Preparing roses for winter is especially important in regions where the climate is quite cool. If it is not carried out correctly, it can lead to the death of flowers. Today's popular hybrids and varieties of garden roses can no longer themselves go into a state of dormancy. That is why, even in late autumn, their stems are covered with foliage, and also flowers along with buds often flaunt on them at this time.
With the onset of the first frost, the rose bushes enter a state of dormancy. However, after the air warms up on the street again and the temperature is above 0 degrees, the bushes begin to wake up, while a resumption of sap flow is observed in them. After it gets cold outside again to minus 3 degrees, the juice freezes in the shoots, which leads to tissue rupture. As a result, frost holes appear, which are cracks of considerable length, inside which there is ice. In these places where there is damage, pathogenic microbes easily penetrate into the tissues. As a result, with the subsequent thaw, the active development of the disease may begin. In order to protect roses from frost damage and disease damage, you will need to create a dry shelter. In it, the juice that can flow out of the cracks formed on the shoots dries quickly, which is why the wounds are easily tightened.
Content
Preparing roses for winter
From the first day of August, fertilizing roses with nitrogen-containing fertilizers is stopped. Moreover, almost at the same time, gardeners feed the bushes for the first time before wintering. To do this, use the following nutrient solution: for 1 bucket of water 3.5 grams of borax (or 2.5 grams of boric acid), 25 grams of superphosphate, and another 10 grams of potassium sulfate. This volume of liquid fertilizer is enough to feed the bushes growing on an area of 4 m2.
The plant is re-fed with the aim of strengthening after about 30 days (at the beginning of autumn). For this root feeding, the following solution is used: a bucket of water, 15 grams of superphosphate and 16 grams of potassium sulfate (or the same amount of potassium monophosphate). However, many gardeners believe that instead of applying nutrient mixture to the soil, it is better to spray the foliage. But at the same time, the concentration of this solution should be 3 times less.
From the first days of September until spring, all loosening of the soil surface near the bushes should be stopped. The fact is that they can cause the dormant buds to awaken, due to which the active growth of young shoots begins. And from the second half of September, they pluck out those buds, the size of which is no more than a pea. Larger buds should be left to fully ripen and form fruit.
Pruning roses in autumn (for winter)
What time is the pruning
Many gardeners are unsure of whether to prune rose bushes before wintering. This must be done. Only ground cover and park species are not pruned. At the same time, climbing roses need only light pruning. Autumn pruning is good in that it helps to make the bush stronger, increases its resistance to frost, and also helps to improve crown ventilation.
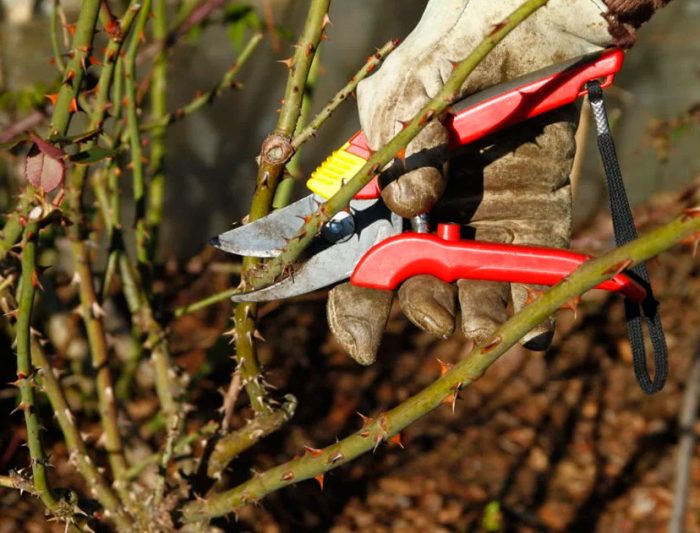
Plants are pruned from mid-October to early November. Do this just before covering the bushes for the winter. For this, a very sharp instrument is used, which should be sterilized in advance.
