Fruit and ornamental deciduous trees and shrubs of the genus Pear (Pyrus) are members of the pink family. This genus unites about 60 species. Such a plant was already grown in Rome, Ancient Greece and Persia. Under natural conditions, a pear can be found in regions with a temperate climate, as well as in the warm belt of Eurasia. Today, there are several thousand varieties of such a plant, among which there are varieties suitable for growing in areas with a cool climate: in the Urals, in the Moscow region and in Western Siberia. The pear is related to the following crops: apple, almond, plum, cherry plum, hawthorn, wild rose, rose, irga, chokeberry, quince, cotoneaster, medlar, mountain ash and spirea.
Content
Features of the pear tree
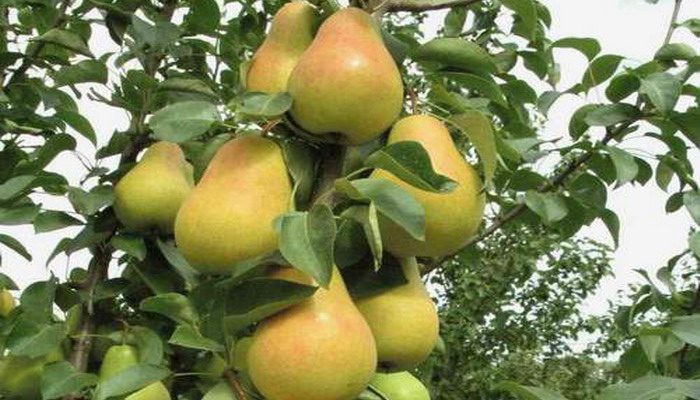
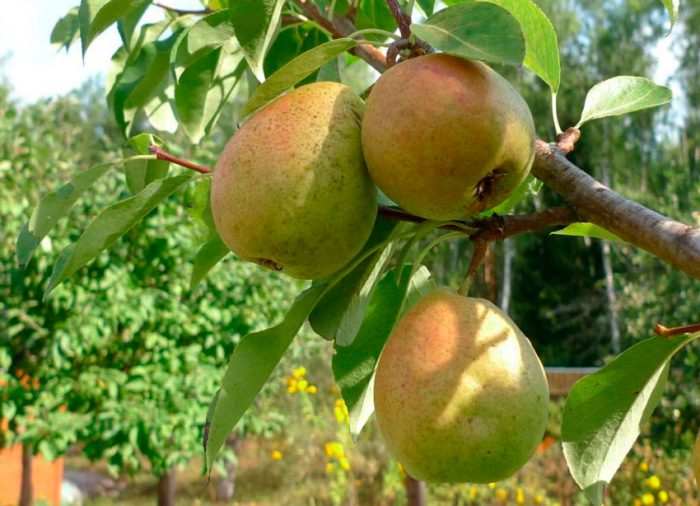
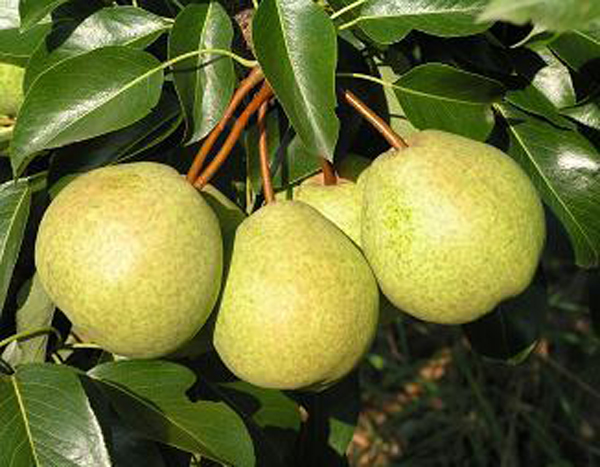
A pear is a tree with a pyramidal or rounded crown. The plant does not exceed 25 meters in height, while the diameter of its crown can reach up to 5 meters. Broadly ovate leaf plates are shortly pointed. Their length can vary from 25 to 100 mm. The front surface of the leaves is glossy dark green, and the back is greenish-blue. In autumn, the leaves change their color to orange-golden. Flowering begins in April – May. Such a tree covered with flowers looks very impressive. Umbrellas consist of 3-9 five-petal fragrant flowers of white color, which can reach 30 mm in diameter. The shape of the fruit is usually elongated, but there are varieties with spherical fruits. Such a culture is grown in order to obtain its tasty and healthy fruits, they can be eaten fresh or used to make compote, juice, jam, jam and dried fruits.
Planting pears in open ground
What time to plant
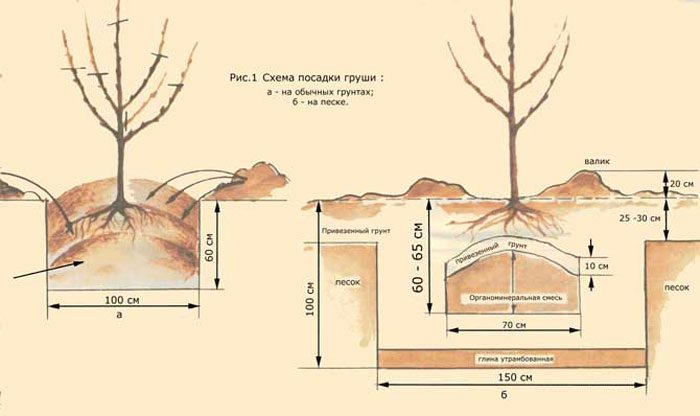
Planting pears in open soil is carried out in the spring, before the start of sap flow. You can also do this in the last days of September, after the slowdown of sap flow in the trees. If you decide to plant a plant in the spring, then you should start preparing the planting pit in the fall. You need to know that experts prefer autumn planting. It is recommended to plant a pear on the south, west or southwest side of the garden. The area should be well lit, but not very hot. Chernozem or gray forest soil with loamy subsoil is best suited for pear. Such a crop should not be planted on sandy, poor or heavy clay soil. Also, areas with a high groundwater level are not suitable for planting pears. The fact is that an adult plant has a powerful root system that can penetrate 6–8 meters deep. In this regard, for planting pears, it is recommended to choose a hill or slope.
Planting pears in autumn
Pear seedlings planted in open ground in autumn take root comparatively better, and trees grown from them are more resistant to diseases, pests and unfavorable climatic conditions. However, planting a pear in the fall also has disadvantages, a fragile tree can be severely damaged by rodents, and it often freezes during severe frosts.
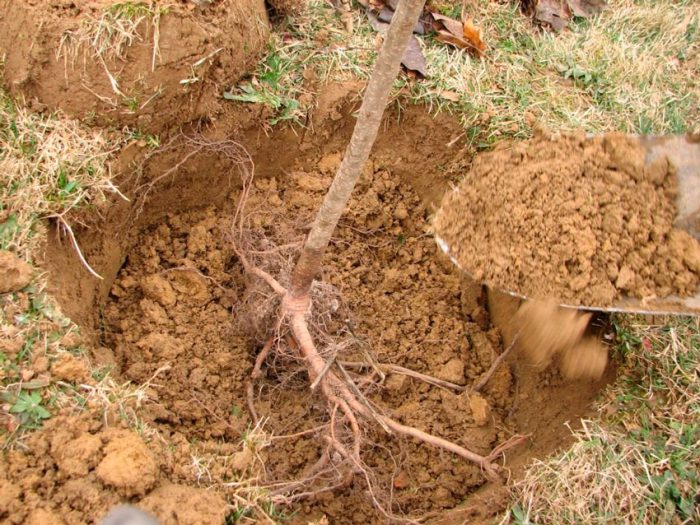
When choosing a two-year-old seedling, it is imperative to check its root system, it should not be rotten or dry. In this case, the stem of the seedling must be flawless and always elastic. In the event that the root system of the plant looks dehydrated, it should be immersed in a container of water for half a day before planting. During this time, their elasticity will be restored.
