Bird cherry (Prunus) - this is the general name of individual species belonging to the genus Plum of the Pink family. Previously, these species were distinguished into a separate genus or subgenus. Often speaking about bird cherry, gardeners mean bird cherry (Prunus padus), which is also called bird cherry or carpal. Under natural conditions, this species can be found in Asia, throughout Russia, in Western Europe and North Africa. Such bird cherry prefers to grow on nutritious forest land, where groundwater occurs quite close to the soil surface, in regions with a temperate climate. It can be found on the edges of the forest, on river banks, on sands and clearings. There are about 20 types of bird cherry.
Content
- 1 Features of bird cherry
- 2 Planting bird cherry in the open field
- 3 Bird cherry care in the garden
- 4 Bird cherry propagation
- 5 Bird cherry pests and diseases
- 6 Types and varieties of bird cherry with photos and names
- 6.1 Bird cherry Maack (Padus maackii)
- 6.2 Bird cherry Maximovich (Padus maximowiczii)
- 6.3 Bird cherry (Padus serrulata)
- 6.4 Pennsylvanian bird cherry (Padus pennsylvanica)
- 6.5 Siori bird cherry (Padus ssiori)
- 6.6 Bird cherry (Padus asiatica)
- 6.7 Bird cherry antipka (Padus mahaleb), or magalenka
- 6.8 Bird cherry (Padus grayana)
- 6.9 Late bird cherry (Padus serotina)
- 6.10 Virginia bird cherry (Padus virginiana)
- 7 Bird cherry properties: benefits and harms
Features of bird cherry
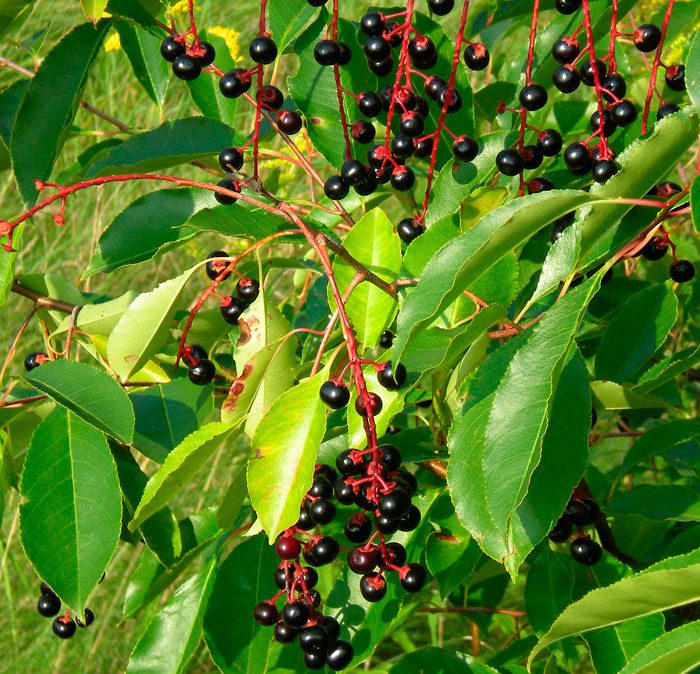
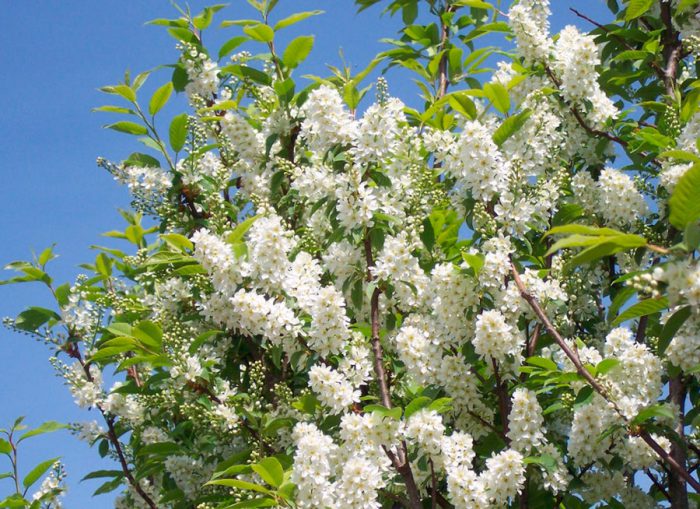
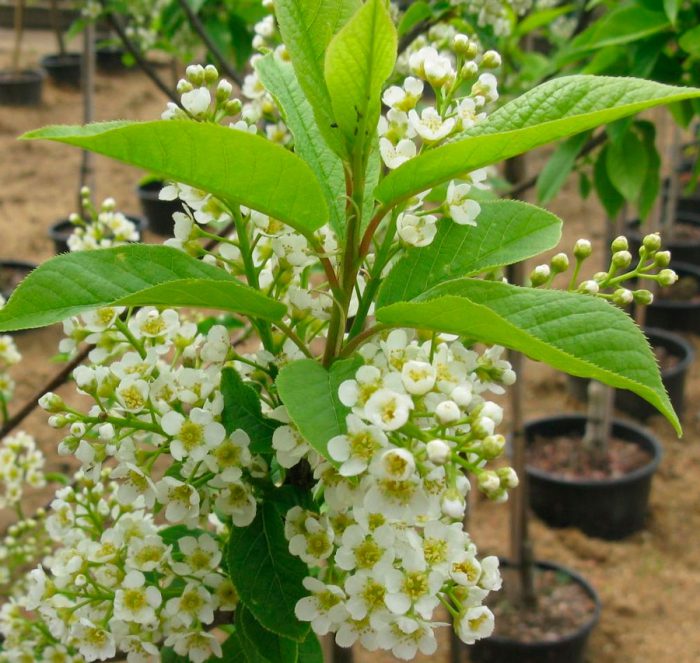
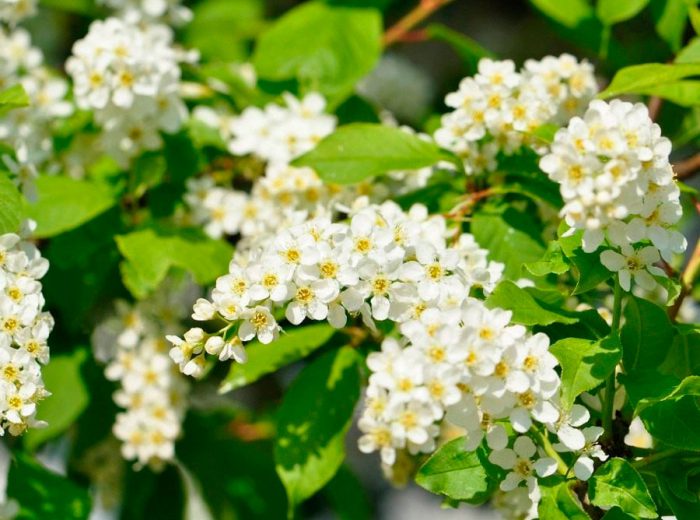
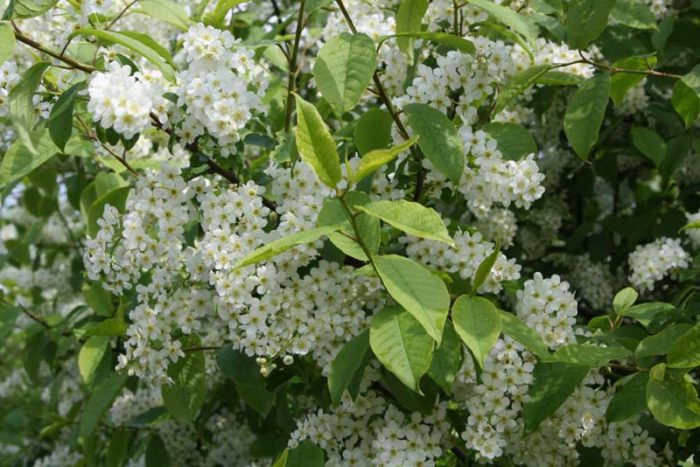
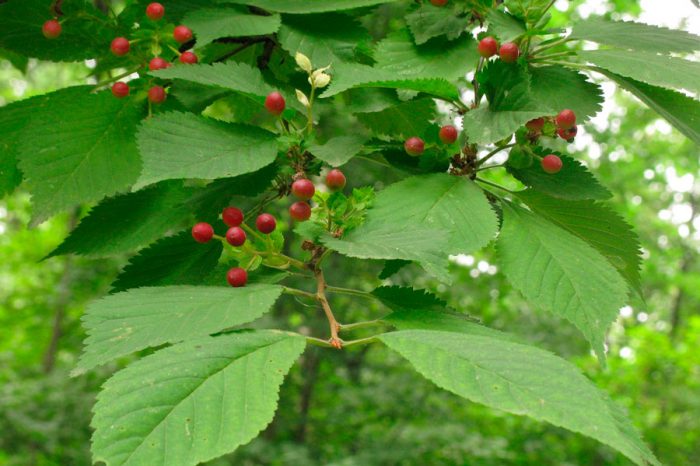
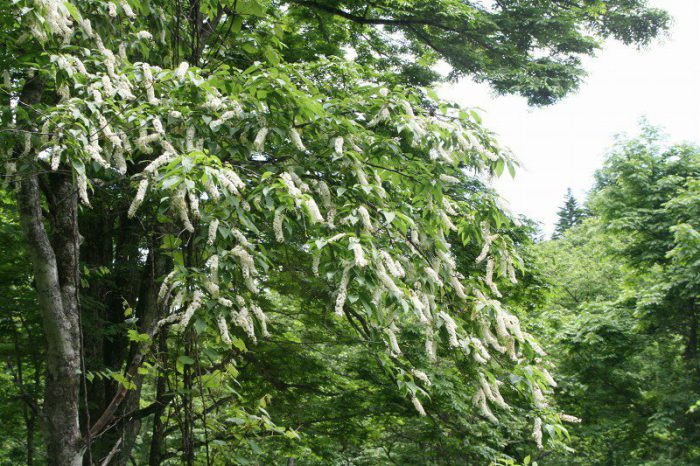
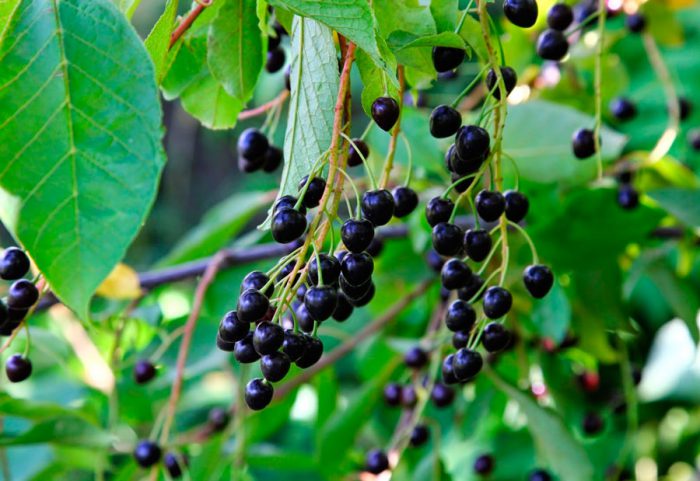
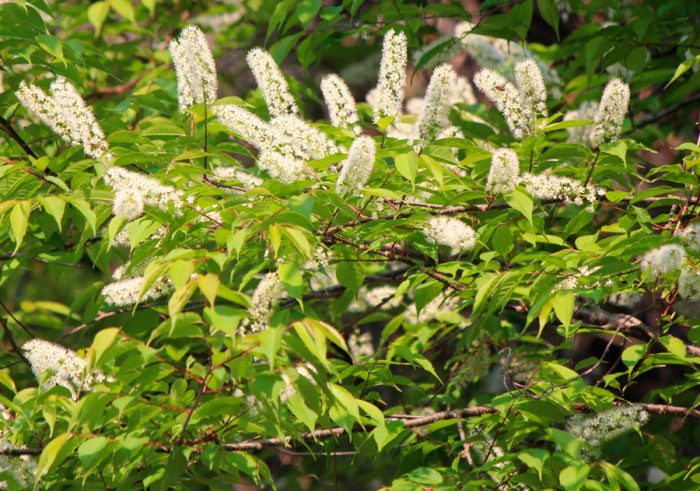
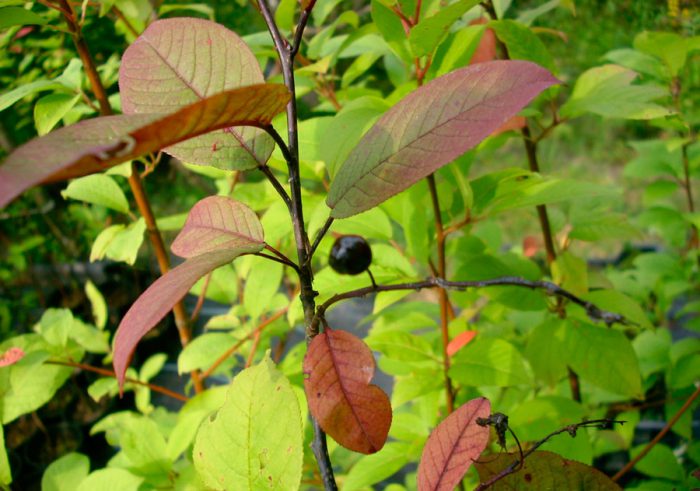
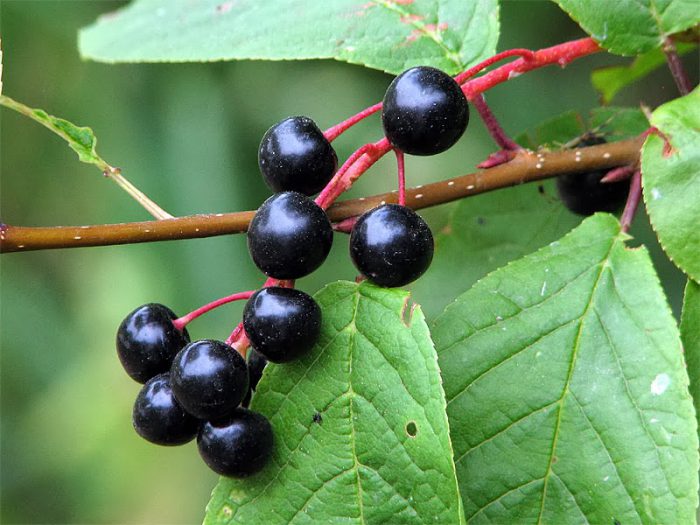
Bird cherry is a shrub or not a very large tree, its height varies from 0.6 to 10 meters. The crown is lush, elongated. Matte black-gray bark has white lentils. The color of young stems and branches is olive or cherry. Alternately located simple bare leaf plates have an oblong or elliptical shape with a pointed tip and a sharp-serrated edge. Their length is 3-15 centimeters. Leaves are located on thin petioles, at the base of the plate there are 2 glands. The length of the racemose