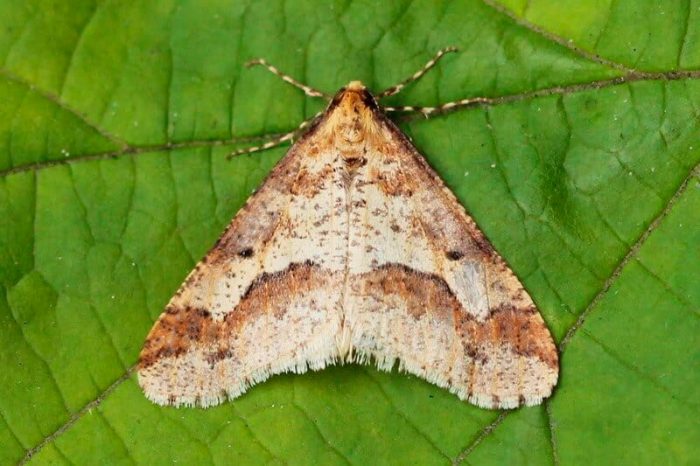
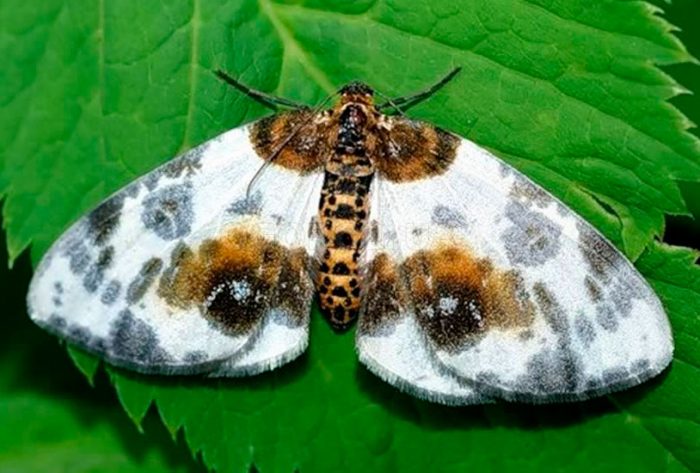
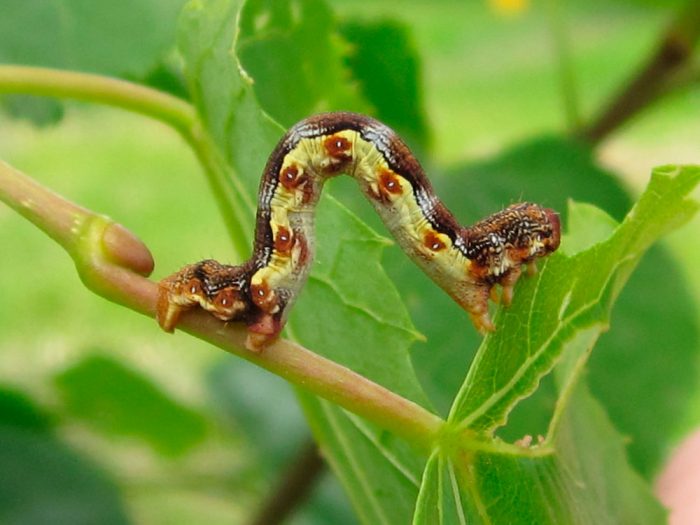
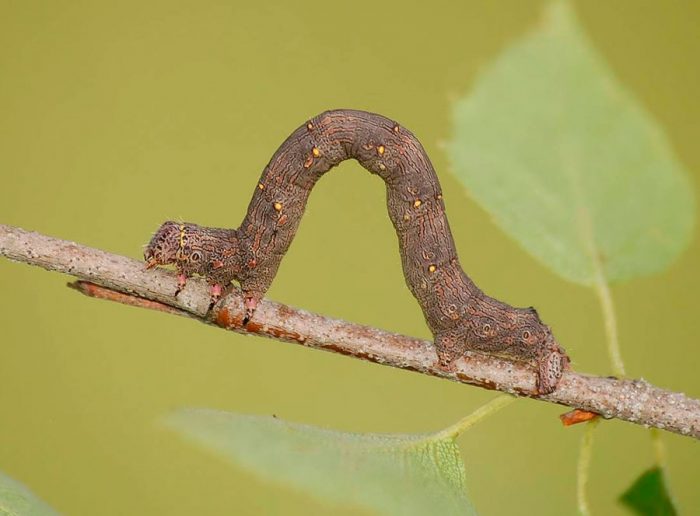
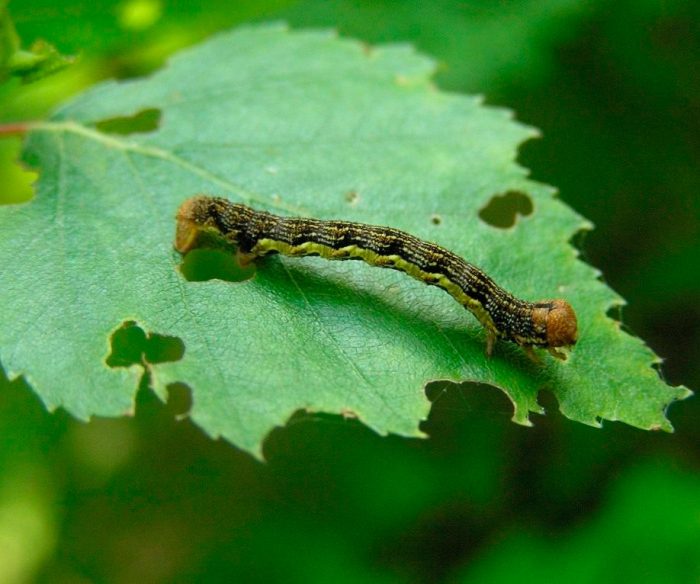
Moths (Geometridae), also called land surveyors, is a vast family of butterflies, which includes more than 2 thousand genera and about 23 thousand species. For crops growing in the garden and in the garden, the greatest danger is the moth caterpillars, which are able to eat not only a cultivated plant, but also a wild one. In the middle latitudes, the most common species are the gooseberry moth (gooseberry), the winter moth, the peppered moth and the pine moth.
Content
Features of the moth butterfly
The wingspan of the moth butterfly can vary from 0.95 to 5.1 cm, but in most individuals it reaches 3 cm. Butterflies have a weak body, as well as delicate and wide wings. But there are also such species that have a thick body, while their wings are underdeveloped. Their legs are thin, there are no eyes, and the proboscis is weak in a spiral shape. As a rule, the hind wings are rounded with a pinch, and the forewings are wide-triangular.
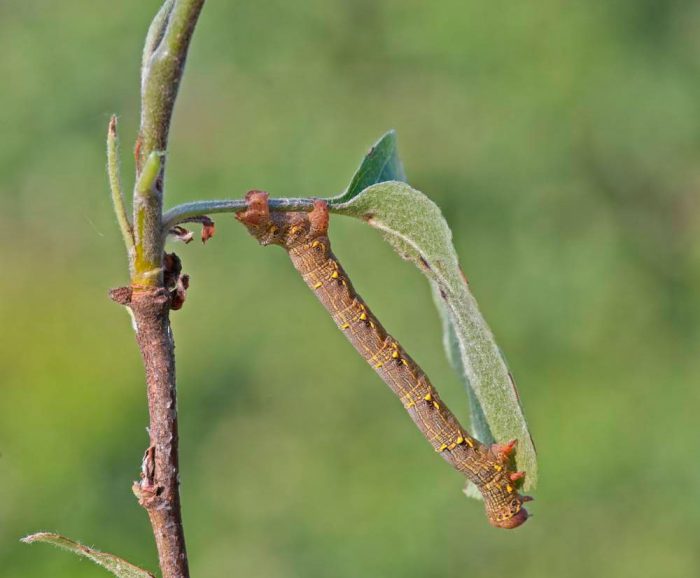
Most often, such butterflies fly at night, while their flight is uneven and weak. When the wings are at rest, they can be folded into a house or flat spread. In males, the color of the wings is patronizing, and they are well developed, while the antennae are feathery. And females in most species either do not have wings, or they are shortened, their antennae are filiform. As a rule, the caterpillar of such a butterfly is long, naked and thin, worm-shaped, they are painted most often in the color of shoots, foliage or bark. Caterpillars have 2 undeveloped front pairs of legs, and therefore they crawl quite unusually, as if they measure space with their body like a span, or with a survey chain, this is what influenced the formation of the name of this family. The musculature of the caterpillars is very developed, it can stand on its hind legs for a long time, stretching its body, at such a time the larvae are similar to a broken branch or to leafy cuttings. In winter, pupae are in cracks in the bark, they are smooth, do not have a cocoon. Pupae can be painted gray, yellow, brownish-red or green, and they are found in spider nests on trees, as well as in the soil or on its surface.When the adults emerge from the pupa, they are nocturnal and eat the nectar of the flowers until they mate. However, there are species that do not need nutrition. When mating occurs, females arrange their eggs on buds, needles, foliage, seed pods or branches. Caterpillars that emerge from the eggs begin to actively feed, after which they pupate.