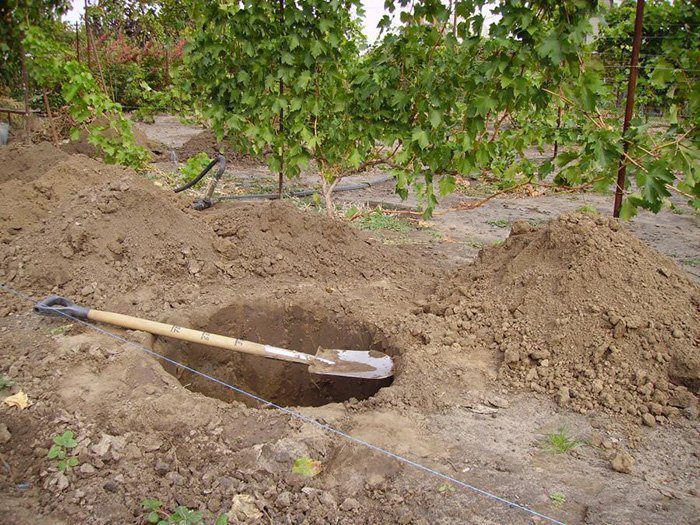
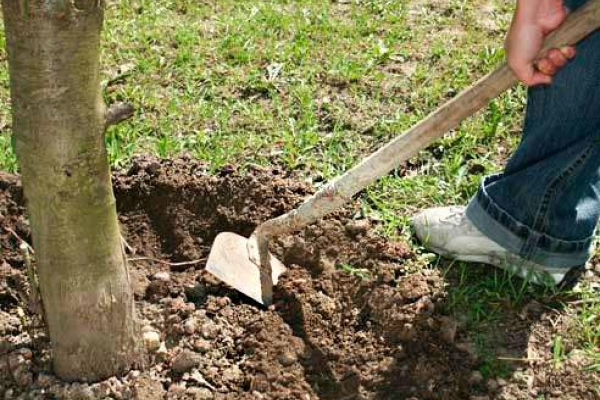
If the soil on the site is suitable for growing this crop, then the planting pit should be made not very large. It should slightly exceed the size of the plant's root system. However, if the soil is not suitable for planting pears, then the size of the planting pit should be 0.7x0.7 m, while its depth should be about 1 meter. Preparing the pit should be done 20-30 days before planting, during which time the soil will settle well in it. A strong peg prepared in advance should be driven in the center of the finished pit, while above the surface of the site it should rise at least 50 centimeters. The top nutrient layer of soil should be discarded separately when digging a hole. It is combined with 30 kilograms of peat, compost or rotted manure, and 1.5 kilograms of lime, 1 kilogram of superphosphate, and 0.1 kilogram of potassium chloride are also added to it. Half of the well-mixed soil mixture must be poured into the pit, it is compacted silently. The rest should be covered with a mound near the peg.
Immediately before planting, the pear root system should be immersed in a clay mash. After that, the plant should be placed on a mound on the north side of the peg. After its roots are neatly straightened, gradually fill the hole with nutritious soil, while do not forget to periodically shake the seedling, which will eliminate all the voids remaining in the soil. After the hole is filled, the surface of the trunk circle must be trampled in the direction from the seedling to the edges. In a planted pear, the root collar should rise 40–50 mm above the soil surface. Pour 20-30 liters of water under the seedling. When the liquid is completely absorbed and the soil has settled, the root collar of the seedling should be at the level of the soil surface. The surface of the trunk circle should be covered with a layer of mulch (sawdust, peat or humus), the thickness of which should be from 5 to 10 centimeters. At the very end, the pear should be tied to a support.


Watch this video on YouTube
How to plant a pear in spring
Planting a pear in spring should be exactly the same as in autumn, however, it should be noted that a pit for planting will need to be prepared in autumn. After the plant is planted, a roller should be made of soil around the perimeter of the trunk circle, then 20-30 liters of water should be poured into the resulting "hole", it does not matter if it is raining or drought.
Pear care
Spring pear care
When cultivating a pear, you should be prepared for the fact that it will need almost year-round care. In spring, the winter shelter must be removed from the pears, the surface of the trunk circle must be loosened, nitrogen-containing fertilizers must also be added to the soil, which activate the growing processes. Sanitary pruning should be done before sap flow begins, while removing all injured, as well as those affected by disease or frost, stems and branches. Also, in spring, pears need preventive treatment, after which all pests and pathogenic microorganisms that survived the winter in the bark of the plant or in the surface of the trunk circle will be destroyed.
Summer pear care
In the summertime, special attention should be paid to the timely watering of the pear. During the dry period, watering is carried out in the evening, when it becomes relatively cool outside, while about 30 liters of water should go to 1 plant for 1 watering. The crown is very often thickened in the pear, therefore, in the summer, it may need thinning pruning so that the fruit-bearing tree can receive enough sunlight. In some varieties of pears, fruits ripen in the summer months, in this regard, you should be ready to pick them.
Pear care in autumn
In autumn, the plant will need sanitary pruning, treatment in order to prevent diseases and pests, which can hide both in the surface of the trunk circle and in the bark of a tree. Also, the pear must be fed with potassium and phosphorus. Also at this time, the plants are prepared for the coming winter. So, it is imperative to whitewash the surface of the trunk and the base of the skeletal branches with lime, this will protect the bark of the plant from the very bright spring sun, otherwise burns may appear on it. You should also make a shallow digging of the near-trunk circles, and then water them abundantly. Then they are covered with a thick (from 15 to 25 centimeters) layer of mulch (sawdust or peat).
Pear processing
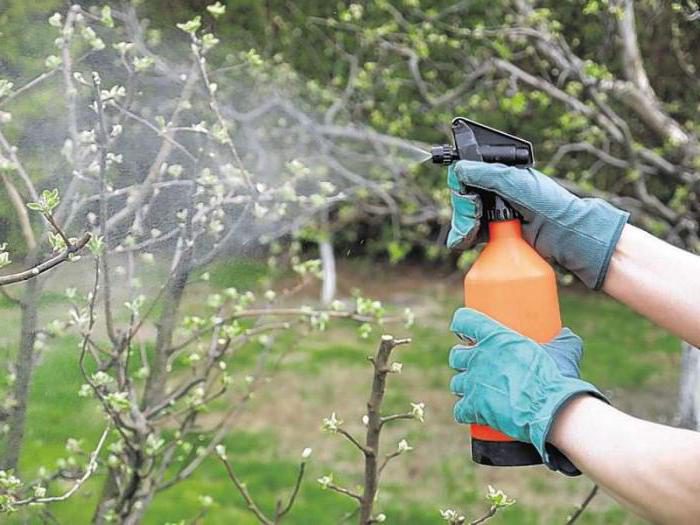
Preventive treatments for diseases and various pests are very important, and experienced gardeners try not to neglect them. The fact is that it is much more difficult to cure a disease or get rid of pests than to prevent their appearance. And some more preventive treatments can be combined with pear feeding. For example, the first pear spraying for the season is done at the beginning of the spring period, a urea solution can be used for it (0.7 kg of substance per bucket of water), this tool will not only destroy all pathogenic microorganisms and pests, but also become a source of nitrogen for the plant ... But it should be remembered that such treatment can be carried out only before the kidneys swell, otherwise, due to urea, burns may appear on them. In the event that you have not sprayed the tree yet, and the buds are already blooming, biological agents are used instead of urea, for example: Agravertin, Iskra-bio, Fitoverm or Akarin.