drooping inflorescences is from 8 to 12 centimeters, they consist of fragrant flowers, painted in pale pink or white. The flower contains: 5 petals and sepals, a pistil, 20 stamens and yellow anthers. The fruit is a black spherical drupe, which reaches from 0.8 to 1 cm in diameter. The fruits have a sweet, strongly astringent taste, and inside them there is an ovoid-rounded bone. Such a plant blooms in May and June, and fruit ripening is observed in July and August.
Planting bird cherry in the open field
What time to plant
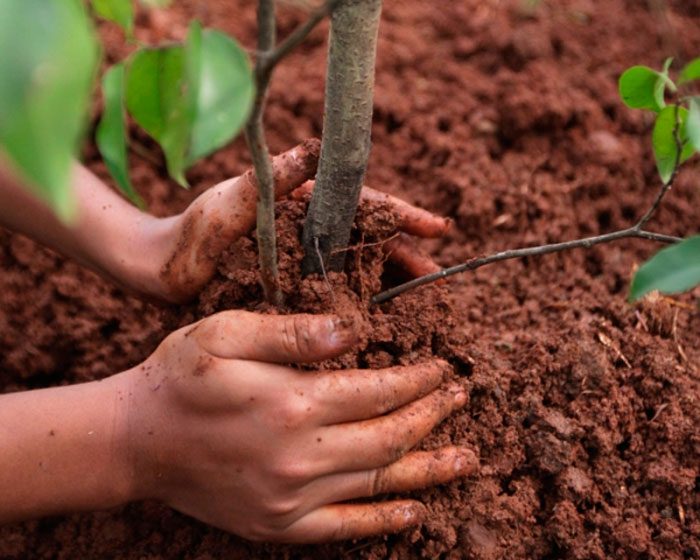
It is recommended to plant bird cherry in open ground in spring and autumn, because it is at this time that the survival rate of seedlings is very high. For planting, it is best to choose a sunny, spacious area with moist nutrient soil, which should be slightly acidic or neutral. If you plant bird cherry in a shaded place, then it will reach for sunlight, while the formation of fruits will occur at the tops of the branches. Experts recommend planting this plant in an area with loamy soil, but it can also be planted in clay and sandy soil. Bird cherry prefers that the groundwater is close enough to the surface of the site.