Moths are needle-gnawing and leaf-gnawing harmful insects, they gnaw both vegetative and generative organs of various plants. They can severely harm fruit shrubs and trees over large areas. Due to their detrimental activity, the quality of the fruits deteriorates significantly, it also negatively affects the yield, resistance to frost and other unfavorable factors becomes lower. This pest is distinguished by systematic outbreaks of mass reproduction, their consequences can last for several years, during these periods insects can eat all leaf plates on trees.
Types of moths with photos
Pine moths
This pest, like all lepidoptera insects, has a protective color, thanks to which it is invisible on the surface of the pine bark. On the wings of a grayish-brown color, there are zigzags, as well as specks of white, black or dark brown. The larvae are colored green and feed on needles. At the very peak of gluttony, whole hectares of young spruce and pine trees may be left without foliage.
Birch moth
This species of moth has changed its color over the course of a century. This happened due to the fact that soot settles on the trunk of the birch, which makes the bark darker. In this regard, butterflies began to produce black pigment. There are black spots on the front surface of its wings, as a result, the insect sitting on a birch trunk is almost impossible to see. The larvae of this species are green in color. They eat the foliage of both birch and hazel, and alder.
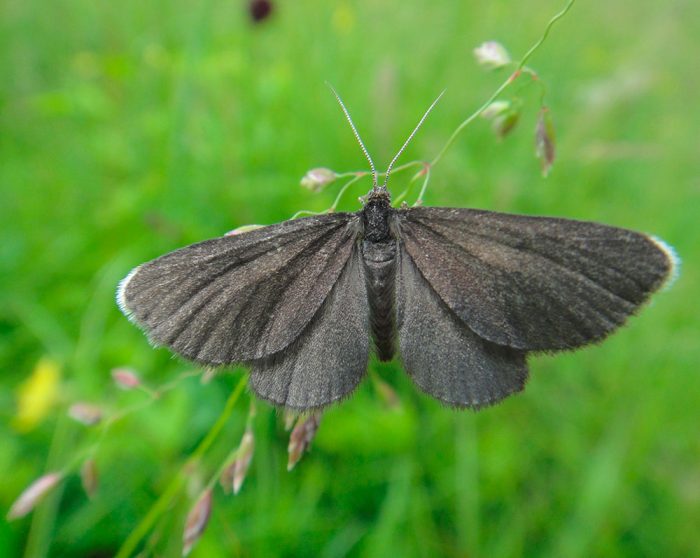
Black moth
This is a forest Eurasian species, its wingspan reaches 1.3–1.5 cm. The wings and body are black in color, and on the front wings there is a thin white border at the top. The velvety green caterpillars mainly prefer to feed on the coupir and earthen chestnut. But if there are no such plants nearby, then they can settle on others.
Fir moth
This species can be found in the east of Siberia and the Far East. On the surface of the pale gray wings, there are white or gray wavy stripes. The caterpillar is outwardly similar to a broken off dry twig. As a rule, they eat the needles of fir, as well as larch.
