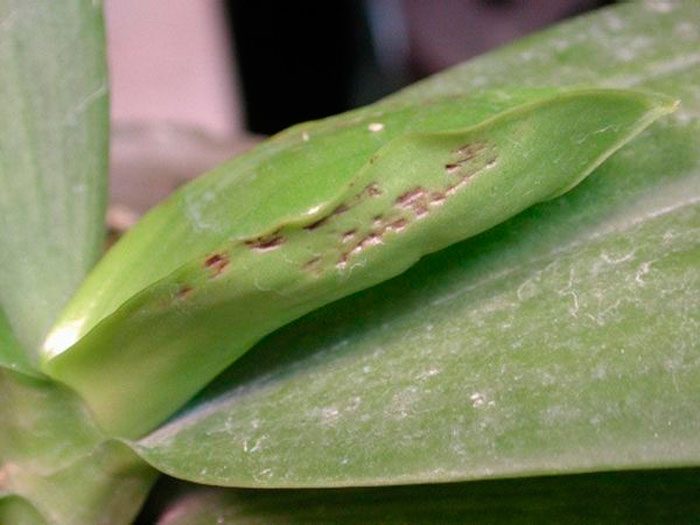
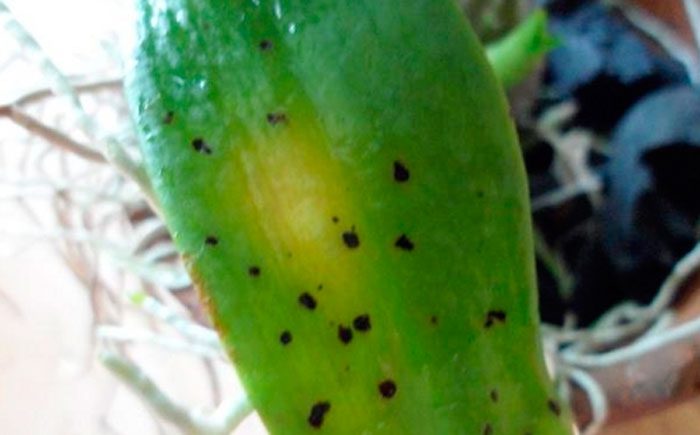
Most often, this orchid suffers from a fungal disease such as fusarium. In the bush, the root system is first affected, after which the disease spreads to the entire plant. Most often, this disease begins to develop if there is an excess of moisture. The affected bush cannot be cured; therefore, it should be burned. However, other rot (for example: brown, gray, black and root), as well as anthracnose, rust and spotting, in some cases can be cured by spraying with a solution of a fungicidal drug (Topsin-M, Fundazol, etc.), you will need 2 treatments with a break of 1 , 5 weeks.
Hives
Quite often, the orchid is sick with urticaria. In a diseased plant, damage to the leaf plates is observed, at an early stage manifested by large specks, reaching 20-30 mm in diameter. The cause of the development of the disease can be high humidity, excessively low air temperature and poor ventilation in the room. It is enough to start taking proper care of the flower and it will recover.
Botrytis
Phalaenopsis gets sick with botrytis also with excessive air humidity and poor ventilation, while flowers are affected. At first, specks of dark brown color form on the surface of the petals, and then they wither. If the room temperature rises, the disease will develop more slowly. In addition, we must try to improve ventilation in the room, and treat the bush with a bactericidal agent.
The development of noncommunicable diseases occurs for several reasons: excessive illumination, uneven watering, the use of pesticides, and improper feeding. In a sick specimen, the tips of the leaf plates begin to dry out, the roots die off, and other orchid tissues are also affected, and various spots develop. Try to find and eliminate the reason why the bush got sick, and you will have a chance to save it. However, it must be borne in mind that it is very difficult to revive such a plant.


