A plant such as iris (Iris) is also called a cockerel or an iris. This perennial plant belongs to the genus rhizomes, to the iris or iris family (Iridaceae). You can meet such flowers in almost every corner of the planet. This genus unites about 700 different species. The name of such a flower is translated as "rainbow". This plant was named by Hippocrates himself in honor of the rainbow goddess Iris. The legend says that at the moment when Prometheus gave people fire, a rainbow shone - it was the jubilation of nature. This rainbow shone throughout the day and night, and after the sunlight illuminated the earth, people were amazed at the sight of unusually beautiful flowers called irises. They looked so much like a rainbow. Florence (which means "blooming") received such a name from the Romans for the fact that a lot of irises grew in the fields located near the city. This amazing plant has been grown for about 2 thousand years. It is a wonderful decoration for any garden, and also valuable raw materials are extracted from irises, from which essences for the perfumery industry are made.
Content
Features of irises
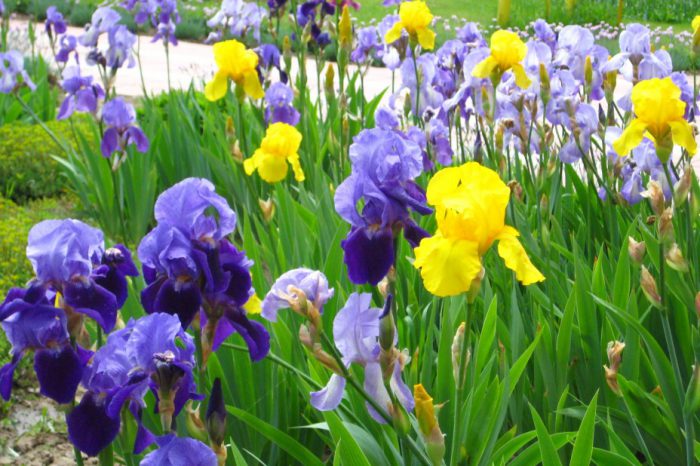
Irises have rhizomes on which roots grow, which have a cord-like or thread-like shape. There are one or several annual peduncles. Flat thin two-row leaf plates have a xiphoid shape, linear are rarely found. There is a thin layer of wax on their surface. They are collected at the base of the peduncle in a fan-shaped bundle, while the stem leaves are practically absent. As a rule, flowers are solitary, but not very large inflorescences are found on such plants. They are, as a rule, fragrant and large in size, they are distinguished by a very unusual shape, as well as a bizarre color. So, the color can be of various color shades, as well as their very bizarre combinations. The flower has 6 petals, which are the perianth lobes. The outer lobes in the amount of 3 pieces are slightly turned downwards and have a color different from the upper lobes. The fused upper lobes resemble a tube in shape. Long bloom from May to July. 2 or 3 flowers bloom at the same time, and they do not fade within 1–5 days. The fruit is a three-nested capsule.
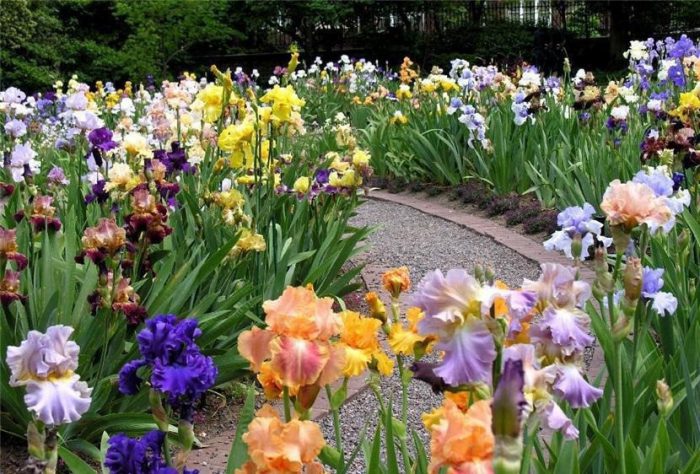
The main types and varieties with photos
Bearded irises
According to the flower shape, root irises are divided into non-bearded and bearded ones. Bearded got this name for the presence of hairy hairs on the surface of the petals. They have their own classification (medium-sized, standard medium-sized, medium-sized binder, tall, border, small-flowered medium-sized, miniature dwarf, standard dwarf, arylbreds, canteen, arylbreds and aryls, aryl-like arylbreds and aryls, non-aryl-like aryls). However, such a classification is used only by scientists, and ordinary gardeners know these plants, like bearded irises of various sizes.