Such a plant requires cross-pollination, and therefore several trees of different varieties should be planted on the site at once, but it must be borne in mind that they must bloom at the same time. When planting between plants, a distance of several meters should be maintained, since they are fast-growing, and their branches can reach a length of several meters.
Landing features
When planted in open soil, seedlings take root perfectly, while there is no need to prepare a special nutrient soil mixture to fill the hole. For planting, a pit should be prepared, the size of which should be such that the root system of the plant being planted can fit in it. At the bottom of the pit, you need to pour a layer of a mixture consisting of mineral fertilizers and humus, dry foliage or peat. Remember that a large amount of organic matter has a negative effect on the bark of the plant, so you should not pour too much of it into the hole. Immediately before planting, a thorough examination of the root system of the plant must be carried out, while all the roots affected by the disease must be cut out and excessively long ones must be shortened. Cut off all the stems from the seedling except the 2 or 3 most powerful ones; they must be shortened to 0.5–0.7 m. The bird cherry root system must be placed in a prepared pit, which should be covered with soil. The trunk circle needs to be compacted, after which the plant is watered very well. After the liquid is completely absorbed into the soil, its surface must be covered with a layer of mulch (sawdust or peat).


Watch this video on YouTube
Bird cherry care in the garden
Bird cherry is not capricious in nature, so there is nothing difficult in growing it. At first, planted plants need to be given frequent, regular watering. When the plant is watered, its near-stem circle must be loosened, while removing all the weeds. To significantly reduce the number of weeding, watering and loosening, the surface of the trunk circle must be covered with a layer of mulch. An older plant must be systematically fed, formative and sanitary pruning, treated against diseases and pests.
An adult tree needs to be watered several times over all summer months, while if there is a drought, then the number of waterings must be increased. If it rains quite regularly in the summer, then the bird cherry can not be watered at all.
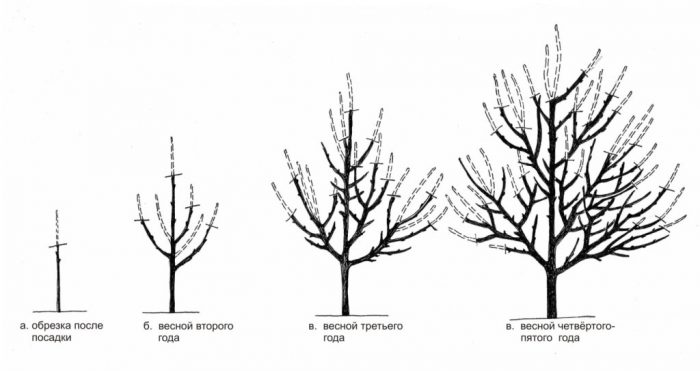
Pruning bird cherry
Every year, they carry out sanitary pruning of bird cherry, for this you need to remove all dried, injured, diseased stems and branches, as well as those that contribute to the thickening of the crown. Places of cuts must be treated with garden varnish. This plant can be formed in the form of a multi-stem shrub or in the form of a tree on a high trunk. In order for the crown of the plant to have a cupped shape, only the central shoot should remain on the seedling after planting, which is shortened to 0.5–0.7 m, all other stems must be removed.When new stems grow from the stem, it is necessary to lay the first tier, for this, 3 or 4 branches are left, which should be well developed, as well as evenly distant from each other. The angle of departure of skeletal branches from the central shoot (conductor) should be approximately 50 to 70 degrees. All other stems must be cut into a ring. The laying of the second tier is carried out in the same way, for this, 2 to 4 branches are used, which must be 0.45–0.5 m away from the branches of the first tier. In subsequent seasons, it is necessary to lay another 1 or 2 tiers, each should have 2 to 3 branches.
When the crown is fully formed, then you need to ensure that it does not thicken. You also need to ensure that the height of the bird cherry is no more than 350-400 cm. For this, it is necessary to regularly make thinning and sanitary pruning, while you need to cut out all the root shoots, and also shorten the longest branches to lateral branching, which should be directed down to help keep the tree from growing.
Bird cherry transplant
It is recommended to transplant such a tree in the spring, but it is necessary to prepare for the procedure in the fall. To do this, you need to prepare a pit for the transplant. Its size should be such that both the root system of the plant and a clod of earth can fit in it. After the temperature of 5 degrees or a little lower on the street in the autumn time (the ground should not be frozen), it is necessary to dig the plant along the border of the near-trunk circle, then it is watered very abundantly, this is done so that the tree root system winters in the frozen earthen coma. In springtime, try to prevent the ground from thawing very quickly. Cover the surface of the trunk circle with a layer of snow, which must be covered with burlap and a layer of sawdust on top. After the snow layer turns into water, you should dig up the tree and pull its root system out along with a lump of earth, which in no case should melt. The earthen lump is wrapped in burlap, which will save it from destruction during transfer to a new landing site. The burlap is very well moistened with water, the plant is laid horizontally and gently moved to a new planting site with its roots forward. When planting bird cherry, you do not need to remove burlap from the roots. It will not interfere with the growth of the root system. In order for the transplanted tree to be in an upright position, you will need wire braces, one end of which must be fixed to stakes deeply driven into the ground, and the other to the trunk. The wire can injure the bark of a tree, so it is necessary to place rags, birch bark or cardboard under it.
