A biennial or perennial herb onion (Allium) is a member of the Onion subfamily of the Amaryllis family. This genus unites about 400 species. In nature, such a plant is found in the Northern Hemisphere, where it prefers to grow in forests, steppes and meadows. Already 4 thousand years ago in China, Iran and the Mediterranean they knew about the existence of onions. This plant got to the territory of Russia only at the beginning of the 12th century from the banks of the Danube. "All" is translated from Celtic as "burning", it is believed that it was because of this that Karl Linnaeus called such a plant onion "allium". There is also an opinion that the Latin name comes from the word "halare", which translates as "smell". Various types of this plant are cultivated. The most popular among gardeners is the type of onion (Allium cepa), as well as many of its varieties. And also quite often they grow onions, leeks, shallots, onions, etc. Onions are also grown as an ornamental plant; landscape designers use the following types to decorate flower beds: inclined, Aflatun, Dutch, gigantic, Karatav, round-headed , Schubert, Christoph, etc.
Content
Bow features
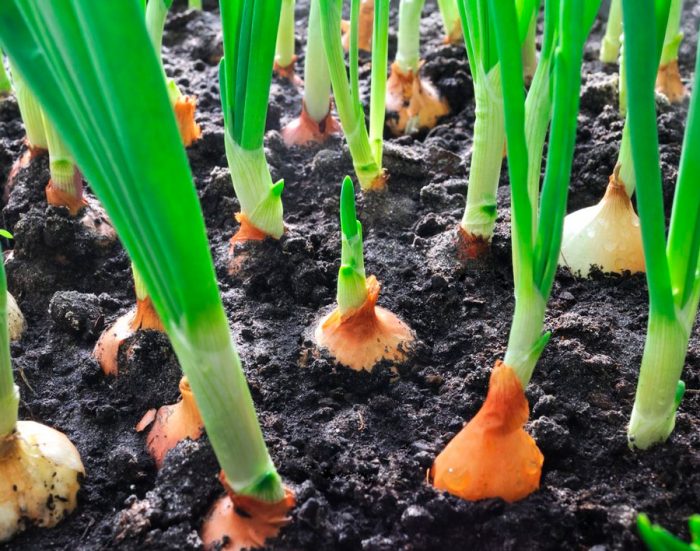
All representatives of the genus onion have a large spherical flattened bulb, which is covered with shells of white, purple or pale red color. Basal fistular leaf plates have a linear or belt-like shape. The height of thick swollen stems reaches 100 cm. Umbrellas consist of small nondescript flowers with long pedicels. In some species, the inflorescences reach 0.4 m in diameter, they are clothed in a cover that persists until the flowers begin to open. The ovary can be three-celled or unilocular. The shape of the seeds is angular or round. Fruiting is observed in August or September. The most popular among gardeners is onion.
Planting onions in open ground
What time to plant
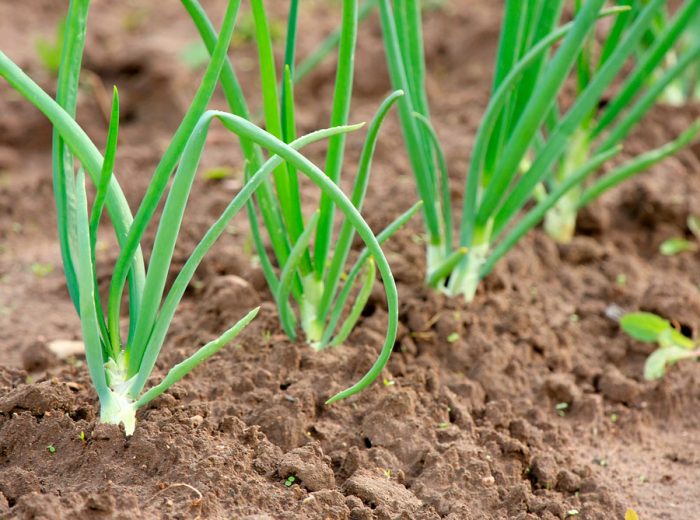
Onions are planted in spring in the first decade of May, while the soil should be very well warmed up. If it is planted in the ground, the temperature of which is less than 12 degrees, then the plants will shoot.You should know the main principle of the cultivation of this culture: in the first year, in the spring, seeds are sown, and by the onset of the autumn period, small bulbs, called sevk, should grow from them, which are planted the next year in spring, and full-fledged bulbs are already harvested in the fall. However, it is very difficult to preserve sowing until spring time, since for this it must be provided with a special temperature regime, as well as optimal air humidity. In this regard, some gardeners sow seedlings in the soil before winter in the year of ripening.
Suitable soil
Onions are light-loving plants. Dry, open and well-lit areas are suitable for planting. The soil should be saturated with organic matter, and its pH is 6.4-7.9. If the soil is acidic, then liming can be corrected.
The landing site must be prepared in advance. In autumn, it is necessary to dig it to a depth of 15 to 20 centimeters, while peat-manure compost or rotted manure must be added to the soil. Fresh manure cannot be brought into the soil, since it causes greens to actively grow, which negatively affects the ripening of the bulbs. To correct acidic soil, wood ash, limestone, dolomite flour or ground chalk must be added to it. In spring, before proceeding with sowing, 10 grams of urea, 60 grams of superphosphate and 20 grams of potassium chloride per 1 square meter of the plot must be added to the soil. Fertilizers are embedded in the ground using a rake. Then you can start planting this culture.
Onions will grow best in areas where cabbage, peas, tomatoes, potatoes, beans or green manures were previously grown. And in the area where carrots, garlic, onions or cucumbers have grown before, this crop can be sown only after 3-5 years.


