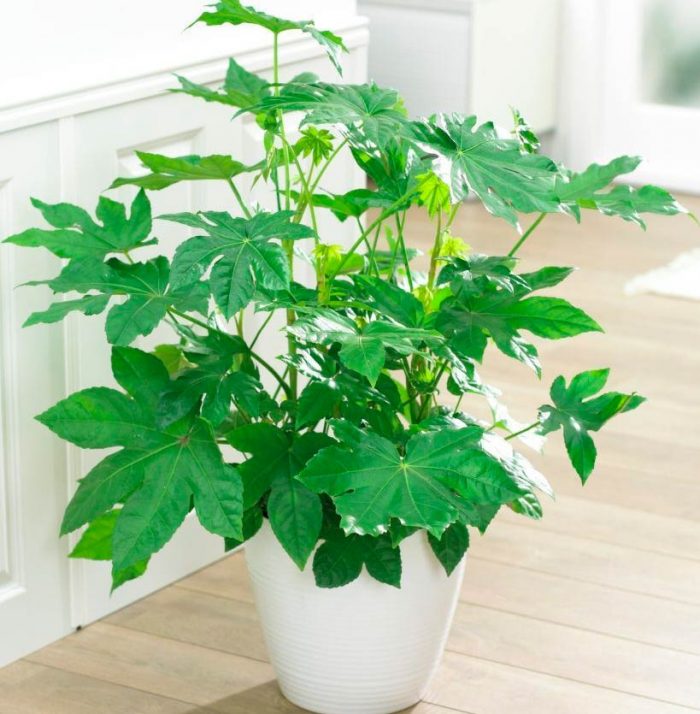
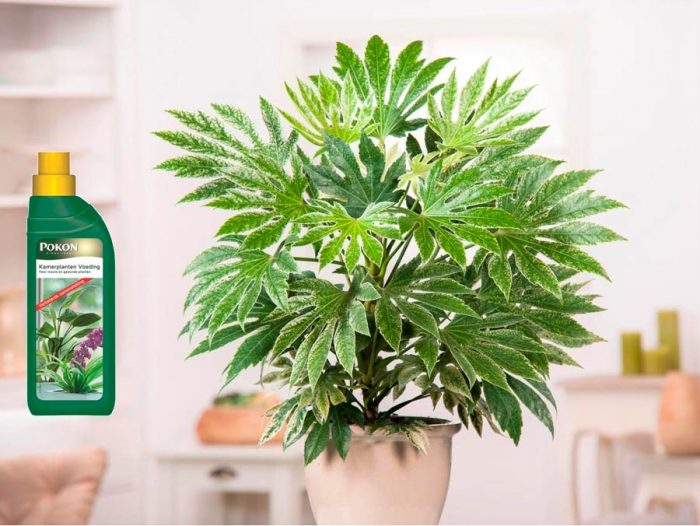
The plant Fatsia (Fatsia) is a monotypic genus that is part of the Araliaceae family. This genus is represented by only one species Fatsia japonica (Japanese fatsia). In 1910, a mixture between fatsia and ivy was born, which was called Fatshedera, and it became very popular with flower growers. Room fatsia is often used to decorate walls, pillars or shop windows. This plant is also used for interior decoration. Such a flower grown in a pot is also used to decorate baskets. If the bush is properly fertilized and provided with good care, then in just 2 years its height can reach about 100 cm. To form a spectacular crown, the bush should not interfere with its growth.
Content
Brief description of cultivation
- Bloom... Fatsia is cultivated as an ornamental leafy plant.
- Illumination... Species with green leaves can also be placed in a slightly shaded place, but variegated species need bright diffused light.
- Temperature regime... In the spring-autumn period, the air temperature should be from 17 to 21 degrees, and in the winter - from 13 to 15 degrees. If the plant is variegated, then it must not be allowed to be colder than 16 degrees in the room where it is located.
- Watering... During intensive growth, the bush is watered immediately after the top layer of the substrate dries. If in the winter it is cool, then watering should be reduced to a minimum, but at the same time you need to make sure that the earthen lump does not dry out completely.
