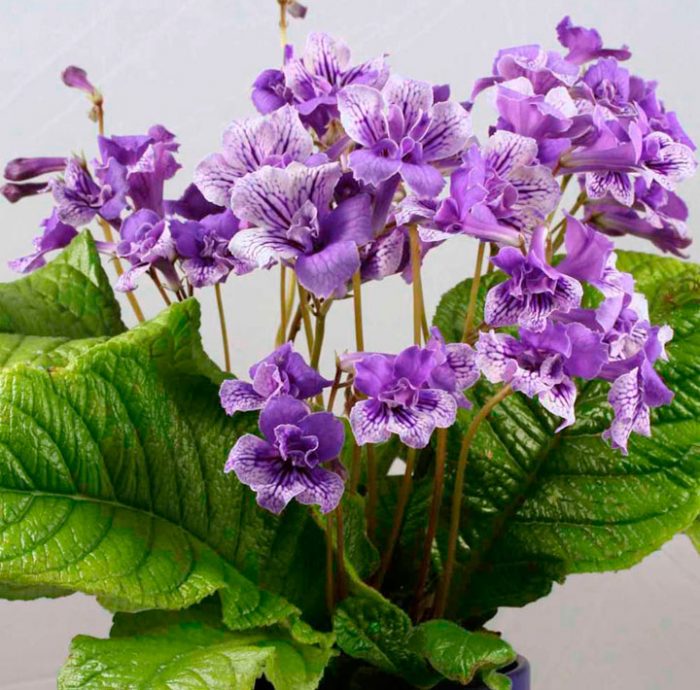
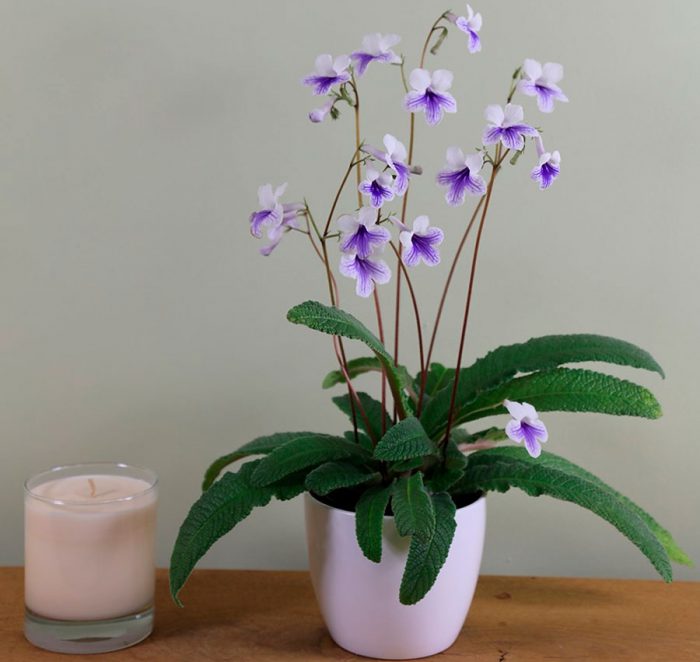
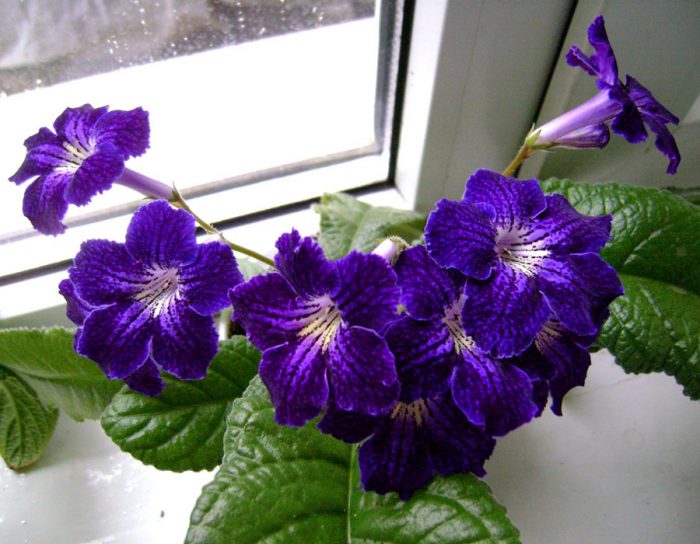
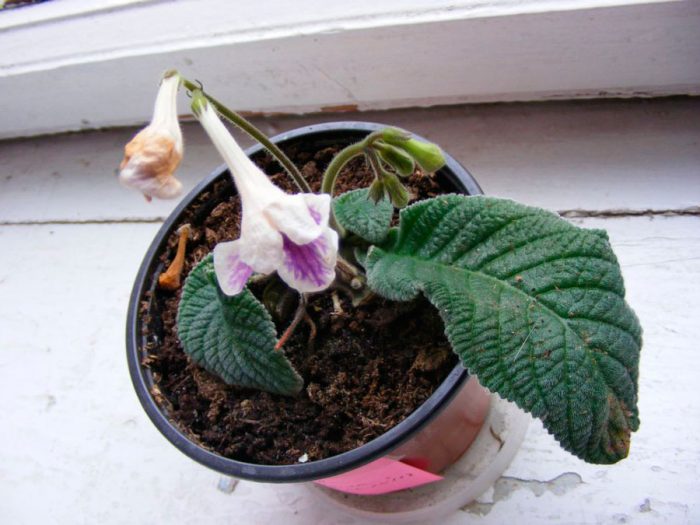
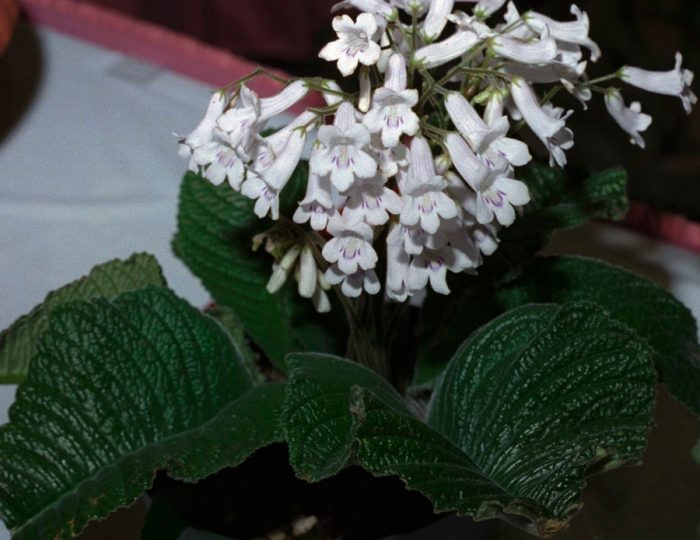
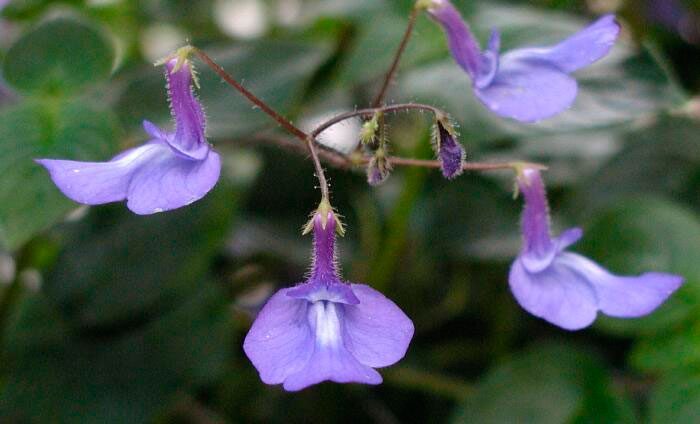
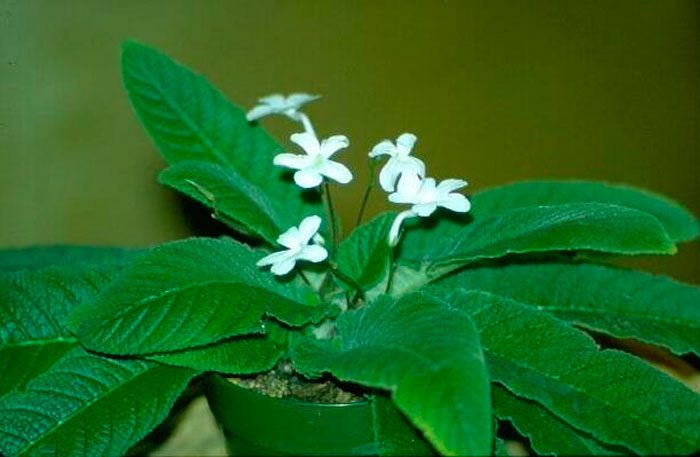
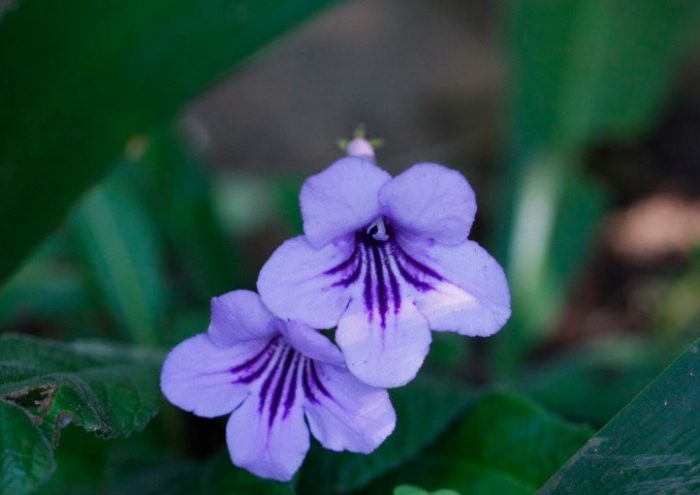
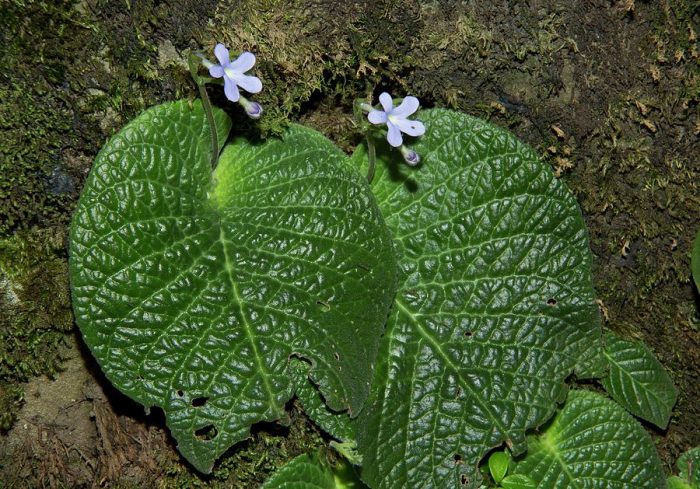
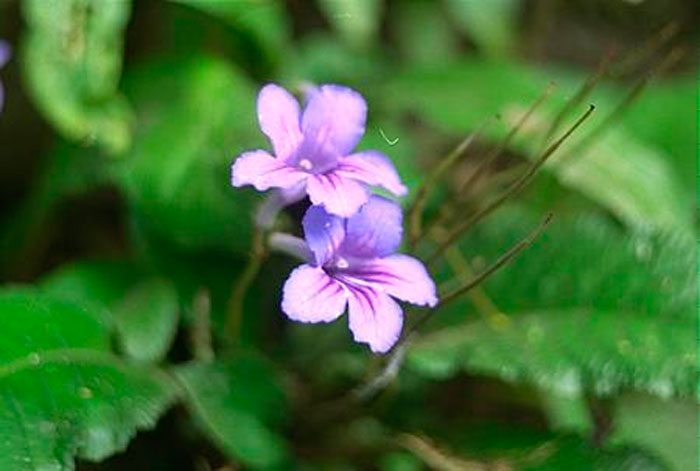
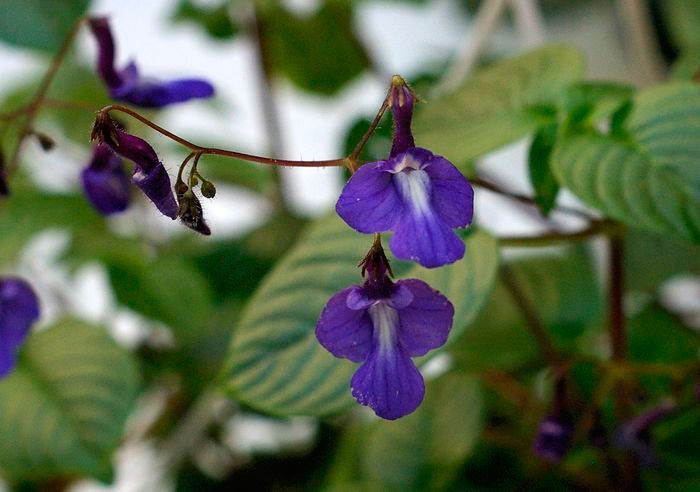
The plant Streptocarpus is a member of the Gesneriaceae family. This genus unites more than 130 species. In nature, such a plant can be found in Asia and Africa. This genus is represented by shrubs and herbaceous plants, which, depending on the species, can be both annuals and perennials. Streptocarpus began to be cultivated at home in the first half of the 19th century. Such a plant is rosette, while its stem is short. The shape of strongly pubescent leaf plates is broad-lanceolate, their color can be green or variegated. The flowers growing from the axils of the leaves can be single or collected in bunches of 