Watch this video on YouTube
Landing rules
There are 3 methods for growing onions:
- Grow as a biennial plant. With this method, you should first grow the sevok.
- Grow as an annual from seeds.
- Grow as an annual from seeds, but through seedlings.
These methods will be described in detail below. For 1 year, this crop can be grown from seeds only in regions with a long summer period, while only semi-sweet and sweet varieties are grown by this method. Before sowing, the seed needs to be prepared, for this it must be stratified or placed in a moistened gauze for swelling for 24 hours. After that, the seeds are sown in the prepared soil, which must first be spilled with a solution of copper sulfate (1 bucket of water 1 tbsp. L. substances). It is necessary to deepen the seeds into the ground by 15 mm, while they are sown according to the scheme of 13x1.5 centimeters. The bed must be watered very well using a divider, and then it is covered with foil on top. The shelter must be removed after the first seedlings appear. Seedlings need to be thinned out, while a distance of 20-30 mm should be kept between the plants, then the surface of the beds is covered with a layer of mulch (humus). It will be necessary to thin out the crops again in 20 days, while the distance between the plants should be increased to 60–80 mm.
Sweet and semi-sharp onion varieties are grown through seedlings. After the seed material is subjected to pre-sowing preparation, it should be sown in boxes, and this is done 50-60 days before planting the plants in open soil. Seeds are sown thickly, they are buried in the ground by 10 mm, while the row spacing should be equal to 40-50 mm. Such seedlings are unpretentious, however, before planting the plant in open soil, experts advise shortening their roots and leaf plates by 1/3.
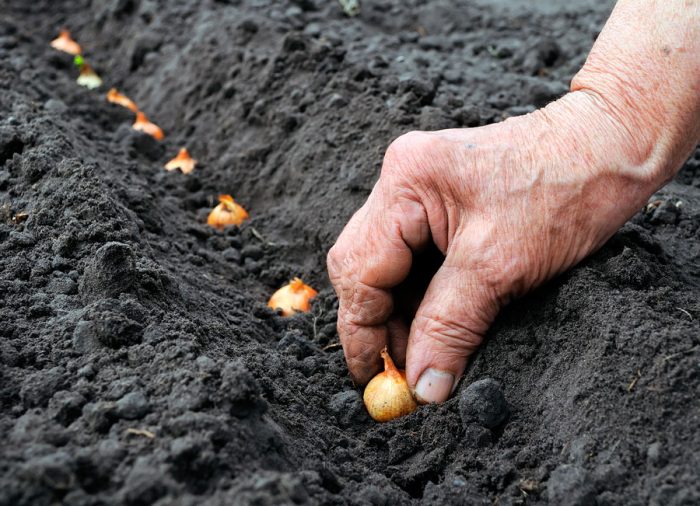
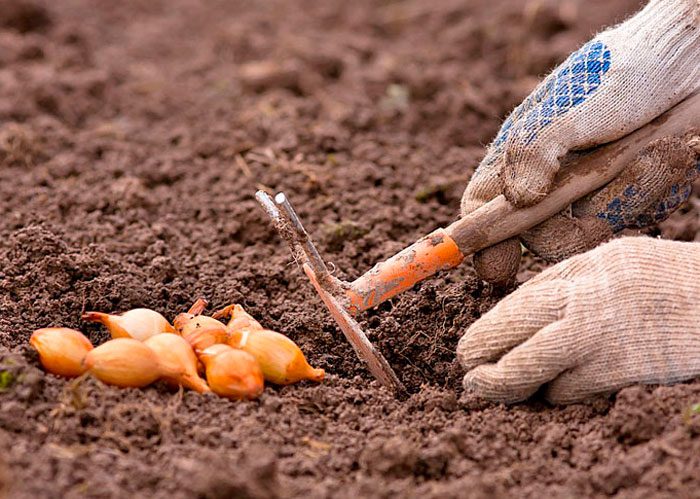
If the summer period in your region is not very warm and short, then in 1 year you will most likely not be able to get full-fledged bulbs from seeds. In this case, you will have to grow onions as a biennial plant. For this, during the first year, it will be necessary to grow a set from seeds, and in the second year onions are already grown from it.This method is great for growing pungent varieties. Sowing seeds in open soil should be exactly the same as when growing onions from seeds for 1 season (see above). With the onset of the next spring period, in the first days of May, the seedlings are planted, deepening it into the ground by 40-50 mm, while leaving a distance of 80 to 100 mm between the bulbs, and the row spacing should be about 30 centimeters. Do not forget to prepare the site before planting (see above). Before you start planting the sevka, it must be sorted out and calibrated. Then it is placed in the sun for 7 days so that it can warm up properly, otherwise the bow will shoot. Before the planting itself, the seedlings are placed in a solution of copper sulfate (1 tsp of water for 1 bucket of water), where it should stay for 10 minutes. If during onion growth you intend to pull out young plants for cooking, then when planting, the distance between the bulbs must be reduced to 50–70 mm, and then it is gradually brought to 80–100 mm.
Planting onions before winter
For sowing before winter, wild oat (small seeding) is excellent, since it has a high resistance to shooting. So that in spring you can cut fresh green onions very early, for this, before winter, you should plant a small amount of large sets. The advantages of planting onions before winter:
- it is not necessary to store the planting material until spring, and this is good because if the seed is stored incorrectly, it will dry out very quickly;
- in spring, an onion fly may appear, however, the winter onion already manages to get stronger so much that it cannot harm it;
- in July it will already be possible to start harvesting;
- in the garden where the onion grew, it will still be possible to plant something in the same season.