- Air humidity... It should be elevated. Experts advise to systematically moisten the foliage from a sprayer and wipe it with a damp soft cloth.
- Fertilizer... During the growing season, the plant is fed 1 time per week with organic matter or mineral fertilizers. If the flower is cool in winter, then you do not need to feed it. And when it hibernates in a warm place, feeding is carried out no more than once every 4 weeks.
- Pruning... Held in the spring. There are varieties of fatsia that need to be shortened regularly.
- Transfer... A flower is transplanted once every 3 years in the spring or in the first summer weeks.
- Soil mixture... Leafy, turf and humus soil, as well as sand and peat (1: 1: 1: 1: 1).
- Reproduction... Seed and vegetative (layering, cuttings) method.
- Harmful insects... Whiteflies, scale insects, spider mites and mealybugs.
- Diseases... If the plant is not properly cared for, or if it is in the wrong conditions, it may have problems with foliage.
- Properties... All parts of such a plant contain poison.
Fatsia care at home
Illumination
Fatsia is a light-loving plant, but direct sunlight can harm it. Views with green foliage do well in shaded areas, so you can choose a north-facing window for them. But variegated species need a lot of light. Fatsia feels best on the windowsill of western or eastern orientation. If such a flower is placed on the south window, then it will need to be shaded from the direct rays of the sun. It also grows quite well under fluorescent lights. In summer, fatsia can be transferred to fresh air, but at the same time it must be protected from direct sunlight.
Temperature regime
In spring and summer, such a culture feels very good at an air temperature of 17 to 21 degrees. She can hibernate at normal room temperature, but experts advise placing her in a cool (no more than 15 degrees) place, which should be well lit. If fatsia is kept warm in winter, then it will need a lot of light, while fluorescent lamps can be used to illuminate it. When growing variegated species, it should be borne in mind that the temperature in the room should not be less than 16 degrees at any time of the year.
How to water properly
In the warm season, watering such a flower is carried out immediately, as soon as the top layer of the substrate in the pot dries out. With the onset of autumn, watering is reduced. During cold wintering, it should be very scarce and rare, but care must be taken that the earthen lump in the pot does not dry out completely. If in winter the flower is warm, then there is no need to greatly reduce the watering, but in this case one must remember to pour out the accumulated liquid from the pan 2-3 hours after each watering. It must be borne in mind that such a culture equally badly tolerates both the drying out of a clod of earth and stagnant water in the root system. So, if the earthen lump dries up completely only 1 time, then the foliage near the bush will fall down and return it to its previous state, it will be extremely difficult, and even if it is watered abundantly, it will not help. In this case, it is recommended to tie up the foliage with ropes, but this does not guarantee that the bush will someday become the same.
Spraying
In fatsia, leafy ones are quite large, so they must be systematically moistened from a sprayer, using well-settled water for this. And they should be regularly wiped with a damp sponge. On hot days, the bush can be given a warm shower. In winter, foliage should be moistened less often (the frequency of such a procedure directly depends on the air temperature in the room).
Fertilizer
In spring, summer and autumn, such a flower must be fed 1 time in 7 days, while organic or mineral fertilizers are used for this. With cold wintering, feeding the flower is not needed. If in winter it will be warm, then it must be fed 1 time in 4 weeks.
Pruning
Indoor fatsia tolerates pruning well. In order for the bush to be thick and effective, while the flower is young, it is necessary to pinch the upper parts of the stems. When growing Fatskhedera Face, it should be borne in mind that it will need to be cut regularly.
Transfer
The transplant is carried out once every 3 years, they do it in the spring or at the beginning of the summer period. Thanks to the root offspring, several new trunks can be formed near the bush. The substrate for planting is neutral or slightly acidic.The most commonly used soil mixture, consisting of humus, leaf and sod land, as well as peat and sand, which are taken in equal shares. You can also use a soil mixture consisting of sod and garden soil, leaf humus, sand and peat (2: 2: 4: 1: 2). Before planting, do not forget to make a good drainage layer at the bottom of the pot, which should occupy ¼ or 1/5 of it. This flower can be grown hydroponically.


Watch this video on YouTube
Virulence
It should be remembered that there is poison in any of the parts of such a plant.... In this regard, after working with the bush, you must thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water.