2 pieces. This plant was named Streptocarpus because of its fruit, as its shape is similar to that of a spiral long capsule. Flowering begins in spring and ends in autumn. In winter, the flower has a short period of rest, but the bush does not shed its foliage.
Content
- 1 Brief description of cultivation
- 2 Streptocarpus care at home
- 3 Reproduction methods
- 4 Possible problems
- 5 Streptocarpus species with photos and names
- 5.1 Streptocarpus snow-white (Streptocarpus candidus)
- 5.2 Streptocarpus large (Streptocarpus grandis)
- 5.3 Streptocarpus cornflower blue (Streptocarpus cyaneus)
- 5.4 Streptocarpus wendlandii
- 5.5 Streptocarpus glandulosissimus (Streptocarpus glandulosissimus)
- 5.6 Streptocarpus johannis (Streptocarpus johannis)
- 5.7 King's Streptocarpus (Streptocarpus rexii)
- 5.8 Streptocarpus primrose (Streptocarpus polyanthus)
- 5.9 Streptocarpus primulifolius (Streptocarpus primulifolius)
- 5.10 Rocky streptocarpus (Streptocarpus saxorum)
- 5.11 Streptocarpus Holst (Streptocarpus holstii)
Brief description of cultivation
- Bloom... It starts in the spring and ends in the fall.
- Illumination... Light is needed bright, but diffused.
- Temperature regime... In the spring and summer period, the air temperature should be at least 20 degrees and no more than 25 degrees. Starting in October, the temperature should be gradually reduced to 15 degrees.
- Watering... Throughout the growing season, streptocarpus should be watered systematically and moderately. From October, watering should be reduced, and in winter it should be scanty, but care must be taken that the lump of earth in the pot does not dry out completely.
- Air humidity... Moderate.
- Fertilizer... During intensive growth, the bush is fed 1 time in 7 days, and a complex mineral fertilizer is used for this.
- Dormant period... From the first days of October to February.
- Transfer... Bushes are transplanted in the first spring weeks: young bushes - once a year, and adults - once every 3-4 years.
- Soil mixture... Ready-made substrate for Saintpaulias. Or you can take a soil mixture consisting of sand, humus, leaf and turf soil (1: 1: 2: 3). If the bush is young, then instead of sod land, leaf is taken.
- Reproduction... Leafy cuttings, dividing the bush, and the seed method.
- Harmful insects... Scabbards, thrips, whiteflies, mealybugs and spider mites.
- Diseases... Gray rot.
Streptocarpus care at home
Illumination
When growing streptocarpus in indoor conditions, it must be provided with bright, but diffused light. Therefore, for such a flower, windows of western or eastern orientation are ideal. If you put it on the south window, then the direct rays of the sun will have to be scattered. And the northern window sill is not suitable for such a plant, since the lack of light has an extremely negative effect on its growth, development and flowering.
Temperature regime
In spring, summer and early autumn, the room should not be colder than 20 degrees and hotter - 25 degrees. From the first days of October, the temperature is gradually reduced, while it must be borne in mind that it should not be less than 15 degrees. The best air temperature for wintering streptocarpus is 15 degrees.