For winter sowing, as a rule, frost-resistant varieties are used, for example: Arzamassky, Danilovsky, Strigunovsky, Stuttgarten. The site for sowing must be chosen in the same way as for sowing onions in spring. However, there are some differences, you should choose a site where in spring the snow cover very early disappears, and melt water should not stagnate on it. Sevok is planted in autumn on October 5–20, under the very frost, but you should not delay it, since the soil should not have time to cool down. Before planting the sevok, it must be sorted out, calibrated and warmed up in the sun. It is planted in grooves, the depth of which should be about 50 mm, while the distance between the bulbs should be 60–70 mm, the row spacing should be about 15 centimeters. When the first frosts come, the top will need to be covered with straw or spruce branches, the shelter is removed in spring, as soon as the snow begins to melt. Do not cover the onion area too early in the fall, as this can cause the bulbs to dry out.


Watch this video on YouTube
Onion care
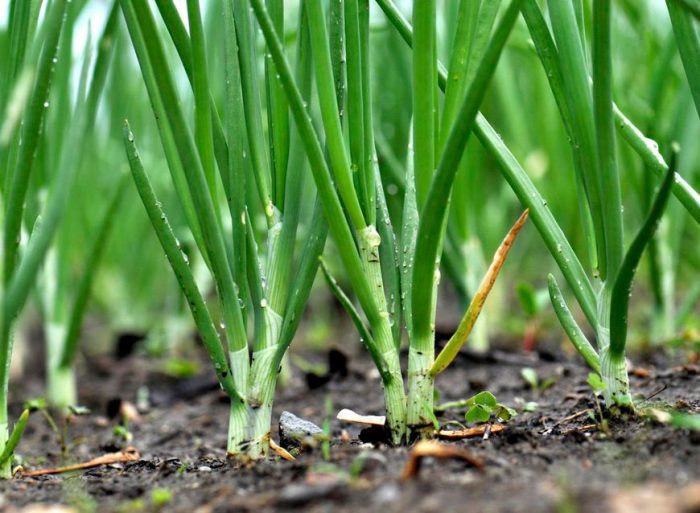
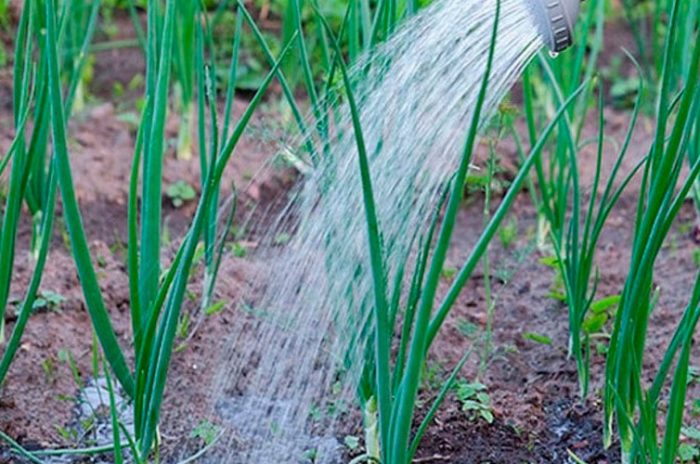
Onions growing in open soil must be watered in a timely manner. When the bed is watered, its surface must be loosened, and all weeds that can strangle young plants should be removed. Also, this culture must be fed on time, and, if necessary, treated against harmful insects or diseases, using insecticidal or fungicidal preparations for this.
How to water
Ideally, onions should be watered once every 7 days, while 5-10 liters of water are taken per 1 square meter of the plot. However, it is best to focus on the weather, which is highly variable. So, if there is a drought, then the onions must be watered much more often (almost every day), and if it rains, then the watering must be delayed, otherwise the bulbs may rot due to stagnant water in the soil. It should be remembered that if the onion needs urgent watering, then its feathers acquire a white-gray tint, and when stagnant water is observed in the ground, the green part of the bushes becomes faded. It is necessary to start gradually reducing watering in July, since at this time the bulbs begin to ripen.However, if there is a severe drought, the plants are watered in the same manner as before.
Fertilizer
It was already said in detail above that in the fall, when digging a site, organic matter should be introduced into the soil, while in the spring, before planting, a complex of mineral fertilizers is introduced into it. In addition, if the growth of foliage is relatively slow, the plants should be fed with an organic fertilizer solution (1 cup of urea, bird droppings or mullein is taken for 1 bucket of water), 3 liters of nutrient mixture are used for 1 square meter of the garden. After half a month, if necessary, re-fertilize with the same mixture. And after the size of the bulbs is similar to a walnut, the onions will need to be fed again with the same fertilizer.
Treatment
Often, gardeners do not know how and how to carry out preventive treatment of onions from diseases. After the height of its feathers is 15 centimeters, the plant is sprayed with a solution of copper sulfate (1 tsp of water for 1 bucket of water), this will protect the culture from fungal diseases. If desired, add 1 tbsp into the solution. l. Laundry soap crushed on a grater, in this case it will be fixed on the foliage.


