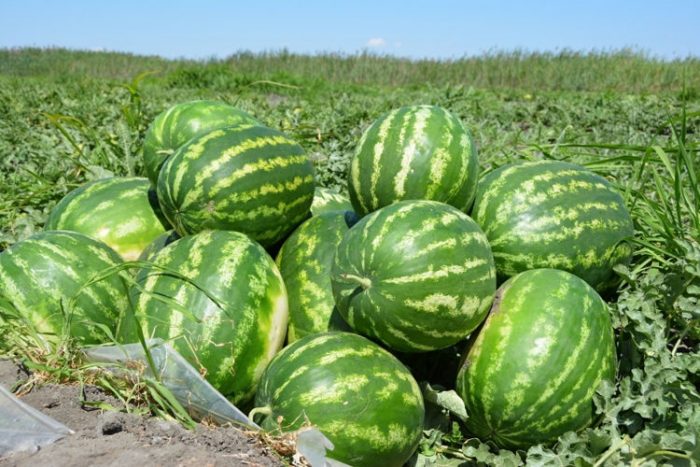
The herbaceous annual watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) is a member of the genus Watermelon of the Pumpkin family. This plant belongs to the melon culture, it comes from southern Africa (Lesotho, South Africa, Botswana and Namibia). Today, in these places you can find the colocynth species, which is related to the watermelon, it is he who is the ancestor of the cultivated watermelon. In the 20th century BC, watermelon was already cultivated in Ancient Egypt. The seeds of this plant were found in the tomb of Tutankhamun. In the verses of Virgil, it is possible to find proof that the ancient Romans knew about this plant, they ate salted and fresh watermelons, and also used them to make honey. They were raised in China, where they were called "melon of the West", and the Arabs were also engaged in the cultivation of watermelon, who ate it before meals to cleanse the body. Thanks to the crusaders, this culture ended up in Europe, while it was brought to the territory of modern Russia in the 13-14 centuries of our era. China is the leader in the cultivation of watermelons, followed by Iran, Turkey, Egypt, the American states, as well as Russia and Uzbekistan, by a small margin. The best conditions for growing watermelons are considered to be a long hot and dry summer period, as well as a short and not very cold winter.
Content
Features of watermelon
Branched thin shoots of watermelon are creeping and climbing, they are often smoothed-pentahedral, and their length can reach 400 cm. While the plant is young, its shoots are densely pubescent. Alternately petiolate rigidish leaf plates have a rough surface on which pubescence is located. The leaves have a triangular-ovoid shape, while at the base they are heart-shaped. The length of the plates can vary from 8 to 22 centimeters, and the width - from 5 to 18 centimeters. Flowering is observed in the summer, the flowers are female, male and hermaphrodite, there are bracts, which are similar in shape to a boat. The fruit is a watermelon berry - a multi-seeded pumpkin, the surface of which is very smooth, its flesh is sweet and juicy, it has a red or pink color. There are varieties with pale yellow flesh, while the crust of such a fruit is rough.
Growing watermelons from seeds
Sowing in open ground
It is possible to grow a watermelon in open soil only in a generative (seed) way. At the same time, this culture can be grown both through seedlings and sowing seeds directly into open ground.
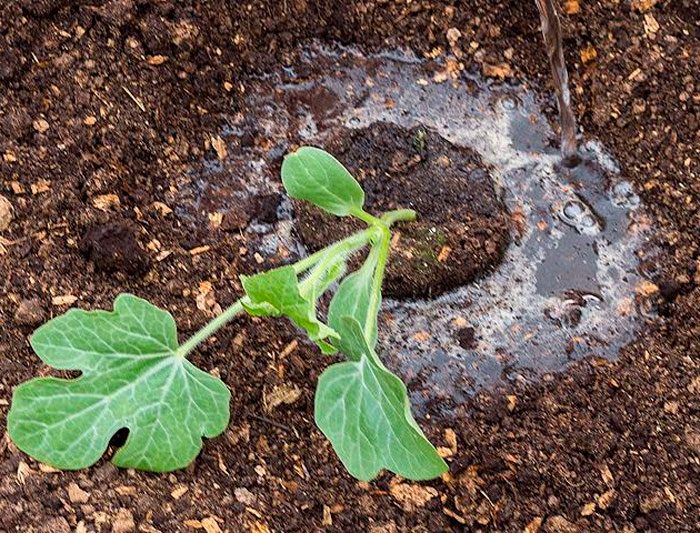
Sowing seeds immediately into the soil is carried out only in regions with a warm climate, while the earth must necessarily warm up to 12-14 degrees, and it must also be prepared in advance. Before starting sowing, the seeds must be prepared. To do this, they are poured into a thermos, which is filled with lukewarm (about 50 degrees) water. After the seeds have sprouts, they are carefully removed. For sowing, it is necessary to prepare holes, the depth of which should be about 80 mm, a distance of 100 cm is observed between them.Pour 1 tsp into each hole. Ammofoski, 1 tbsp. l. wood ash and 1 kg of humus, everything must be thoroughly mixed with the ground. Then a couple of liters of water must be poured into the landing hole. After the liquid is completely absorbed, 2 or 3 seeds are placed in the well, while they are not placed very close to each other. After that, the hole is filled with soil, which is well trampled. After the sowing is done, there is no need to water the area. After a little more than 7 days, the first seedlings may appear. If sowing is done in cold soil, the seedlings will appear later, and sometimes they even die. To avoid this, sowing seeds in open soil should be done no earlier than the third decade of May. After the seedlings begin to form 3 or 4 true leaf plates, they should be thinned out, for this removing weak plants. To do this, the seedlings are cut directly above the surface of the plot.