Watering
In the spring-summer period, the flower is watered systematically and in moderation, while it is necessary to ensure that the lump of earth in the pot is not dry for a long time. From the first days of October, watering is reduced, and in winter it should be scanty, while try not to dry out the substrate in the pot, and also there should be no stagnation of water in it. For irrigation, use well-settled water (at least 24 hours) at room temperature.
Spraying
If there is an excessively low air humidity in the room, then the tips of the leaf plates near the bush will begin to dry. They must be cut in a timely manner using a sharp knife, while a board must be placed under the sheet.
Fertilizer
Top dressing is carried out throughout the growing season 3 or 4 times a month, for this, a complex mineral fertilizer is used.
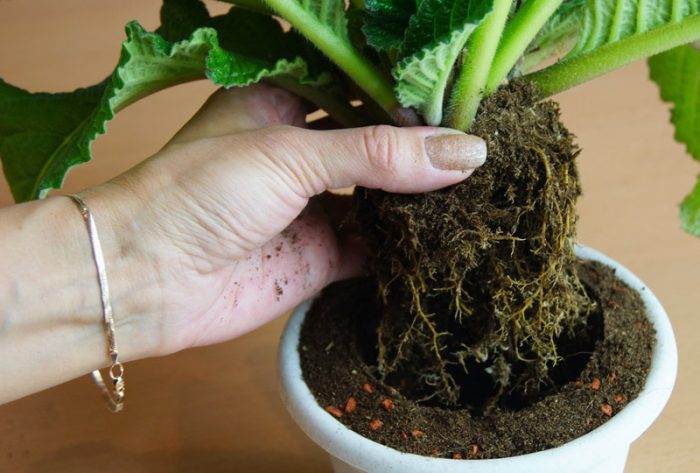
Streptocarpus transplant
Young bushes need regular replanting, which should be done once a year. Adult specimens are transplanted less often, or rather, once every 3 or 4 years. This procedure is carried out in the first spring weeks, for this they use wide low pots, which are filled with a soil mixture consisting of leaf and sod soil, as well as sand (4: 1: 2). For transplantation, you can also use a substrate consisting of sand, humus, sod and deciduous soil (1: 1: 3: 2). For this purpose, you can use store-bought substrate for Saintpaulias. To avoid excessive waterlogging of the substrate, a small amount of fine charcoal should be added to it. If a young plant is transplanted, then sod land will need to be excluded from the soil mixture.


Watch this video on YouTube
Reproduction methods
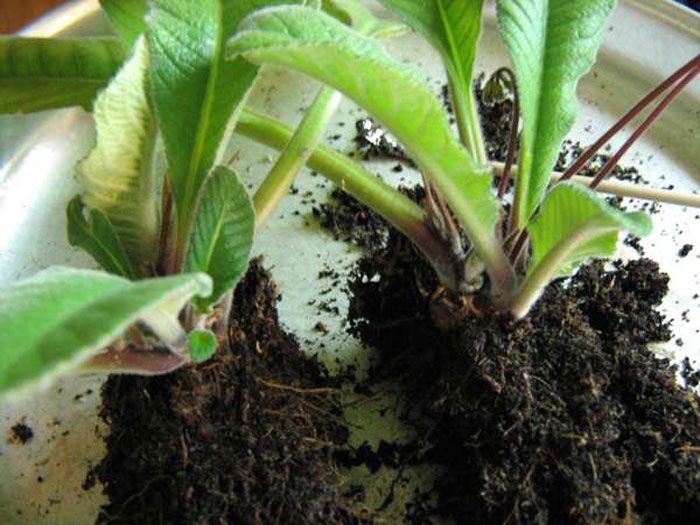
Dividing the bush
It is possible to propagate by dividing the bush a highly overgrown streptocarpus. To begin with, the substrate in the pot is watered with a small amount of water, then the bush is pulled out of the container, and the remnants of the soil mixture are removed from the root system. Then a sharp instrument is taken, with which part of the thick root with foliage is separated. Leave the cuttings for some time in the fresh air so that the cut points dry well, then they must be treated with charcoal powder. The prepared pot is filled 2/3 with fresh substrate, then a cut rosette is placed in it and sprinkled with soil mixture to the level of the root collar. Further, the substrate must be slightly compacted, and the bush must be poured with lukewarm water. In order for the division to take root better, cover the pot with cellophane on top. You can also speed up rooting and activate the growth of young foliage by shortening large leaf plates in half, or they can be completely cut off. After a little time, the bush that has grown from the cut will begin to bloom.