The first days of the transplanted bird cherry, it is necessary to provide protection from direct sun rays, so that the restoration of the root system is successful. For irrigation, use solutions of agents that stimulate the formation and growth of roots. A normally established plant should be looked after as a simple adult bird cherry, but it must be prepared differently for wintering. To do this, in late autumn, its trunk is very high, and the soil surface must be covered with manure or humus, which will protect the root system from freezing.
Bird cherry propagation
For propagation of such a plant, cuttings, root shoots and grafting are used. Also, if you wish, you can grow bird cherry from seeds that are sown in August – September, however, it should be noted that the trees that have grown from them very rarely inherit the varietal characteristics of the parent plant.
Propagation by cuttings
It is quite simple and quick to propagate bird cherry by cuttings, therefore this method is most popular among the gardener. Cuttings are harvested in the autumn. Young branches are used for cutting, while the length of the cutting can vary from 18 to 20 centimeters.The cuttings must be saved until spring, for this they are wrapped in paper or cloth and removed to a cool place. In spring, half a month before planting the cuttings in open soil, they are disinfected using a solution of manganese potassium, and then put in a glass of water and wait until the roots grow back. When this happens, the cuttings should be planted in moist, loose soil. It is very simple to take care of the cuttings, for this they need to be watered in a timely manner and carefully loosen the soil surface around them. After the plant has a good root system, it should be transplanted to a permanent place. Most gardeners advise to root the cutting directly in a permanent place, because it is extremely difficult for them to tolerate transplanting.


Watch this video on YouTube
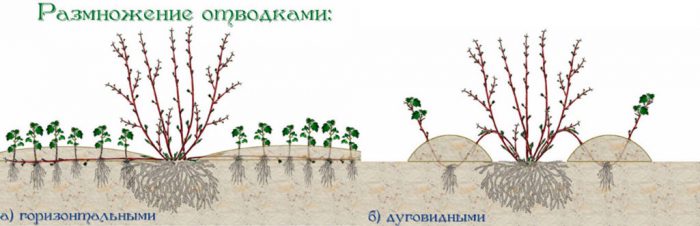
Reproduction by branches
To propagate this crop by layering, you must select a branch on the bush that grows very low. An incision must be made on its bark, and then the branch is bent to the surface of the soil and laid in a trench thirty centimeters deep, which must be prepared a couple of days before the procedure and put peat in it. Fix the branch in this position and cover the trench with soil, while the top of the cutting should remain on the surface of the soil. In the autumn, the cut is separated and transplanted to a new place. The advantage of this reproduction method is that the layers take root relatively well.
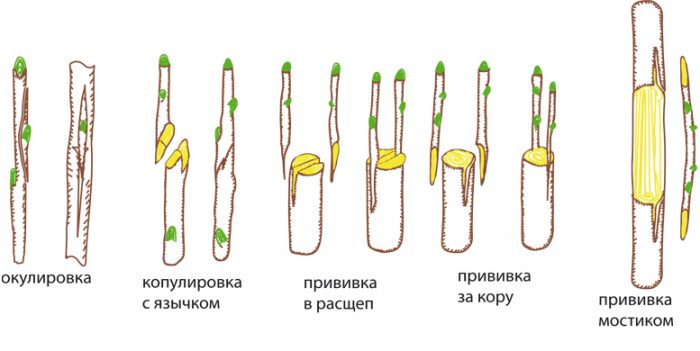
Graft
It is also quite simple to propagate this culture by grafting, especially when you consider that 9.5 out of 10 scions on the rootstock take root. The vaccination is carried out in the middle of the summer period. As a scion, cuttings cut from young shoots are used.
Bird cherry pests and diseases
Bird cherry is susceptible to diseases such as leaf spots (rubella, coniothyroidism, cercosporosis), powdery mildew, cytosporosis, wood rot, flower and fruit pockets. Of the pests, aphids, herbivorous bugs, a mining moth, an unpaired silkworm, a hawthorn, an ermine bird cherry moth and weevils can settle on it.
Cytosporosis
Cytosporosis damages the branches and stem of the plant, resulting in shrinkage. In the affected plant, pycnidia of the fungus (small white bumps) can be found on the surface of the trunk. On a wet, rainy day, such pycnidia show the release of threads of a light red color. As soon as the first signs of such a disease are noticed, the infected stems must be cut and destroyed, along with the loose leaves and fruits. In spring, before the foliage opens, it is necessary to process the bird cherry with a Bordeaux mixture (1%) or copper oxychloride. In March, large branches and the trunk must be rinsed with iron vitriol. In the autumn, the surface of the trunk must be whitewashed using lime for this.
Wood rot
Wood rot begins to develop due to the tinder fungus. The plant becomes infected through the wounds on the bark of the bird cherry. As the wood rots, there is a change in its physical and chemical properties, as well as its structure. If you find the place of penetration of the fungus in a timely manner and clean it up to healthy wood, and also cover it with clay mixed with a fungicide, this can save the plant. If the disease is neglected, the bird cherry cannot be saved.