Planting watermelon seedlings
In regions where the summer period is relatively short, this crop is recommended to be grown through seedlings. Sowing seeds for seedlings is carried out in May. Since pumpkin seeds react quite negatively to picking, individual containers should be used for sowing, the volume of which should be at least 300 ml. For sowing, you will need a substrate, which includes sod land, peat and sand (1: 1: 1). In every 5 liters of the resulting soil mixture, add 50 grams of ammonium nitrate, potassium sulfate and dolomite flour, and another 100 grams of double superphosphate. Seeds will need pre-sowing preparation. For this, the seed for 30 min. immersed in lukewarm (about 55 degrees) water, and then they are placed in moistened sand for germination, while the air temperature should be about 25 degrees. When the seeds show small sprouts, you can start sowing. To do this, they are laid out in 2-3 seeds on the surface of the soil mixture, which must be filled in individual cups. The seeds should be sprinkled on top with a layer of sand, then the containers should be covered with glass or polyethylene. The cups are removed to a place where the air temperature is at least 30 degrees.
The first seedlings should appear after 7 days, after which you need to remove the shelter. The containers are transferred for 9 days to a cooler place (from 16 to 18 degrees). Such seedlings must be watered in a timely manner, fed, and if necessary, then supplemented, because the duration of daylight hours required for a given culture should be at least 12 hours. Watering is carried out in several stages, while you should wait until the liquid is completely absorbed into the substrate, and do not allow it to fall on the foliage of the plants. During the formation of the third true leaf plate, plants will need feeding with a liquid mullein or a solution of complex mineral fertilizer. About 1.5 weeks before the watermelons are transplanted into open soil, they need to be hardened. For this, the seedlings are transferred to fresh air, while the duration of this procedure must be increased gradually, so, they start from one hour and bring up to 24 hours.


Watch this video on YouTube
Watermelon pick
It was already mentioned above that it is extremely undesirable to dive watermelon seedlings, because you can severely injure the root system of the plants.Pinching is also highly undesirable.
Planting a watermelon in open ground
What time to plant
Seedlings of watermelons should be planted in open soil 1 month after sowing seeds in the formation phase 5–6 of this leaf plate. As a rule, this time falls on the last days of May or the first ten days of June. For landing, you should choose a well-heated sunny area that has reliable protection from the wind. It should be located on the southeast or south side, while herbaceous perennial plants (sweet clover, alfalfa or sainfoin), cabbage, winter wheat, onions, and annual legumes should have grown on it before this melon crop. For planting, areas where pumpkin (zucchini, watermelon, melon or squash) and nightshade (tomatoes, peppers, potatoes and eggplants) grew up to watermelons are not suitable. It should be noted that in the area where watermelons were grown, it will be possible to plant this crop again only after 6–8 years.
Suitable soil
For planting watermelons, sandy loam or sandy soil is best suited, while its pH should be 6.5–7. Prepare the site in advance and do it in the autumn. During the digging of the soil, fertilizers should be added to it, so 40–45 grams of superphosphate, 24–35 grams of ammonium sulfate, 4–5 kilograms of rotted manure and 15–25 grams of potassium salt are taken per 1 square meter of the site. If the soil is heavy, then it is necessary to add 1–2 buckets of sand to it for each square meter. Fresh manure cannot be introduced into the soil.