It is also necessary to spray the plant with a solution of Ekoberin or Zircon, this will make it more resistant to adverse conditions, as well as to various diseases.
Before the first frosts, a preventive treatment of the pear is also carried out, which at this time begins to go into a state of rest. This will destroy all pathogens, as well as pests that hid for the winter in the cracks in the bark of the tree, as well as in the surface of the trunk circle.For spraying, it is recommended to use Bordeaux mixture (1%) or Nitrafen. It is necessary to process both the tree itself and the surface of the soil under it.
Fertilizing pears
For the first time, the pear should be fed before the sap flow begins in the spring, and for this, a urea solution is used. If you did not manage to make such spraying in time, then nitrogen-containing fertilizers will need to be applied directly to the soil of the trunk circle. In this case, you can use a solution of chicken manure, saltpeter or urea. For example, 30 g of nitrate is taken per 1 square meter of the trunk circle, which should be diluted with water in a ratio of 1:50. 1 plant should take 80-120 grams of urea (carbamide), while this substance should be diluted in half a bucket of water. To improve the quality of the fruit, the pear is fed in May, when it blooms. In this case, it is recommended to apply green fertilizer for digging, burying it into the soil by 8-10 centimeters. This fertilizer is a source of organic matter, and it contributes to the activation of vegetative processes. Instead of organic matter, you can feed the plant with a solution of Nitroammofoska (1: 200), at the rate of 30 liters of water per plant.
From the middle to the end of June, foliar feeding of pears with nitrogen-containing fertilizer should be performed. The fact is that in hot and dry times, trace elements from the soil to the roots come extremely slowly, while this transport process is significantly accelerated through the leaf plates. In July, such foliar dressing should be repeated, and after half a month a mineral fertilizer (potassium and phosphorus) must be added to the soil for an adult plant. Pear seedlings that have just been planted in the garden will not need additional fertilizing for 2 years, because they have enough nutrients that were introduced into the soil during planting. Moreover, young plants need only nitrogen-containing fertilizers.
This plant should not be fed in August. Until the second half of September, if you wish, you can make the last foliar feeding of the plant with a nitrogen-containing fertilizer (urea) for the season, while this procedure is carried out in the same way as in the spring. At this time, it is not recommended to apply nitrogen-containing fertilizers to the soil. Also, in the autumn, liquid mineral fertilizer is applied to the trunk circle. For such feeding, you can use, for example, the following composition: for 1 bucket of water, 2 large tablespoons of granular superphosphate and 1 large spoonful of potassium chloride are taken. The nutrient solution is thoroughly mixed, then it is poured into the tree trunk circle. If the tree is young, then, if desired, it can be fed with wood ash, for this it is evenly distributed over the surface of the trunk circle (150 grams per 1 square meter), which is then dug to a depth of about 10 centimeters.
Wintering pear
Young seedlings may suffer from frost in winter. To avoid this, at the end of the autumn period, they should be strapped with pine branches, while the needles must be directed downward. From above, spruce branches are tied with burlap. It is not necessary to cover adult specimens for the winter, but at this time rodents are a great danger for them, which damage their bark. To protect pears from such pests, their trunks should be wrapped in a thick cloth or paper, which must first be soaked in a rodent repellent. When snow falls, it should be poured with a thick snowdrift onto the surface of the tree trunk circle. If the pear has a heavy snow cap, then it must be shaken off from an adult plant, otherwise its branches and stems may be injured during a thaw. If the plant is young, then in autumn it will be necessary to pull off its branches with twine, while they should press against the trunk.
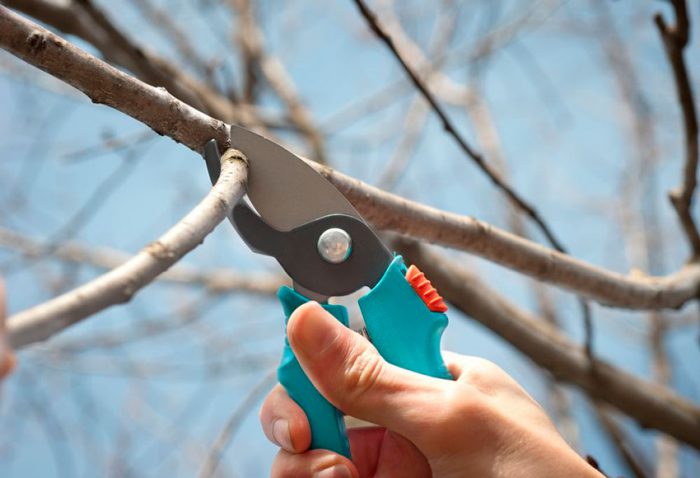
Pruning pear
What time is pruning
The best time for pruning pears is spring, and you need to be in time before the sap flow begins. Such a culture tolerates pruning well only if the outside air temperature is above minus 8 degrees.
Pruning of such a culture in the summer is carried out only when the crown thickens very strongly, which negatively affects the ripening of the fruit. But the pinching of the shoots (pinching) that grow on the top of the tree is carried out strictly in June.
In autumn, pruning of such a tree should be done before frost, the fact is that with a decrease in air temperature, the sensitivity of the cut sites increases, which significantly slows down the process of their healing. In autumn, as a rule, only sanitary pruning is performed. No pruning is done during the winter months.
How to prune a pear
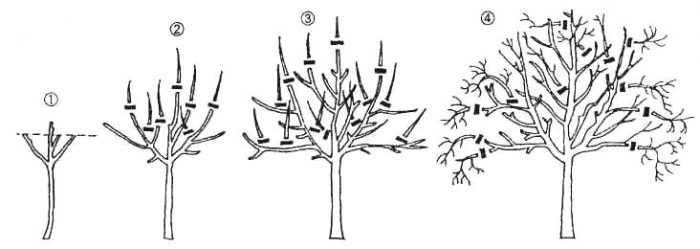
After the seedling is planted in open ground, it must be cut, leaving only skeletal branches, and the rest should be removed. The center conductor must be shortened by ¼ part. It is necessary to clean the trunk from branches below the beginning of the first tier of skeletal branches. The next year, the conductor is shortened by 0.25 m. The crown is also formed, for this the skeletal branches must be shortened by 5-7 centimeters, while taking into account that the lower branches should be longer than the upper ones.
Pruning old wood is a comparatively more laborious process. The fact is that it will be necessary to cut not only the shoots, but also the branches, as a result of which the crown will lighten and rejuvenate.