Reproduction methods
Fatsia propagation by cuttings
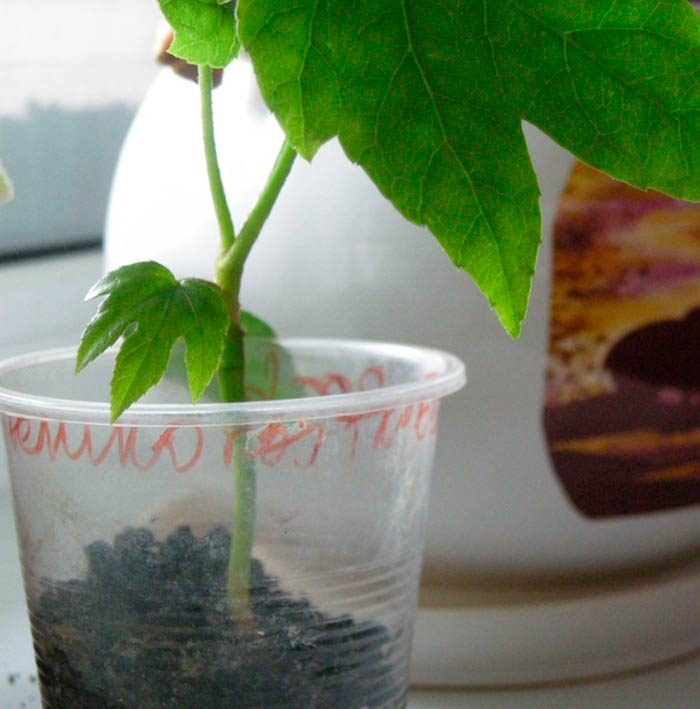
Apical cuttings can be used to propagate fatsia. It is recommended to propagate it in this way in the spring. Such a cutting is planted in a substrate consisting of moistened peat and sand, and the container is removed to a warm place (from 23 to 27 degrees). If everything is done correctly, then rooting will be successful and will not take much time. The cuttings should have several buds, after planting them in the substrate, they are covered with a glass jar on top and wait until their roots grow. When the rooting of the cuttings is over, they are transplanted into individual pots. Such bushes will be relatively low, but very lush.


Watch this video on YouTube
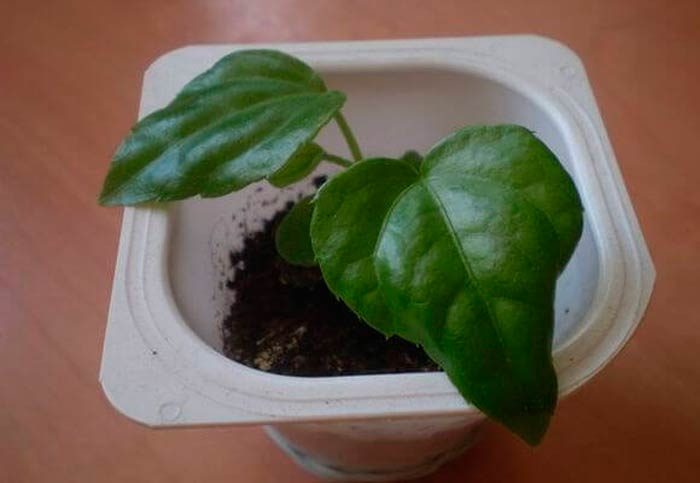
Growing from seeds
For sowing seeds, use pots or boxes filled with a substrate consisting of turf and leafy soil, as well as sand, which are taken in equal shares. They need to be buried in the soil mixture by only 10 mm. Crops are kept in a cool place (about 18 degrees). Fortified seedlings dive into individual pots, reaching from 9 to 11 centimeters in diameter, while using a soil mixture consisting of humus and sod soil, as well as sand (1: 2: 1). Only one plant is planted in one container, after which it is removed to a well-lit place.