Watch this video on YouTube
Seedling planting rules
On the prepared bed, holes should be made, the distance between them can vary from 100 to 150 cm, and a distance of 200 cm should be left between the rows. 1.5 to 2 liters of water should be poured into each hole. When planting seedlings, it must be buried in cotyledonous leaf plates. After planting, the soil must be compacted, after which its surface near the plant within a radius of 10 centimeters must be covered with sand, which will help to avoid the development of root rot. The planted seedlings should be watered with lukewarm water. It should be remembered that until the leaf plates restore turgor, the plant must be protected from direct sunlight.
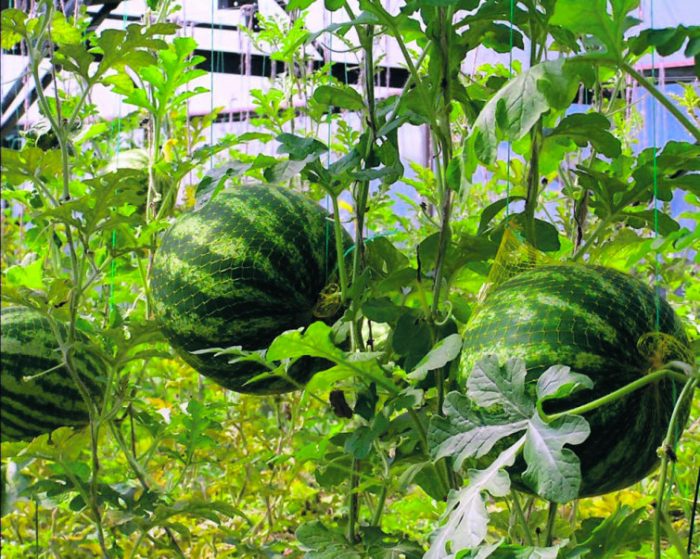
Growing a watermelon in a greenhouse
If the summer period in the region is rather short and cold, then it is recommended to grow watermelons in greenhouses, since the duration of the growing season of such a plant in some cases reaches 150 days, and in the northern regions there are much less warm summer days. To speed up the process, it is recommended to grow seedlings in room conditions, then they are planted in a greenhouse under a double film coating.
Sowing seeds for seedlings is carried out in the third decade of April. Planting grown seedlings in a greenhouse can be carried out immediately after the ground in it warms up well (up to 12-14 degrees). Do not forget to prepare the soil in advance in the garden; for this, its upper layer must be removed to the depth of the shovel bayonet. In the resulting trench, lay humus with hay, sprinkle this layer with nitrogen-containing fertilizer on top, and then spill it with hot water. On top of this layer, you need to lay the previously removed layer of soil. From above, the bed must be covered with a covering material of black color, it will need to be removed only before the direct planting of seedlings.
Planting holes are located on the beds at a distance of 0.7 m from each other. During planting, do not forget to bury the plant to a depth of 10 centimeters into the soil. After planting, you can immediately install the trellis, to which the growing lashes will be tied. In order to harvest a good harvest, you must not forget to put a few bees into the greenhouse. However, it is much better if you pollinate the flowers yourself, while taking into account that the life expectancy of male flowers is only a few hours. It is necessary to tear off several male flowers and carefully tear off all the petals from them. Apply their anthers to the stigmas of the female flowers one by one.It is very good if each of the female flowers is pollinated by several male flowers at once. It is necessary to artificially pollinate watermelons in the morning, while the air temperature in the greenhouse should be between 18-20 degrees. It should also be noted that at night before pollination, the air temperature in the greenhouse should not be less than 12 degrees.
In order for the lashes to grow faster, they need a pinch, while taking into account that no more than 3-5 leaf plates should remain above the fruit, and all those shoots that are very weak must be removed. It should be noted that 1 bush should have no more than 5 ovaries, so the extra ones will have to be cut off.
The first time the plants are fed after their lashes reach from 0.25 to 0.5 m in length.To do this, grooves are made at a distance of 0.2 m from the plant, it is recommended to fill them with fermented liquid chicken droppings (1:20) or mullein solution (1:10). The second time the watermelon is fed before the formation of buds, and the third - when the ovaries are formed, however, it should be taken into account that in the first and second cases, the grooves will need to be made, stepping back from the bushes at least 0.4 m.Organic fertilizers (chicken droppings or mullein) very well suited for feeding this plant, therefore they are used in the first and second cases. After the fruits begin to grow actively, they must be regularly turned over, which will allow them to ripen evenly. It is also very important to systematically ventilate the greenhouse.