Iris German
The tall bearded iris is also called Germanic. This plant has several hundred different varieties and is the most popular of all bearded irises. The most popular varieties are: Baltic Sea - a strong corrugated flower with an intense blue color and blue barbs; Bewilderbest - corrugated flowers are painted in burgundy-reddish-cream color, and on the surface there are streaks and stripes of whitish and yellow color; Acoma - sky blue combined with ivory and lavender border. It is very popular in America.
Non-bearded irises
The same irises include: Japanese, spuria, Californian, Siberian, Louisiana, marsh, as well as other irises (interspecific and specific). The most popular in mid-latitudes are:
Siberian iris
It can be painted in various shades from deep purple to blue. However, at the moment there are about 1,000 different varieties, the color of which can be very different. For example, white Snow Queen; Betts & Suga has a yellow color and a whitish border; the Imperial Opal bush reaches a height of 80 centimeters, and its lavender-pink flowers have a diameter of about 10 centimeters. The flowers of such a plant are very beautiful, but they have no smell.
Japanese iris (Kempflera, xiphoid)
Orchid flowers are very large (up to 25 centimeters in diameter), and they lack aroma. Thanks to breeders in Japan, terry (also called hana-shobu) and multi-petal Japanese iris were born. But these species are not resistant to frost. For middle latitudes it is recommended to choose: "Nessa-No-Mai" - the diameter of the whitish-purple flowers can reach 23 centimeters; "Solveig" - flowers are painted in a pale lilac color; "Vasily Alferov" - non-double flowers have an ink color.
Iris spuria
A very graceful plant similar to the bulbous iris xyphyum, but it stands out for its large size. Not afraid of drought and frost. The most spectacular varieties: Lemon Touch - lacy lemon-yellow flowers have a signal of dark golden color, the height of the bush is up to 100 centimeters; Transfiguration - a bush can also reach 100 centimeters in height, the color of the flowers varies from blue-violet to dark purple, the signal is bronze; Stella Irene - the bush reaches 90 centimeters in height, the black-purple flowers have a small golden signal.
Marsh iris (pseudoair)
This species, unlike others, prefers to grow only in moist soil. Flowers can be painted in various shades of yellow, and it is most often used to decorate artificial reservoirs. The most popular varieties are: "Golden Queen" - yellow flowers; "Flore Pleno" - has double flowers; "Umkirch" pink color.
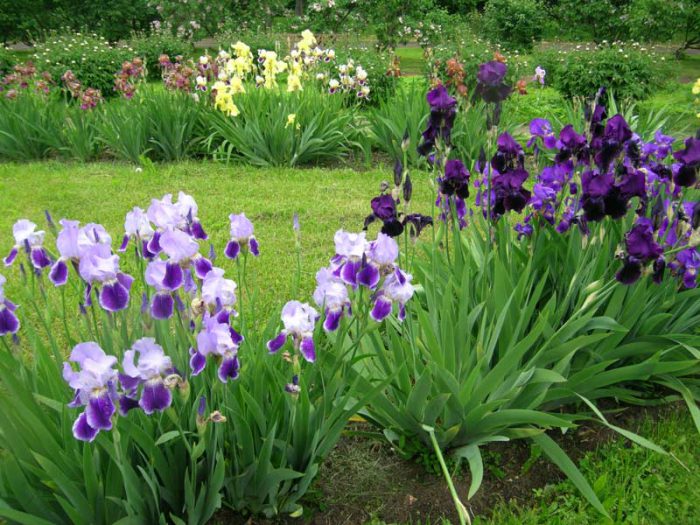
Depending on the color of the flowers, the varieties are divided into:
- monochromatic - all lobes have the same color;
- two-tone - the lobes located below and above are painted in different shades of the same color;
- two-color - the color of the lower and upper lobes is different;
- variegata - the lobes are yellow on top, and reddish-brown below;
- amena - the upper lobes are white;
- bordered or plikata - there is a border of a contrasting color either on all shares, or only on the lower ones;
- iridescent - the transition from one color shade to another is very smooth.