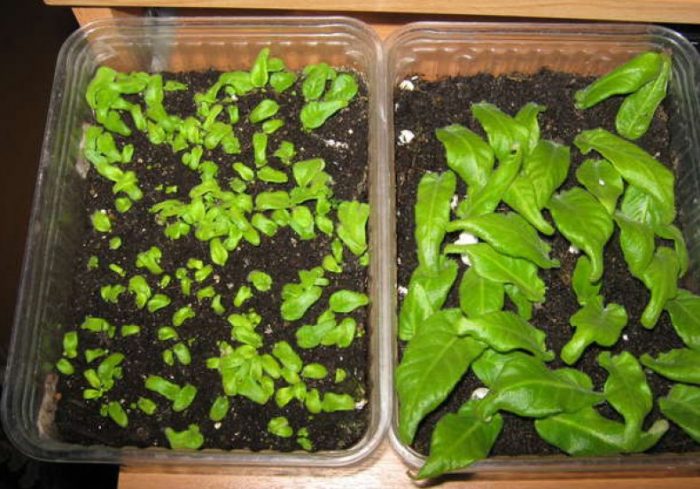
Growing from seeds
Seeds are sown in a small container, while they are evenly distributed over the surface of the substrate. Then the container is covered with glass on top. Crops need bottom irrigation through the pallet, they also need to provide systematic ventilation, lighting should be bright, but diffused, and the air temperature should be constantly about 21 degrees.In order for the temperature not to drop, put a piece of paper on top of the glass. However, it is better to keep crops not on the windowsill, but under the lamps. After 6 weeks, the shelter must be slightly moved, and then removed completely. For the first picking of seedlings, a container is used, which should be slightly larger than the old one, while the distance between them should be increased only slightly. In order not to injure the seedlings during the dive, they must be transplanted carefully. To begin with, you need to lightly knock on the walls of the container, then carefully pry the plant with a needle and, holding the foliage with your fingers, transplant it into a new container. The substrate is slightly compacted, then the transplanted seedlings are watered, after which the container is placed on a pallet and transferred to a warm place, while on top it is covered with glass or film. Individual pots are used for the second pick. In order for the plant to develop better, it is recommended to feed them.
Seeds can be sown several times a year, and this can be done at any time of the year. Thanks to this, you can get bushes that will bloom at different times.
Cuttings
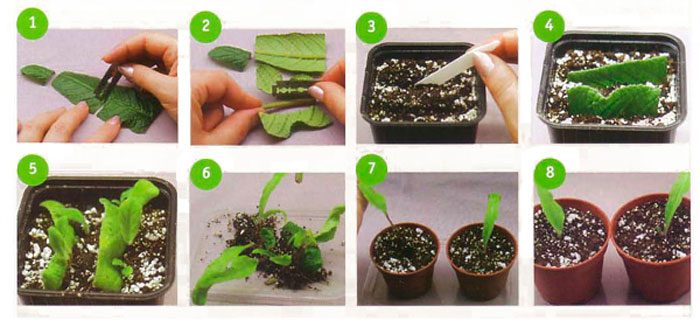
A young leaf plate that is well developed and absolutely healthy (there are no signs of disease or harmful insects) must be cut off from the bush, and then the stalk must be cut with a sharp blade. After the places of the cuts are dry, the leaf stalk must be planted in a small pot, while it is placed vertically. Then it is sprayed with a solution of a fungicidal preparation, and the container is covered with a film on top. After that, the pot is removed to a well-lit and warm place. After 4–6 weeks, young shoots should appear. After the plant grows a little and gets stronger, it needs to be transplanted into a permanent pot. If bushes of streptocarpus of various species are cultivated, then it is recommended to stick labels with the name of the variety on the pots.