Watch this video on YouTube
Phalaenopsis pests and methods of dealing with them
Various harmful insects sometimes settle on such an orchid.
Mealybug
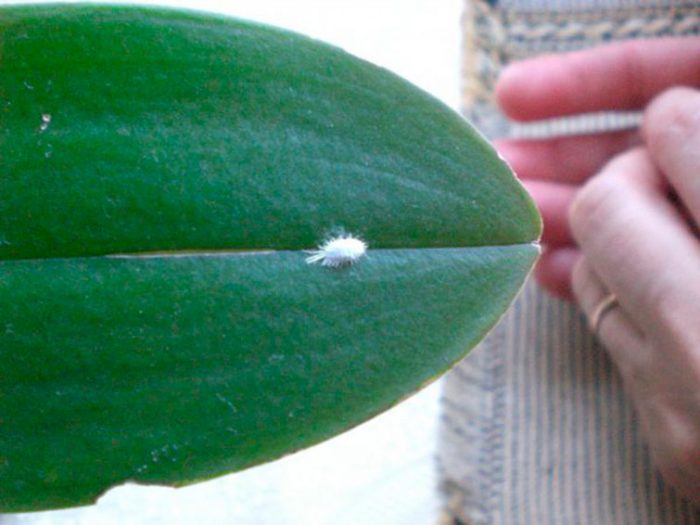
If a mealybug is present on the bush, then because of this, the foliage turns yellow and flies around. To get rid of it, foliage and shoots need to be treated with a solution of laundry soap.
Spider mite
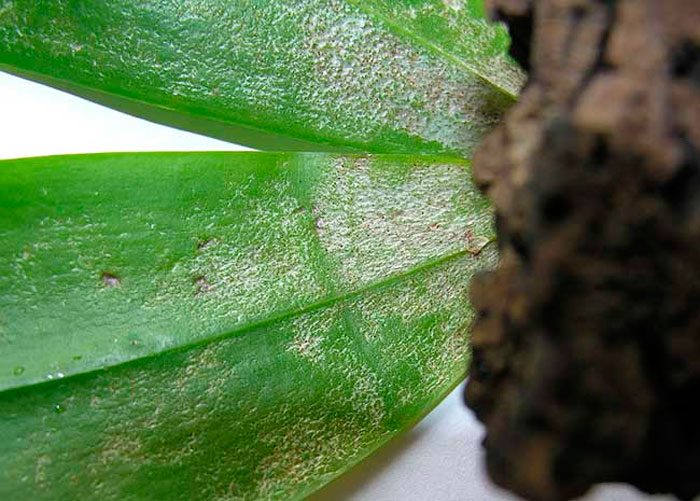
A spider mite appears on a flower only if the air humidity in the room is very low. You can understand that such a pest has appeared on the bush by the presence of a silver cobweb on the foliage, which is as if pricked with a needle. If there is not much such a pest on the plant, then you can get rid of it by treating it with soapy water, which will also help remove aphids and worms from the orchid. If there are a lot of ticks on the bush, then to destroy them you will have to use a solution of an acaricidal drug.
Thrips
Even on the phalaenopsis, thrips can settle, which infect flowers and leaf plates, specks of brown color are formed on their surface. In order to get rid of such a pest, treatment with a systemic insecticide (for example: Aktellik, Isatrin or Hostakvik) will be required, however, experts recommend using Fitoverm for this purpose, which is less toxic.
Shields
If tubercles have formed on the surface of the leaf plates, then this is a sign that scale insects have settled on the plant. Such a pest sucks the juice from the flower, and it gradually fades. You can get rid of such a harmful insect in the same way as from the worm; for this, the orchid will need to be treated twice with soapy water with a break of 7 days.
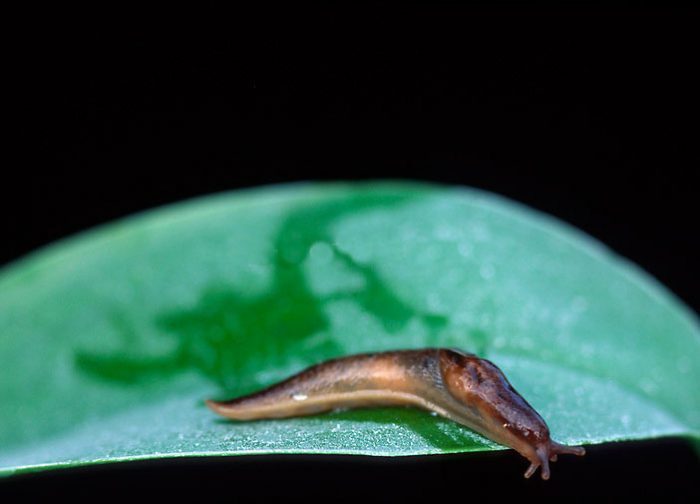
Slugs
The greatest harm to the flower is caused by slugs. Since this pest is relatively large in size, it is able to eat the shoots, flowers and foliage of the plant in a short time. To catch such a gastropod, a cucumber or carrot, cut into pieces, must be spread over the surface of the substrate, then you must wait until the slug crawls out of the shelter, after which it can be removed. If it is not possible to get rid of such a pest with the help of baits, you can treat the bush with an insecticidal preparation such as mesurol or metaldehyde.
Phalaenopsis differs from other orchids in that it is easy enough to grow. If you do everything right and provide the plant with proper care, then it will grow strong and healthy, and not a single pest or disease will be afraid of it. This plant in an urban environment, with proper care, is capable of growing and blooming for many years, delighting everyone with its beautiful flowers. The main thing is to remember that the orchid remains healthy and blooms in a timely manner, it should be provided with correct watering and temperature conditions, sufficient illumination and timely feeding.


Watch this video on YouTube






























Everyone, my children from phalaenopsis, bloom immediately after planting.
This time, my phalaenopsis got the trunk of the peduncle with a hook and did not turn around, but when I tried to turn it around, it broke off, what will happen now?
I answer to myself. Nothing needed to be done. After a while, a lateral stem, on which 6 large flowers developed, recently (in July) they bloomed, and a new straight trunk with buds emerged from the broken proboscis after a while.
And if there is no moss, where can you plant it?
I plant all my phalaenopsis in pine bark. It is desirable not very large-piece, but medium or small - for some reason they like it more.