Flower and fruit pockets
The most dangerous fungal disease that bird cherry can get is the pockets of flowers and fruits. In the process of the development of the disease, deformation of the fruits is observed, seeds do not grow in them, and plaque appears on their surface, which consists of bags of the pathogen fungus. Infected flowers most often die, while the ovary is not formed, and the whole tree is suppressed. Pick off any affected fruit or flowers. Before the tree blooms, it should be sprayed with a solution of copper sulfate (1%), iron sulfate (3%) or Bordeaux mixture (1%).
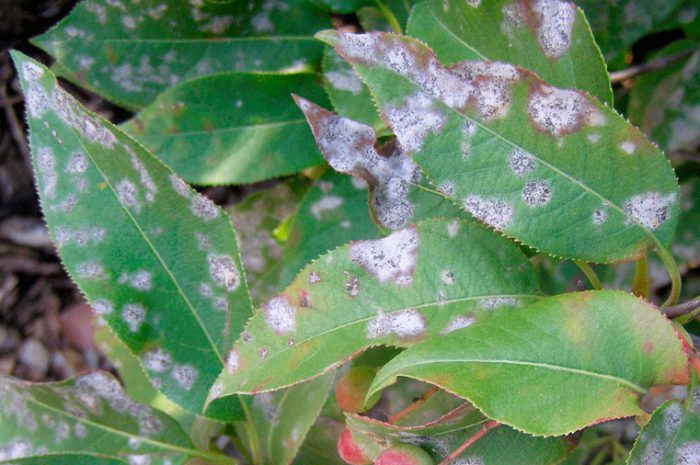
Powdery mildew
If a cobweb bloom of white color appears on the stems and foliage, it means that the specimen is infected with powdery mildew. This plaque after some time becomes less noticeable, however, fruiting bodies of a dark-colored fungus appear on it, which are clearly visible. In the spring, there is a resumption of the disease.
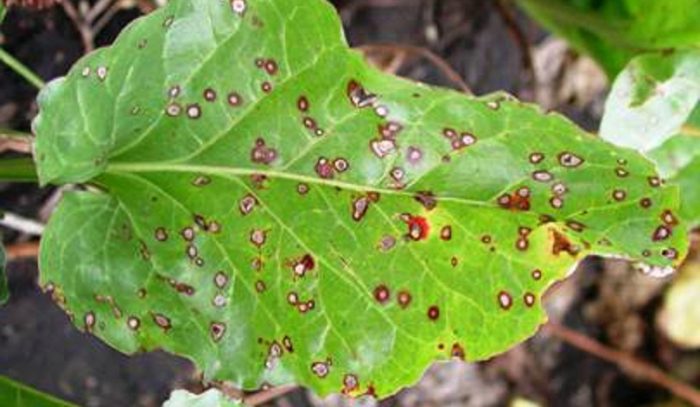
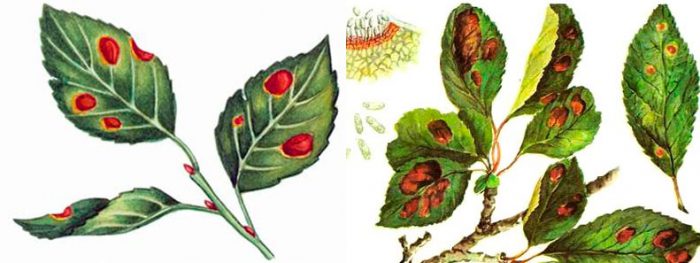
Polystygmosis
Polystygmosis, either rubella or red spotted foliage, is a fungal disease. In the affected specimen, specks of deep red color are formed on the surface of the foliage, which are clearly visible against a green background. Before the buds open, the infected plant and the surface of the trunk circle must be sprayed with a solution of Nitrafen or copper sulfate, while its concentration should be 3%. When the plant has faded, it is treated with Bordeaux liquid (1%). If the bird cherry is very strongly affected, then it should be sprayed with a fungicidal preparation for the third time 15–20 days after it has faded.
Cercosporosis
If small irregular necroses appear on the surface of the leaf plates, this means that the tree is affected by cercospora. On the front surface of the sheet plate, they have a whitish color, and on the seamy side, they are brown. Over time, they merge, and destruction and rash of the affected tissue is also observed. To get rid of such a disease, the tree must be treated with Topaz, which must be used in accordance with the instructions.
Coniotiriosis
Coniotiriosis damages the bark of branches, foliage and fruits. On the affected parts of the plant, the appearance of merging or single necrosis of an irregularly rounded brown or yellow color with a dark orange edging is observed. Black pycnidial dots appear in the central part of these necrosis. To cure bird cherry, it must be treated with a fungicide.
During the season, 2 preventive treatments for harmful insects are carried out: at the beginning of spring, before the foliage opens, and also at the end of flowering. The plant is sprayed with a solution of Karbofos (60 grams for 1 bucket of water), while about 2 liters of such a product should be spent on one copy.


Watch this video on YouTube
Types and varieties of bird cherry with photos and names
Gardeners cultivate not only bird cherry (description can be found at the beginning of the article), but also several other species.