Autumn pruning rules
Before wintering, both adult rose bushes and recently planted ones are cut off. To do this, cut out all diseased, excessively old, weak or dried out shoots, and also remove all leaf plates, flowers and buds from the bush. Experts recommend leaving only 3 to 5 of the most powerful stems on one bush, while it is desirable that they be equidistant relative to each other. You should also remove all those young stems that did not ripen before the fall. It is highly likely that rot may form on them during wintering, and this can cause the death of the entire plant.
Recommendations for pruning:
- Cut off the bushes on a fine day, while there should be no strong wind.
- Thick shoots covered with slightly dried bark, which are at least three years old, are difficult to cut with a simple tool. Therefore, a hacksaw is used to remove them.
- All cuts, as well as cuts, must be done at an angle. This will save the cut points from the stagnation of the liquid, which will flow down.
- The cut is made, stepping back from the kidney about 5 mm. In this case, the kidney should not be sprouted, but swollen.
- It is recommended to cut the stems on the outer bud. In this case, the young stems that emerged from it will not thicken the crown and intertwine with each other.
- The shortening of the shoots is carried out to a white core.
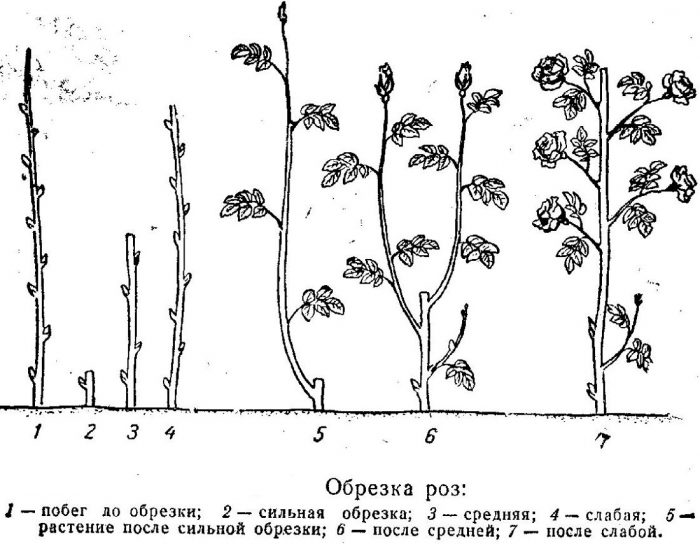
It is also important to know which shoots for what length the shoots are shortened during pruning. In total, there are 3 types of stem trimming:
- Long cut... In this case, only a small part of the stem is cut. It should have at least nine buds.
- Medium cut... The stem is shortened at a height of 0.35 m from the surface of the earth, while five buds should be left on it.
- Short cut... It is very rare. The stems are cut almost completely, and no more than two buds should remain on them.
Hybrid tea, floribunda and polyanthus roses are shortened, leaving 4 or 5 buds, which should be well developed. Only young bushes of the standard cascade rose (in the first year of growth) are subjected to short pruning, and their stems are shortened to 15 centimeters. In older bushes, only those stems that have faded are subject to pruning, while young shoots are only slightly shortened.
After pruning the remontant varieties, as well as the grandiflora rose, only five buds should remain on the stems. In shrub and Old English varieties, the stems are shortened by 2/3 or ¾. Park roses, which are highly resistant to frost, need only sanitary pruning. For this, all injured, old and weakened branches are cut out from the bushes, while powerful young stems need only be slightly shortened.
When the pruning is complete, all you have to do is rip off all the foliage from the stems, be sure to protect your hands with gloves. In order not to accidentally injure the buds during the removal of leaves, move your hand along the stem from the bottom to the top.


Watch this video on YouTube
Pruning climbing roses for the winter
During the preparation of climbing roses for wintering, they also need pruning. In this case, all dried, injured and weakened stems, as well as buds and opened flowers, are cut out. Powerful, well-developed stems only need to be shortened slightly. Select 1 or 2 old long stems and shorten them to 0.35‒0.4 m. This is necessary to activate the growth of replacement basal shoots.
It is highly undesirable to carry out a full pruning of this type of roses. The fact is that because of this, in the coming season, the bush can grow many vegetative stems that will not bloom. Such a plant is cut in the last days of September or the first in October. When the bush is pruned, be sure to rip off any remaining foliage from it. After that, clean the surface of the soil near the roses from grass, leaves and cut shoots.