Watch this video on YouTube
Watermelon care
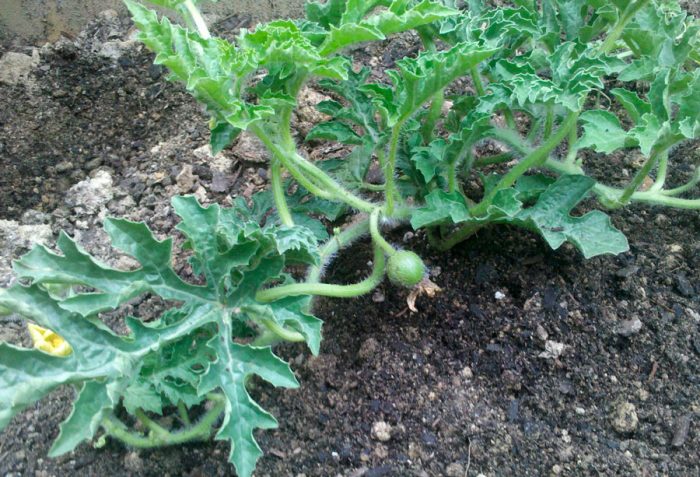
If watermelons grow outdoors, then caring for them is quite simple. But in order to harvest a good harvest, you should consider several important nuances regarding the care of this crop. When caring for watermelons, you need to thin out the seedlings in time, water and weed the plants in a timely manner, and also pinch the lashes and loosen the soil surface. During the formation of 3 or 4 leaf plates, the seedlings will need to be thinned out, while one or two plants should remain on the hole, all excess seedlings should be cut off directly above the soil surface. You can, if you wish, try to jig the extra plants, because there are great chances that it will be successful. When the ovaries on the bush are fully formed, you need to select only 6 pieces, and remove the rest. If the fruit lies on the surface of the ground, then a non-rotting material (a piece of plastic, roofing material or foil) must be placed under it.
How to water
Watering is carried out 1 time in 7 days, but it should be abundant, for this, 30 liters of water are taken per 1 square meter of the plot. If the weather is hot outside or the flowering period has begun, then a couple of such irrigations will be needed per week, while it will be necessary to moisten both the soil surface around the plants and the ground between the rows. After the fruits are formed, a gradual reduction of watering is carried out, and half a month before harvesting it should be stopped altogether. During the summer period, plants need 3-4 plentiful watering: during the formation of 5-7 leaf plates, during the flowering period, and even at the very beginning of fruit formation.
At the beginning of the growing season, when 1-2 days have passed after irrigation, it is necessary to loosen the surface of the plot to a depth of 60 mm, and all weeds should be pulled out. After the plants close the rows, the weed can no longer cause them any harm. In this regard, from this time it is recommended to stop removing weeds, as well as loosen the soil, since the watermelon root system extends in different directions, and it is extremely easy to injure it with a hoe.
Fertilizer
When half a month has passed after transplanting the seedlings into the ground, the watermelons will need feeding. For the first feeding, it is recommended to use a solution of ammonium nitrate (for 10 liters of water, 20 grams of the substance), while a couple of liters of such a nutrient mixture is taken for 1 bush. Instead of nitrate, you can use chicken manure (1:20) or mullein (1:10), while 15 grams of calcium chloride and 30 grams of superphosphate will need to be dissolved in 10 liters of the mixture.
The second time the plants are fed during the formation of buds, while for 1 bush they take 6 grams of superphosphate and 4 grams of ammonium nitrate and calcium chloride. If you feed watermelons with dry fertilizers, then the area must be watered both before and after feeding.