For reproduction, you can also use part of the leaf plate. To do this, the sheet is laid with its front surface on a board, after which, using a sharp blade, it is divided into strips, the width of which should be 50 mm. It is necessary to cut the leaf plate perpendicular to the median vein. The lower and uppermost parts of the leaf plate must be thrown out, and the remaining segments are planted in the grooves with the base of the cutting down at an angle of 45 degrees. A distance of at least 30 mm should be kept between the cuttings. They must be sprayed with a solution of a fungicidal preparation, then the container is covered with a transparent bag on top and removed to a humid place where the air temperature should be from 20 to 22 degrees. Watering the cuttings is carried out through the pallet, and they also need daily ventilation. Young shoots will appear out of the ground after 6-8 weeks.
For reproduction, you can also use the longitudinal part of the sheet plate. To do this, the leaf is laid on the board face down, and then the median vein is separated with a sharp blade. In the resulting two parts of the sheet plate, the places of the cuts must be sprinkled with coal powder. After that, they are planted in grooves with a cut vertically downwards, deepening them by 1/3 of the height of the leaf petiole, then the substrate is slightly compacted, after which it is watered, and the container is covered with a film from above. The container is moved to a well-lit and warm place. Young plants will appear along the entire leaf plate from side veins. On the seamy surface of the plate on the median vein, it is necessary to make twenty-millimeter cuts every 2 cm. Then the leaf cutting with the seamy surface is pinned to the surface of the moistened substrate, after which it is sprayed with a fungicidal agent. From above, the container with cuttings must be covered with glass, and then it is transferred to a well-lit place, protected from direct sunlight. After the young shoots appear, the shelter must be slightly moved.
When the grown and matured bushes are transplanted into individual pots, the first few days they will need to be covered with a transparent plastic bag. After the shelter is removed, the plants must be looked after in the same way as for the adult specimens.


Watch this video on YouTube
Possible problems
- Gray rot... If streptocarpus is watered excessively abundantly, it can be affected by gray rot.
- The buds turn brown... This happens when the room temperature is excessively high.
- The edge of the sheet plates turns brown... This can happen due to stagnation of liquid in the substrate or if the room has an extremely low air humidity.
- Harmful insects... Most often, thrips, spider mites, scale insects, whiteflies and mealybugs settle on such a flower.


Watch this video on YouTube
Streptocarpus species with photos and names
Streptocarpus snow-white (Streptocarpus candidus)
Such a plant is rosette, its wrinkled leaf plates reach about 15 centimeters in width and up to 45 centimeters in length. Lush flowering. On the surface of the white flowers, up to 25 mm in length, there are purple lines. There are purple streaks on the lower lip of the flower, and dots of the same shade in the fauces.
Streptocarpus large (Streptocarpus grandis)
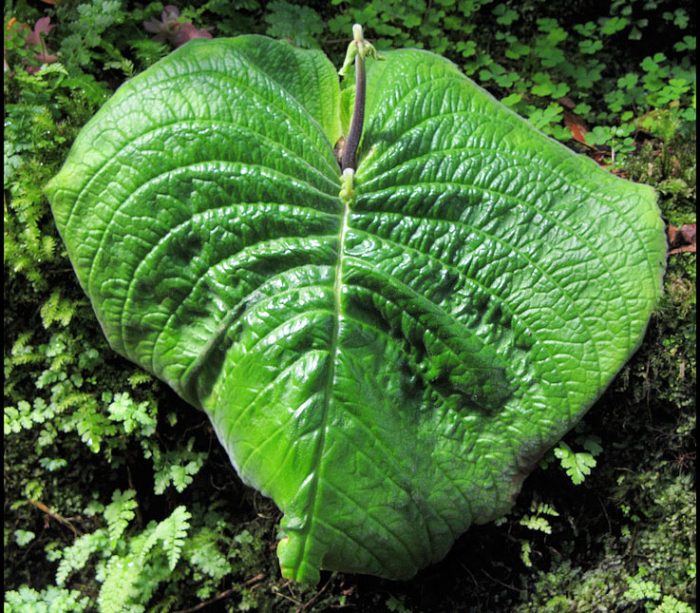
This plant has only one leaf plate, the width of which is about 0.3 m, and the length is up to 0.4 m.The height of the stem is about 50 cm, in its upper part a racemose inflorescence grows, consisting of flowers, the corolla of which is pale purple , and the pharynx is a darker shade, the color of the lower lip is white.