Gooseberry moth, or gooseberry
This type of butterfly has a very spectacular color. On the head and back there are yellow hairs, as well as small black spots that form a T-shaped pattern, which is clearly visible on a white background. And on the lower part of the wings there are yellowish-black stripes and large spots that merge into a wavy line. On the surface of the caterpillars there are many specks of large size, dark color, because of which they also look very impressive. Such a caterpillar eats the foliage of gooseberries, red and black currants, and also rosaceous crops (for example: apple, plum and apricot). Caterpillars eat the buds, foliage and seeds of the fruit, and those areas that they injured are glued together with cobwebs and pupated in them.
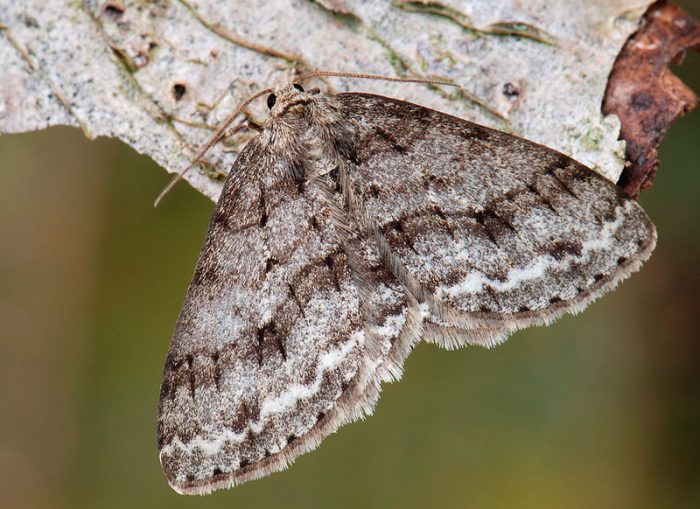
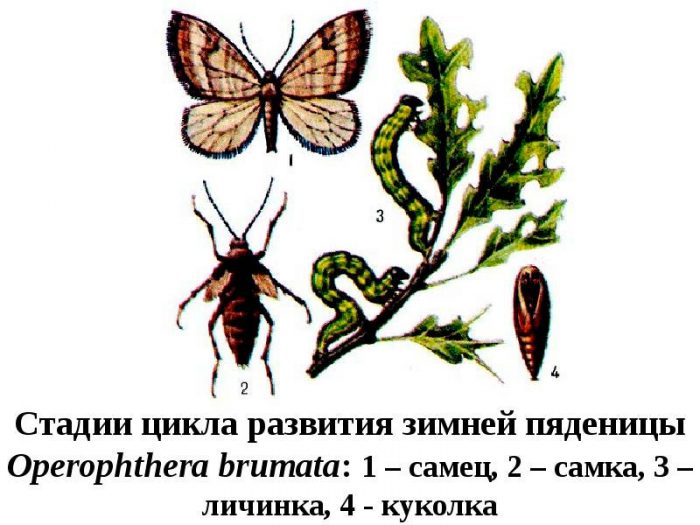
Winter moth
They have an inconspicuous appearance. On the surface of the gray wings, there are transverse lines of a dark color. Caterpillars of this species settle on pome and stone fruit cultivated plants, and also on deciduous trees growing in the wild. They gnaw young seeds and buds from the inside.In autumn, females lay eggs in cracks in the bark, where they are able to withstand temperatures down to minus 7 degrees during the winter months. In order for the cycle to proceed fully, such pests need low temperatures.