Watch this video on YouTube
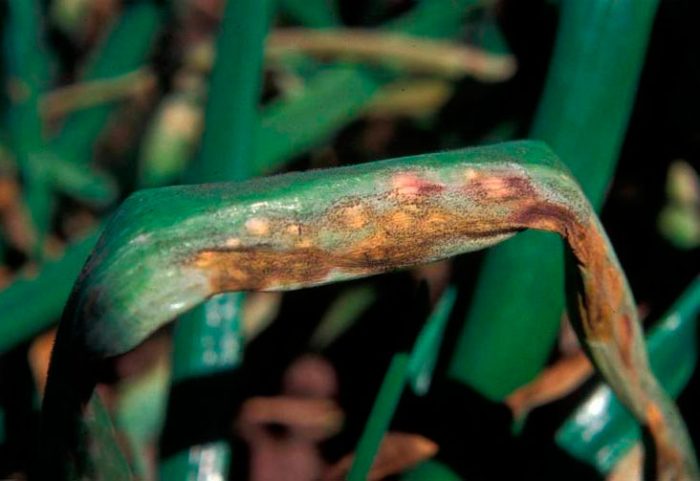
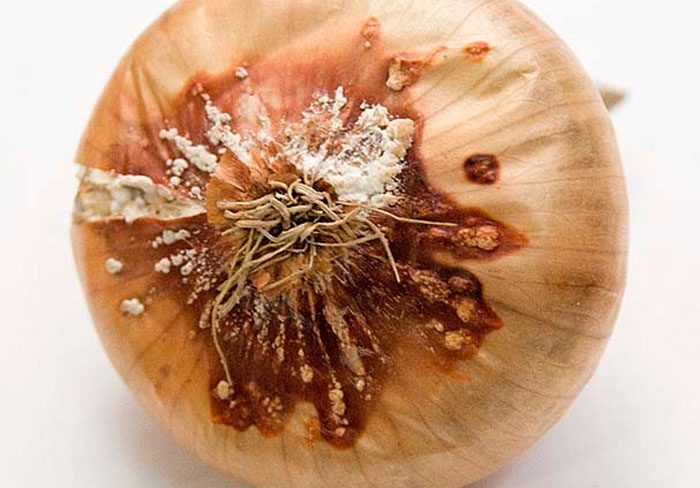
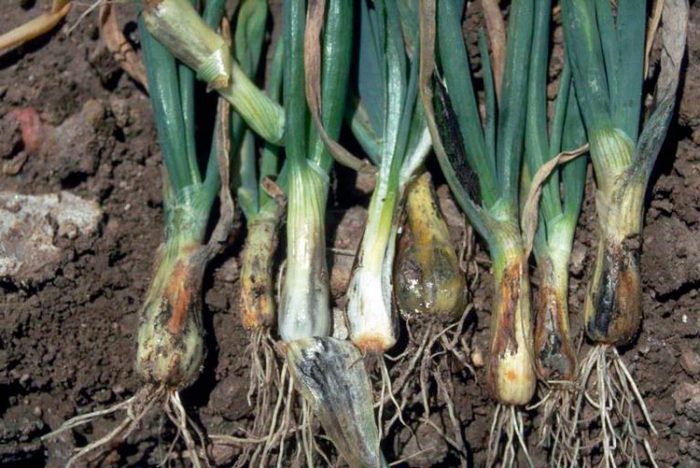
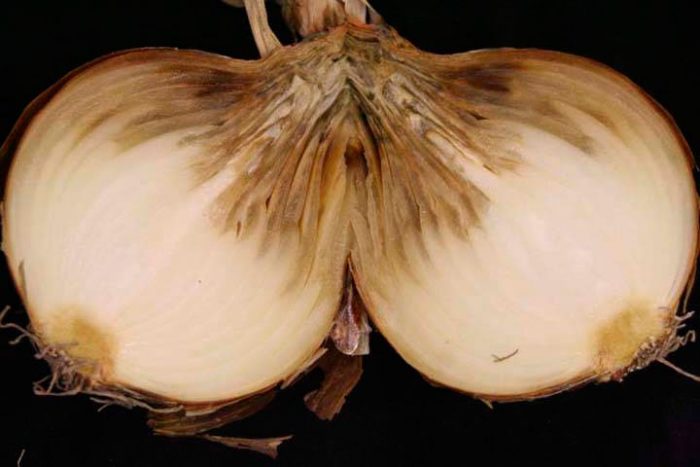
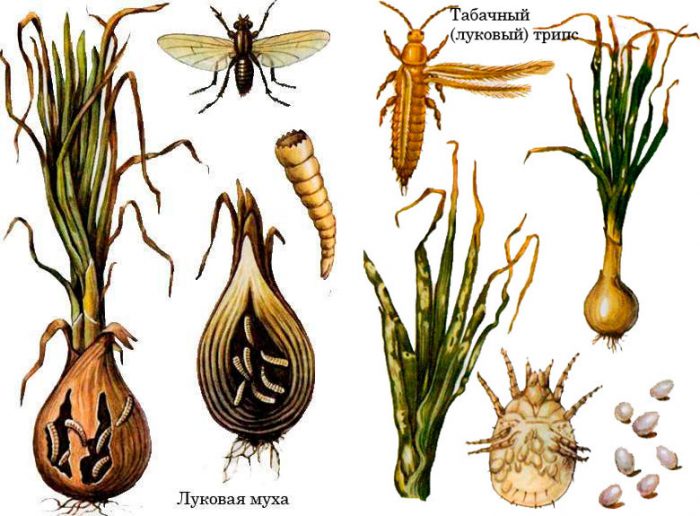
Diseases and pests of onions with photos
Onion diseases
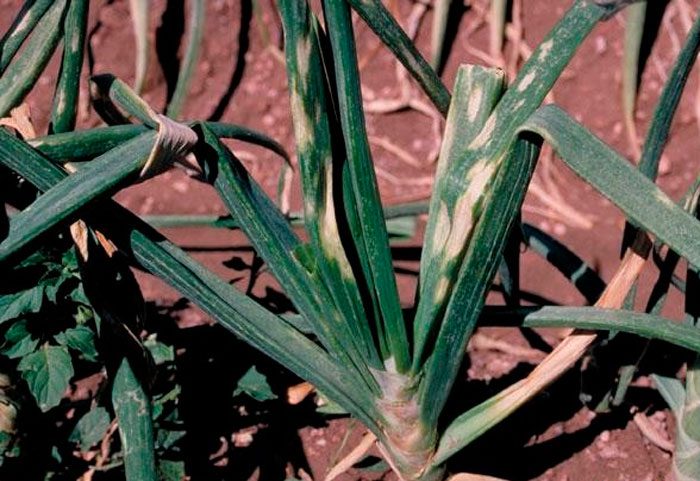
Before you start growing onions, you need to find out what it can hurt, and which of the pests poses the greatest danger to it. This culture can be affected by diseases such as: cervical, gray and white rot, jaundice, fusarium, downy mildew (downy mildew), smut, rust, mosaic and tracheomycosis.