Bird cherry Maack (Padus maackii)
In the wild, it is found in the Amur Region, Korea, Primorsky and Khabarovsk Territories and Northeastern China. This type of landscaping is used most often. This species got its name in honor of the researcher of the nature of Siberia and the Far East, as well as the Russian naturalist RK Maak. In height, this tree can reach about 17 meters, the shape of the crown is wide-pyramidal. The surface of the trunk is covered with a rather spectacular bark of a yellow-golden or orange-red color, which peels off in thin films. Glossy foliage has an elliptical or oblong shape, it is sharp-toothed, the top is drawn back. The leaves reach 13 centimeters in length. In spring, they are greenish, in summer - dark green, in autumn - red-yellow or deep yellow. Erect racemose inflorescences of an oblong shape consist of white flowers in diameter reaching 0.6 centimeters, the smell of which is completely absent. Small black fruits with a rounded shape have a bitter taste. They are very fond of bears, in connection with which such a plant is also called "bear berry". Frost resistance in this species is very high, it can withstand a drop in air temperature to minus 40 degrees. Cultivated since 1870
Bird cherry Maximovich (Padus maximowiczii)
This species is also found naturally in the Far East. It got its name in honor of the researcher of the Far East K.I.Maksimovich.Unlike other species, this tree has bracts on the racemose inflorescence, while they remain on the fruits. The inflorescences consist of 3-7 white flowers, which reach about 0.6 cm in diameter. Small red fruits, as they ripen, change their color to black. Not very large leaf plates are slightly lobed, in autumn they turn red. This type is one of the most decorative.
Bird cherry (Padus serrulata)
In nature, this species is found in Korea, Northeast China and the Far East. This species first belonged to the genus Plum, and then to the genus Cherry. Bird cherry, along with other species, was used to create the Japanese sakura. This species began to be cultivated a long time ago. The height of such a spreading tree can reach 25 meters. The shape of the crown is ovoid. Lentils, located on a smooth brown-gray bark, persist for a long time. Elliptical or ovoid leaf plates are rounded at the base, and strongly narrowed towards the apex. In early spring, the foliage is purple or bronze, in summer it is greenish and orange, and in autumn it is purple and brown. The seamy surface of the leaf plates is painted in a lighter color, while the veins are covered with an adpressed pubescence. Short corymbose inflorescences consist of 2-4 pinkish or white flowers, reaching 30 mm in diameter. The flowers open at the same time as the foliage. Such a plant looks very impressive during flowering. And the most decorative are such forms as pink terry and white terry.
Pennsylvanian bird cherry (Padus pennsylvanica)
The homeland of this species is North America. This bird cherry prefers to grow on forest edges and along rivers. It is a tree or a large shrub, reaching a height of 12 meters. The slender trunk is covered with red cherry bark, glossy branches are painted red. The shape of the crown is oval. Glossy green leaf plates have an oblong-lanceolate or ovoid shape, as well as a sharp-serrated edge and a sharp apex. In autumn, the leaves turn red. The racemose inflorescence consists of 3–8 white flowers. The fruits are small drupes that can be eaten. This bird cherry looks most impressively blooming in the autumn. It is resistant to drought and frost. Cultivated since 1773
Siori bird cherry (Padus ssiori)
In nature, this species is found in the Far East, Southern Sakhalin and Northern Japan, and it prefers to grow in mountain forests. The tree reaches a height of 7 meters. On the surface of the dark gray bark, there are large white lentils. With age, the crown becomes spreading. The length of the leaf plates with a heart-shaped base is about 14 centimeters, they are unevenly serrated along the edge, pointed to the apex, have an obovate or elliptical shape. The length of the multi-flowered racemose inflorescences is about 15 centimeters, the diameter of the flowers is about 10 mm. The fruits are large fleshy drupes of a spherical shape and black color.
Bird cherry (Padus asiatica)
It occurs naturally in the Far East and Eastern Siberia; this species prefers to grow in forests and river floodplains. In height, such a tree reaches 17 meters, it looks very similar to the common bird cherry. The difference between this species is that it has a pale reddish pubescence on the surface of young shoots and a very high resistance to frost.
Bird cherry antipka (Padus mahaleb), or magalenka
In the wild, it is found in Asia Minor, in Central Asia to the Pamir-Altai, in the southern part of Europe and in the Caucasus, this bird cherry prefers to grow on limestone soil in thickets of bushes. The Latin name of this plant is of Arabic origin; in America it is called Saint Lucy's cherry, or fragrant cherry.This species differs from others in the structure of inflorescences - it is a shortened and flattened raceme, consisting of 5-14 flowers, which outwardly is very similar to the scutellum. This species is represented by a not very tall shrub or tree. The bark is dark brown in color and has a specific smell. The shape of the crown is spherical. In length, glossy, rounded crenate along the edge, leaf plates can reach 9 centimeters, their front surface is pale green, and the back is painted in an even lighter color, while it is covered with light yellow pubescence. The length of the inflorescences is about 7 centimeters, they consist of small flowers in diameter reaching 15 mm. Juicy ripe fruits are colored black, their diameter is about 10 mm. Garden forms:
- weeping - the branches are down;
- yellow-fruited - as they ripen, the fruits do not turn black;
- motley - the color of the foliage is spotty;
- white-bordered - the edge of the sheet plates has a white border;
- ugly - the lush crown has a spherical shape.
Bird cherry (Padus grayana)
This tree is native to East Asia, its height is about 10 meters. Frost resistance is very high. Gardeners rarely grow this species.
Late bird cherry (Padus serotina)
It occurs naturally in America from the Gulf of Mexico to the Great Lakes. This species was named so because of the late flowering that occurs in the last days of May or June, while the fruits ripen around the last days of August. This tree is also called black cherry (associated with the color of the bark) or rum cherry (because of the taste of the fruit). This plant is represented by shrubs with a wide crown or a tall tree (height about 20 meters). The bark is a very dark cherry color. Glossy bare leaf plates have a broad-lanceolate shape and dark green color, they reach about 12 centimeters in length. The color of the front surface of the plate is darker than the back one. In autumn, the color of the leaves changes to various shades of yellow and red. The cylindrical racemose inflorescences, leafy at the base, reach about 14 centimeters in length, they consist of white flowers, up to 10 mm in diameter, that are odorless. Black fruits have a bitter taste. Decorative forms:
- pyramidal - the shape of the crown is narrow pyramidal;
- weeping - branches directed downward;
- motley - on the surface of green leaf plates there are strokes and specks of yellow color;
- cartilaginous - glossy sheet plates are relatively long;
- willow - narrow leaf plates are outwardly similar to willow foliage;
- fern-leaved - sheet plates are repeatedly dissected;
- terry - double flowers.