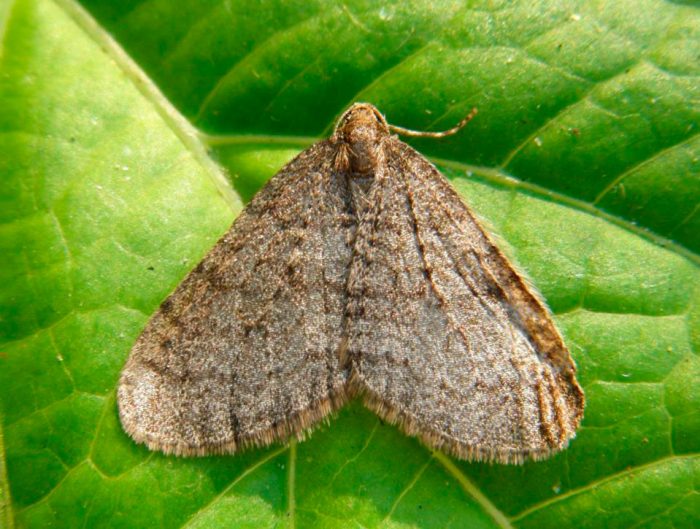
Ripped off
In this species, the butterfly can be colored cream, brown or pale green. There are 2 wavy stripes on the surface of the wings. Caterpillars of this butterfly feed on buds, foliage and buds, while they settle both on garden crops (cherry plum, sweet cherry, apple, mountain ash and blueberries) and on wild plants (birch, oak, maple, linden and rose hips). These larvae have characteristic ragged bite marks.
Big green moth
The butterfly is very large, its wings in span reach from 4.5 to 5 cm. Butterflies, which have just pupated, have a rich green color, and are decorated with clearly visible transverse stripes of white color. This species is found in forests throughout Europe. Most often, caterpillars can be found on the foliage of birch and hazel, but they can also harm other plants. Caterpillars are colored brown, and their length can vary from 2.5 to 3 cm. For wintering, the pest hides in cracks in the bark or buries itself in the ground, and in springtime it turns green and brown spots appear.
Mulberry moth
Most often, this species can be found in the territory of Central Asia. Males have gray-brown wings, while females lack them. The larvae gnaw the foliage and buds of such plants as: mulberry, apricot, plum, poplar, peach, quince, apple and acacia.
How to get rid of a moth
To get rid of moths, you need to deal with them in a complex way using chemical, biological, agrotechnical and mechanical methods.
Agrotechnical methods
Most often, gardeners resort to the following agrotechnical control methods:
- It is necessary to systematically inspect trees and shrubs in the garden in order to find settled moths as early as possible.
- The surface of the trunk circle must be loosened regularly from the beginning of spring to the last days of April, as well as from the first weeks of autumn until the beginning of frost.
- In summer and autumn, the soil must be dug up near the trees.
- Removing moss and dead bark from trees mechanically.
- In the first days of March and October, trees must be whitewashed.
- Mechanical methods of struggle
Mechanical methods
Mechanical methods of struggle are the most laborious, but they are distinguished by their safety:
- Gather the caterpillars regularly with your hands or shake them off on a cloth previously spread under a bush or tree. Then they are burned.
- Using glue belts.
- Collect and burn spider nests found in trees or bushes. Be sure to clean the trunk circle from plant residues.
Chemical methods
To get rid of moths, spray plants, fruit storage and containers with special chemicals, namely: organophosphate compounds, pyrethroids or neonicotinoids.
Biological methods
These methods imply that the natural enemies of the moths, which include tahina flies and wasps, need to be attracted to the garden. To do this, it is recommended to grow clover, sunflower, phacelia or decorative onions on the site. Also treat crops with biological pesticides.
Means for moth (preparations)
Experts advise that insecticides to combat moths should be used for prevention; for this, garden crops are treated in early spring. During the growing season, plants are sprayed only with biological agents, even if there are a lot of harmful insects on them. For preventive purposes, treat berry bushes and fruit trees before flowering begins. It is recommended to spray crops with the following means:
- Akarin... It is a biological insecticidal acaricidal agent of contact-intestinal action, which is capable of destroying various harmful insects.
- Karbofos... Acaricidal and insecticidal broad-spectrum preparation, which belongs to the class of organophosphorus compounds. It is used for complete and quick extermination of leaf-eating and sucking insect pests.
- Zolon... It is an acaricidal and insecticidal preparation of contact-intestinal action, which remains highly effective even at low air temperatures. But this agent is highly toxic for warm-blooded animals.
- Kinmix... Such an insecticidal preparation of contact-intestinal action is used to destroy sucking and gnawing pests.