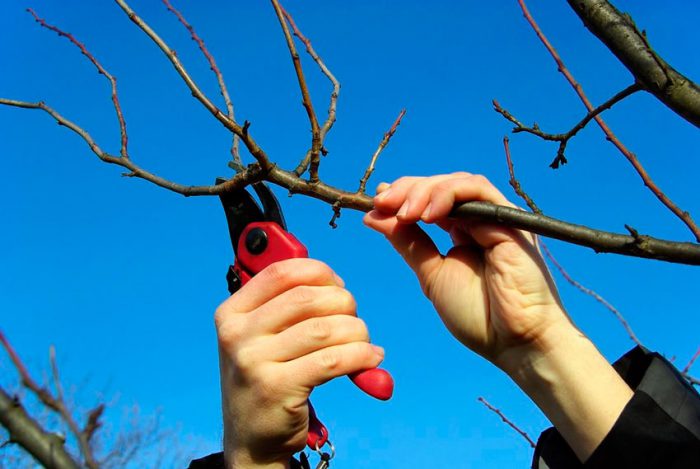
Pruning pears in spring
From the second year of the pear's life, it will be necessary to cut all available competing branches into the ring, while there should be no hemp left. When shaping a tree, it should be borne in mind that all skeletal branches should have several pieces of fruit branches. Those shoots that grow vertically should be removed, and those growing horizontally should be supported. All slices need processing, for this they use Ranet or garden var. During pruning, fertilizing pears with nitrogen-containing fertilizer is unacceptable. A similar procedure will need to be carried out only after tightening the slices.
Pruning pears in autumn
In autumn, pruning should be carried out from the last days of August to mid-September. In this case, it is necessary to cut out all injured, dried out, and also diseased branches, they should be destroyed. You should not cut off annual shoots by more than 1/3 of the part, several buds should remain on the pruning, it is from them that new branches will grow. If you want to conveniently harvest the fruits, you should give the crown a pyramidal shape, which also contributes to the fact that the harvest will be richer. The formation of this crown must be dealt with from the second year of the plant's life.
Reproduction of pear
The pear can be propagated by seeds and vegetatively. Growing from seeds, as a rule, is used in order to develop new varieties, for this artificially crossing different varieties, species and hybrids. And also rootstocks of cultivated and wild species of this plant are obtained from seeds, then cultivars are grafted onto them.
The pear can be propagated by the following vegetative methods: cuttings, layering and grafting.
Propagation of pears by layering
As a rule, in order to obtain layering, it is necessary to bend the branch to the soil surface, but this cannot be done with a pear. However, there is one way. To do this, you need to fill a box with nutrient earth, the walls of which are preliminarily covered with a film, which allows you to slow down the process of evaporation of water from the soil. It should be placed under the selected branch. The branch must be bent to the container, in the place of its contact with the soil on the surface of the bark, several transverse cuts must be made. Then the branch is fixed in this position, and the place of its connection with the ground in the box must be covered with soil.In order for the roots of the cuttings to appear faster, the incisions made must be powdered with a means that stimulates the growth of roots, and then the branch is buried in. Or you can simply water the layering, instead of water using Kornevin's solution. Then the surface of the soil in the container must be covered with a film, roofing felt or covered with a layer of mulch (compost). Make sure the soil is always slightly damp. Layers will take root only at the very end of the season, but the transplant should be postponed, since at this time the root system of the plant is still very weak. The branch for wintering should be covered with spruce branches, and then a thick layer of snow should be spread over the container with the layering. It is necessary to grow the cuttings for two years, then it is separated from the parent plant and transplanted to a permanent place along with a lump of earth. It is necessary to plant layers in the same way as a simple seedling. A tree grown from cuttings begins to bloom and bear fruit somewhat earlier than that obtained from a conventional seedling. This propagation method is very simple, and another plus is that such seedlings are able to preserve absolutely all the varietal characteristics of the parent tree.
Seed propagation of pear
To grow a seedling, which will later be used as a stock, it is necessary to select seeds of zoned frost-resistant varieties. Sowing seeds in open soil is carried out in the autumn. In late-ripening varieties, seeds ripen in fruits by mid-winter during storage. The seeds that have ripened and extracted from the fruits must be placed in a gauze bag, which is immersed in the toilet bowl for 2-3 days, so that during each drain, inhibitors will be washed out of the seeds, which slow down their development. Further, the seeds that have already swelled should be combined with a moisture-absorbing substrate, for example, with sawdust, peat chips, sand or expanded clay, in a ratio of 1: 3. The mixture must be moistened and placed in a polyethylene bag, which is removed on the refrigerator shelf. You need to store the seeds at a temperature of 3-5 degrees in an ajar sachet until the sprouts appear. At the same time, do not forget to gently mix this mixture 1 time in half a month and, if necessary, moisten it. Immediately after the sprouts appear, the air temperature must be reduced to minus 1–0 degrees. Seeds in this state should be stored until sowing.
Sowing seeds into open soil is carried out at the very beginning of the spring period, burying them into the soil by 30–40 mm. A distance of 8 to 10 centimeters should be maintained between the seeds, the row spacing should be 8–10 centimeters. During the summer period, seedlings need watering, weeding and several additional fertilizing. After the thickness of the stems is 10 mm, in August it will be possible to start grafting varietal cuttings on them. If in the future they develop normally, then after 2 years they are transplanted to a permanent place.
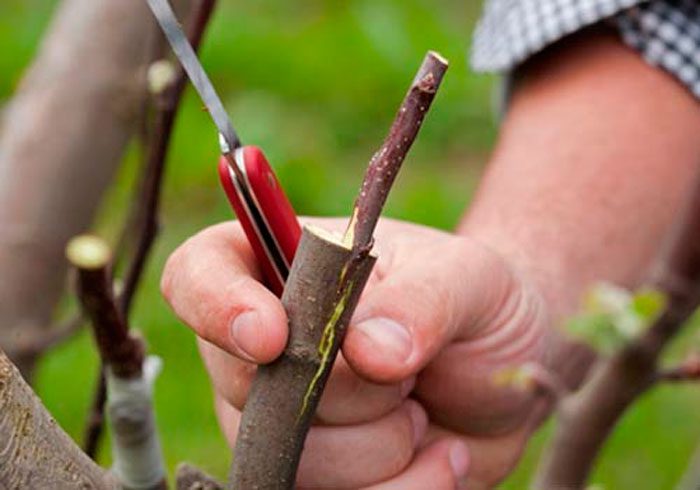
Pear grafting
In order to propagate a pear by grafting, you can use seedlings of quince, apple, pear, irgi, hawthorn, chokeberry, cotoneaster and forest pear. If you use quince seedlings as a rootstock, the tree will be low, it will begin to bear fruit relatively early, while its fruits will be very tasty. But the disadvantage of such trees is that they can live no more than 25 years. If you use an apple tree seedling as a stock, then the grafting will easily and relatively quickly take root. Grafting on a rowan seedling is rarely done. The fact is that the thickening of the trunk of the mountain ash occurs more slowly than the trunk of the pear, which is why an influx appears on the tree during the growth process, while the stem becomes less durable, and the plant itself does not live long. The fruits grown on rowan rootstocks are distinguished by their astringency, low sugar content and juiciness.When using a hawthorn seedling as a rootstock, it should be borne in mind that it grows together with a pear rather rarely.
Before you start grafting, you should start preparing the stock. 30 days before the procedure, it must be spud high (to a height of 15 to 20 centimeters). When there are several days left before copulation, the soil will need to be removed from the stem, also remove all the growth and water it.
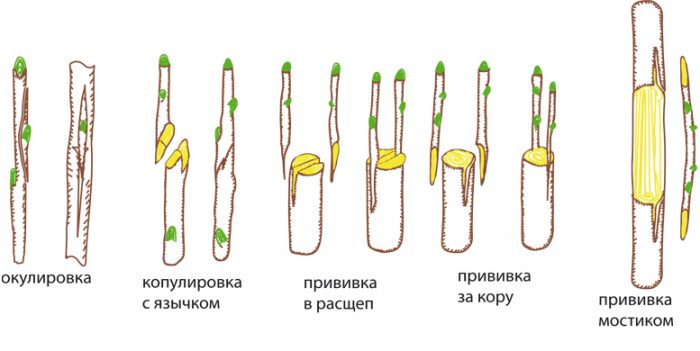
The most commonly used methods of vaccination are:
- Simple copulation (grafting "in the butt")... This method is applicable only when the rootstock and scion are of equal thickness. This method is notable for its simplicity. An oblique cut should be made on the rootstock and scion. Then they are applied with these slices to each other, and then the vaccination site is wrapped tightly with a film.