Cultivated since 1629
Virginia bird cherry (Padus virginiana)
Native to the eastern regions of North America, it prefers to grow along rivers. This species is very similar to the common bird cherry, but differs in small buds spaced from the shoots. At the same time, in bird cherry, racemose buds are pressed against the stems, and their length is 1.3 cm. This species is represented by a tree, the height of which can reach 15 meters, the crown is spreading. The finely fractured bark is dark in color. Dense glossy sheet plates have an oblong-ovoid shape, sharp-serrated along the edge, they reach 12 centimeters in length. During the opening, the leaf plates are green-brown, in the summer months they are dark green, and in the fall the color changes to a rich red-yellow. Multi-flowered racemose inflorescences reach 15 centimeters in length and consist of white flowers, reaching about 1.3 cm in diameter. Ball-shaped fruits have a juicy pulp. They are red at first, but turn dark red when ripe. Of great interest is the form of this species, called Schubert: at 15 years old, this tree has a height of 300 to 400 cm, young shiny leaves are painted green, which eventually changes to purple-red, hanging racemose inflorescences consist of white flowers, reaching 10 mm. It has been cultivated since 1950. This species has other interesting forms:
- Atropurpurea... It is represented by a large shrub or tree, characterized by fast growth and reaching a height of 15 meters. The color of the bark is black, the foliage is purple. The edible dark red fruit has a tart taste.
- Dawn... A low-growing partially self-fertile tree, the height of which does not exceed 300 centimeters. The inflorescences are relatively large. The taste of the fruit is tart, sweet-sour, and the color is dark red.
- Narym and Taiga... The height of such self-fertile trees is from 350 to 400 cm. The crown is spectacular, the inflorescences are relatively large. The color of the fruit is red, and the sweet-sour tart pulp is yellow.
Gardeners cultivate a large number of varieties of bird cherry, for example:
- Sakhalin black... The height of such a self-fertile tree is from 6 to 7 meters. The lush crown has a pyramidal shape. The leaf plates are large, the inflorescences are multi-flowered. The fruits ripen early and have a sweet, slightly tart green pulp.
- Tenderness... The height of the tree is from 350 to 400 cm. Long racemose inflorescences consist of small fragrant flowers. Their color at the very beginning of flowering is dark red, and then it is replaced by white.
- Captivity... Double flowers are highly decorative.
- Gull... The height of the tree is from 4 to 4.5 meters. Large racemose inflorescences consist of large white flowers.
- Meteo... The flowers are white, the brushes are very long (about 20 centimeters).
There are a large number of hybrid varieties that were born through the crossing of various species:
- Purple candle... The tree has a lush narrow-pyramidal crown and reaches a height of about 5 meters. The green color of the leaf plates by the middle of the summer period is replaced by dark purple. The length of semi-drooping racemose inflorescences is from 10 to 14 centimeters, they consist of white flowers.
- Late joy... The hybrid was created by crossing the bird cherry and the virgin bird cherry. The height of the tree is about 8 meters, the shape of the crown is narrow-pyramidal. The rough bark is light gray in color, the leaf plates are elliptical. Dense racemose inflorescences have a length of 14 to 15 centimeters, which consist of 35-40 white flowers, reaching 1.5 cm in diameter. Rounded fruits have a dark brown, almost black color, the taste of juicy yellow-green pulp is sweet-sour, tart.
- Mavra... The shape of the crown is wide-pyramidal, the branches droop at the ends. Inflorescences, flowers and foliage are similar to Late Joy, but the color of the fruit is darker.
- Black glitter... Mid-early hybrid. The height of such a self-fertile tree is from 5 to 6 meters. Medium-sized leaf plates are dark green in color. The multi-flowered cylindrical inflorescences consist of large flowers. Fruits are black, green-yellow pulp has a pleasant taste.
Bird cherry properties: benefits and harms
Useful properties of bird cherry
Not so long ago, scientists confirmed that the foliage and fruits of bird cherry have medicinal properties, but long before that they were widely used in alternative medicine. Decoctions, tinctures are prepared from it and lotions are made.
The fruits contain pectins, tannins, sugars, organic acids. The composition of the bark, seeds, foliage and flowers includes the glycoside amygdalin; during its splitting, the release of hydrocyanic acid is observed. The leaves and fruits contain essential oil, resin, flavonoids, phenolcarboxylic and ascorbic acids, gum and trimethylamine.
Bird cherry has antimicrobial and fixing properties, and therefore it is used for diarrhea and other intestinal disorders. For this, infusions are used. Decoctions with diuretic properties are prepared from the bark; they are recommended for diseases of the heart and kidneys. Such a decoction also has diaphoretic properties, so it is used for heat and colds. It is also used for gastrointestinal cramps. Tincture of bird cherry rinse your mouth with stomatitis, wash your eyes with purulent conjunctivitis, gargle with an upper respiratory tract disease and sore throat. It also helps with women's diseases.


Watch this video on YouTube
Contraindications
It is impossible to eat bird cherry seeds, because during the breakdown of phytoncides in the body, the release of hydrocyanic acid is observed, due to which severe pains in the head area may appear. Pregnant women are forbidden to inhale the scent of bird cherry and use any products prepared on its basis. Alkaloids are found in any part of the plant, and therefore it is not used in traditional medicine.