Streptocarpus cornflower blue (Streptocarpus cyaneus)
This plant is rosette, its stem is about 15 centimeters high. On the stem, pink flowers grow, collected in bunches of 2 pieces. The middle of the flower is yellow, while on the surface of the pharynx there are stripes and dots of purple color.
Streptocarpus wendlandii
This species is native to South Africa. The bush grows a single leaf plate, the length of which is up to 100 cm, and the width is slightly more than 50 cm, on its dark green surface there are veins of a paler shade. Five-centimeter flowers grow from the sinuses of a relatively long peduncle, the corolla is dark purple, and there are white stripes on the surface of the pharynx.
Streptocarpus glandulosissimus (Streptocarpus glandulosissimus)
In nature, this species is found in the Ulugur and Uzambar mountains. The stem is about 15 centimeters long. Flowers can be colored in various shades from dark blue to purple.
Streptocarpus johannis (Streptocarpus johannis)
The stem of such a rosette plant is straight. The width of the leaf plates is about 10 centimeters, and their length is up to 50 centimeters. The stem grows about 30 bluish-lilac flowers almost twenty millimeters tall.
King's Streptocarpus (Streptocarpus rexii)
It is a rosette plant native to South Africa. On the surface of the elongated lanceolate leaf plates, there is pubescence, their width is about 5 centimeters, and their length is up to 25 centimeters. Axillary flowers can be single or collected in bunches of 2, the length of the funnel-shaped corolla is about 50 mm, and in diameter it reaches about 25 mm. The color of the flowers is pale lavender, and there are purple stripes on the surface of the pharynx and corolla tube. This species has a long and bright flowering.
Streptocarpus primrose (Streptocarpus polyanthus)
This univalent species comes from South Africa. The length of the densely pubescent leaf plate is about 0.3 m. On high peduncles, forty-millimeter pale blue flowers with a yellow center grow. His throat color is paler and somewhat similar to a keyhole.
Streptocarpus primulifolius (Streptocarpus primulifolius)
In such a rosette plant, no more than 4 flowers are formed. The color of the flowers ranges from white to pale purple, and there are dots and stripes on their surface. Stem height is about 25 centimeters.
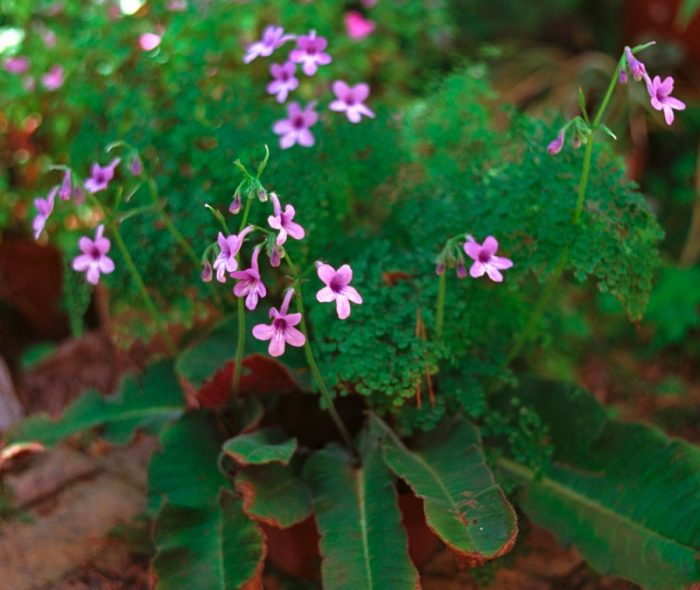
Rocky streptocarpus (Streptocarpus saxorum)
In nature, this plant is found in the mountains of the tropical zones in eastern Africa at an altitude of over 1000 meters above sea level. The length of the hanging stems is about 50 cm. The foliage on the stem is opposite. The bluish, slightly downward-tilted flowers are similar to those of Saintpaulia.
Streptocarpus Holst (Streptocarpus holstii)
Under natural conditions, the species is found in the tropical regions of eastern Africa. The height of very flexible fleshy shoots is about 50 cm. On the surface of wrinkled opposite leaf plates there is pubescence, their length is about 50 mm. The purple three-centimeter flowers have a white corolla tube.


Watch this video on YouTube