- Improved copulation (copulation "with tongue")... On oblique cuts of the stock and scion, deep serifs should be made, which are called "tongues". Then these two parts must be attached to each other so that the tongue of the stock goes behind the tongue of the scion. Then the vaccination site must be very tightly wrapped with tape or electrical tape.
- Bark grafting"... This method is used if the scion diameter is less than the rootstock diameter. This method of grafting can be used only after the sap flow begins, since during this period the separation of bark from wood is easiest. The graft must be cut down, while the cut must be horizontal. After the cut is cleaned with a very sharp tool, a longitudinal cut in the bark should be made, the depth of which should be 2.5–3.5 cm, while the oblique lower cut on the scion handle should be the same length. At the rootstock, the bark is unscrewed, and a cut of the scion is inserted into the cut (directly to the wood of the rootstock). It should be noted that the entire part of the scion cuttings, which will be located in the rootstock cut, must be cleared of bark. The grafting site must be tightly wrapped with foil, and then the top cut of the scion and the cut of the stock must be coated with garden varnish. To speed up the fusion of the grafting site, a transparent plastic bag must be put on the plant itself. It should be firmly fixed below the inoculation site.
- Cleavage vaccination... Shorten the stock by making a horizontal cut. The stem of the stock must be split in the center of the cut to a depth of 40 to 50 mm. In the resulting split, you need to install a wedge for a while. The scion should have from 2 to 4 buds on the graft; the cut should be made on both sides with a wedge from 40 to 50 mm long. The scion wedge must be inserted into the rootstock split. The temporary wedge should then be carefully removed from the cleft. The vaccination site is tightly wrapped with foil. The scion cut, located on top, and the open section of the rootstock cut must be coated with garden varnish.
After both parts grow together, you can notice the appearance of new growths on the scion. When this happens, the bag and film should be removed, and any shoots that have grown below the grafting site are cut out.


Watch this video on YouTube
Propagation of pears by cuttings
Cuttings are harvested in winter. This will require a mature branch with two years of wood. It should be broken in such a way as not to break the integrity of the bark. If the branch is long, then several breaks can be made on it, while it should be borne in mind that the recommended length of the cutting is 15–20 centimeters. Places of breaks must be wrapped with tape for budding (tape or plaster) in a bent form. Then this branch should be tied to a wire or a stick, and at the end it is fixed in this position. Before the onset of spring, the pear will have to accumulate a large amount of growth substances in those places where the fractures are located for better tissue fusion. In the last days of March, everything is carefully removed from the branch, and it itself is divided in places of breaks into cuttings.
Take a dark colored 2 liter plastic bottle with a cut neck. It needs to be filled 5-7 centimeters in height with melt water, to which 2 tablets of activated carbon are added. Submerge the bottom cuts of 10-12 cuttings in this water. The container must be removed to a well-lit windowsill. In cuttings, callus cones appear on the lower sections after 20–30 days, and the beginning of root growth is also noted. After the length of the roots of the cuttings is 5–7 centimeters, they should be planted in a garden plot in soil saturated with nutrients, while at first they will need to be protected from direct sunlight. Planted cuttings must be systematically watered, weeded, and fed. If everything is done correctly, then in the fall the cuttings will not differ in any way from the seedlings that are 2-3 years old.
Diseases of a pear with a photo
The pear grown in the garden is prone to diseases such as: scab, fire blight, fruit rot, subcutaneous viral spot, mosaic disease, rust, powdery mildew, black cancer, sooty fungus and cytosporosis.
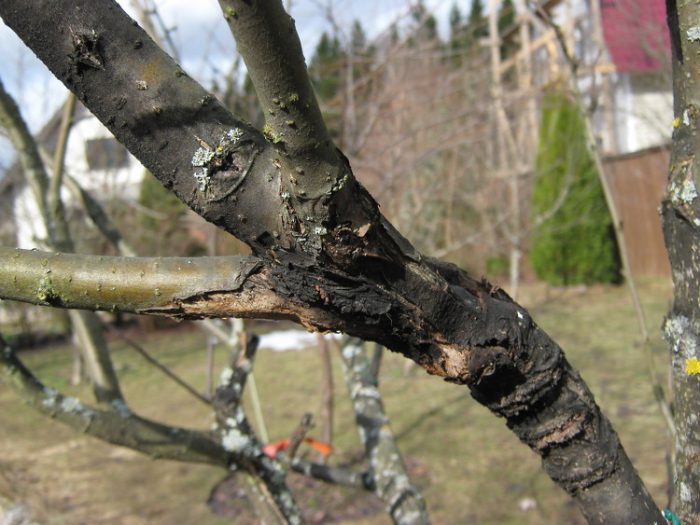
Black cancer
Antonov fire, or black cancer, affects the leaf plates, skeletal branches, bark and fruits of the plant. At the very beginning, small wounds form on the tree, they increase in size over time, and brown specks appear along the edges. Red spots appear on fruits and foliage. Fruits are damaged by black rot, their gradual drying and mummification is observed. In autumn and spring, it is imperative to spray pears in order to prevent various diseases and pests. When the autumn leaves fall, the flown leaves should be collected and destroyed. Those parts of the trees that are affected by the disease must be cleaned, grabbing healthy wood, for this they use a very sharp knife. Next, the wounds need to be disinfected; for this, a mixture of mullein with clay or a solution of copper sulfate is used.
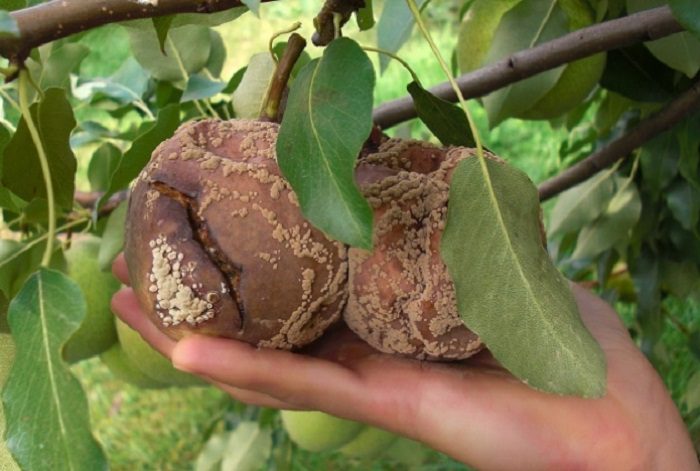
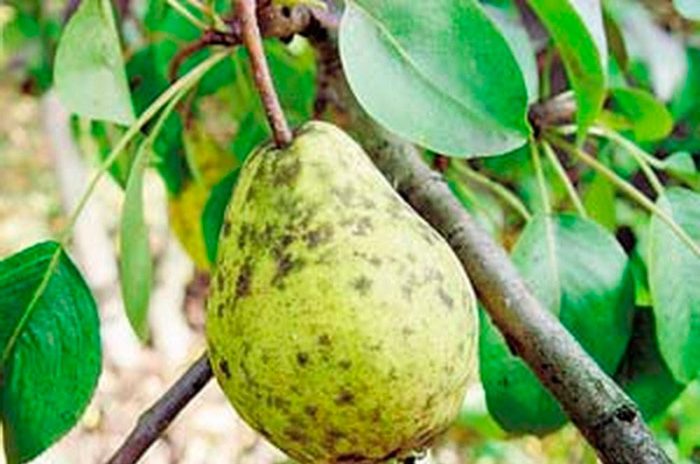
Fruit rot
If small brown spots appear on the surface of the fruit, this indicates that the specimen has been damaged by moniliosis or fruit rot. Over time, the entire fruit becomes covered with spots. At the same time, the fruit remains on the branches, due to which the disease spreads very quickly. To get rid of the disease, the infected fruits must be collected from the surface of the soil and from the plant itself, then they are burned. Next, the pear must be sprayed with Bordeaux liquid or copper chloride.