Reproduction of fatsia by layering
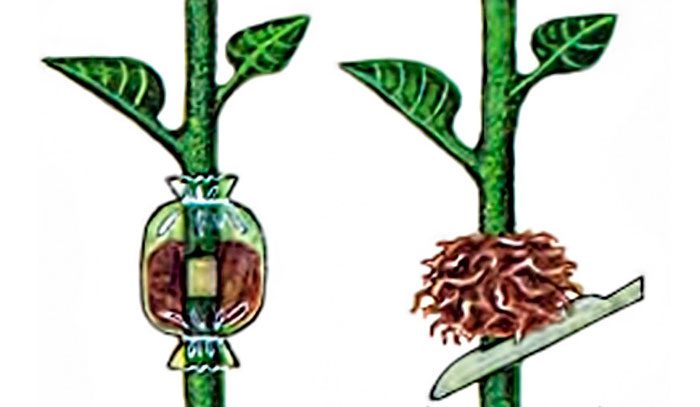
If the plant is properly cared for, it will be completely covered with foliage. But it happens that part of the trunk is exposed, and in order to fix this, you can use the air cut of the fatsia. In spring, on one of the bush's trunks, you need to make a small incision, which is then covered with moss, previously soaked in the nutrient mixture (for 1 liter of water, 1 gram of complex fertilizer). From above, the place of the incision is wrapped with a film. Make sure that the moss does not dry out; therefore, it must be systematically moistened. At the cut site, the roots should form after a few months. And after another 8 weeks, the layers are separated from the mother plant, while the cut is made slightly below the place where the roots were formed, then it is planted in a new container.
If necessary, you can cut the trunk of the old bush to the very root, then the stump must be covered with a layer of moss and do not forget to water it regularly, after a while it may have several shoots. There is another option, not to cut the trunk at the root, but instead graft ivy, which belongs to the same family as Fatsia, to it. Ivy will quickly take root on the trunk. As a result, a spectacular tree with hanging branches will form.
Possible problems
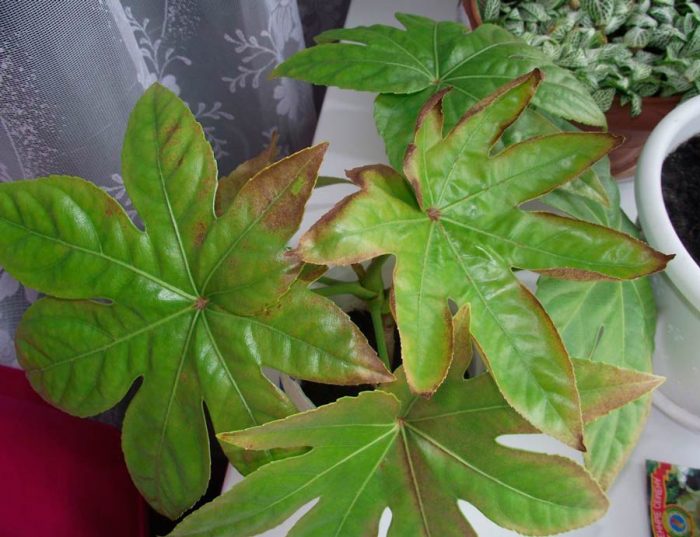
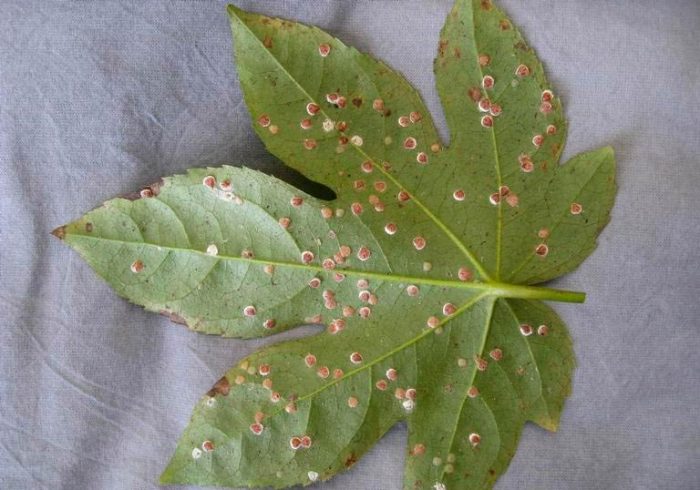
If the flower is not properly looked after, then various problems can arise with its foliage.