Shelter roses for the winter
What time to shelter
After all leaf plates are removed from the shoots of roses, the plant will "understand" that it is time for a dormant period. You need to start covering it only after the places of cuts and cuts dry well. But remember that haste in this matter is not acceptable. In the event that the autumn period is warm, then the bushes, even after removing the foliage, will still actively grow. And if the plant is covered during this period, this can lead to damping of the buds, and to the death of roses.
What is the optimal air temperature for hiding garden roses? The bushes should be at an air temperature of minus 2 to minus 5 degrees for about half a month. In this case, they will have time to properly prepare for the period of rest, all life processes in them will practically stop. At the same time, remember that self-rooted roses can die when the temperature drops to minus 3 degrees, and those bushes that have been grafted onto rose hips can withstand frosts down to minus 10-12 degrees.


Watch this video on YouTube
The approximate time of sheltering roses in the Moscow region and in the middle latitudes
On the territory of Russia in the central regions, it is recommended to build a shelter for roses for the winter from the first to the twentieth of November. The day should be fine, and the air temperature should be from minus 5 to minus 7 degrees.
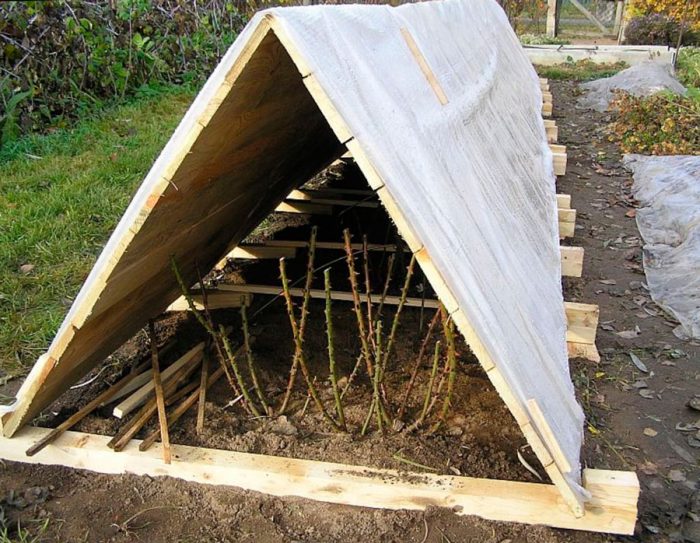
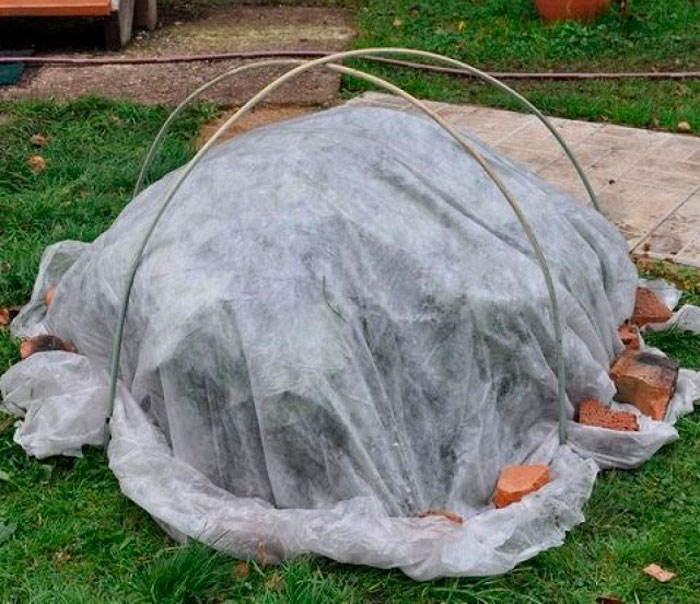
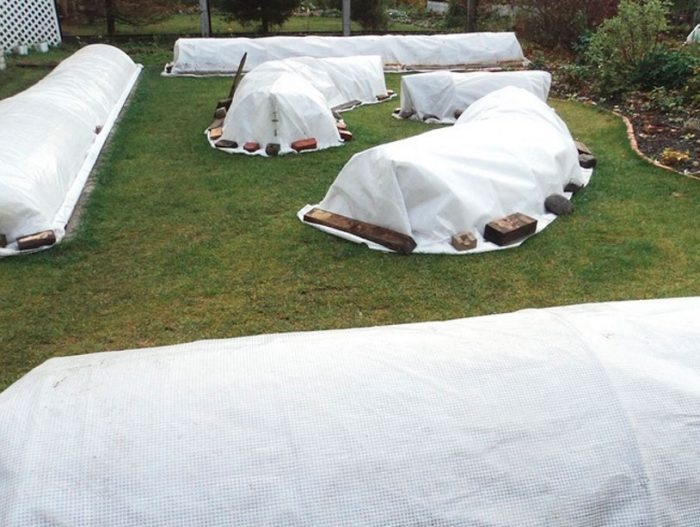
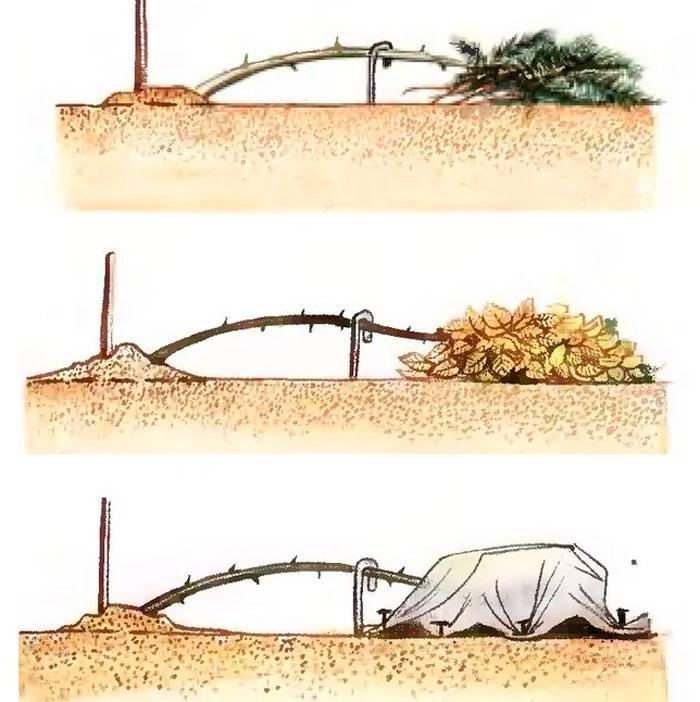