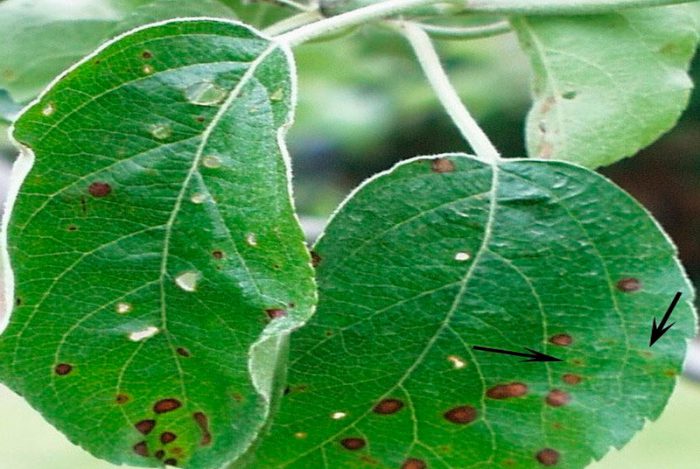
Scab
Scab is a dangerous disease that affects leaf plates, flowers, fruits and stems. Initially, small spots 0.2–0.4 centimeters in size are formed on the leaf plates, which eventually grow to 2–3 centimeters. The fruits become smaller, harden, cracks appear on them, and their number decreases. Dark spots are formed on the surface of the skin, which eventually combine into one large velvety spot. For the purpose of prevention in the autumn, it is necessary to rake and destroy all the leaf plates that have flown around. In springtime, the surface of the trunk circles and the trees themselves should be sprayed with a urea solution or Bordeaux liquid.
Cytosporosis
Stem rot, or cytosporosis. This disease is especially dangerous for trees that are old or weakened, have frost or sun burns, exhausted by a lack of moisture or improper care. In affected specimens, the bark becomes dark red over time, and the tree itself dries up. As soon as the disease is detected, it is necessary to cut out all the affected areas with a sharp knife, then the wounds should be smeared with garden varnish or sprayed with a solution of copper sulfate. In autumn, the warping of skeletal branches and the trunk of a pear must be whitewashed with lime. All affected branches must be cut and burned.
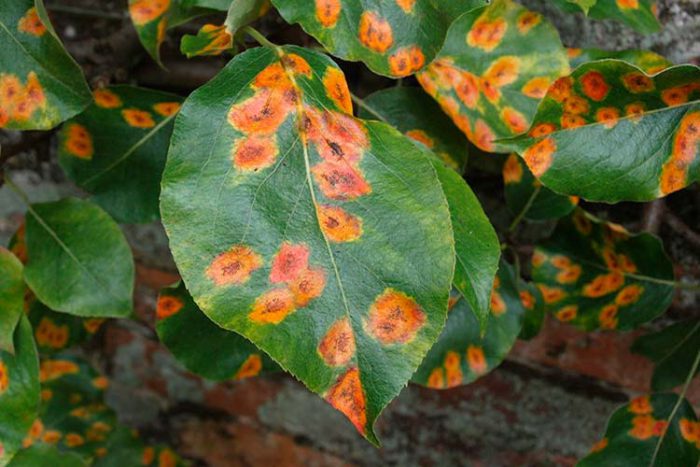
Rust
If spots of a deep orange color are formed on the leaf plates, this means that the pear has contracted such a fungal disease as rust. The affected plant is weakened, and its immunity is markedly reduced. If a juniper is grown at the same time as a pear in the garden, then the likelihood that the tree will get sick with scab increases significantly. Affected foliage and fruit must be harvested and burned. Every year, in autumn and spring, for prevention purposes, trees should be sprayed with Bordeaux liquid or colloidal sulfur.
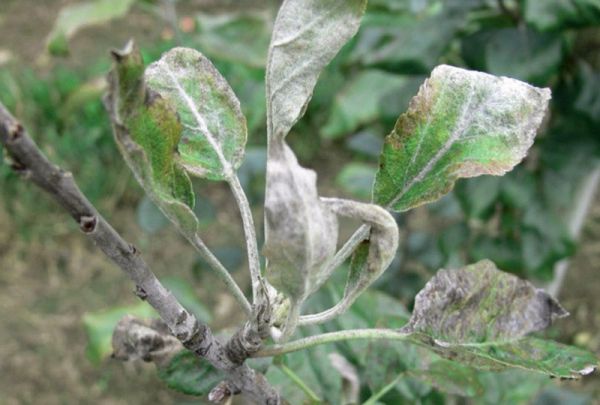
Powdery mildew
The greatest danger to pears is a fungal disease such as powdery mildew. In the affected specimen, a whitish bloom appears on the surface of the stems, flowers and leaf plates, representing the spores of fungi. As a result, all affected parts of the plant are deformed. In the affected specimens, the ovaries fall off. Collect and burn any loose leaves. The pear should be sprayed several times with Fundazol or Sulfite before flowering and after it ends.
Bacterial burn
The development of a fire blight occurs very quickly, while pathogenic bacteria are carried through the vessels by the plant sap. As a result, the process of tissue death occurs rapidly. Over time, the tree dies, and it will need to be uprooted and destroyed. As soon as the disease is detected, it is necessary to treat the flowers and foliage with an antibiotic. Several sprays are carried out at intervals of 5 days. In order to avoid the spread of the disease, the plant must be cut with a tool disinfected in boric acid.
Mosaic disease
Mosaic disease is a dangerous viral disease. The point is that today it is impossible to cure such a disease. In affected specimens, angular specks of yellowish or light green color appear on the leaf plates. Typically, the plant becomes infected during grafting. Since the disease cannot be cured, the affected tree should be uprooted and destroyed. To avoid contamination, a very careful inspection of the seedlings in the nursery is necessary. As soon as the first signs of the disease appear, the plant is immediately destroyed, which will prevent the spread of the disease.
Sooty fungus
From the middle to the end of the summer period, a sooty fungus may appear on the surface of the green parts of the plant, which is a dark bloom. As a rule, this disease appears as a result of the vital activity of aphids or other pests. To get rid of the fungus, it is necessary to destroy those pests that caused its appearance; for this, the tree is sprayed with an insecticide. Then the plant is sprayed with a copper-soap solution or Fitoverm.