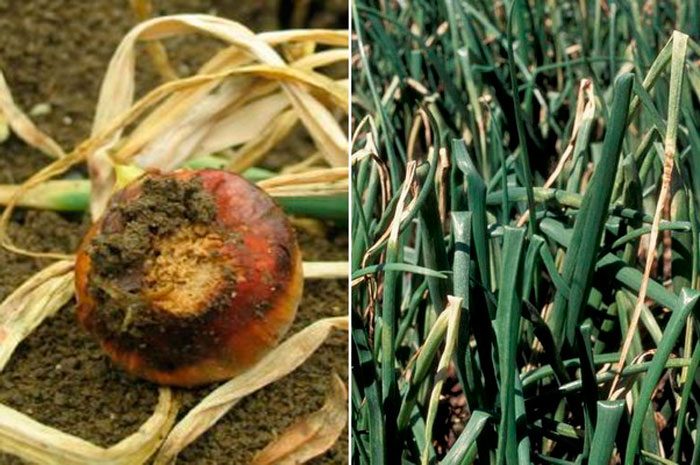
White rot
White rot - its development is observed when grown on acidic soil. Therefore, if the soil on the site is acidic, it must be limed. It also often affects those plants that grow in soil with a high nitrogen content. Diseased plants need to be dug up and destroyed, and for preventive purposes, before planting a crop, it is necessary to dust the bulbs with chalk.
Gray rot
Gray rot is a fungal disease, its active spread and development is observed in wet and rainy weather. Diseased plants must be removed from the ground and burned. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to adhere to the rules of agricultural technology of this culture, and even in the spring the plants are treated with a solution of copper sulfate.
Onion jaundice
Onion jaundice is a viral disease. Deformation of flowers is observed in the affected plant, and chlorotic specks appear on its foliage. This disease is incurable, in this regard, the affected bushes need to be dug up and burned, while all weeds must be removed from the rows and beds in time immediately after they appear. And you also need to adhere to the rules of crop rotation.
Peronosporosis
Peronosporosis (downy mildew) - in the infected plant, oblong spots of light color are formed on the stems and foliage, there is a gray bloom on their surface. The spots turn black over time. Infected bulbs, laid for storage, germinate very early, and in the bushes that have grown from them, seed formation is not observed. After the harvest is harvested, to exterminate the causative agent of the disease, before the onions are stored for storage, the bulbs are heated for 10 hours at a temperature of about 40 degrees. Also, for prevention purposes, do not allow the plantings to thicken.
Fusarium
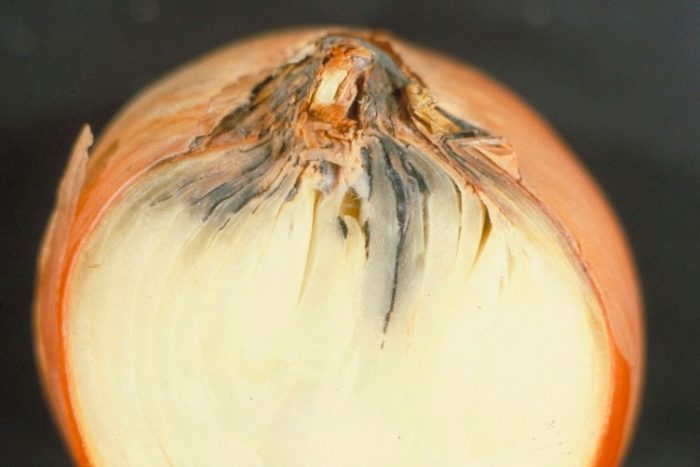
Fusarium - in diseased plants, the tips of the feathers turn yellow, since rotting and dying off of tissues is observed in the bulbs in the bottom area. This disease is most active when the weather is hot for a long time. Also, this disease can develop due to the fact that the onion fly has settled on the plants. For the purpose of prevention, before starting planting, the seed must be warmed up.
Smut
Smut - the infected plant forms translucent convex stripes of a dark gray color, as the disease progresses, they crack, while the spores of the fungus come out.Also, the tips of the leaf plates dry out in plants. For prophylactic purposes, before laying the crop for storage, it should be warmed up for 18 hours at a temperature of about 45 degrees. You also need to clear the area of weeds in time and not plant different varieties of onions on the same garden bed.
Rust
Rust - red-brown swellings appear on the foliage of the affected onion, in which there are fungal spores. For the purpose of prevention, before storing the harvested crop, it is heated for 10 hours at a temperature of about 40 degrees. Also, the planting should not be allowed to thicken, and it is also necessary to dig up and destroy the affected specimens in time.
Tracheomycosis
Tracheomycosis - this disease is a consequence of fusarium. First, the lower part of the bulb rots, and then the rot gradually covers it completely, as a result, the roots of the plant die off, and the foliage turns yellow. All diseased plants must be dug up and destroyed. For prevention purposes, adhere to the rules of crop rotation and agricultural technology.