Watch this video on YouTube
Diseases and pests of watermelon
Diseases
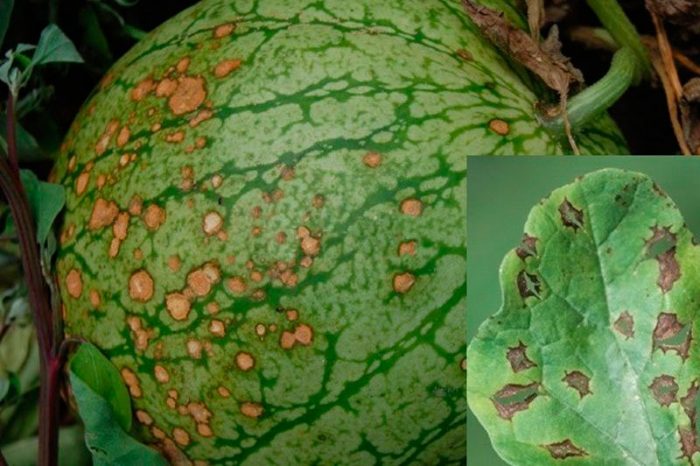
Most often watermelons are affected by white, gray, black and root rot, powdery mildew - real and false, anthracnose, angular and olive spots and mosaics. In order to significantly increase the resistance of this crop to diseases and pests, it is necessary to properly prepare the seeds for sowing and the soil for planting, and you must also follow all the rules of agricultural technology of this crop. In this case, the bushes will not hurt at all, and not a single pest will settle on them. Still, there is a danger of disease and pest damage to watermelons, and therefore you need to be able to timely identify diseased plants and treat them.
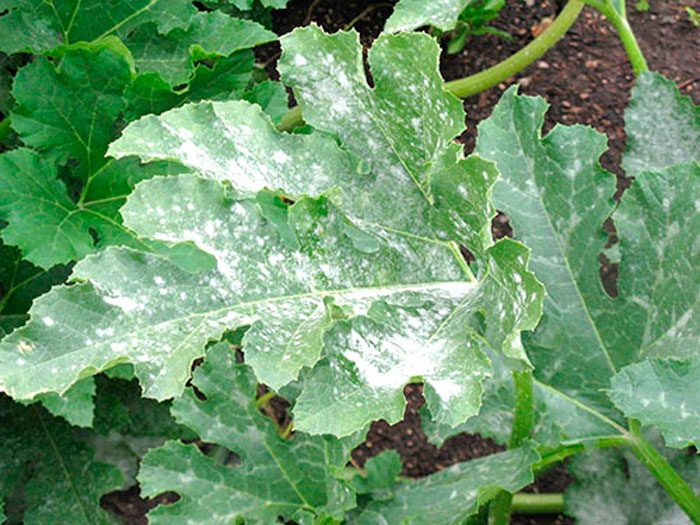
Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease. A bloom of white-gray color appears on the surface of the foliage. The dying off of the affected leaf plates is observed, the fruits lose their taste and become unsweetened, and their deformation and decay are also observed.
Peronosporosis
Peronosporosis (downy mildew) is also a fungal disease. However, in this case, first, only old leaf plates are affected and only then young ones. On the surface of the foliage, angular spots of yellowish color are formed, while a purple-gray bloom appears on the seamy side. The fruits take on an ugly shape, and their development stops.
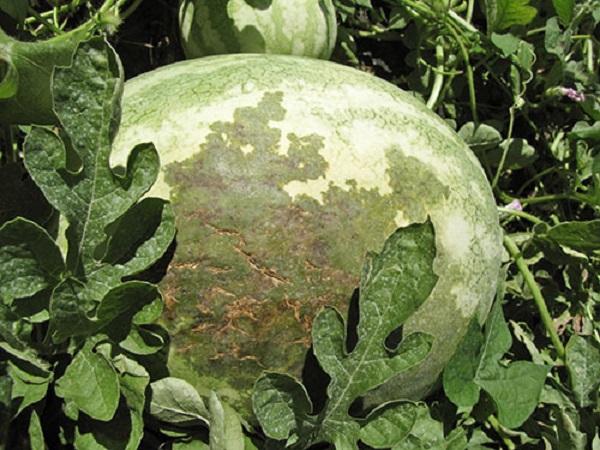
Olive spot
If the bush is affected by olive spot, then irregular specks are formed on its entire aerial part. Because of this, the leaf plates become corrugated, while ulcers of olive color appear on the petioles and shoots. Drying and dying off of the ovaries is observed.
Angular spotting
The main vectors of bacteriosis (angular spotting) are pests. In the affected bushes, oily specks of a whitish color appear on the aerial parts. Over time, holes form on the leaf plates, then they die off, the shoots wither, the fruits become transparent, soft and their growth stops.
Anthracnose
Copperhead (anthracnose) is also a fungal disease. Because of it, spots of yellow or brown color with pinkish-yellow pads on the leaf plates. If the weather is humid, then a bloom of pink appears on the surface. With severe damage, the bush dries up and dies.
Gray rot
Gray, white, black, and root rot are also considered fungal diseases. It should be borne in mind that each of these diseases can lead to the death of plants and crops. Gray, black and white rot lead to the destruction of shoots, foliage and fruits of this culture, while root rot affects the root system of the bushes.