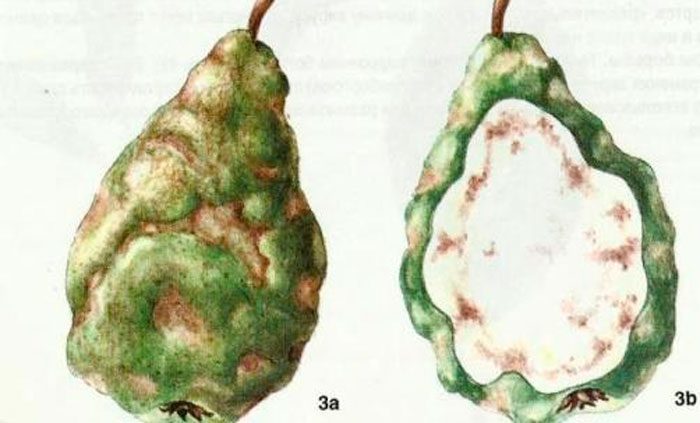
Subcutaneous viral spotting
If tasteless solid formations appear in the pulp of the fruit, then this means that the plant is infected with subcutaneous viral spot. In places of such formations, the development of the fetus stops, dents appear, because of which the fruit becomes ugly. There is a decrease in the number of fruits and a deterioration in their quality, the color of the leaf plates becomes mosaic, and cracks form on the bark. The probability of freezing out of plants weakened by the disease increases in winter. The pear can become infected during pruning or during vaccination, if non-sterile dirty tools were used. Sucking insect pests are also carriers of the disease. For prevention purposes, pests should be prevented from appearing on the plant, the purchased seedling should be carefully inspected, inoculation and pruning should be carried out only with a well-disinfected tool.
Also, a pear can get sick with the following diseases: rubbery, dying off of branches, common cancer, fly-away, mosaic ringed, false tinder fungus, white spot, or septoria.


Watch this video on YouTube
Pear pests with photo
A large number of pests can settle on a pear tree and harm it. Below will be described those pests that cause problems for gardeners when growing pears most often.
Leaf roll
The leafworm is a movable little caterpillar. It damages only the leaf plates of the plant, which is why they become smaller and fold into a tube. For prevention purposes, the plant is sprayed with a solution of Cymbush.
Subcrustal leaf roll
The subcrustal leafworm causes damage to the pear bark at a height of about 50 centimeters from the site level. Due to the damage received, gum begins to flow out of cracks in the bark. If you do nothing, the plant will gradually dry out and die. The layers of bark that have died out should be removed from the trunk, and then these places are sprayed with a strong solution of chlorophos.
Pear Copper
Pear sap is a sucking pest that feeds on plant cell sap. Thanks to its vital activity, substances are produced that are favorable for the appearance and growth of a sooty fungus. Due to the lack of vegetable juice, wrinkling and shedding of foliage, buds and buds occurs, deformation of fruits. Such a pest has an extremely negative effect on the quantity and quality of the crop. To get rid of the sucker, you need to treat the tree with Agravertine and Iskra, following the instructions on the package. If you wish, you can use proven folk recipes: a decoction of chamomile, yarrow, tobacco dust or dandelion.
Gall mite
Mites, such as red apple or gall, also suck the cell sap from the pear. The gall mite sucks it out of the buds, while the red apple mite settles on the foliage, which is why it acquires a red color. For prevention purposes, at the beginning of spring, the tree should be sprayed with acaricide, namely, Fufanon or a solution of colloidal sulfur (10%). The second time the plant is sprayed after it has faded. If necessary, you can spray the pear again, but this treatment should be carried out no later than 4 weeks before harvest. It is recommended to alternate the drugs used, otherwise, with repeated processing, the pests develop immunity.
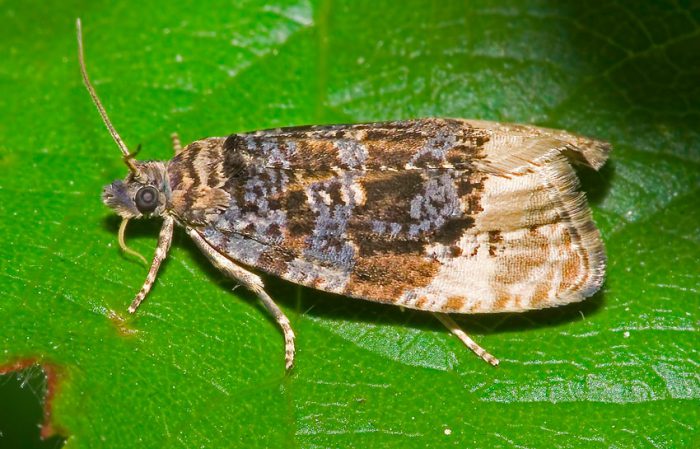
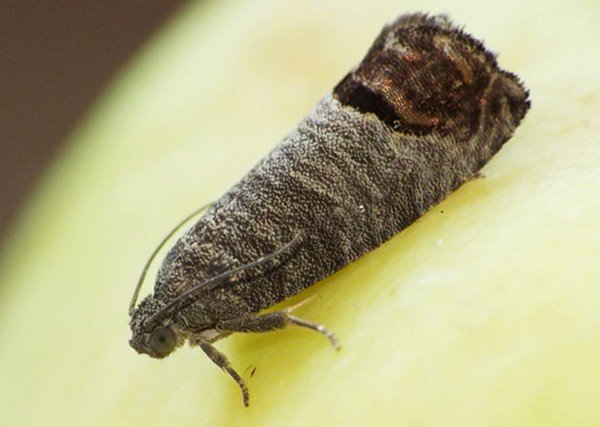
Fruit moth
The moth is a butterfly that lays its eggs on a pear tree. Caterpillars hatch from them, which damage the flesh of the fruit. In order to prevent the pear before flowering and after it is sprayed with Agravertine. 20 days after flowering, the plant is treated with Kinmix, and after another 7 days - with Iskra. In the event that the caterpillars were found in the stems, then after all the fruits have been collected, the pear must be processed again. For example, late varieties of pears are processed up to 7 times during the season. After all the leaves fall from the tree in the fall, they must be collected and destroyed. At the same time, they dig up the soil in the trunk circle.
Aphid
Aphids, green apple or blood, they can settle not only on the pear, but also on other trees. Because of such a pest, the leaf plates and tops of the stems curl and dry out. A fairly effective preventive measure is spraying the pear in early spring before the buds open, with such means as Oleocubrite, Kemifos, Nitrafen or Karbofos, while the air temperature outside during the procedure should not be lower than 5 degrees. The second treatment is carried out in the period from the opening of the buds to the beginning of flowering of the plant, while using Antio, Cyanox, Metaphos, Phosphamide, Karbofos or Decis. In the summer, it is necessary to re-spray with the same preparations. If desired, you can use folk remedies to spray pears, for example, soap solution (0.3 kg of soap for 1 bucket of water).And you can also use an infusion of white mustard, for its preparation you need to combine 1 liter of water and 10 grams of mustard powder, and stand for 2 days. Before spraying, pour 200 mg of infusion into a liter container and fill the container to the top with water.
Also, harm to the plant can be caused by apple glass, blue-headed scoop, peppered moth and winter moth, fruit moth, unpaired, oak-leaved and ringed silkworms, mining moth, western unpaired bark beetle, sapwood, pear and apple flower beetles, pear leaf worm and fruit gall midges, pear pruritus, hawthorn.


Watch this video on YouTube
Pear varieties
Pear varieties for the Moscow region
As a result of the painstaking work of breeders, today there are many varieties of pears, which are adapted for growing in regions with frosty and long winters. Recommended varieties for growing in the Moscow region:
- Lada... This early summer variety is resistant to drought, frost and fungal diseases. A medium-sized plant has a pyramidal crown. Fruits are yellow with a blurred blush of pale red color, weighing about 150 grams. The sweet-sour, slightly tough pulp contains a large amount of fructose. Keeping quality is poor.