In the Moscow region, the stems of floribunda, polyanthus and hybrid tea roses are pre-bent to the soil surface. In this case, do not forget to put a small layer of spruce branches under them in advance. You can fix the shoots in this position with pins made of metal or wood. Conduct a high hilling of the base of the plant using dry peat, humus, soil or compost for this. Bushes should be piled up to a height of approximately 0.35‒0.4 meters. Only after that, the shoots bent to the ground are thrown over with spruce branches or with flying leaves. If desired, strong metal arcs can be installed over the roses bent to the ground surface, over which a special covering material is stretched.
Floribunda, hybrid tea and standard roses have stems that are less flexible and more fragile than climbing roses. In this regard, it is rather difficult to tilt them to the soil surface. That is why, in this case, the bushes do not bend to the ground. Instead, arched metal supports are installed above them, while their height should correspond to the height of the roses. Pull the film over the arcs. But before covering the plant, it is imperative to carry out a high hilling of its base.
Only some varieties of roses need to be sheltered for the winter.Most park hybrids and cultivars are so resistant to frost that they don't need to be covered at all. And in order to protect those park varieties that are less winter-hardy from frost, you just need to wrap the bushes with paper, and also carry out high hilling.
Shelter roses for the winter in the Urals
In the Urals, it is recommended to start sheltering rose bushes in the last days of October. And you should wait until the time when the temperature on the street is set in the region of minus 5 degrees. If at this time the ground is covered with a layer of dry snow, it will be very good. The fact is that the snow does not allow the soil to cool down too quickly. However, you shouldn't hope that nature will take care of your roses. You cannot do without sheltering plants for the winter.