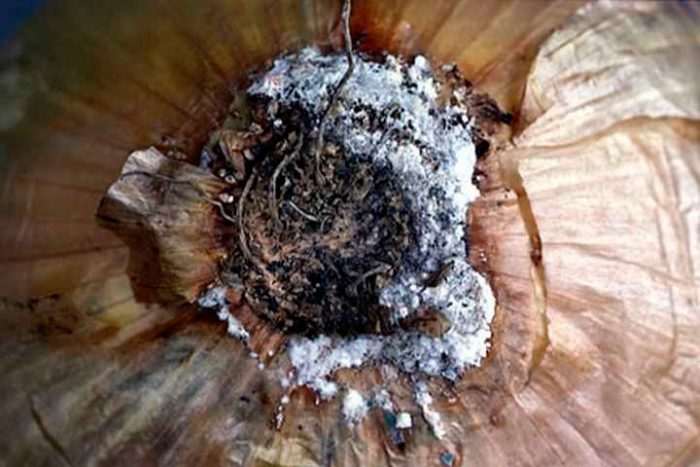
Cervical rot
Cervical rot - in affected plants, a dense mold of gray color appears on the outer scales, with the development of the disease, they become black spots. The first symptoms of the disease appear after harvest, and after about 8 weeks, other symptoms appear. The lowest resistance to neck rot is found in late onion varieties. As a rule, the infection of plants occurs when they are cultivated in unfavorable conditions. Therefore, for the purpose of prevention, it is necessary to adhere to the rules of agricultural agricultural technology, and it is also necessary to warm up the seedlings before planting, and also the onions before storing them, while the temperature should be about 45 degrees.
Mosaic
Mosaic - in diseased bushes, the foliage becomes similar to corrugated and flat patches, on the surface of which there are stripes of yellow color, the inflorescences become smaller and the number of seeds decreases, as well as lagging onion in growth. This viral disease is incurable, therefore all necessary preventive measures should be taken so that the plant does not become infected.
All fungal diseases are easily treated with fungicidal preparations. However, it should be borne in mind that both useful substances and poisons from chemicals can accumulate in the bulbs.


Watch this video on YouTube
Onion pests
The greatest danger to onions is posed by onion burrowers, moths and flies, sprout flies, bear, cabbage, garden and winter moths, and tobacco thrips.
To destroy the caterpillars, the onion should be sprayed with a solution of Gomelin (0.5%) or Bitoxibacillin (1%). For the extermination of tobacco thrips, spraying with Actellik or Karbofos solution (0.15%) is used. You can get rid of the lurker with systemic insecticides. To destroy the onion fly larvae in the fall, a deep digging of the site should be carried out. It is known that the onion fly does not tolerate the aroma of carrots, therefore, when planting, it is recommended to alternate rows of onions with rows of carrots. To get rid of the onion moth, weeding must be carried out regularly throughout the season, and after harvesting, all plant residues must be removed from the site, and the rules of crop rotation and agricultural techniques must be adhered to.
To get rid of the common bear, you need to use bait. To do this, it is necessary to make several holes on the site with a depth of 0.5 m, horse manure should be put in them. Do not forget to cover the pit with wooden shields on top. When the bears climb into the manure to warm up, it should be burned along with them.
Harvesting and storing onions
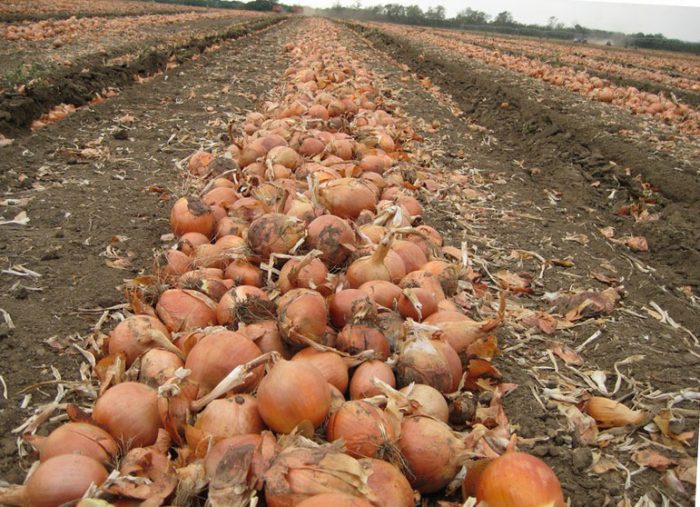
Collecting onions is carried out after the new leaf plates stop growing, as well as feathers fall, while the bulbs should have the shape, volume and color characteristic of the cultivated variety. As a rule, this time lasts from the second half of August to the first ten days of September. Choose a dry and sunny day for harvesting. Do not delay harvesting, as the bulbs may begin to grow again and cannot be stored.
The bulbs extracted from the soil must be distributed over the surface of the beds for drying, then the dried soil should be removed from them. Before laying the crop for storage, it is dried by spreading it out in the sun or in a dry and well-ventilated room. Some gardeners use an oven to dry the bulbs. First, they are dried at a temperature of 25 to 35 degrees, and then at 42–45 degrees for 10 hours. After that, the bulbs should be carefully examined, and those that have rotted or are affected by the disease must be discarded. Also, you can not store the onions without husks, and even spoiled ones. When the crop is dried, the foliage must be removed from each bulb using sharp scissors, while the length of the remaining neck should reach 40-60 mm. Plain yellow onions are best stored because they have a dense shell and are unpretentious. Bulbs grown from seeds are stored worse than those obtained from seedlings. And you also need to take into account that semisweet and sweet varieties have an excessively thin husk, so they are more susceptible to various diseases and are stored much worse than bitter varieties.