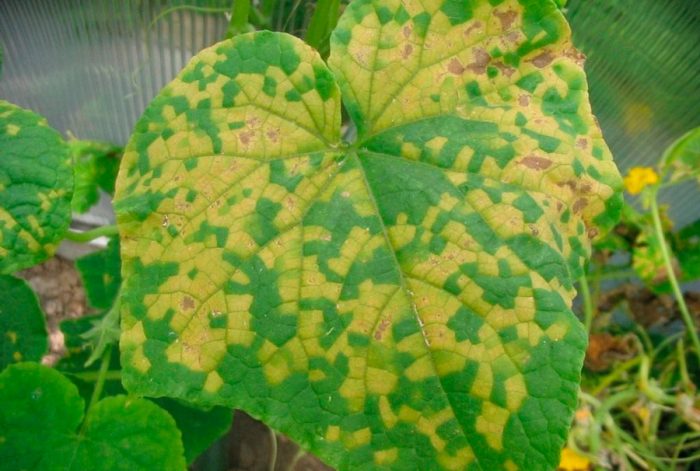
Cucumber mosaic
Cucumber mosaic is a viral disease that is currently considered incurable. In the affected bush, a mosaic pattern is formed on the leaf plates, painted in pale green and green. There is a lag in the growth of the bush, and bumps, swellings and dots appear on the surface.
Pests
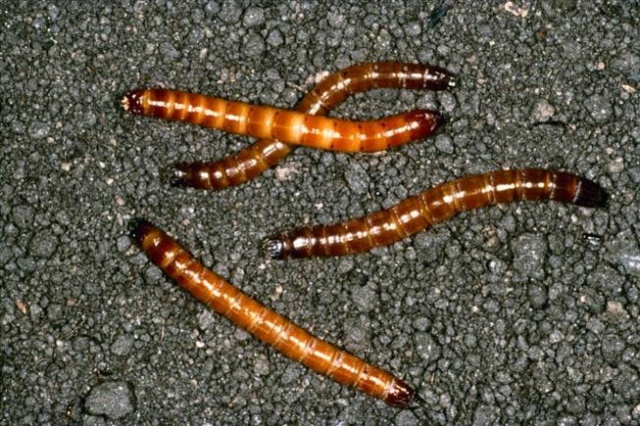
The greatest danger to this plant of all harmful insects is gnawing moths, melon aphids and wireworms.
Wireworms
The wireworm is the larva of the click beetle that looks like a tough piece of wire. Such an insect damages the seeds, as well as the seedlings of this plant.
Melon aphid
The melon aphid causes significant harm to the watermelon, as it sucks the vegetable juices out of it. And this pest is considered the main carrier of such an incurable viral disease as mosaic.
Winter scoops
Winter crops, as well as gnawing scoops, arrange egg-laying on the watermelon. Caterpillars emerge from the eggs, which begin to eat the plant, gnawing at its roots. Because of this, it turns yellow and dies.
Watermelon processing
Experts advise to fight fungal diseases with the help of fungicidal preparations: Bordeaux liquid, Decis, Fundazol, Skora, etc. You will be helped to choose the appropriate drug in a specialized store. But it will be much better to prevent the plants from getting sick instead, for this it is necessary to adhere to the rules of agricultural technology of the given culture and crop rotation, and also to properly care for the ripening fruits. In this case, problems with watermelons should not arise at all, and you can forget about fungal diseases.
If aphids have settled on the bushes, then you can use the folk method to destroy it. To do this, dust the parts of the plant on which the pest is located with a mixture of tobacco dust and wood ash (1: 1), sprinkle it with water. A third of an hour after processing, the soil surface on the site must be loosened, which will allow the destruction of those pests that have fallen to the ground. To get rid of the caterpillars, baits are made for them from plant residues of sweet taste or pieces of cake. After some time, they are collected, this procedure will also help get rid of the wireworm. In order to install the bait, it is necessary to make a half-meter depression in the ground, then pieces of sweet root vegetables and cake are thrown into it. Such holes should be covered with shields. The traps are opened after 1–2 days, the contents of the hole are taken out and burned. It should be remembered that harmful insects, as a rule, settle on weakened bushes, which are improperly looked after.