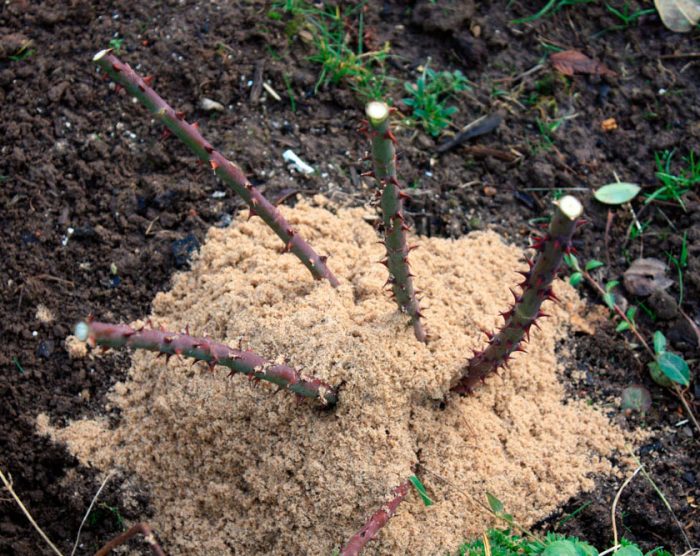
Around the middle of the autumn period, the bushes should be shortened to the height of the shelter. After that, all young stems that have not matured are cut out from them, and the foliage is also cut off. Clean the surface of the soil near the roses from plant debris. Often, various rodents are taken under the shelter, which gnaw the bark at the bottom of the stems. To avoid this, experienced gardeners recommend putting special baits with poison under the plants. To do this, you need sawdust. They should be soaked in a solution of 10 liters of water and 1 tbsp. l. creoline. Then all that remains is to distribute the sawdust under the plants. The base of the rose is sprinkled with dry soil or peat at 1/3 of the height. Those stems that were not covered with spruce branches should be tied.
Single roses that have undergone a short cut can be covered with wooden boxes on top. Take the film and cover the boxes on top. And so that the shelter is not blown away by the wind, the edges of the film are sprinkled with soil or pressed with stones, bricks, etc. Leave small vents for ventilation. For this, the film is not pressed tightly in several places.
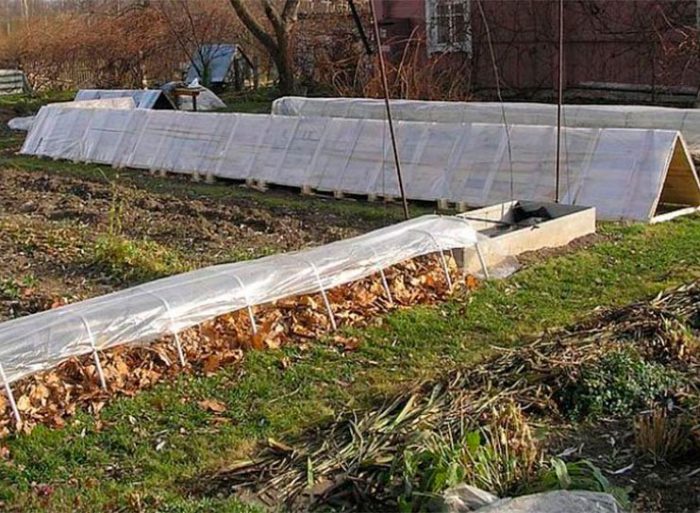
In the event that forecasters predict a very cold winter, it is recommended to build a kind of hut of plywood or boards over the plant. A film is laid on top of it. Please note that the height from the "ceiling" of the hut to the top of the bush should be about 10 centimeters. If you build such a shelter correctly, then the bushes will not mate and will not freeze. In the event that several rose bushes grow in your garden at once, and they are located next to each other, then a frame of boards can be installed over the entire width of the planting above the plants, which is covered with a film on top. Do not forget to press the edges of the film with something heavy to the surface of the site.
Features of the shelter of roses in Siberia
When sheltering bushes for the winter in Siberia, several features of the climate in this region should be taken into account. If the roses are not covered correctly, they can freeze or start to rot.