- Cathedral... This mid-summer early ripening variety is popular in the Moscow region. It is resistant to infection and frost, and is suitable for transportation and storage. The slightly sour green-yellow fruits have an oily surface and weigh about 100 grams.
- Lumpy (prominent)... The late summer variety is resistant to fungal diseases and frost. The fruits ripen by September. They are irregular green-yellow with orange stains. They can hang on the branches for a long time, but the fruit is not suitable for transportation and storage.
- Chizhovskaya... The variety is late summer self-fertile, resistant to fungal diseases and frost. The yellow-green fruits have a pink blush. The sweet-sour friable pulp has a whitish color. In order to collect a rich harvest from this plant, you need to plant a pear of the Lada variety next to it.
- Tenderness... This is the best late summer variety obtained by crossing Lyubimitsa Klappa and Tema. Sweet-sour fruits are 1/3 green and 2/3 red. The fruit weighs about 200 grams. The variety is resistant to frost and high yields.
- Muscovite... Early autumn variety. There are green blotches on the surface of pale yellow fruits. Juicy fragrant pulp is a little oily.
- Fabulous... The plants are tall. Large yellow-green fruits weigh about 250 grams. The tasty pulp is juicy enough. The fruits can be eaten fresh or used for processing because they do not store well.
- Petrova and Pervomaisky... These varieties are very similar to each other. The fruits of these winter varieties ripen in mid-October, they can be stored until spring if certain rules are followed. The fruits are harvested while still green. Over time, the fruits of the Pervomaysky variety turn yellow, and their flesh becomes creamy. During storage, Petrov's fruits do not change.
Early varieties of pear
All varieties of pears are divided into summer (early), autumn (medium) and winter (late). Fruit ripening in summer varieties is observed from the second half of July to the last days of August. Popular varieties:
- Lipotics... The earliest variety that is scab resistant. Fruits are golden with a ruddy side and become ripe by the last days of June. The pulp is fragrant, melting in the mouth. This variety comes from Bulgaria, therefore, its resistance to frost is low. Very resistant to aphids.
- Early summer... The crown shape of this medium-sized pear is broad-pyramidal, the branches are straight. The green-yellow fruits have a slight pink blush and weigh about 120 grams. The sweet-sour tender pulp has a white color.The fruits do not fall off the branches for a long time, but at the same time they can be stored for no more than 1.5 weeks.
- Moldavian early... This hybrid was created by crossing the varieties Lyubimitsa Klappa and Williams. The crown of such a tall plant is compact of medium size. The color of the fruits is green-yellow, they weigh about 150 grams. The oily, fragrant, creamy pulp has a sweet and sour taste. This self-fertile, winter-hardy variety is scab resistant. To collect a rich harvest from such a plant, it is recommended to grow such pear varieties as: Swallow, Beautiful or Bere Giraffe next to it.
- July early... An early summer variety resistant to frost. Elongated yellow fruits have a delicate pulp with a sweet and sour taste. Fruit ripening is observed by the second half of July.
- Mlievskaya early... This early ripening winter-hardy variety is resistant to bacterial cancer. It was created by crossing the Esperen variety with the Ukrainian Gliva variety. Medium-sized fruits have a wide pear-shaped shape, they are covered with thin skin and weigh about 100 grams. Juicy buttery sweet-sour pulp has a creamy color. Fruit ripening is observed in the first days of August, they are placed for storage on a refrigerator shelf. They can be stored for no more than 8 weeks.
- Refectory... This variety is very good, but it has a serious drawback that its fruits cannot be stored in the refrigerator for more than 5 days. In this regard, it is recommended to collect unripe fruits.
Also, gardeners often grow such early varieties as: Skorospelka from Michurinsk, Allegro, Severyanka red-cheeked, Pamyatnaya, Avgustovskaya dew, Rogneda, ELS-9-7.
Medium pears
Ripening of fruits of medium varieties of pears is observed in the last days of September or the first - in October. The fruits are not suitable for long-term storage. Popular varieties:
- Veles... The variety is resistant to frost and disease. The fruits are large, yellow-green, weighing about 200 grams. The cream-colored pulp has a high taste.
- Thumbelina... The variety is frost-resistant. The small brown-yellow fruits weigh about 80 grams. Delicious juicy flesh is very sweet and creamy. The fruits can be stored until December.
- Elegant Efimova... The variety is fast-growing, resistant to scab and frost. Fruit ripening is observed in September. The yellow-green fruits weigh about 120 grams and have a creamy flesh. It is recommended to harvest them unripe. They can be stored for 15–20 days.
Also, gardeners often grow the following autumn varieties: Caucasus, Autumn Favorite, Margarita Marilya, Williams, Lyubimitsa Klappa, Otradnenskaya, Cheremshina, Admiral Gervais, Memory Zhegalov, Duchesse, etc.
Late varieties of pears
Ripening of late varieties is observed in October. But you can't eat them right away. You should wait until the fruits reach full biological maturity and only then collect them. But this should be done before the fruit falls. The keeping quality of these varieties is not the same. Popular varieties:
- Bere Bosc... As a rule, the fruits are oblong. Their surface in some areas is covered with rust. During storage, they develop a bronze tint. Delicious tender pulp melts in your mouth. Fruits can be harvested in the last days of September, but you can start eating them after 15–20 days. These fruits can be stored for 4-6 weeks.
- Belarusian late... The variety is early-growing, characterized by frost resistance. The tree bears its first fruits already in the third or fourth year of life. Ripening of green fruits is observed in the last days of September, but they can be eaten only after they turn orange-yellow. Fruits weigh about 120 grams. The sweet-sour flesh is white in color. With proper storage, these fruits can last until February – March.
- Rossoshan late... Winter-hardy variety. The fruits weigh about 350 grams.They can be harvested in the last days of September while they are still green. However, such fruits can only be eaten after they turn yellow. The juicy pulp, pleasant to the taste, has a creamy color. Fruits can lay for 3 to 4 months.
- Bere Ardanpon... Fruits are large, lumpy yellow-green color, weigh about 300 grams, outwardly similar to quince. Oily sweet pulp is slightly tart. Fruits are harvested in the first days of October, but they can only be eaten after 4–6 weeks. The fruits can lie until January.
- Winter decan... The fruit is barrel-shaped, weighing about 300 grams. They are harvested in the second decade of October, while the color of the fruit should be green with a reddish blush. After 8 weeks, they will turn yellow-green and can be eaten. The fragrant tender pulp is slightly sour. The fruits can lie until March.
- Malyavskaya late... Yellow fruits weigh about 110-225 grams, 1/3 of them are covered with blush. The creamy juicy pulp has a slightly tart taste.
- Winter Kubarevnaya... This hybrid was created using varieties such as Duchess, Bergamot and Lyubimitsa Klappa. The fruits weigh up to 200 grams. They are harvested pale green with a light red barrel, but when they reach consumer maturity, they will turn yellow-golden with a raspberry blush. Juicy white medium density pulp is very sweet and has a slight sourness.
Also among gardeners, the following late varieties are quite popular: Hera, Bogataya, Dekabrinka, February souvenir, Wonderful, Late, Melting, Yuryevskaya, Yantarnaya, Elena, Nadezhda, Nika, Lyra, Paskhalnaya, Perun, Malvina winter, Curé, Etude Kievsky, Kyrgyz winter, November, etc.


Watch this video on YouTube