Growing features
Most inexperienced gardeners find it difficult to grow irises. However, in reality, this is far from the case. Simply, in order for these plants to grow and develop normally, do not forget a few simple rules for caring for them:
- The rhizomes of such flowers grow in a horizontal direction, and at the same time its part is exposed, as it comes to the surface. Before winter, these plants are recommended to be covered with peat or soil in order to protect them from freezing. In springtime, this layer must be carefully removed.
- The peculiarity of such plants is that they are able to move. So, during the season, they can move to the side by several centimeters. Therefore, it is recommended to plant them in a fan of sheet plates along the row. In this case, the rows will be more even.
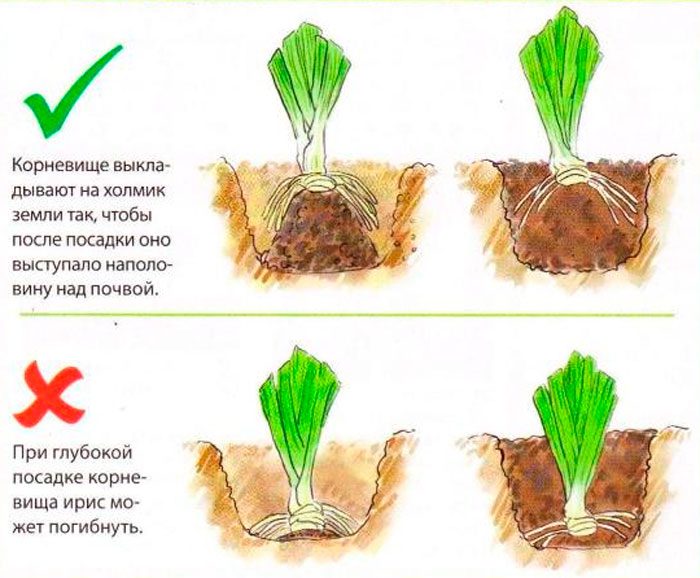
- The bearded iris is planted using sand. Sand is poured into the prepared hole at the bottom with a slide, and the roots are already straightened along it. It should be noted that if you deeply deepen the plant, then it may die or it will not bloom.
- You can not use organic fertilizers for feeding. Liquid mineral fertilizer works best.
How to plant correctly
When to plant irises? Seat selection
Most gardeners believe that immediately after the irises have finished blooming, they should be dug up, divided and planted in their permanent place. Because otherwise they may not have time to be taken before the onset of the winter period. However, if in your area there is a long and warm enough autumn, then you can take your time with replanting irises. Such flowers can actually be transplanted from spring to autumn, but only after they have finished their flowering period. Remember that irises should be replanted at least once every 3 or 4 years. However, Siberian irises can grow in one place for about 10 years. If you do not transplant, then the overgrown bushes stop blooming.
For bearded irises, you should choose a sunny place away from drafts, which should be located on a hill or slope, since it is very important that the place is well drained, and there is also an outflow of melt water. It is recommended to disembark from morning until lunchtime. For the Siberian and marsh species, you need to choose places with wet soil. Absolutely all irises need nutrient-rich soil. To correct poor soil, before planting irises in the spring, you need to add compost or garden fatty soil, as well as phosphorus-potassium fertilizer. It is recommended to add chalk, dolomite flour or wood ash to acidic soil. It is recommended to add sand and peat to loam, and clay soil to sandy soil. It is recommended to disinfect the soil before planting irises. To do this, it must be watered with a fungicide, and also treated with herbicides from weeds. You cannot bring manure into the ground.