- Fatsia leaf spots... When the earthen coma is dried out, brown specks form on the surface of the foliage. In the worst case, it wilts, and it is extremely difficult to return it to its previous state.
- Fatsia leaves wrinkle... If the air humidity in the room is too low, then because of this, the foliage becomes fragile. If very intense lighting is observed at the same time, foliage shrinkage may occur.
- Fatsia leaves wither... Leaf wilting is observed due to stagnation of liquid in the root system. In the event that this happens constantly, then rot may appear on the roots.
Pests
Most often, mealybugs, spider mites, whiteflies and scale insects settle on the bush.


Watch this video on YouTube
Types of Fatsia
As mentioned above, there is only one type of Fatsia, namely Japanese Fatsia (Fatsia japonica), or Japanese Aralia (Aralia japonica).
Japanese fatsia (Aralia japonica)
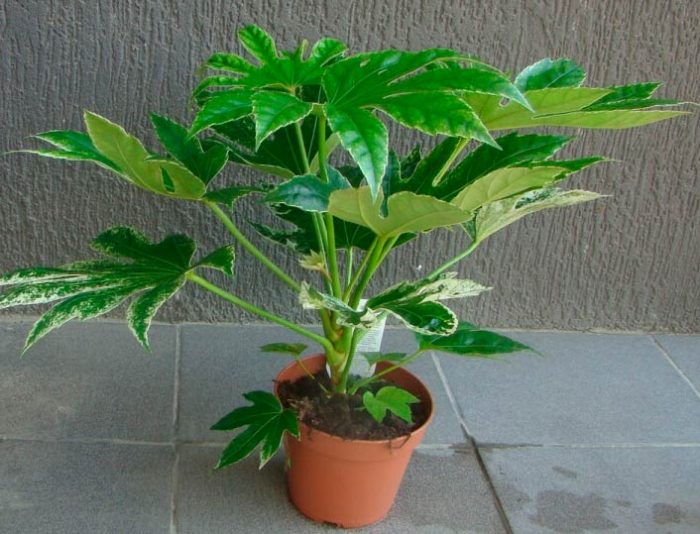
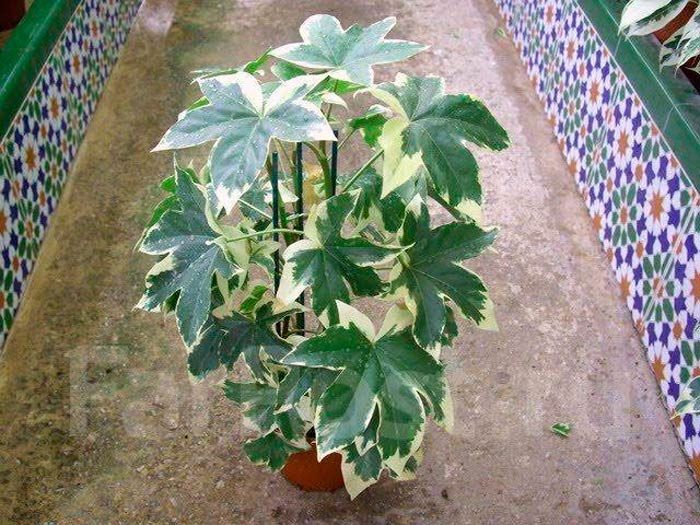
It is found naturally on the Japanese seaside. The height of such unbranched evergreen shrubs is about 200 cm. Leathery shiny long-petiolate 5-9 lobed leaf plates are heart-shaped and round in shape and reach about 30 centimeters in diameter. The foliage can be variegated white, green or variegated yellow. The umbrellas are composed of white flowers. Fatsia japonica aureimarginatis - yellow edging runs along the edge of the leaf plates. Fatsia japonica var. argenteimarginatis - the leaves have a white border. Fatsia japonica var. moseri is a squat, dense bush.
Fatshedera Lizei
The height of such an evergreen shrub is about 500 cm. It has lush foliage. Dark green leathery leaf plates 3–5 clawed.