Remember that the shelter of these flowers for the winter must be carried out in a timely manner. Never cover them ahead of time. To determine the exact time of shelter for the bushes, you should carefully monitor the weather forecasts. Sometimes it happens that in late autumn it is still quite warm in Siberia.
Young bushes that have been planted recently can be protected from frost by covering them on top with a 5 liter plastic bottle, from which the bottom should be cut off. From above, the plant is covered with flown foliage. To prevent the bush from starting to rot, remove the cap from the neck of the bottle. Adult roses that have undergone short pruning should be sprinkled with dry soil high and sprinkled on top with a thick layer of fallen leaves. Since there is relatively much snow in Siberia in winter, your only task is to protect the bushes from the first severe frosts until they are covered with a thick layer of snow from above.
Shelter climbing roses for the winter
Since the buds of climbing roses are formed on last year's stems, they should not be heavily pruned in autumn. And this greatly complicates the process of sheltering bushes for the winter.In this regard, the lashes of such roses are bent to the surface of the site (like in raspberries), while it should first be covered with spruce branches. Shelter of the plant is carried out only after the air temperature outside is constantly below zero. From above, the whips are thrown over with flown foliage or spruce branches. Then they are insulated with a covering material or film.


Watch this video on YouTube
Covering material for roses for the winter
Rose bushes will be protected from freezing in winter by such covering material as:
- lutrasil;
- geotextile;
- polyethylene film;
- spunbond;
- flying foliage;
- rags and burlap;
- plywood and boards;
- spruce branches;
- unnecessary coats or blankets.
The choice of a suitable covering material is influenced by the method of shelter, as well as the variety of roses. Large powerful bushes can only be covered with spruce branches or foliage. And thermophilic varieties need a better shelter. For them, it is necessary to install frames that are covered with film, while the stems are additionally tied with rags and bags.
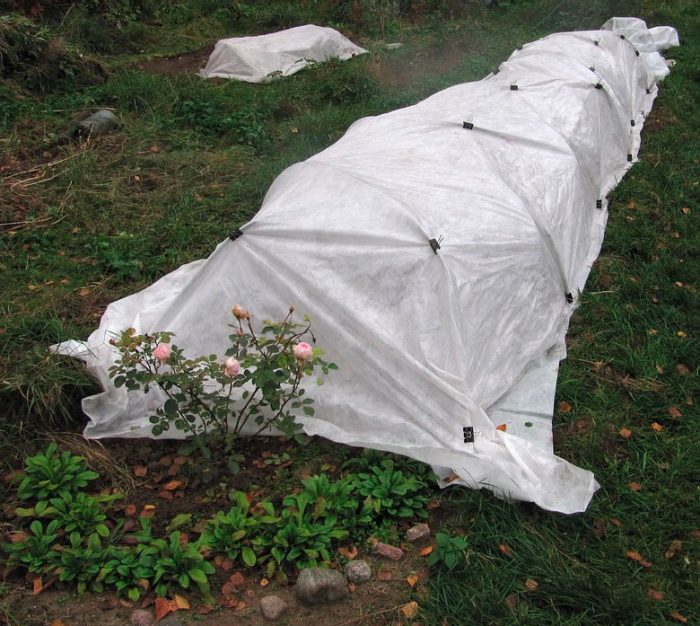
To cover several bushes at once, film is most often used, but it is better to opt for lutrasil, geotextile or spunbond. They cover a frame made of wood or metal. These materials will protect the bushes not only from frost, but also from damping, as they are able to remove fumes.
Pay attention to the density of the covering material, it must be at least 200 g / m2... In this case, the material is folded in several layers. The edges of the non-woven shelter, which is stretched over the frame, must be pressed with stones, boards, etc. When covering with a film, you need to leave a few vents for ventilation. And when using lutrasil, spunbond and geotextiles, this is not required. On the contrary, their edges are reliably pressed against the soil surface so that there are not a single hole.
If you are covering climbing roses with non-woven fabric, then their lashes do not need to be laid on the ground. First, the hilling of the base of the bush is carried out to a height of about 0.3 m. After that, the shoots are wrapped in several layers of covering material, which is fixed using ordinary clothes pegs or a stapler and staples.


Watch this video on YouTube