Watch this video on YouTube
Spring planting
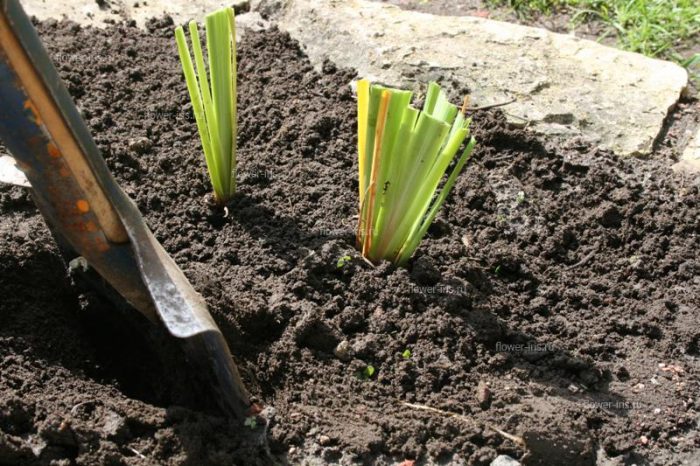
The purchased planting material, as well as the one that was stored throughout the winter period, must be treated with a growth stimulating agent (Zircon or Ecoel). If the roots are long, then they must be trimmed; places where there are signs of decay must be carefully cut out. The root should be dipped in a potassium manganese solution for a third of an hour for disinfection. Make a not very deep hole and pour sand into it with a mound. The rhizome of the bearded iris must be laid so that it is horizontal. Spread the roots and sprinkle the hole so that only the upper part of the rhizome remains above the soil surface. Then the iris should be watered abundantly. In the event that the entire rhizome is underground, then this, as a rule, leads to the appearance of rot.Beardless species, on the other hand, must be buried a few centimeters into the ground. A layer of mulch (peat or fallen needles) should be poured on top, which will help retain moisture. The wells must be spaced from each other at a distance of at least 50 centimeters.
Autumn planting
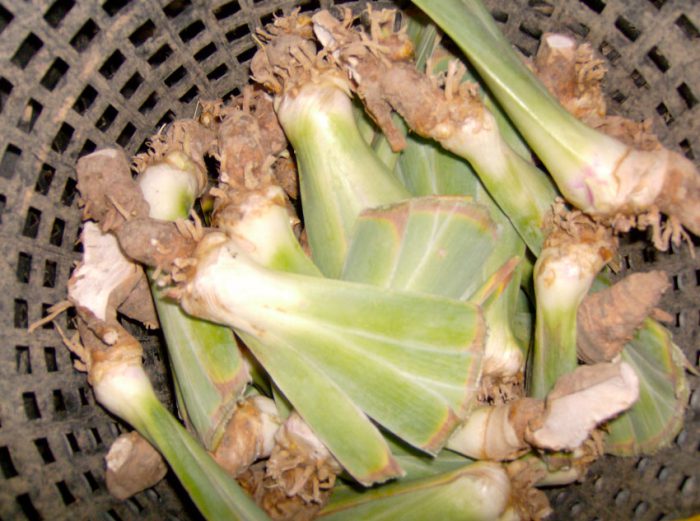
Autumn planting is not much different from spring planting. It is recommended to be carried out at the end of the summer season, when the flowering period ends. As a rule, it is advised to transplant from August to the last September days, but it must be borne in mind that an earlier transplant will allow the plants to take root and grow stronger. Dig the bush with a pitchfork, then divide it into annual links with a blade. The cord-shaped roots must be carefully shortened, remove those places where there is damage or signs of decay. Then the delenki must be placed in a dark pink solution of potassium manganese for 2 hours for disinfection. After that, they need to be placed in a sunny place for 4–5 hours. The cuttings should be planted in the same way as in spring. Between the holes of high grades, a distance of about 50 centimeters should be left, between medium-sized ones - 20 centimeters, between undersized ones - 15 centimeters.
Iris care


Watch this video on YouTube
Rules for caring for garden irises
It is a warm and light-loving plant. It is especially important to water irises regularly and relatively abundantly during the budding period. The rest of the time, watering should be done only when the surface of the soil near the rhizome is very dry.
If in the spring, before planting iris, you applied fertilizer to the soil, then during the entire season, as a rule, the plant will not need additional fertilizing. In the event that you nevertheless decide to apply fertilizers to the soil, then for this you should use potash-phosphorus fertilizer in liquid form. It should be applied directly under the root during the period of intensive growth. It is prohibited to feed irises during the flowering period.
All season it will be necessary to remove weeds in a timely manner. Weeds will have to be removed manually. The fact is that the root system is located horizontally and very close to the soil surface. In this regard, when weeding with a hoe, you can accidentally damage it. Although rare, loosening of the soil should be done. This procedure must be carried out with extreme caution, trying not to damage the roots. Experienced gardeners are advised to remove wilted flowers, as they can cause pests to settle on the plant.