Collection and storage of watermelons
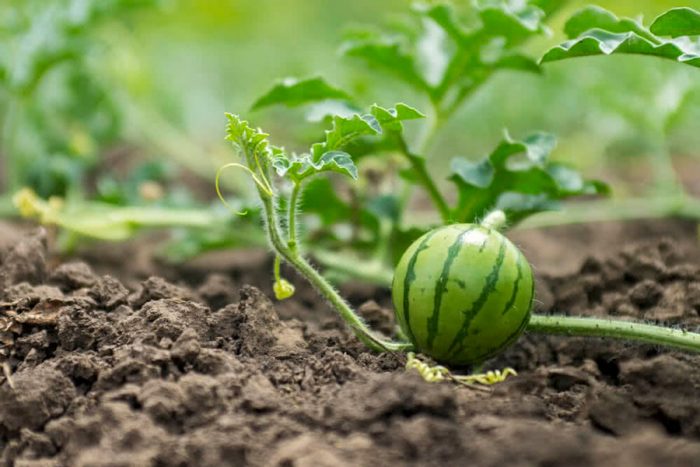
Collecting watermelons is carried out only after they reach the first stage of removable maturity, most often it occurs five days before full maturity. If the fruits are harvested ahead of time, then there is a high probability that they will not ripen in storage. Watermelons harvested later are not suitable for long-term storage.
To determine the state of first maturity, it is necessary to evaluate the color of the seeds and pulp of the fruit, which is characteristic for each individual variety. Timely collected fruits have pink flesh, during maturation they ripen and its color changes to red, while the watermelon does not lose its sweetness. Late varieties of watermelons are suitable for the longest storage, they have a thick and dense skin, while the structure of the flesh is rough.
Watermelons of mid-season and early varieties are harvested as they ripen, they can be used for processing (for pickling, pickling or making jam), as well as eaten fresh. At the same time, the harvesting of late varieties of watermelons, which are intended for long-term storage, is carried out before frost, for this using a sharp knife or pruner, they are cut off together with a peduncle about 50 mm long. It is not recommended to tear off the fruit from the shoot, since there is a high probability that rot will appear in the place of separation.
Suitable for long-term storage are fruits that have an average size and a glossy thick rind, which should not be injured (there should be no scratches, dents, cracks, as well as soft areas). During transportation, it is forbidden to throw fruits, and they should not be laid on a hard surface, gloves must be used during work. When laying fruits, care must be taken that they do not touch each other, which will prevent the development of fruit rot.The best conditions for storing watermelons are considered to be a well-ventilated room, with an air humidity of 75 to 85 percent and a temperature of 1–4 degrees. There are several storage methods:
- In the forest, you need to collect dry moss, do it on a fine sunny day. Take a wooden box and line the bottom with a layer of moss, which should be thick enough. Then a watermelon is placed on top, it must be overlaid with the same moss on all sides. After that, you can put other watermelons in the same box, and do not forget to cover each of them with moss.
- Moss can be replaced with wood ash if desired. Watermelons can be placed in barrels or boxes, while sprinkling them with ashes. The containers are tightly closed and put into the cellar for storage.
- Each of the fruits must be dipped in alabaster or clay mash, the consistency of which should be similar to thick sour cream. Wait until the coating is completely dry and store the watermelons in the cellar.
- You can replace alabaster or clay with paraffin or wax. They must be melted with a water bath. After that, each watermelon should be covered with a layer that reaches 0.5 cm in thickness. After that, the fruits are lowered for storage in the cellar.
- Each watermelon must be wrapped in a thick cloth, which must be natural. Then they are laid in a net and suspended from the ceiling in the cellar.
- It is necessary to install racks in the cellar, while straw is stacked on their shelves in a sufficiently thick layer. The fruits are laid out on these shelves, while do not forget to wrap them in straw.
- Find a cool and completely dark place in your house or apartment. It is there that you need to put the fruits for storage, while every day they should be turned over.
Whatever storage method you choose, experts advise regularly inspecting watermelons (about once every 7 days), in this case you will be able to remove rotten fruits in a timely manner, which will avoid further spread of rot. If you choose the right variety, as well as the right way and place for storage, then watermelons can be stored until spring.
Types and varieties of watermelons
All watermelons that gardeners grow on their plots, as well as those that can be purchased in a store or in the market, are a species of the genus Watermelon. There are 2 varieties: the African melon tsamma (Citrullus lanatus var.citroides), this plant in natural conditions can be found in Botswana, South Africa, Namibia and Lesotho and the woolly watermelon familiar to almost everyone (Citrullus lanatus var.lanatus), this variety is found only in the cultural form. The woolly watermelon has a large number of varieties, while most of them were born thanks to European, American and Asian breeders. These varieties will be described in more detail below.