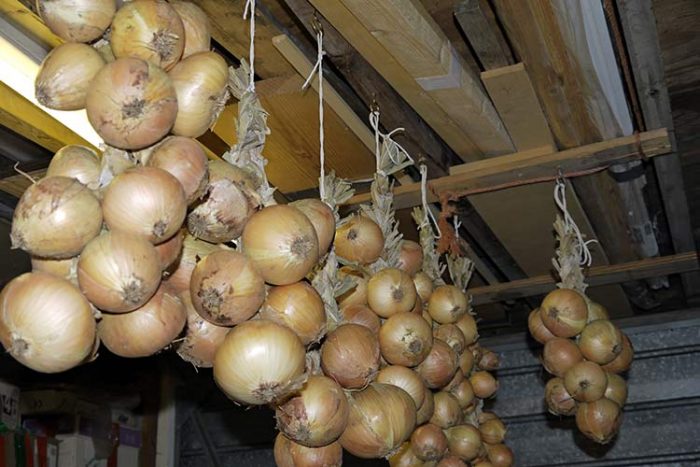
You can store this vegetable in a dry cellar, the temperature in which should be about 0 degrees (it can be slightly warmer), but it should not be stored next to beets, potatoes, carrots and other vegetables that need high humidity. The bulbs can be folded into fabric bags, baskets, boxes, nets or oversized stockings. But you need to remember that the bulbs do not rot, dry air must constantly flow to them, so you cannot put them in a thick layer in any container. Bulbs stored in a basement or dry cellar should be regularly inspected, which will allow timely identification of sprouted or rotten specimens. In order for the crop of this crop to be stored longer than usual, you need to cauterize the roots of the bulbs.
Onions can also be stored in an apartment by choosing a relatively cool place (from 18 to 20 degrees), which should be away from heating appliances, while braids must be weaved from the bulbs. But to do this, you do not need to cut off the foliage from the bulbs during harvest.
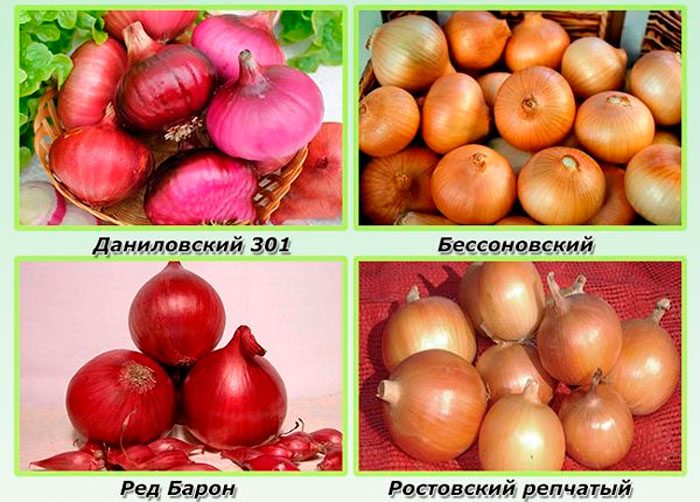
Types and varieties of onions with photos and names
Bulb onions
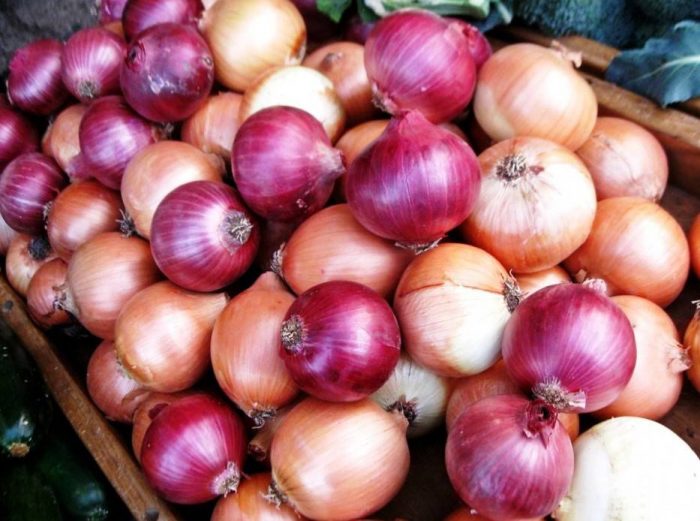
Onions are the most popular among gardeners. It was known to people more than 6 thousand years ago; mentions of this vegetable were found in ancient Egyptian papyri. The height of this perennial is about 100 cm. The fleshy bulbous spherical-flattened shape reaches 15 centimeters in diameter, the color of its outer scales can be white, yellow or purple. The tubular leaves are colored green-gray. Lush umbellate globular inflorescence consists of white-green flowers with long stalks. The swollen hollow arrow can reach a height of 150 cm, the shape of the fruit is spherical. Numerous varieties of this type are divided by taste into:
- bitter and pungent - they contain 9-12% sugar;
- semi-sweet - they contain sugar from 8 to 9%;
- sweet - they contain 4–8% sugars.
It is noteworthy that bitter varieties of onion contain more sugar than sweet ones, but they also contain a lot of essential oils, so they have a more bitter taste. In order to prepare the first or second course, they take semi-bitter, spicy or bitter varieties, and sweet varieties are used to prepare desserts and salads. The most popular varieties:
- Alice Craig... The bulbs have a high taste, and they are well stored, they can be used for cooking various dishes. Their upper scales are white.
- Feng Globe... The large bulbs are covered with light yellow scales and have a mild flavor.They keep well for a long time, and are also suitable for preparing a variety of dishes.
- Sturon... The juicy bulbs are medium in size, and they are covered with yellow scales. They store well and are used to prepare hot meals.