Pests and diseases
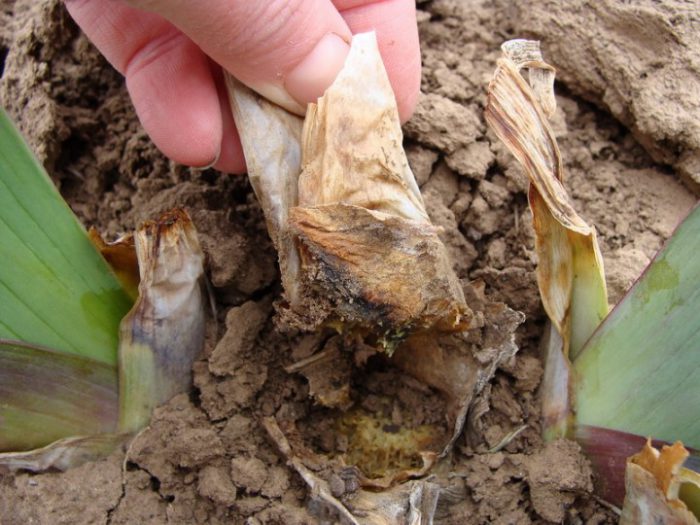
The most spectacular and variegated varieties are most susceptible to various pests and diseases. In order to protect irises from diseases, it is imperative to adhere to all the rules of agricultural technology of the species. Also, be sure to watch how your plants feel throughout the season. As soon as you notice that something is wrong with the irises, you should take appropriate action. When a bush is infected with fusarium or other rot, you need to act very quickly. The infected plant must be dug up and destroyed. For preventive purposes, other bushes must be watered under the root and along the roots with a solution of foundation, which should be two percent. It is also recommended to treat the rhizomes with this tool before planting them in the soil. In this case, the risk of rot will be much lower. A solution of Bordeaux mixture (1%), which should be sprayed on foliage, can protect plants from a variety of spots.
Often, scoops settle on plants. They eat the base of the peduncles. After that, the peduncles turn yellow and dry out. Preventive measures should be taken at the very beginning of the growing season. To do this, you need to treat the plants 2 times with a solution of karbofos (10%), while an interval of 7 days should be made between treatments. Gladiolus thrips can also settle.They lead to a violation of photosynthesis in the foliage, which is why it becomes brown and dies off. If the plant is infested with thrips, the buds will be ugly and discolored. Thrips do best in dry summer months. Such insects can be fought in the same way as with scoops with the help of karbofos; an infusion made from 400 g of makhorka, which should be kept for one and a half weeks, is also highly effective. Also added to it 40 g, crushed with a grater, laundry soap. Slugs can harm such plants. To get rid of them, it is necessary to put fresh burdock leaves or moistened rags in the aisles. When the slugs hide under them, you will only have to collect them together with rags and destroy. If there are a lot of slugs, then in sunny weather, in the early morning or in the evening, metaldehyde, released in granules, should be distributed over the area, simply by scattering it. In this case, from 30 to 40 g of the substance should go per 1 square meter.
Irises after flowering
In the event that the planting is not expected in a given year, it is recommended to remove the peduncles after the plant has faded. If the yellowing of the leaf plates begins, it is recommended to cut them off, making the tip semicircular. So, irises will also remain a good decoration of the garden and will have time to gain the necessary nutrients, as well as strength, before winter. During the warm autumn period, secondary flowering often occurs. After the leaf plates become withered, they must be trimmed, leaving only 10-15 centimeters. The cuttings must be destroyed (burned), since pathogens, as well as eggs of harmful insects, can be on their surface.
Before the winter cold, bare rhizomes should be covered with soil, as well as with a thick (8-10 centimeters) layer of mulch (peat or sand). In the case when a strong drop in temperature is expected in autumn or winter, you need to cover the irises with spruce branches or dried leaves. In the case when a lot of snow falls in winter, it is not necessary to cover the plants.


Watch this video on YouTube
Iris storage
Dug out or acquired rhizomes of bearded irises in autumn can be saved until spring by placing them in a dry and cool place. Dry the rhizomes well and put them in a cardboard box that you need to close tightly. It should be placed on a loggia or balcony. At the same time, it is recommended to wrap each rhizome with a cloth or a sheet of paper, and you can also sprinkle them in a box with dry peat or the same sawdust.
Other irises prefer a humid habitat, in this regard, for conservation, it is necessary to plant them in a flowerpot. Before planting, you need to remove long roots, and the rhizome itself should be lowered and held in a not very strong solution of potassium manganese for disinfection. Then it must be dried. It is not necessary to deepen the rhizome; it is only sprinkled with soil a little. In springtime, the sprouted rhizome should be taken with a clod of earth and planted in open soil.