All varieties of watermelons intended for cultivation in open soil are divided into early ripening, medium and late ripening (they are grown in regions with a long and rather warm summer period). When choosing a suitable variety of this plant, it is recommended to take into account several factors: drought resistance and cold resistance, resistance to pests and diseases, and also the ability to grow and the need for fertilizers.


Watch this video on YouTube
Early maturing varieties
- Victoria... It is an American hybrid that ripens for 62 days (sometimes slightly longer). Watermelons are round in shape and weigh about 10 kilograms on average.
- Skorik... Small greenish watermelons weigh about 4 kilograms. They have blurry scalloped stripes along the edges. Delicate sweet pulp is colored red, it has a high taste. The rind is thick.
- Jenny... This American hybrid is ultra-early, maturing is observed from 54 days.One bush grows from 4 to 6 green-white watermelons of a standard size, they have thin stripes of dark color. On average, they weigh about 1.5 kilograms. The skin is thin and the seeds are about the size of a grape seed. The pulp has a rich color and excellent taste.
- Stabolite... This variety is the best of all seedless hybrids. Maturation is observed from 62 days. Large, strong fruits have an elongated shape and tasty pulp. For pollination of such a hybrid, use the varieties Lady, Trophy from the Nunems variety series.
- Twinkle... This variety was bred by Russian breeders. Small watermelons, covered with a thin skin, have a very tasty pulp, on average they weigh about 2 kilograms.
- Dolby... This large-fruited American hybrid is stress-tolerant and productive. Maturation is observed after 60 days.
Medium ripening varieties
- Sluggard... Ripening period 75-90 days. The variety is resistant to drought, diseases and pests. Medium-sized greenish watermelons weigh about 5 kilograms. On the surface of the thin peel, there are prickly stripes. The flesh of medium density is pink-red in color and tastes good.
- Top Gun... This variety is one of the most popular American fruit varieties. Ripening period 70-75 days. Large rounded watermelons weigh about 10 kilograms. The pulp is crispy, it is colored dark red, the seeds are small. This variety is resistant to anthracnose, and its fruits are well stored.
- Dumara... This hybrid is distinguished by its yield, maturation is observed from 75 days. The shape of watermelons is oval-cuboid, the flesh is tender and sweet, the seeds are also very tender.
- Antaeus... Oval-shaped watermelons have a delicate flesh that is sweeter than other varieties. It is recommended to feed with organic fertilizers.
- Ataman... This variety, created by domestic breeders, ripens in 66–86 days. Round-shaped spiny watermelons weigh about 10 kilograms. The pulp is very tasty, has a red color and medium density.
Late-ripening varieties
- Spring... This variety is suitable for growing both in a greenhouse and on melons. Smooth watermelons have an elongated spherical shape and weigh about 3 kilograms. On the surface of the peel, they have a barely noticeable mesh of green color on an olive background. The sweet and tender flesh is grainy and dark red in color. Ripening period is about 105 days.
- Icarus... The variety is drought tolerant and productive. Ripening period 88-110 days. Watermelons weigh 3-16 kilograms. The dark green crust is very strong with barely noticeable stripes on its surface. The flesh is very sweet and has a raspberry red color. The fruits keep very well (sometimes until March).
- Chill... This variety is the most popular of all the late varieties. Ripening time is about 100 days. Elliptical watermelons weigh 15-25 kilograms, they are poorly segmented, on the surface of the strong bark, painted in green, there are almost black stripes. Intense red with a pinkish tinge, the flesh is very sweet. Watermelons can be stored for 3 months.
- Melania... It is a hybrid of the Early variety and ripens after 80 days. The shape of watermelons is oval, they weigh about 12 kilograms. On the surface of the green crust, there are wide stripes of dark green color. The dark red flesh is very crispy, the seeds are small.
If you have a desire to grow some unusual variety, then you can choose the American hybrid California Cross, the fruits of which are very large, or the Japanese variety from the island of Densuke Hokkaido, rarely grown in mid-latitudes, the rind of its watermelons is almost black. The Pepkinos variety has very small watermelons that can be placed whole in your mouth. The seedless variety King of Hearts is suitable for those who do not like seeds in watermelons.A rather unusual variety was created by a breeder from Astrakhan, its fruits have a nutmeg taste, and he also created the Lunny variety: the flesh of watermelons is yellow and has a lemon flavor.


Watch this video on YouTube