- Stuttgarter... Large sweet bulbs have a deep yellow color and can be stored well for a long time. Suitable for preparing main courses and main courses.
- Long Red Florence... The soft red onions have a sweet taste similar to shallots. They are eaten fresh, and sauces are also prepared from them. This variety is not suitable for long-term storage.
- Red Baron... Large red onions have a pungent taste and can be stored well for a long time.
Of the salad varieties, Redmate and Furio red onions are very popular, as well as Gardsman, which has long white stems, and the White Lisbon variety for greenhouses, which is distinguished by high yields. And also the Prince of Wales variety, which is a perennial. Similar to a batun onion, it is highly branching, and its foliage is often used as a chives.
Leek or pearl onions from the Mediterranean
People knew about this bow a long time ago, in the days of ancient Rome, Greece and Egypt. This biennial has lanceolate leaves, on the surface of which there is a waxy bloom. These plates fold along the central vein than are similar to garlic ones, but they are larger in size. This plant is very demanding on soil moisture and care.
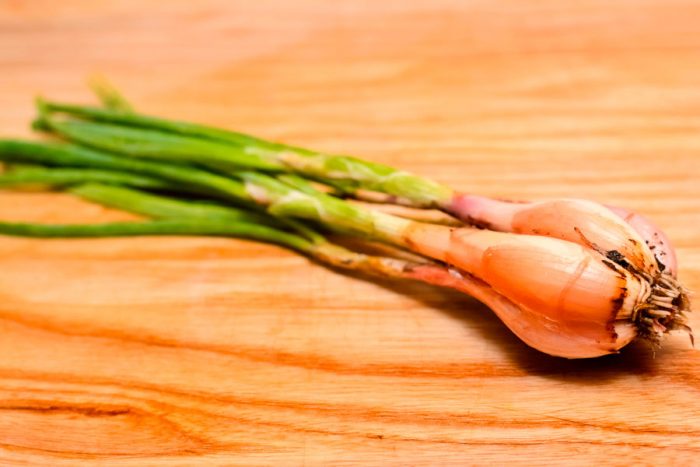
Shallot
This early maturing species is cultivated in the Middle East and Central Asia. Bulbs can be white, yellow or purple. This onion keeps well and is multi-nested. It is very popular among French chefs because it has a relatively weak onion flavor and makes the most exquisite sauces. Popular varieties:
- Picasso... The flesh of the bulbs is pink and has a high taste.
- Yellow moon... This early maturing variety is resistant to shooting and keeps very well.
- Golden Gourmet... Large bulbs have a high taste. The variety keeps very well.
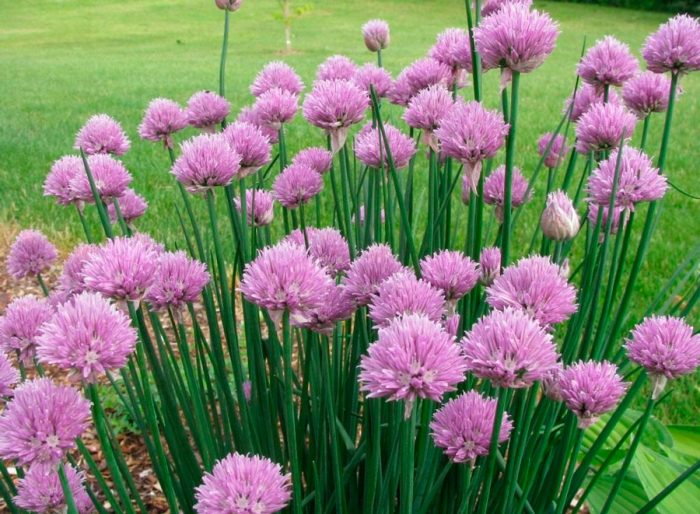
Chives or chives or chives
This onion is cultivated throughout European territory. The young plant is used fresh for the preparation of salads, and the mature shoots are used to make the filling for the pie. Spicy leaves are outwardly similar to the foliage of the onion, but they are smaller. This species is resistant to frost, pests and diseases.
Sweet onion
This species is cultivated in China, where various Asian dishes are prepared from it, it goes especially well with fish and soy sauce. Its flat leaf plates have a strong garlic smell. Flowering is observed for 2-3 years, spectacular honey inflorescences have a size of 50 to 70 mm, as well as a very pleasant smell.
Tiered bow
This species is also grown in China. Salads, side dishes and seasonings are prepared from such onions. Pickled onions are delicious and are served alongside fatty meats. This species differs from the rest in that it contains much more phytoncides and vitamins.
Onion
There are 3 varieties: Japanese, Chinese and Korean batun. It is popular in Asian cuisine, where it is used for cooking in a wok, it is also added to marinades or salads with fish or seafood. Such Japanese and Korean onions have a more delicate taste.
Aging bow
In the wild, it is found in Southeast Asia. It is used to prepare dishes of Korean national cuisine, and fresh it is added to salads, soups and kimchi.
Dropped Onion or Slime Onion
This perennial plant is found in nature in the European part of Russia and Siberia.It has a viscous juice similar to mucus, which explains its name. These onions are very tasty and resistant to frost and disease. Flat juicy sheet plates of linear shape have a slightly sharp taste. The bulb is not formed in this species. This product is considered dietary, and it is eaten fresh, as well as canned food is prepared from it.
In addition to these species, Regel, Suvorov onions are also grown, stalked, giant or gigantic, blue, bearish, oblique, Aflatunsky, Christophe or the Star of Persia, bowed or wild, yellow, karatavsky, round-headed or Drumsticks, Maclean's, Mole or golden, Sicilian or Honey garlic, etc.


Watch this video on YouTube