- Decis... The insecticidal agent of contact-intestinal action belongs to the group of synthetic pyrethroids. It is used to get rid of leaf-eating and sucking harmful insects.
- Fitoverm... Biological insectoacaricide, characterized by intestinal contact action, is used to get rid of pests that have settled on crops growing in open or closed ground.
- Bitoxibacillin... It is an insectoacaricidal preparation of biological origin, which is able to protect various crops from harmful insects. The last time before harvesting, any plants are sprayed 5 days, and medicinal plants - 1.5 weeks.
- Lepidocide... Such an intestinal and biological insecticide is very effective. It can be used for processing at any time throughout the season.
- Dendrobacillin... This insecticidal agent is used to treat crops during the growing season in order to destroy leaf-eating and other harmful insects. Any crops can be last treated with the product 5 days before harvesting, and medicinal plants - 10 days before harvesting.
Folk remedies
Pesticides are very effective against many harmful insects. But it should be borne in mind that they contain toxic substances that can accumulate in fruits. If there are not very many pests, then experts recommend not using powerful insecticidal preparations, they can be replaced with folk remedies, of which there are many. If we compare the effectiveness of folk remedies and chemicals, then it is no more than 30-40 percent, which is why several regular treatments are required to destroy the pest, but in the end you will be able to save not only the plant itself, but also the quality of the fruits.
Most often, gardeners use the following folk remedies:
- Tomato leaf decoction... Pour 1 kilogram of finely chopped tomato tops into a bucket of water, mix everything and leave the mixture for 4-5 hours. Then bring it to a boil and keep it on low heat for 2 to 3 hours. The cooled and strained product is diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 1 ...
- Burdock infusion... Fill the bucket 1/3 with finely chopped burdock foliage, then pour water into it to the brim. The infusion will be ready after three days, filter it and start spraying the bushes.
- Milkweed decoction... Half a bucket of water is combined with four kilograms of finely chopped shoots of milkweed. The mixture is boiled for 2.5–3 hours, the cooled and strained broth is poured into a bucket and water is added to it to the brim. This tool will be enough for a couple of treatments, while the first of them is carried out after the appearance of the caterpillars, and the second - four days after the first.
- Hot pepper decoction... Combine a liter of water with 0.1 kg of crushed fruits of hot pepper, boil the mixture for 60 minutes and leave it for two days to infuse. Then crush the pepper directly in the broth until mushy. The filtered broth is used as follows: 1 tbsp is poured into 1 bucket of water. products and 50 mg of liquid soap (for better adhesion).
- Wormwood decoction... Combine 2 liters of water with 1 kilogram of wilted wormwood grass, the mixture is boiled for 10 to 15 minutes. The cooled broth is filtered and poured into a bucket, into which water is then poured to the brim. Plants are treated with the agent regularly once a week.
- Infusion of yarrow... Pour 0.8 kg of dried yarrow herb, which is collected during flowering, into a container. It is poured with freshly boiled water and left for 30-40 minutes, after this infusion is poured into a bucket and water is poured into it to the brim, and the product is again allowed to brew for 40 minutes. Strain and mix with 50 ml of liquid soap before spraying plants.
- Tansy powder... Dried shoots, foliage and flowers of tansy are ground to a powdery state and dusting of plants is carried out with it.
Prevention measures
In order to protect plants and crops from moths, preventive measures are taken in the fall, namely, clear the soil surface near the plants from loose leaves and destroy them. Then dig up the soil in the near-trunk circle of bushes and trees. From early spring, it will be necessary to carry out two preventive spraying of horticultural crops, for this they use Karbofos or another means of similar action. The first treatment is carried out after the buds begin to open, and the second - when the plants have faded. After the fruits are formed on the bushes or trees, it is recommended to use only herbal infusions or decoctions for spraying them.
As a preventive measure, try to take good care of the plants and follow the rules of agricultural technology, since all gardeners know that harmful insects do not settle on strong and healthy plants. In this regard, clean the surface of the trunk circles, remove weeds in time, carry out regular weeding and watering, and then maybe moths will never settle on your trees and bushes.